Art History Exam #2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms

Temple of Portunus
Date: Officially built in 3rd or 4th century BCE; rebuilt between 120-80 BCE
uses the Greek architecture plan of peristyle (perimeter columns with some open space)
copies the porch style of steps going to the temple
to honor the god of harbors and ports, since during this time markets and wealth came from ports and sailing
In the 9th century, transformed into a Christian church
dedicated to either the worship of Fortuna Virilis or Portunus
Pseudoperipteral
Roman practice of covering a building with veneer or stucco

Dionysian Mystery Cult Villa of Mysteries
Date: 70-60 BCE
believed to depict a rite associated with a mystery cult of Dionysus or Bacchus
the god of win, fertility, threatre, madness, and ecstasy
Dionysiac frieze scene runs around continually around three walls
creates a sense of depth, everyone is standing a blue ledge
people are standing, sitting, or resting
figures act as if on edge
rich color to resemble exotic stone
initation of womanhood or marriage

Arch of Titus
Date: 81 CE
Artist: Domitian, after the death and deification of his brother, Titus
2 reliefs that depicted the Triumph of Titus and the Spoils of Jerusalem
one barrel vault
engaged Corinthian columns
to celebrate the victories Titus had in the Jewish war Judea
shows the earliest examples of columns of the composite order
the sculpture attempted to create an illusion of depth/ space
made out of marble
Basilica
secular buildings used as law courts and markets and for public assemblies
Mosaic
the art of creating images with an assemblage of small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials

Pantheon
Date: 118-125 CE
the only dome-shaped building that remained intact in Rome
had 16 columns that stood at 40 geet tall
built on specific ratios that equaled 12 to honor the 12 different Gods
Oculus=eye
the dome was open to the skt
building served as a sundial
building is a combination of a circle and a rectangle
rotunda dome
dome ceiling is astronomically aligned
on April 16th the sunlight hits the door exactly to honor the founding of Rome
the oculus let in ambient light and spotlights
represents the merging of the earth and the heavens
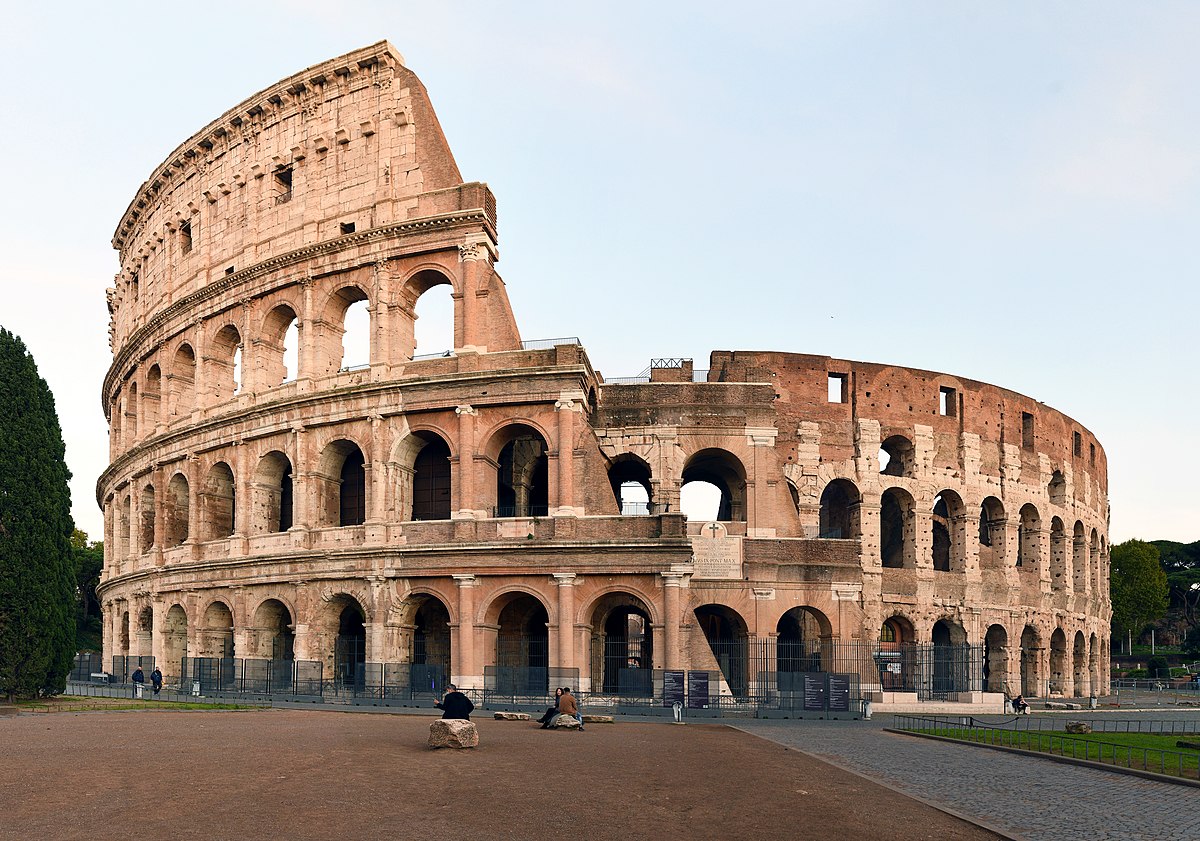

