Psych Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/266
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:23 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
267 Terms
1
New cards
consciousness
the awareness of our internal and external environment
2
New cards
Meditation
an altered state of consciousness that may involve focused and regular breathing, specific body position, minimization of external distractions, mental imagery, and/or mental clarity.
3
New cards
Focused attention meditation
directing attention toward an object for the entire meditation session
4
New cards
Open monitoring meditation
Type of meditation that involves nonjudgemental observation of all aspects of experience
5
New cards
selective attention
conscious focus on one stimulus or perception at a given time
6
New cards
Cocktail party phenomenon
the ability to tune into a particular message while filtering out others in a crowded, noisy, or chaotic environment
7
New cards
Selective inattention (inattentional blindness
the environmental stimuli screened out or ignored while your attention is selectively focused on something else
8
New cards
Change blindness
a form of inattentional blindness where the visual stimuli in the environment change during a moment of interruption but go unnoticed by the observer
9
New cards
Multitasking
attention divided among two or more stimuli or activities
10
New cards
Most psychologists define consciousness as the awareness of our ______ and __________ environment.
internal; external
11
New cards
This altered state of consciousness involves training the mind by using focused and regulated breathing, minimization of distractions, and mental imagery.
Meditation
12
New cards
Syed is sitting in a bustling restaurant listening to his friend talk about the test he just took. Syed is interested in the conversation because he is taking the test tomorrow but all of a sudden his interest is drawn across the room because he heard his name spoken. This is called ___________________.
cocktail party phenomenon
13
New cards
Sasha has her laptop open in class and is watching funny cat videos while the professor talks. After class is over, she hears the other students talking about the quiz they are having Friday. Which phenomenon explains why Sasha didn't hear her professor talk about the quiz?
Selective inattention
14
New cards
Multiple studies have shown that when students multitask during class or studying
they do not learn effectively, which leads to lower grades.
15
New cards
Sleep
the daily, natural loss of consciousness controlled by the brain
16
New cards
Circadian rhythm
biological clock that regulates various bodily functions on an approximately 24 hour cycle
17
New cards
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
the small part of the hypothalamus that controls the circadian clock
18
New cards
Rapid Eye Movement (REM)
a deep stage of sleep consisting of rapid eye movement (REM) typically associated with dreaming; sometimes referred to paradoxical sleep
19
New cards
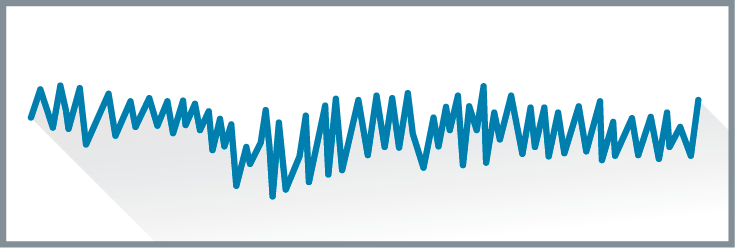
Beta waves
low amplitude, high frequency and irregular brain waves present during active wakefulness
20
New cards
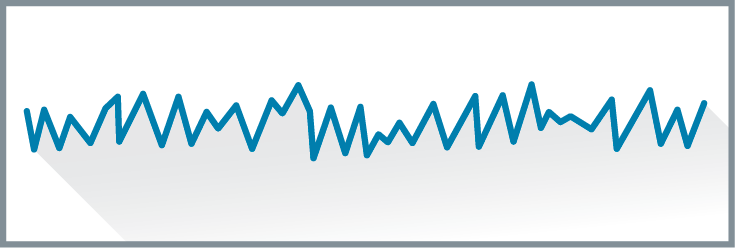
Alpha waves
high frequency, low amplitude brain waves characteristic of a relaxed or drowsy state
21
New cards
N1
the first stage of sleep where alpha wave activity decreases and slower theta waves become more active
22
New cards
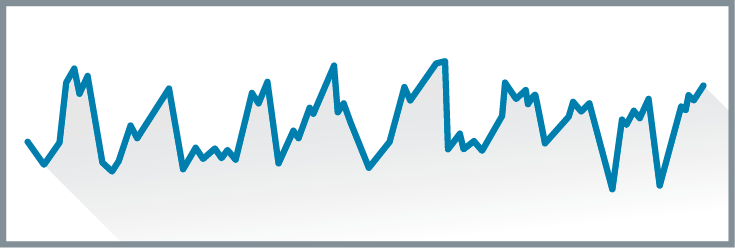
Theta waves
