Inorganic Chemistry I: Atomic Structure, Bonding, and Molecular Geometry
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
What is the focus of Inorganic Chemistry?
Inorganic Chemistry is concerned with the properties and reactions of inorganic compounds, excluding organic compounds based on carbon chains or rings.
What are the fundamental particles of an atom?
Protons, electrons, and neutrons.
What does the atomic number represent?
The atomic number (Z) represents the number of protons in the nucleus and is equal to the number of electrons.
How is the mass number defined?
The mass number (A) is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
What is the relationship between mass number and number of neutrons?
The number of neutrons can be calculated as A - Z.
What is Quantum Mechanics?
Quantum Mechanics is the branch of physics dealing with atomic and subatomic systems, based on the concept of quanta.
Who is associated with the discovery of quanta?
Max Planck.
What does the de Broglie relationship describe?
The de Broglie relationship shows that a particle with momentum has an associated wavelength, given by λ = h / mv.
What is Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle?
Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle states that it is impossible to know both the momentum and position of an electron simultaneously.
How is the probability of finding an electron determined?
The probability of finding an electron at a given point is determined from the function Ψ², where Ψ is the Schrödinger wavefunction.
What does the Schrödinger wavefunction represent?
The Schrödinger wavefunction describes the behavior of an electron in a region of space called an atomic orbital.
What is the equation for the Schrödinger wavefunction in Cartesian coordinates?
Ψcartesian(x,y,z) = Ψradial(r)Ψangular(q,f) = R(r)A(q,f).
What is the significance of atomic orbitals in Quantum Mechanics?
Atomic orbitals represent regions in space where electrons are likely to be found, based on the solutions to the Schrödinger equation.
What is the distinction between inorganic and organic chemistry?
Inorganic chemistry deals with compounds not based on carbon chains or rings, while organic chemistry focuses on carbon-based compounds.
What is the role of wave mechanics in understanding electrons?
Wave mechanics combines classical mechanics with wave-like properties to describe electron behavior.
What is the importance of studying atomic spectra in inorganic chemistry?
Studying atomic spectra helps in the interpretation of electronic configurations and the behavior of electrons.
What is the relationship between momentum and wavelength according to the de Broglie hypothesis?
A particle's momentum is inversely proportional to its wavelength.
What does the term 'organometallic chemistry' refer to?
Organometallic chemistry is a sub-discipline that overlaps between inorganic and organic chemistry, focusing on compounds containing metal-carbon bonds.
What should students do when they are stuck in class?
Students should ask questions when they are stuck.
What are the three quantum numbers that uniquely label an atomic orbital?
n (principal quantum number), l (orbital quantum number), and ml (magnetic quantum number).
What does the principal quantum number (n) represent?
It represents the energy level of an electron in an atom, with values ranging from 1 to infinity.
What is the range of values for the orbital quantum number (l)?
It can take values from 0 to (n-1).
What are the possible values for the magnetic quantum number (ml)?
It can take values from -l to +l, including zero.
What are the four types of atomic orbitals?
s, p, d, and f orbitals.
What is the value of l for an s orbital?
l = 0.
What is the value of l for a p orbital?
l = 1.
What is the value of l for a d orbital?
l = 2.
What is the value of l for an f orbital?
l = 3.
What is the magnetic spin quantum number (ms) for a spin-paired electron?
One electron has ms = +1/2 and the other has ms = -1/2.
What does it mean for orbitals to be degenerate?
Degenerate orbitals have the same energy.
What is the significance of the Aufbau Principle in determining electronic configurations?
It states that orbitals are filled in order of increasing energy, starting with the lowest energy orbitals.
What does Hund's rule state regarding degenerate orbitals?
Electrons must occupy each degenerate orbital singly before any orbital can be spin-paired.
What is the Pauli exclusion principle?
No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
What is the ground state electronic configuration for the hydrogen atom (H)?
1s¹.
What is the ground state electronic configuration for helium (He)?
1s².
What is the sequence of relative energies of orbitals in neutral atoms?
1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p < 5s < 4d < 5p < 6s < 5d ~ 4f < 6p < 7s < 6d ~ 5f.
What is the definition of ionization energy?
The energy change associated with the removal of the outermost electron from a neutral atom in the gas phase at 0K.
What is the significance of multi-electron atoms in quantum mechanics?
They involve complex interactions between multiple electrons and the nucleus, making exact solutions to the Schrödinger equation impossible.
What happens to the degeneracy of orbitals with the same value of n in multi-electron atoms?
They are not degenerate; orbitals with the same n but different l values have different energies.
What is the first electron affinity of an atom defined as?