Colosseum
Date: 70 CE
Built by: great emperor Vespasian and was completed after his death by his son Titus
the Vespasian commissioned the Colosseum to gain back the support of the Roman people after the reign of Nero
used as a showcase for exotic wild animals from all corners of the Roman empire
staged reconstructions of famous Roman battle victories encouraging Roman patriotism
used for entertainment to glorify Rome as it replaced Nero’s Golden House
created a diversion for the poor
seated 50,000 people
Seating in 4 levels with 80 entrances
4 entrances were for imperial family
awnings could be rolled out to protect people from the sun

Sanctuary of Fortuna
Date: 110 BCE
Made of mixture of limestone and volcanic ash called pozzolana
one of the most important pilgrimage sites in ancient Rome
reflected the colossal design of Greek Hellenistic style
converted entire hillside into the man-made temple
way to show the Roman assertion of power and domination over nature

Trajan’s Forum
Date: 112 CE
Artist: Apollodorus of Damascus
functioned as the center of commerce and politics for the Roman Empire
made out of brick and concrete and marble for the columns
to commemorate Trajan’s victory
built with riches collected from Trajan’s victory over the Dacians
originally held an equestrian monument dedicated to Trajan in center
a public square in Roman city

Trajan’s Column
Date: 113 CE
Artist: Apollodorus of Damascus
commissioned by the Emperor Trajan
depicting his victory against Dacia (now Romania)
spiral narrative
stacking so they could fit more people
depicts 2 epic battles and campaigns against the Dacians
about 39 meters high including the basement and statue
made with 10 blocks of stone one on top of the other
propaganda piece
Fragments of Constantine
Date: 312-315 CE
made of Parian and Carrara marble
include the head and neck, the right leg from the knee to the foot, the left leg below the knee and the left food, part of the right arm and the right hand
the long face, neatly arranged hairstyle, and clean-shaven appearance of the head are deliberate attempt to evoke memories of earlier rulers
style differs from earlier roman royal art because it is abstract and simplified
it is similar because it is still a recognizable portrait
perhaps meant to convey the transcendence of the other worldly nature of the Emperor over the human sphere
placed in the Basilica of Maxentius and Constantine
made of marble
originally 40 feet high

Nave, Santa Croce
Date: 1294-1442 CE
nave finished 1385
Architect: Arnolfo di Cambio
place where Florentine greats are buried
place where a tomb is found for Dante
largest Franciscan Basilica in the world
uses wooden trusses to span the nave while French Gothic churches would have uses moldings to support the vaulted ceiling

Baptistery, Florence
Date: 1128 CE
baptistery- part of a church used for baptism
octagonal shape
there is a north, south, and east door
each with a different design made from different artists
until 1935, the only place where Florentines were baptized
east door was made by Lorenzo Ghiberti and labeled the door “Gates of Paradise”
north doors were also made by Lorenzo Ghiberti
dedicated to Florence’s Saint Jogn

Pisano, South Doors
Date: 1330-1336 CE
commissioned from Pisa by the guild of wool importers
cast of bronze and gilded, 28 separate panels across the two panels of the door
mostly represent scenes from the life of john the baptist
each vignette is framed by gothic quatrefoil