brain waves associated with the transition of sleep, may be present in N1 and N2 stages of sleep
23
New cards
N2
the second stage of sleep characterized by increased relaxation and light sleep
24
New cards
N3
the third stage of sleep consisting of deep sleep characterized by higher amplitude delta waves
25
New cards
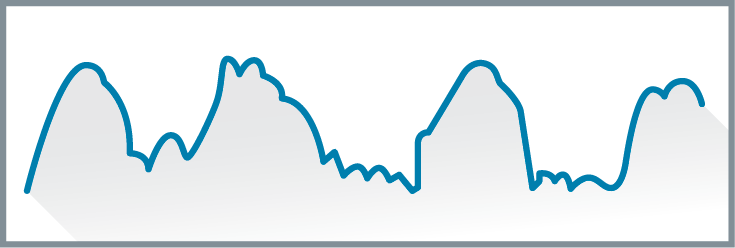
Delta waves
high amplitude, low frequency brain waves that appear when sleep deepens.
26
New cards
Stage R
a deep stage of sleep consisting of REM typically associated with dreaming, sometimes associated with paradoxical sleep
27
New cards
Brain waves that are lowest in frequency and highest in amplitude are called _____________ waves.
delta
28
New cards
Select the correct order of brain waves from actively awake to deep sleep.
beta, alpha theta, delta
29
New cards
Choose the correct pairing of characteristic brain waves with their stages of sleep.
Stage W || Beta Waves; Stage N1 || Alpha Waves; Stage N2 || Theta Waves; Stage N3 || Delta Waves
30
New cards
Insomnia
sleep disorder characterized by dissatisfaction with sleep quality or duration
31
New cards
Narcolepsy
a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and periodic, uncontrollable sleep attacks
32
New cards
Sleep Apnea
a sleep disorder involving regular interruptions of breathing during sleep
33
New cards
continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
treatment for sleep apnea that involves wearing a mask the uses air pressure to keep the airway open during sleep.
34
New cards
Parasomnias
abnormal behavioral, experiential, or psychological events that occur in conjunction with sleep (nightmare, sleep terrors, and sleepwalking)
35
New cards
Nightmares
scary dreams that almost always occur during REM sleep
36
New cards
Sleepwalking
a parasomnia that occurs during NREM sleep in response to an abnormal transition to light sleep
37
New cards
Sleep terrors
a parasomnia characterized by scary dreams and increased autonomic nervous system activity; typically occurs during NREM sleep so it can be accompanied by movement
38
New cards
Dreams
the sequence of images, feelings, ideas, and impressions that pass through our minds as we sleep
39
New cards
Manifest Content
the actual, remembered content of the dream, including storyline, characters, and specific details
40
New cards
Latent content
the underlying meaning of the dream where the unconscious, repressed wishes, and drives of the dreamer are expressed
41
New cards
Activation-synthesis hypothesis
the theory of dreaming that dreams are a result of the brain's attempt to make sense of this random neural activity
42
New cards
Our ___________is a biological clock responsible for the regulation of body temperature and levels of arousal during our sleep and wake cycle.
circadian rhythm
43
New cards
One of the many reasons psychologists believe we need to sleep is that our bodies tire during the day, and sleep helps the body recuperate and function at maximum capacity. This is a description of which theory?
Body restoration
44
New cards
In which stage of sleep do vivid dreams typically occur?
REM
45
New cards
The brain waves with the highest amplitude are referred to as _________ waves.
delta
46
New cards
Beta waves are associated with ___________, while theta waves are characteristic of the __________ stage.
alert wakefulness; N2
47
New cards
Billy is having trouble with insomnia. He has difficulty going to sleep and wakes up numerous times throughout the night. Based on what you know about sleep hygiene, what should you recommend he start doing?
