bio
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Elasmobranchs
sharks, skates, rays, oldest and largest vertebrates
Agnatha
jawless fish: lamprey and hagfish
Chondrichthyes
cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays)
Osteichthyes
bony fish
Agnatha characteristics
-muscular circular mouth with rows of teeth -long cylindrical body-lack paired fins and scales
Hagfish
-feed on dead and dying fish-burrow in soft sediment-make slime for defense
Lamprey
-large portion of life in the sea, return to freshwater to breed-sucker like mouth for consuming blood, tissue and body fluids
Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes characterists
-highly efficient gills-scales-streamline-paired fins-variety of jaw and feeding types-lateral line and sensory organs
Ratfish
-deep water-mouth with plate like grinding teeth-tiny tail-venomous spine-head clasper-no scales-skin flap covers 1 gill slit-fused jaw-heterocercal tail-fin rays (tiny support rods) in the fins
elasmobranch characteristics
-some travel up rivers -heterocercal tail-2 dorsal fins-carnivorous or planktonic-350 extant species-cartilage skeleton-paired fins-spongy cartilage snout-well-developed teeth with movable jaws -5 to 7 gill slits-male have claspers
Spiracles
opening on head used to bring water directly in for respiration without opening the mouth
Chondrichthyes Breathing
-ram ventilation-buccal pumping-spiracle breathing-obligation ram ventilators
Chondrichthyes scales
placoid scales made for drag and noise reduction
lateral line
a visible line along the side of a fish consisting of a series of sense organs that detect pressure and vibration.
Ampullae of Lorenzini
sensory organs in the head of cartilaginous fishes to detect electrical charges, important in detecting prey
shark liver
no swim bladder so large liver rich in oil
Demersal
live on the bottom
Neritic
Swim next to continental shelf
oceanic pelagic
swim in open blue water
people affect sharks
-disastrous fishing -fished for oil -skin is turned into leather -skin also used as sandpaper -fished for fin soup
Skates and rays
-dorsoventrally flattened bodies -spend much time on the bottom covered in sand -large flattened teeth -fleshy long whip-like tails -enlarged Pectoral Fins
skates
-dorsoventrally flattened body -have a fleshy tail without a spine -always lay egg cases -demersal and feed on molluscs -spiracles behind eyes -found at depths greater than 4000 meters
rays