It is minus the internal energy change at 0K associated with the gain of one electron by a gaseous atom.
What is the general nature of the attachment of an electron to an atom?
It is usually exothermic, but can be endothermic when an electron is added to an anion.
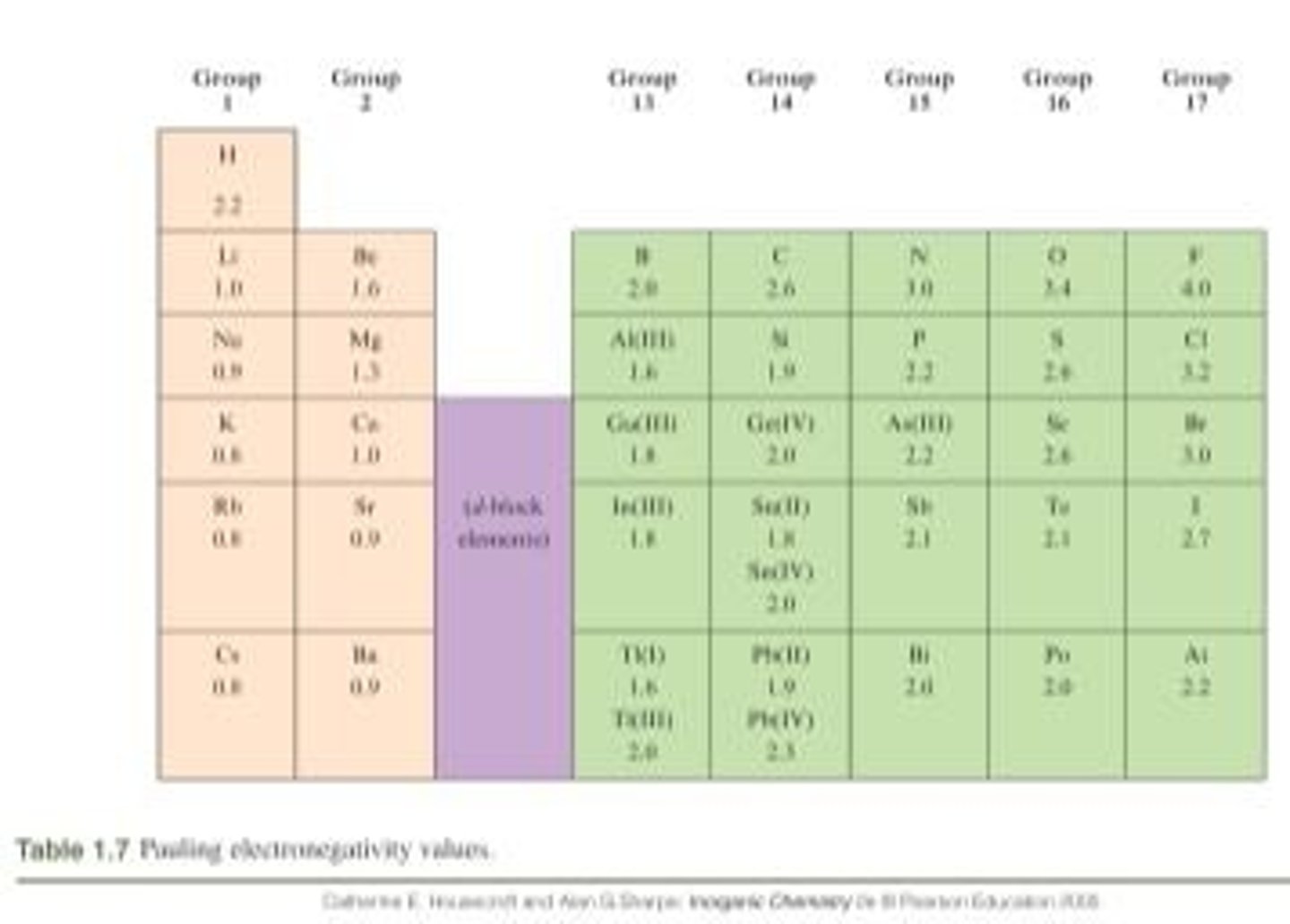
How did Linus Pauling define electronegativity?
As the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself.
What is the most useful scale for measuring electronegativity?
The Pauling scale, based on thermochemical data.
What distinguishes covalent species from ionic species?
In covalent species, electrons are shared between atoms, while in ionic species, one or more electrons are transferred between atoms to form ions.
What is the purpose of Lewis structures?
They provide a simple method for the arrangement of valence electrons in molecules.
What does valence bond theory suggest about molecule formation?