Go to bed and get up at the same time each day
48
New cards
According to Freud, the latent content of our dreams is __________ and contains the repressed _______ and drives of the dreamer.
unconscious; wishes
49
New cards
Psychoactive drug
a chemical substance that alters brain function resulting in changes in consciousness, perception, and/or mood
50
New cards
Psychological dependence
process in which the body becomes physically dependant, or reliant, on the drug; typically involves tolerance and/or withdrawal
51
New cards
Tolerance
a form of psychological dependance where the body becomes used to a drug, resulting in an increased need for the drug to achieve the same affects
52
New cards
Withdrawal symptoms
psychological symptoms produced by the body when the drug is absent from the system
53
New cards
Physiological dependence
the emotional or motivational symptoms that include intense cravings for the drug, inability to concentrate on other nondrug-related activities, and/or feeling restless when not taking the drug
54
New cards
Substance use disorder
a psychological disorder characterized by a pattern of drug use leading to distress or significant impairment in functioning
55
New cards
Depressants (alcohol, barbiturates, and benzodiazepines)
class of drugs that depress of slow down the central nervous system and other bodily functions
56
New cards
Stimulants (caffeine, nicotine, amphetamine, cocaine)
a drug that excite or increase the functioning of the central nervous system and speed up the body
57
New cards
Narcotics (codeine, morphine, hydrocodone, oxycodone)
a type of depressant use medically in the management of pain
58
New cards
Heroin
a narcotic that activates specific opioid receptors that stimulate dopamine in the reward centers of the brain causing the sensation of pleasure
59
New cards
Hallucinogens
class of drug that can produce unusual sensations, distortions in the perception of reality and, in some cases, intense emotional mood swings
60
New cards
Marijuana
a drug containing tetrahydrocannabinol (THC); can produce some altered sensations, feelings of well-being, and changes in cognition
61
New cards
Depressants _____________ the functioning of the central nervous system. Some examples of these drugs include alcohol, __________, and ____________.
decrease; barbiturates; benzodiazepines
62
New cards
Which of the following correctly pairs the class of drugs with specific drugs from that category?
depressants = Xanax; stimulants = Methamphetamine; narcotics = Oxycodone; hallucinogens = LSD
63
New cards
Kirsten started taking her mother’s prescription for Vicodin. While this drug use doesn’t appear to be significantly affecting her life in any way, she has noticed over the past few months that she needs to take more Vicodin to feel its effects. Kirsten is experiencing ____________.
physiological dependence
64
New cards
Physiological dependence on a substance typically includes __________ and __________
tolerance; withdrawal
65
New cards
Markita promised her parents she would stop smoking marijuana. Every time she worried about school and bills, she would remember how marijuana relaxed her and made her feel good. She ended up smoking again and again, even though she hated disappointing her parents. This is an example of what type of dependence?
Psychological
66
New cards
Rina works hard all week long. On the weekend, she engages in binge drinking with her friends. How many drinks must she have in one night for it to be considered binge drinking?
4
67
New cards
Which neurotransmitter receptors does methamphetamine destroy in the brain?
Dopamine
68
New cards
Benzodiazepines come from the class of drugs called _______________, which ______________ the functioning of the central nervous system.
depressants; decrease
69
New cards
Heroin is classified as a ________ and directly _______ stress-related emotions.
narcotic; decreases
70
New cards
Petra feels really alive and an overwhelming sense of well-being after her 4-mile morning run. We could say Petra has entered a(n) __________state of consciousness after exercise.
altered
71
New cards
This type of meditation trains a person to become a nonjudgmental observer of all their thoughts and emotions.
Open monitoring meditation
72
New cards
_________ perception is an example of awareness without attention.
Subliminal
73
New cards
In a study on inattentional blindness, what percentage of radiologists failed to detect the intentional insertion of the image of a gorilla in CT scans?
83%
74
New cards
Justin installed a blue tooth device in his car. He now believes he will be safe from distracted driving because he does not have to use his hands to hold his phone. Justin doesn't understand that distracted driving stems from impaired _______ caused by redirection of ________.
cognition; attention
75
New cards
This small part of the hypothalamus controls the circadian clock and is responsive to light.
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
76
New cards
Quincy notices that he feels much more focused and aware later in the day and struggles to concentrate in his 8 a.m. meeting at work. Based on his circadian rhythm, Quincy is most likely in what age group?