-rays pectoral fins are expanded into wings and entire body is dorsoventrally flattened -long whip like tails, spines at the base of the tail with poison gland
manta ray
plankton feeder in mid-water; gill rakers used for filtering water
electric rays
have large electric organs on each side of head
claspers
-male shark -pair of organs between pelvic fins that transfer sperm -rolls of cartilage that become stiffened with calcium
Cloaca
females have a cloacal opening
Vivipary
live birth with placenta
Ovipary
egg laying
Ovovivipary
development of an embryo within an egg inside the mother's body but without the embryo receiving any nourishment from the mother
Osteichthyes characteristics
-gills for respiration -hinged jaws allow for a variety of different ways of feeding -homoceral tail
homocercal tail
symmetrical tail
lobe-finned fish
Fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone
ray-finned
-may contain only spiny rays, only soft rays, or both -stiff and sharp -soft, flexible, segmented, and may be branched
Gill arch
Supports the structure of the gill
gill rakers
On the forward surface of the gill arch
gill filaments
trail behind the gill arch
operculum
covers gills and provides protection
swim bladder
used for buoyancy control
shark buoyancy
Large oil filled liver
Sharks
-Tend to sink when not in motion -Use pectoral fins to aid in lifting
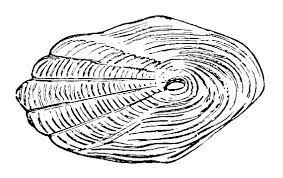
ctenoid scales
thin flexible and overlapping scales in bony fish that have tiny spines
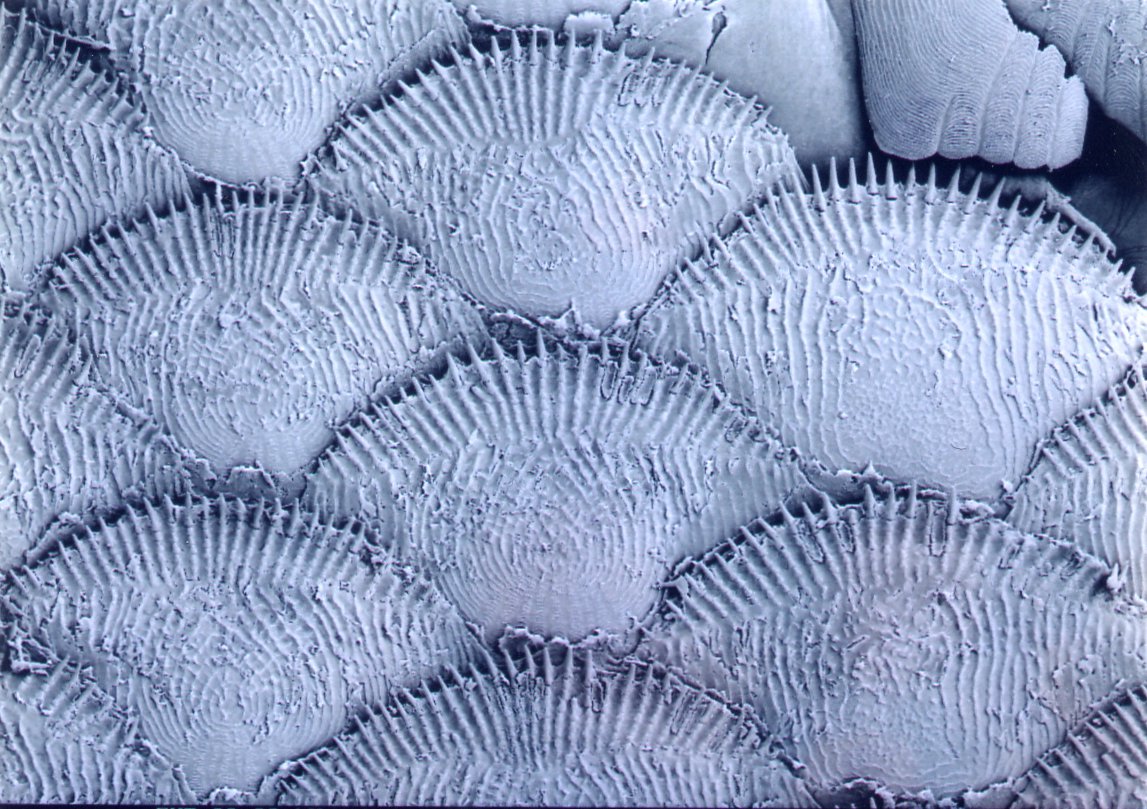
Cycloid scales
Thin, large, round, arranged in an overlapping pattern
Countershading
Ventral (belly) side is lighter than the dorsal side.

cryptic coloration
Camouflage; makes an organism difficult to spot.

disruptive coloration
bars or stripes that help break up the silhouette

Eye spot mimicry
Circular patterns near caudal fin -Confuses predator who are not sure where the head is
warning coloration
advertise themselves as dangerous
fuisform
Fast moving, predators, long, streamlined, very little flexibility

Compressiform
compressed from side to side, quick bursts of speed over short distance
Depression
Flattened top to bottom, live on bottom, slow, flap fins up and down
Filliform
Elongated, live in soft sediment, slow, slither
Pectoral fins
Side fins on fish
Pelvic fin
Underside of a fish
dorsal fin
top fin
Adipose fin
The fatty fin on some species of fish, on top
anal fin
an unpaired fin located on the underside of a fish posterior to the anus.
