exam 2 - joints & lever systems
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
fibrous
structural classification
connected by dense connective tissue and have no joint cavity
cartilaginous
structural classification
connected by hyaline cartilage and have no joint cavity
synovial
structural classification
have a synovial, fluid-filled cavity that surrounds the articulating bone
joints
permit effective movement and protect soft organs
articulation
where 2 bones meet (bone and cartilage)
synarthrosis
functional classification
DO NOT move
amphiarthrosis
functional classification
small degree of movement
diathrosis
functional classification
allow free movement
Suture
synarthrotic and fibrous
ex: sagittal suture
gomphosis
synarthotic and fibrous
extooth in socket
syndesmoses
amphiarthoracic and fibrous
ex: distal ends of radius/ulna and tibia/fibula
synchrondroses
synarthotic and cartilaginous
connected by hyaline cartilage
ex: sternum ribs 1-12
symphesis
amphiatoracic and cartilaginous
bones connected by fibrocartilage
ex: pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs
fully moveable articulations
plane, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, ball and sockett
ALL: diathoracic and synovial
plane
classification: D & S
flat surfaces come together
ex: tarsals, carpals
hinge
classification: D & S
convex into concave
ex: humerus/ulna, humerus/radius, femur/tibia
pivot
classification: D & S
round surface firs into rings of ligaments
ex: axis and atlas
condyloid
classification: D & S
convex oval fits into epillitical cavity
ex: radius/scaphoid
saddle
classification: D & S
ball and socket
classification: D & S
spherical head fits into concave socket
ex: femur and pelvic / humerus and scapula
bony joint
synostosis - immovable joint
tendon
dense regular connective tissue
attaches muscle to bone
stablizes joints
ligament
connective tissue attaches one bone to another
bursa
fibrous sac filled with synovial fluid located between the adjacent muscles
tendon sheath