It treats the formation of a molecule as arising from the interaction of complete atoms that largely retain their original character.
What does molecular orbital theory allocate electrons to?
Molecular orbitals formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals.
What is a homonuclear covalent bond?
A bond formed between atoms of the same element.
What is the definition of a homonuclear molecule?
A molecule that contains one type of element.
How is the single bond covalent radius defined for an atom X?
It is half of the internuclear separation in a homonuclear X-X single bond.
What is the van der Waals radius of an atom X?
It is half the distance of closest approach of two non-bonded atoms of X.
What characterizes a diamagnetic species?
All electrons are spin-paired.
What characterizes a paramagnetic species?
It contains one or more unpaired electrons.
What do Lewis dot structures illustrate about bonding?
They show that atoms share electrons in the valence shell to form chemical bonds.
What does a single bond represent in terms of electron sharing?
A single bond represents a shared pair of electrons.
What does a double bond represent in terms of electron sharing?
A double bond represents two shared pairs of electrons.
What is the octet rule?
An atom obeys the octet rule when it gains, loses, or shares electrons to achieve an outer shell containing eight electrons with the configuration ns2np6.
How many valence electrons does an oxygen atom have?
Oxygen has six valence electrons.
What is the bond order for a single bond?
A single bond has a bond order of 1.
What is the bond order for a double bond?
A double bond has a bond order of 2.
What is the bond order for a triple bond?
A triple bond has a bond order of 3.
Can bond orders be fractional?
Yes, fractional bond orders such as 1½ or 1⅓ are also possible.
What does a single line represent in Lewis dot structures?
A single line represents a single bond, which is a shared pair of electrons.
What is the bond order of the sulfur dioxide (SO2) molecule?
The bond order of SO2 is 1½, as it can be represented by two resonance structures.
How many valence electrons does carbon have in the CH4 molecule?
Carbon has four valence electrons.
What is the bond order of the nitrate anion (NO2-)?
The bond order of the nitrate anion is 1½, as it has two resonance structures.
What is a resonance structure?
A resonance structure is one of two or more valid Lewis dot structures for a molecule that cannot be represented accurately by a single structure.
What is the significance of the double line in Lewis dot structures?
A double line represents a double bond, which consists of two shared pairs of electrons.
What is the bond order of the nitrate anion based on its canonical structures?
The bond order is calculated as the average of the bond orders from its canonical structures, resulting in 1½.
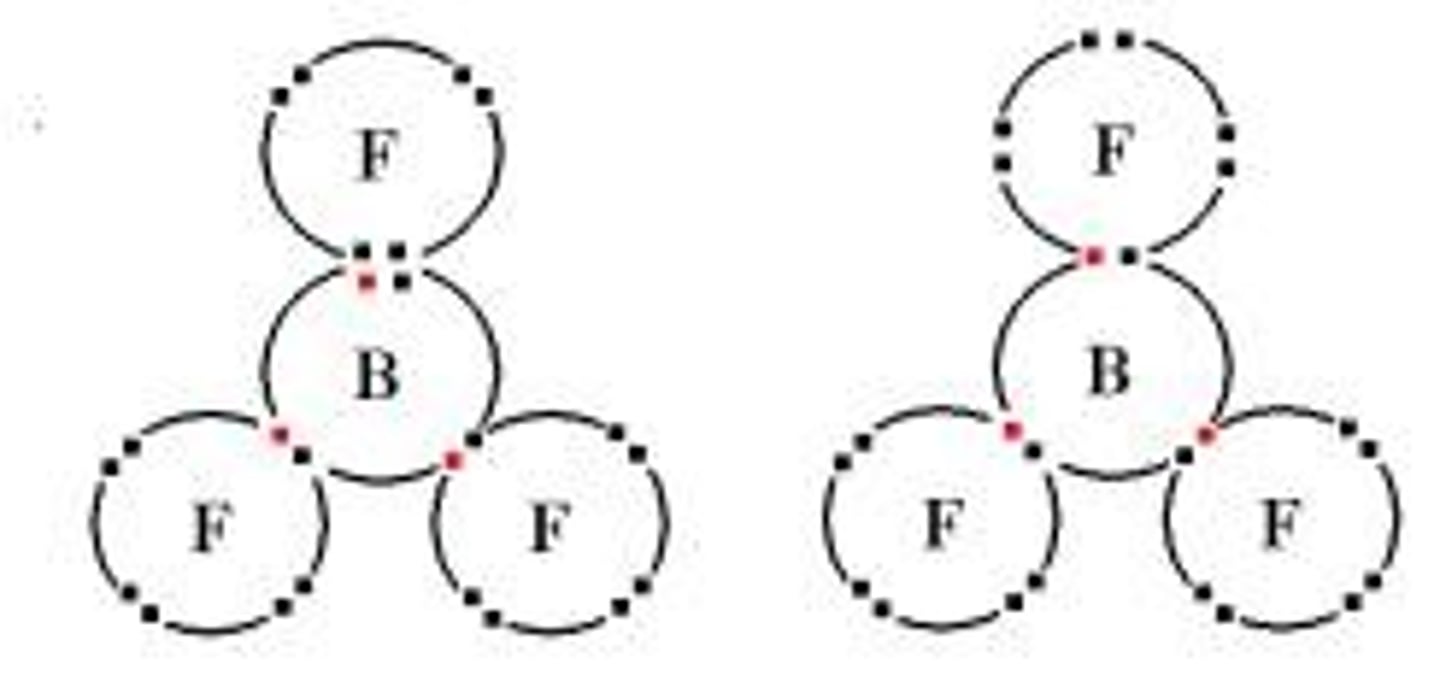
What is an example of a molecule that does not obey the octet rule due to having fewer than eight electrons?