Palazzo della Signoria
Date: 1299 CE
holds a copy of Michelangelo’s David statue
known as the Old Palace
most important historic government building in Florence
increasing open civic space symbolic of increasing power of civic government
surrounds a loggia and Palazzo Vecchio (city hall) so it makes its claim as the political hub of Florence

Giotto Madonna Enthroned
Date: 1280 CE
Artist: Cimabue
shows the Virgin Mary with Christ Child on her lap with angles and saints surrounding them
east church influence
tempera panel
tempera is made from a mixture of water, plaster, and egg yolk so it would sick on panel give it a more vibrant color
this painting marks the end of medieval painting in Italy and the beginning of a new naturalistic approach to art
forms are foreshortened and modeled in light and shade to create figures that sculptural solidity and weight

Robert Campin Merode Triptych
Date: 1427-1428
full of hidden symbols meant to lead the viewer into deep reflection on the mysteries of the Incarnation, or God taking on a human form in the person of Jesus
reflects the emerging merchant class and new wealth
oil on wood
everyone is in the lower half of the image
left side are the donors, the people who commissioned it

Jan Van Eyck Arnofino Portrait
Date: 1434 CE
medium- oil on canvas
the surplus of cloth implies Mrs. Arnolfini is soon to be pregnant
further affirmed through the ripening oranges and the pinnacle on the bed post being the patron saint of child birth
the dog was originally viewed as a symbol for loyalty and fidelity

Brunelleschi Dome, Florence Cathedral
Date: 1420-1436 CE
the largest dome of its time and still the largest brick dome in the world
the creation of the dome, baptistery doors , the ox hoist were competed over between Ghiberti and Brunelleschi
dome was transformed into a sundial by Paolo Toscanelli
painting on the inside of the dome painting on the inside of the dome is The Last Judgment
estimated weight is 36,000 tons
started working on in the 1296 to show off Florence because it was one of Europe’s economic and culture capitals

Ospedale delgi Innocenti
Date: 1419-1424 CE
“hospital of the innocents”
originally a children’s orphanage
publicly commissioned by the Seta Guild
guild of silk merchants and goldsmiths
first hospital for foundling children in the world which was not run by the church
the function of the building suggests the idea of civic responsibility and sense of pride amongst the cities people
considered the first clean break from the Gothic style
first Renaissance building

nave of San Lorenzo
Date: 1421 CE
Architect: Brunelleschi and Michelozzo
the only church with an unfinished facade
no oculus or lighting at dome
very dark and does not quite match classical styles
flat coffered ceiling over nave
emphasis on proportionality perspective
classical details represented all’antica (ancient-inspired) style common in Florence
the Medici family church
one of the first centrally planned churches of the Renaissance

Alberti, facade, Santa Maria Novella
Date: 1458-1470 CE
the first pediment supports a broad band of decorated squares
used gothic forms of older parts of building in order to reconstruct the older style
became a prototype repeated by Renaissance designers
contains motifs of temple front and has 3 opening arches referencing Triumphal Arch

Ghiberti Gates of Paradise
Date:
called the Gates of Paradise because of its remarkable beauty and grandeur
made after a prestigious competition arranged by the Calimala guild to make a new set of doors for the Baptistery’s north entrance in Florence
competition between Brunelleschi and Ghiberti
after winning and making the north door he was commissioned to do create the East door
worked on the door for 27 years
compromised of 10 panels from the Old Testament in chronological order
started with the creation of Adam and Eve and ending with the meeting between Solomon and the Queen of Sheba
Used a lost bronze wax technique to make the door
Made a wax mold of the door and then poured melted bronze into the molds and then wax was peeled off and added to the door and painted with a small amount of gold and mercury

Masaccio Holy Trinity
Date: 1427-1428 CE
took 28 days to make
have to look up at the painting
is directly above the entrance to the Cathedral
God is actually represented as a human in this painting
Jesus looks realistic with anatomical accuracy and application of gravity
color palette is Earth bound colors, natural, more relatable for people of all classes
had cloth down far enough to show his pubic hair to show that he was also human
under the painting there is an inscription that states “As I am now, you shall be”
uses invisible geometry
there are upward and downward pointing triangles
upward triangles represent teh humanities desire to ascend to god
downward triangles represent the spiritual descent down to the physical world

Micelozzo Medici-Ricardi Palace, Florence
Date: 1459
widely considered to be the birthplace of the Renaissance
placed in the center of Florence as it was a focus of the community
three levels
the lower level was made of rustication of bricks with big arched openings
middle level has less roughness of bricks with windows with double arches forms, bifore windows
high level has perfectly smooth surface and bifore windows
first palazzo of Renaissance period that stands alone in its context to show Medici power

Donatello bronze David
Date: 1440 CE
symbolizes Florence’s triumph over Milan and the Medici family’s connection to the city’s greatness
first unsupported standing work of bronze cast during the Renaissance
first freestanding nude male sculpture made since antiquity
made by using the lost wax technique
represented in heroic classical nudity
very effeminate especially compared to Michaelangelo’s David

Botticelli Primavera
Date: 1477-1482 CE
one of the most written about, and most controversial paintings in the world and one of the most popular paintings in Western art
central theme is love and marriage, sensuality, and fertility
illustrated the renewed interest in Greek and Roman mythology
shows mythological, Roman Gods/Goddesses and characters but not from any particular story
can assume by the three women’s beauty, dancing, and number that they are the Three Graces
central figure is an idealized beauty, lovely curvature to form, emphasizes femininity
Aqueduct
an artificial channel for conveying water
ashlar masonry
a type of stone construction where all stones are dressed or cut to a uniform shape, size, and surface appearance
entrance hall
where patron greets people
needs to represent owner’s status
an inner courtyard
often at the entrance of a public building
coffer
a square or polygonal ornamental sunken panel used in a series as decoration for a ceiling or vault
sunken panel in a ceiling
rectangular indentations in the dome that decrease its thickness
used to lighten the load at the top
considered of the Column of Trajan, Basilica Ulpia, and Markets
bedrooms
normally very simple because they were only for sleeping
a small cubicle or bedroom that opened onto the atrium of a Roman house
a chamber in an Early Christian catacomb
roundel, spandrel, Dayton
roundel- a picture which is round in format
small circular decorative plate used extensively in Renaissance courtyards and arcades
spandrel- a triangular space enclosed by the curves of arches
apse, ata, attic
apse- a large semicircular or polygonal niche protruding from the end wall of a building
arched or with a domed roof
in Christian church, contains the altar
attic- a storey or low wall above the corince of a classical facade
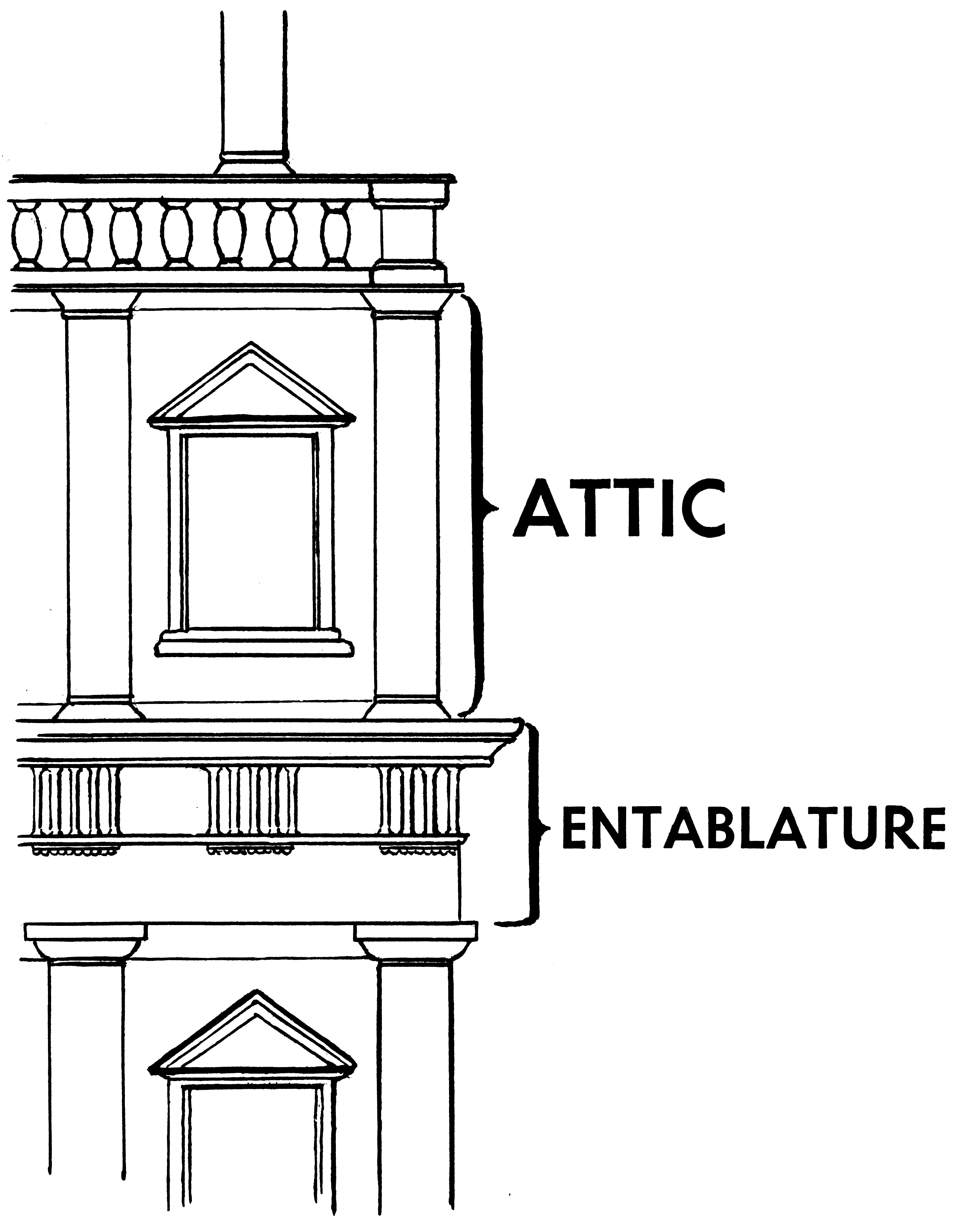