caudal fin
tail fin
Homoceral
Symmetrical
Heterocercal
asymmetrical
homocercal rounded
-large amounts of surface area allows sharp turns and quick starts -creates drag - fish tires easily
homocercal truncate
-allow short bursts of speed to escape predators or constant slow swimming -less drag -bottom dwelling fish
homocercal, forked
-constant swimming over long distances, reduces drag -open water fish -do not need speed to feed or for protection
homocercal lunate
-half moon shaped -fast moving -less drag, great acceleration, reduced maneuverability
Heterocereal tail
-medium speed -provides lift when no air bladder -reduced maneuverability
Swimming Patterns
-fish have an S-shaped pattern -bony fish fins are flexible and used for maneuverability -slower swimming species, forward movement is provided by pectoral fins -fins may be flexible and highly modified for camouflage
acquiring and processing food
-mouth structure reveals dietary preferences of fish -beak (fused teeth) allows for these fish to scrape algae and other organisms off of hard surfaces -tube like mouth to feed on corals -sharp teeth and wide mouth to capture prey
schooling
-possible for a group of smaller fish to appear much larger -harder for predators to capture any one fish
Territoriality
-fish maintain their territories normally by posturing to show their aggression -posturing can include raised fins, open mouth, darting
reproduction of fish
-hermaphroditic (possess male and female reproductive organs) -simultaneous hermaphrodites (have these structures at the same time) -sequential hermaphrodites (possess the structures at different times during life)
Types of Sequential Hermaphrodites
-Protogynous (female to male) -Protandrous (male to female)
Class Reptilia
reptiles
Class Aves
birds
Class Mammalia
mammals
Nekton
All organisms that swim actively in open water, independent of currents
Marine Reptiles
-air breathers -dry skin and scales -egg layers on land -cold-blooded
Ectotherm
an animal whose body temperature varies with the temperature of its surroundings -doesn't use energy -thrive in warm
Endotherm
An animal whose body controls and regulates its temperature by controlling the internal heat it produces
Homeotherm
an animal with a constant body temperature
poikilotherm
an animal whose body temperature varies with the temperature of its surroundings
sea turtles
-poikilotherms and ectotherms -breed at sea -internal fertilization -can have many males -breed every 2-4 years -return to land to lay eggs -lay 120 eggs
Sea Turtles Eggs
-soft and leathery -lay where they were born -incubation of 60 days -temperer determines the sex (cool is male)
turtle hatchling
-hatch in 2 months -wait until night to leave nest -head for water
Papillomavirus
virus that affects sea turtles
Sea turtle diet
-babies are omnivorous -adults are carnivores -green turtles are vegetarian
sargassum refuge
use seaweed as an area of refuge, rest, and/or food
Green Sea Turtle
-vegetarian -fat in body is green from diet -considers tropical nesting turtles -endangered
Leatherback
-largest sea turtle -feed on jellies -backward facing spines in mouth
Hawksbill Sea Turtle
tropical spices -feed coral, sponge
loggerhead
least vulnerable -eats crabs and mollusks
Turtle threats
-killed for eggs, meat, skin, shell -poached and over exploration -habitat destruction -fishing gear -climate change
sea snakes
55 species -found in Indian and Pacific Ocean -laterally flattened body with paddle like tail -3-4 feet -venomous
saltwater crocodile
found in estuaries, mangrove swamps, rivers, open ocean -eat all types of prey
marine iguana
-Galapagos -portion of life in water -dive to feed on sea weed and sea grass -most of day they are basking on shore -laterally flattened tails -limb bones -salt is expelled from cranial exocrine glands -blunt noses
Seabirds
feathers that cover the body are coated in oil from glandular secretions to waterproof -colonial nesters- near shore, cliffs, shrubs, and trees
Penguins
flightless with flipper like structure -Antarctica -layer of fat and trap air in the feathers to keep warm -share parenting responsibilities
marine mammals
-vertebrates -hair -make milk -torpedo like fusiform bodies to reduce drag -modified limbs for propulsion or steering -tails for propulsion and balance
Thermoregulation
-dense fur or blubber -countercurrent heat exchange -large body size -behavioral adaptations
counter current exchange
the transfer of heat between fluids that are flowing in opposite directions -transferred from arteries to veins
diving
-pinnipeds and cetaceans have large and complex blood vessel systems which serve to store oxygen -reduced heart rate -shunting of oxygen to vital organs