20–25
77
New cards
In order to study sleep in natural conditions, researchers took people out to camp in the woods for one week. What did they discover about the influence of natural light on the participant's biological clocks?
It shifted the increase and decrease of melatonin in their bodies to 2 hours earlier to correspond with the natural light-dark conditions.
78
New cards
Cal was worried because of how much his newborn son was sleeping. He called the doctor to check how many hours a typical 2-month-old sleeps. The doctor told him newborns are supposed to sleep _____ hours each day.
14–17
79
New cards
Adolescents need _____ hours of sleep each night but on average only get ______ hours of sleep each night.
8–10; 7
80
New cards
Jaebok stayed up studying most of the night for his calculus final. He only slept about 4 hours. According to research, his memory and cognitive functioning will be decreased by approximately what percentage?
30%
81
New cards
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine changed the sleep cycle system in 2012 and now recognizes which stage of sleep as the deepest stage?
N3
82
New cards
Andre sometimes will wake himself up because his body jerks as he is drifting off to sleep and he says it feels like he is falling. Researchers refer to this bodily sensation as a _______________.
hypnagogic jerk
83
New cards
____________ waves emerge in sleep Stage N1 and continue into Stage N2.
Theta
84
New cards
This disorder involves excessive daytime sleepiness and periodic, uncontrolled sleep attacks that may leave the sufferer falling asleep at odd and inconvenient times.
Narcolepsy
85
New cards
Katie who is 10 years old will occasionally find herself asleep at the foot of her parents' bed in the morning, even though she went to sleep in her own bed. She never remembers leaving her room and walking to her parents' room. Katie is experiencing _______, which tends to occur during ______ sleep.
sleepwalking; NREM
86
New cards
Cyan told her friend that she believes her dreams are just random neural activity and they have no deeper meaning. Cyan believes in:
the activation-synthesis hypothesis.
87
New cards
The information-processing perspective on dreaming suggests dreams allow us to consolidate experiences from the day into ___________.
memories
88
New cards
People commonly dream of their teeth falling out; if you ascribe to the idea that dreams have hidden meanings, what is a way to interpret this dream?
Anxiety about self-image and appearance
89
New cards
Drugs that alter brain functions resulting in changes in consciousness, perception, and/or mood are called ___________ drugs.
psychoactive
90
New cards
A person can be diagnosed with a substance use disorder when the pattern of drug use causes _________ impairment or ___________ in the person's life.
significant; distress
91
New cards
Mia gets so drunk at college parties that she passes out and wakes up in a different location. She is not concerned about her behavior; however, her actions would fit into which diagnostic criteria for substance use disorder?
Using the substance in risky situations
92
New cards
What is one of the most commonly prescribed benzodiazepines on college campuses?
Xanax
93
New cards
What is the most widely used stimulant drug in the world?
Caffeine
94
New cards
Ritalin, a stimulant drug, is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. How does a stimulant help people who already have difficulties with distraction and hyperactivity?
By providing internal stimulation of neurotransmitters within the brain instead of the person seeking external stimulation
95
New cards
Narcotics are a type of __________that work by stimulating the body's internal pain management system or ___________.
depressant; endorphins
96
New cards
Sam has been taking opioids she buys from her friend for more than a year. She has spent all her savings on buying these pills and is considering dropping out of school so she can work more to make more money to buy drugs. If she goes too long without taking a pill, she begins to sweat and feel nauseated. Sam is experiencing ______________.
a substance use disorder and physiological dependence
97
New cards
Drew is an 18-year-old senior in high school. He has been using marijuana for 2 years on a daily basis and believes it has no long-term side effects. What does the research show as a potential side effect for Drew?
Lower IQ score
98
New cards
Which of the following can lead to a decreased level of consciousness?
Alcohol
99
New cards
Janel goes to sleep at night around 11 p.m. and usually drifts off quickly. She wakes up every morning at 3:45 and tosses and turns for 2 hours until she falls into a restless sleep to wake up at 6:30 feeling tired and groggy. She struggles throughout her day to stay awake and concentrate. Janel most likely suffers from which sleep disorder?
Insomnia
100
New cards
Sex
our biological classification as male or female based on the sex chromosomes contained in our DNA, our reproductive organs, and our anatomical features (biological)