elongated bursae wrapped around a tendon
meniscus
cartilage absorbs shock and pressure
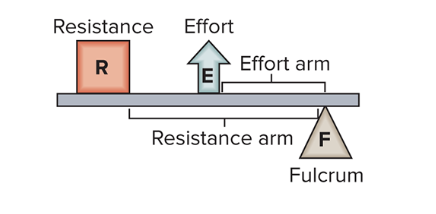
lever
any elongated object that rotates around a fixed point called a fulcrum
rotation occurs when an effort overcomes resistance (load) at some other point
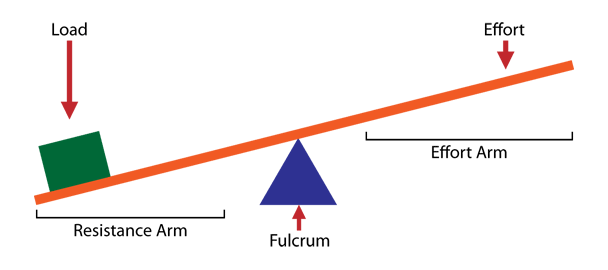
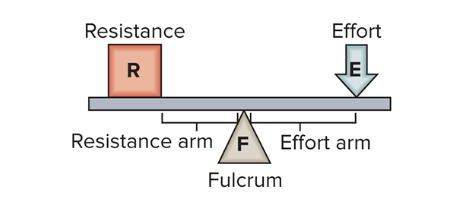
first class lever
fulcrum in the middle between effort and resistance
ex: head nodding motion (atlanto-occipital joint)
fulcrum: atlas
effort: posterior neck muscles
load: weight of head
function: helps balance and extend the head
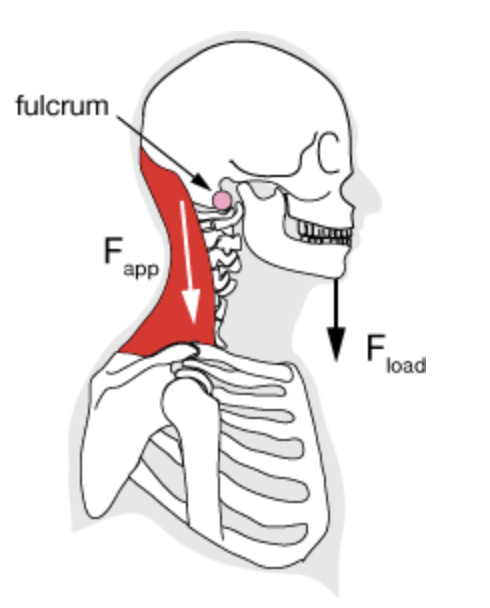
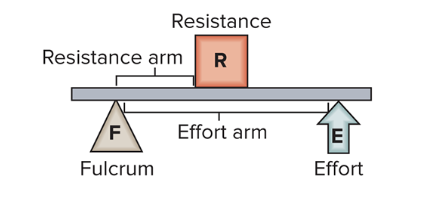
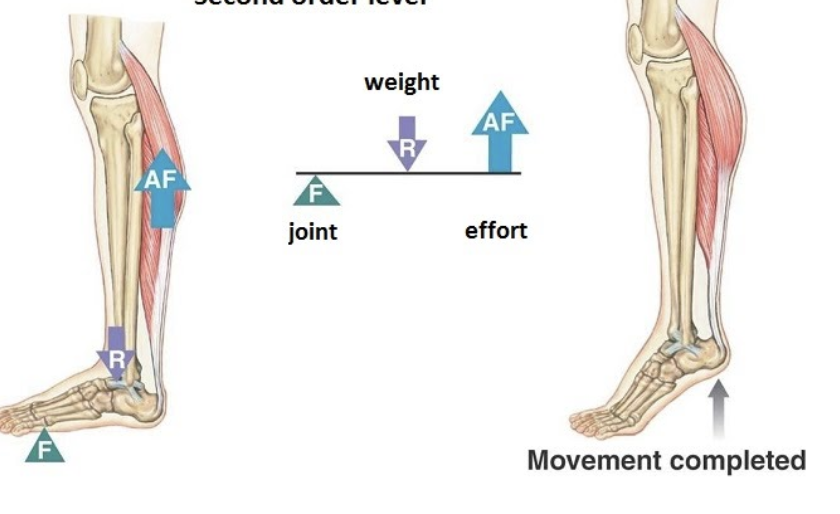
second class lever
resistance between fulcrum and effort, load is between the fulcrum and effort
ex: flexion at the ankle (standing on tiptoes)
fulcrum: ball of the foot
effort: calf muscles (being used to push up)
load: body weight
function: allows powerful movement with less effort
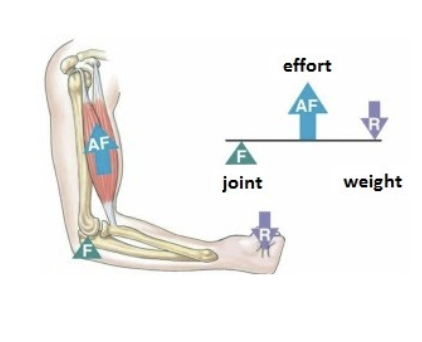
third class lever
effort is between the fulcrum and the load
ex: elbow flexion (bicep curl)
fulcrum: elbow joint
effort: biceps brachii pulling on radius
load: weight of forearm
function: most common type, allows speed and range of motion but requires more force
uniaxial
bone moves in just one plane or axis
ex: plane joint, hinge, pivot
biaxial
bone moves in two places or axes
ex: saddle (between thumb), condylar (knuckles)
syndesmoses
bones that join together and are held in place with sheets of collagen
dense regular connective tissue
radius and ulna
synchondroses
bones joined together with hayline cartilage between ends of the bone
synovial
most complex joint with varying amounts of mobility
cartilaginous joints
intervertebral discs
and pubic symphysis
multiaxial
bone moves in multiple planes
ex: ball and socket (hip and shoulder)
Symphyses are slightly mobile joints where the articulating bones contain a pad of _________ blank between them.
fibrocartilage