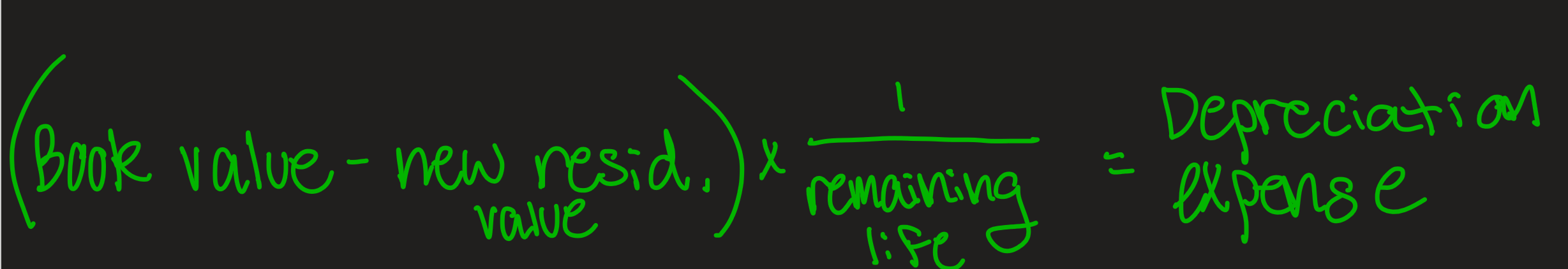Ch 9: Long-Lived Tangible and Intangible Assets
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Long-lived assets
for use over one/more years, not intended for resale
Tangible assets
Assets subject to depreciation, called “fixed assets” bc they are fixed in place. Ex: Land, building, equipment, furniture, fixtures
Acquisition cost of tangible assets
Purchase price AND all necessary expenditures to acquire the asset and prepare it for use
Basket purchase
Land & Buildings purchased at the same time.
Total cost is allocated in proportion to relative market values
Component allocation
cost of an individual asset’s components are allocated to each component which depreciates separately over their useful life
Ordinary repairs & maintenance
Expense/ Revenue Expenditure
small recurring expenditures
doesn’t increase productivity
doesn’t extend life beyond original
Extraordinary repairs, replacements, and additions
Capitalize
large, infrequent expenditure
may extend useful life
may increase productivity or efficiency
Cost allocation (depreciation)
costs of operational assets matched to periods of use
Depreciation values are based on? (3)
Asset cost
Useful life
Residual value
Asset cost
Purchase & all capitalized costs
Useful life
estimate of asset’s useful economic life
Residual value
estimate of amnt company could receive if they dispose of the asset
What are the 3 depreciation methods?
Straight line
Units of Production
Declining balance
Straight Line Method
Used when an asset will be used in equal amounts each period
The depreciation expense is the same each year
s

Units of production method
If the amount of asset production varies significantly from period to period

Declining-Balance Method
When an asset loses its usefulness over time
Use to report more depreciation expense in early years when the asset is more efficient
looks better for investors, used as a tax loophole

Partial year depreciation
when in asset is acquired during the year, depreciation is calculated for the fraction of the year the asset is owned
Deferred income tax
tax payment is temporarily put off as a result of large tax deductions for depreciation
Asset impairment losses
sudden drop in value due to impairment
Accounted for by:
Eliminate the asset’s accumulated depreciation against the asset account
Write down the asset to its fair value
Disposal of tangible assets
sell, trade, retire
Update depreciation to date of disposal
record the disposal
Gain if cash is greater than asset’s book value, loss if less than book value
Recording disposal of tangible assets
Book value - Value received on disposal = Loss/gain
Intangible Assets
No physical substance, exclusive rights privileges, copyrights, useful life is difficult to determine since they are usually long lived
Acquisition of intangible assets
Cash cost + legal fees + set up fees + any other costs
Amortizing intangible assets
Use straight-line method to spread out the cost of a patent over the years you will use it
Trademarks & copyrights
a symbol, design, or logo associated with a business
lasts forever
amortize cost over the period benefited
Patents & Licensing rights
last 20 yrs, after 20 yrs, becomes public knowledge
Amortize costs during the 20 yrs
Technology assets & franchises
software & web development, usually a short time (3-7 yrs)
Goodwill
Value not on the balance sheet (reputation, brand, fan base, location)
Only purchased goodwill is an intangible asset
Recognized when one company buys another company
Not amortized bc we cannot predict how long smth will be popular
What happens if you sell a patent?
It is still only private for 20 yrs, and becomes public afterwards
Fixed Asset Turnover
measures sales dollars generated by each dollar invested in fixed assets

Impact of depreciation differences
Selling an asset w/ a low book value (accelerated depreciation) may result in a gain
Selling the same asset w/ a higher book value (straight-line deprec) might result in a loss
EBITDA
Earnings Before Interest Taxes Depreciation & Amortization
Depletion
the process of allocating a natural resources over the period of its extraction
Changes in depreciation estimates
when estimate of remaining life changes