Boron trifluoride (BF3) is an example, as it has only six electrons in its valence shell.
What are free radicals?
Free radicals are molecules that have an odd number of electrons, making them very reactive.
What happens to the bond order in resonance structures?
The bond order is averaged among the resonance structures to determine the effective bond order.
How many valence electrons do oxygen atoms have in carbon dioxide (CO2)?
Oxygen atoms have six valence electrons.
What is the structure of the ozone molecule represented by?
The ozone molecule can be represented by two equivalent Lewis dot structures, with the actual structure being the average of these two.
What does the notation O=S-O indicate in the context of sulfur dioxide?
It indicates that sulfur dioxide can be represented with both a single bond and a double bond between sulfur and oxygen.
What is the bond order of phosphorus pentafluoride (PF5)?
Phosphorus pentafluoride (PF5) has a bond order that does not conform to the octet rule due to the presence of more than eight electrons around the phosphorus atom.
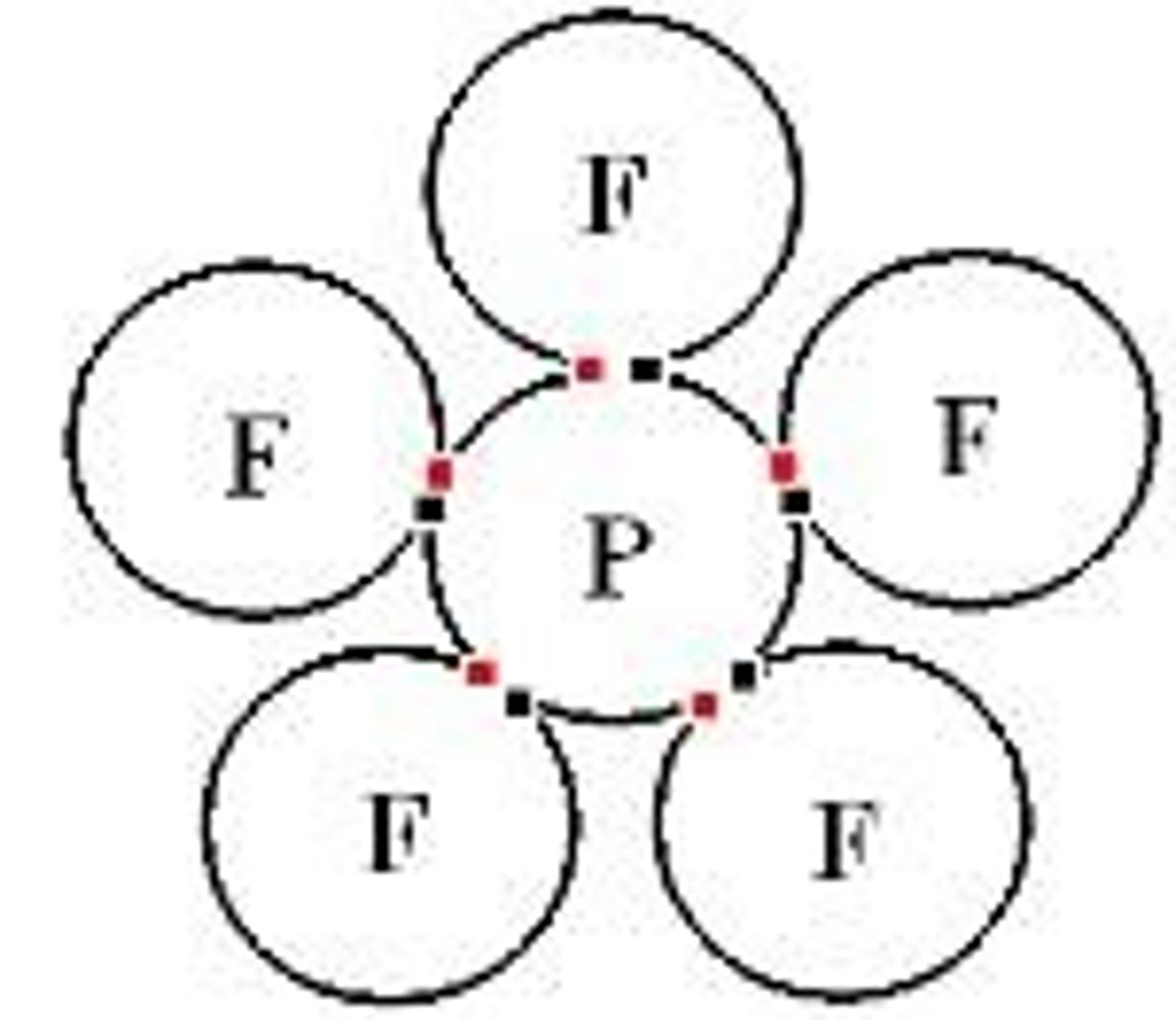
What is the average bond order for the nitrate anion based on its resonance structures?
The average bond order for the nitrate anion is 1⅓.
What is the Lewis dot structure for carbon dioxide (CO2)?
The Lewis dot structure for CO2 is O=C=O, indicating a double bond between carbon and each oxygen.
What must be considered when drawing Lewis dot diagrams for anions?
An extra electron must be added for each negative charge on the anion.
What is the bond length of O-O bonds in ozone?
The O-O bond length in ozone is approximately 2.78 Å.
What is the significance of the notation 'double arrow' in resonance structures?
The double arrow indicates that the actual structure is an average of the contributing resonance structures.
What is the average bond order for the nitrite anion based on its resonance structures?
The average bond order for the nitrite anion is 1½.
What is the role of resonance in molecular structure?
Resonance allows for a more accurate representation of a molecule's structure by averaging multiple valid Lewis structures.
What is the valence electron count for phosphorus in PF5?
Phosphorus has ten electrons in its valence shell in PF5.
What is the significance of the Octet Rule in phosphorus compounds?
Many phosphorus compounds, such as PF3 and [PO4]3-, do obey the Octet Rule.
Which compounds are examples of species that exceed the octet of electrons?