caryatid
female figure used in a place of a column as an architectural support for a porch or entryway
colonnade, cupola, plasters
colonnade- a series of columns in a straight line carrying an entablature
cupola- a small, dome-like structure on top of a building, crowning a roof or dome
plasters- a soft mixture, generally composed of lime, and mixed with sand, and other substances
oculus
the round central opening of a dome
quadriga
a two-wheeled chariot drawn by four horses harnessed abreast
tesserae
a small block of stone, tile, glass, or other material used in the construction of a mosaic
frigidarium
the cold room of an ancient Roman bath complex
fresco, buon and secco
buon- painting technique in which water-based pigments are applied to a surface of wet plaster
secco- technique where tempera is applied to plaster that has been allowed to dry first
chiaroscuro
means “light-dark”
clear tonal contrasts which are often used to suggest the volume and modelling of the subjects depicted
sfumato
the smoky quality which blurs contours so that figures emerge from a dark backgroud by means of gradual tonal modulations without any harsh outlines
technique of allowing tones and colors to shade gradually into one another, producing softened outlines or hazy forms
impasto
describes paint, usually oil paint, applied very thickly
tondo
a circular painting, relief carving, plaque, or mural design
sprezzatura
a certain nonchalance so as to conceal all art and make what one does or say appear to be without effort

campanile
bell tower usually built beside or attached to a church
a free standing tower which is adjacent to a church or abbey
palazzo
means “palace”
a large building in the city, regardless of whether it functioned as a governmental or institutional facility, a private residence, or both
refers to an architectural style of the 19th-20th centuries based upon the palazzi (palaces) built by wealthy families of the Italian Renaissance
foreshortening
technique of depicting an object or human body in a picture so as to produce an illusion of projection/extension in space
linear perspective
a system of creating illusion of depth on a flat surface
vanishing point
point at which the orthogonals meet and disappear in a composition done with scientific perspective
the central feature of scientific perspective: a single point towaeds which any set of parallel lines will seem to converge
orthogonals
imaginary lines which are parallel to the ground plane and the line of sight of the viewer
transversals
lines parallel to the picture plane (horizontally) that denote distances
cartoons (sinopia)
a red to reddish-brown earth pigment used by the ancients that depends for its color on its content of red ferric oxide