IF7 and XeF6 are examples, as both iodine and xenon have 14 valence electrons.
What does Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory describe?
MO Theory describes how molecular orbitals arise from interactions between atomic orbitals, depending on symmetry, overlap, and energy.
What is required for the formation of molecular orbitals?
The number of molecular orbitals formed must equal the number of atomic orbitals from the constituent atoms.
What determines the polarity of a bond in heteronuclear diatomics?
The differing electron withdrawing powers of the two atoms determine the bond's polarity and electric dipole moment.
How does molecular shape affect dipole moments in polyatomic species?
The net molecular dipole moment depends on the magnitudes and directions of all bond dipole moments in the molecule.
What is the role of lone pairs in determining molecular shape according to VSEPR theory?
Lone pairs are stereo-chemically significant and their repulsions are greater than those of bonding pairs.
How are electron-electron repulsions ranked in VSEPR theory?
Lone pair-lone pair > lone pair-bonding pair > bonding pair-bonding pair.
What is geometrical isomerism?
Geometrical isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula and structural framework but differ in spatial arrangement.
What types of isomers can octahedral species exhibit?
Octahedral species can exhibit cis- and trans-arrangements or fac- and mer-isomers depending on the arrangement of identical groups.
What is the significance of isoelectronic species?
Isoelectronic species contain the same number of electrons and often have similar structures.
What are the implications of the VSEPR model for predicting molecular shape?
The VSEPR model predicts molecular shape based on the repulsions between electron pairs around a central atom.
What is the relationship between molecular shape and bond angles?
Molecular shape influences bond angles, which are affected by the type and arrangement of electron pairs.
What is the effect of electronegativity differences on bond polarity?
Greater differences in electronegativity between bonded atoms increase bond polarity.
How does the presence of multiple bonds affect electron-electron repulsions?
Electron-electron repulsions decrease in the order: triple bond-single bond > double bond-single bond > single bond-single bond.
What is a dipole moment?
A dipole moment is a vector quantity that represents the separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule.