a&p unit 4 exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:39 PM on 4/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, smooth, & cardiac muscle
2
New cards
describe skeletal muscle:
\
a __striated & voluntary__ tissue, located in skeletal muscles, whose (fibers) cells are multinucleated.
a __striated & voluntary__ tissue, located in skeletal muscles, whose (fibers) cells are multinucleated.
3
New cards
describe smooth muscle:
a nonstriated & involuntary tissue, located in the wall of hollow visceral organs (such as the stomach), whose cells are uninucleate.
4
New cards
describe cardiac muscle:
a __striated & involuntary__ muscle, located in the heart, whose cells are uninucleate.
5
New cards
What does striated mean regarding muscle tissues?
Refers to the alternating dark & light bands visible through a microscope
6
New cards
Structure of muscular system:
skeletal muscle, tendons, & aponeurosis
7
New cards
Function of the muscular system: (1)
Movement: as a skeletal muscle contracts, tension (force) develops. Generally, this force is transmitted in such a way that a muscle’s insertion (moveable
8
New cards
Function of the muscular system: (2)
Maintenance of posture
9
New cards
Function of the muscular system: (3)
Production of heat for thermoregulation
10
New cards
Define tendon:
a cord-like structure made of dense connective tissue which transmits force from a skeletal muscle to a bone.
11
New cards
Define aponeurosis:
a flat sheet of dense connective tissue which joins muscle to muscle
12
New cards
Approximately, how many skeletal muscles occur?
406
13
New cards
**Define myo:**
muscle
14
New cards
Define sarco:
**denoting flesh or striped muscle**
15
New cards
Define fiber:
cell for muscles
16
New cards
Define fascicle:
small bundles of nerve or muscle fibers enclosed by connective tissue
17
New cards
Define fascia:
connective tissue between skin & bones
18
New cards
describe Sarcolemma:
the cell membrane of a muscle fiber
19
New cards
describe Transverse tubule:
**inward extension from the sarcolemma which conducts impulses into the muscle fiber**
20
New cards
describe Sarcoplasmic reticulum:
smooth endoplasmic reticulum specialize for the storage & release of calcium ions (Ca+2)
21
New cards
Sarcoplasm:
**the cytoplasm of a muscle fiber**
22
New cards
describe Myofibrils:
**a cylindrical bundles of contractile proteins**
23
New cards
What do myofibrils include?
actin & myosin
24
New cards
describe Actin:
**thin myofilament protein. Actin possesses binding sites for attachment of myosin “heads” to form cross-bridges during contraction.**
25
New cards
describe Myosin:
thick myofilament. Myosin possesses “heads” which form cross-bridge links to actin’s binding sites during contraction.
26
New cards
describe Troponin & Tropomyosin:
inhibit actin’s binding sites prior to and after contraction.
27
New cards
How are actin & myosin arranged?
**Into sarcomeres**
28
New cards
Describe sarcomere:
the basic unit of striated muscle tissue
29
New cards
Describe z lines:
**functional unit of a skeletal muscle fiber**
30
New cards
Describe I band:
**actin only; during contraction, it becomes smaller & disappears.**
31
New cards
Describe A band:
**actin & myosin; during contraction, it remains the constant length.**
32
New cards
Describe neuromuscular junction:
the point at which a motor neuron provides the Ach stimulus to a muscle fiber’s sarcolemma
33
New cards
Describe synaptic vesicles:
**releases ACh, which provides the stimulus to the muscle fiber’s sarcolemma**
34
New cards
Describe acetylcholine ACh:
\
**provides the stimulus for muscle contraction**
**provides the stimulus for muscle contraction**
35
New cards
**Describe events of skeletal muscle fiber relaxation.**
\
* ACh is decomposed by the enzyme AChE (acetylcholinesterase)
* Calcium ions are actively transported back into the SR
* Myosin cross-bridge links release from actin’s binding sites
* The sarcomere resumes its resting length
* ACh is decomposed by the enzyme AChE (acetylcholinesterase)
* Calcium ions are actively transported back into the SR
* Myosin cross-bridge links release from actin’s binding sites
* The sarcomere resumes its resting length
36
New cards
What is the 1st energy source (immediate energy source)?
**ATP is the source of energy for muscle fibers.**
37
New cards
What is the 2nd energy source?
**creatine phosphate** donates energy to regenerate ATP.
38
New cards
What is the 3rd energy source?
**glucose** is initiated to supply energy to regenerate ATP.
39
New cards
What is the 4th energy source?
**Glycogen** reserves are mobilized to supply energy sources.
40
New cards
What is required for the aerobic stages of cellular respiration of glucose?
**oxygen**
41
New cards
When there’s insufficient oxygen, muscle fibers initiate the production of?
Lactic acid
42
New cards
what contributes to muscle fatigue and eventually to muscular soreness?
lactic acid
43
New cards
During intense muscle activity, what develops as muscle fibers produce and accumulate lactic acid?
oxygen debt
44
New cards
within skeletal muscle fibers, what protein temporarily stores oxygen?
myoglobin
45
New cards
“fast” muscle fibers contain ____ ____ and appear what color?
little myoglobin; pale/whitish
46
New cards
what type of muscle fibers are specialized for rapid responses to stimulus, but will fatigue rapidly?
fast muscle fibers
47
New cards
**“slow” muscle fibers** contain ____ ____ & appear ____/_____ in color.
abundant myoglobin; dark/reddish
48
New cards
what kind of fibers respond relatively slowly to stimuli, but are specialized for endurance
slow muscle fibers
49
New cards
contraction/relaxation period:
**a single response of a muscle to a single stimulus.**
50
New cards
describe Minimum in twitch response
the stimulus must be of “threshold” intensity or greater.
51
New cards
latent period:
time in which the impulse travels across the sarcolemma, into the T-tubules, and into the SR.
52
New cards
label the diagram for the twitch response
\-
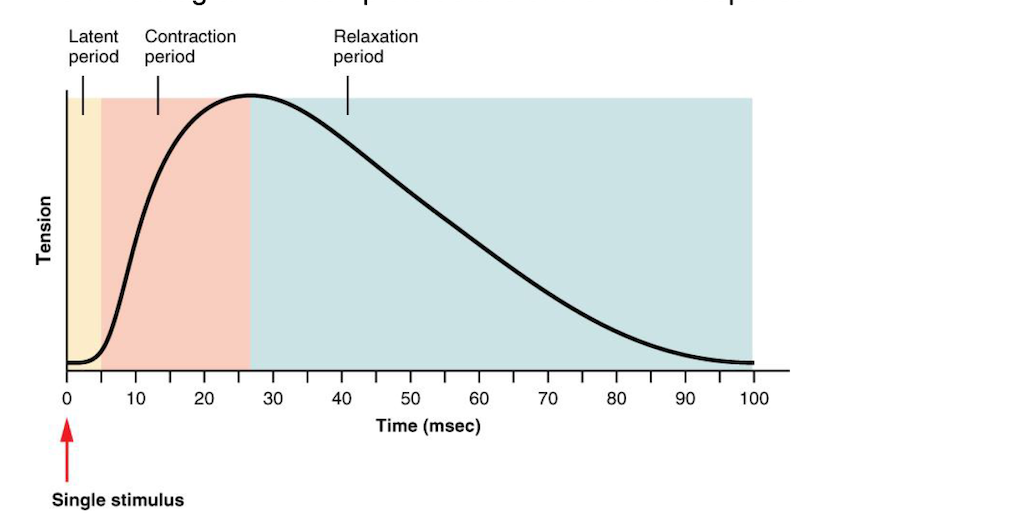
53
New cards
Define tonus:
**the natural and continuous slight contraction of a muscle**
\
\
54
New cards
Define isometric contraction:
**contraction that tenses a muscle, but does not produce joint movement.**
55
New cards
Define isotonic contraction:
contraction that produces movement
56
New cards
Define atrophy:
**decrease in size (and strength) of a muscle**
57
New cards
Define hypertrophy:
**increase in size (and strength) of a muscle**
58
New cards
**Describe the relationship between bones & skeleton muscles in producing movement.**
muscles are attached to bones by tendons at their origins and insertions. Skeletal muscles produce movements by pulling on the bones.
59
New cards
Define origin:
the attachment point of a muscle to a stationary bone
60
New cards
Define insertion:
**the attachment point of a muscle to a moveable structure (ex: bone)**
61
New cards
Define innervation:
\
\
**the nerve supply of a muscle**
62
New cards
define action:
the movement produced when a muscle contracts (ex: elevation, flexion, adduction, etc.)
63
New cards
**Define agonist** (primer mover)**:**
**the primary muscle that contracts to produce an action (primer mover)**
64
New cards
Define synergist:
a muscle which assists a prime mover
65
New cards
Define antagonist:
a muscle with an opposite action of the prime mover
66
New cards
Describe ways in which skeletal muscles are named
**direction, location, size, number of origins, & origin & insertion**
67
New cards
Describe ways in which skeletal muscles are named
**direction, location, size, number of origins, & origin & insertion**
68
New cards
Define rectus:
fibers run parallel to the body’s midline
69
New cards
Define oblique:
fibers run diagonal to the midline
70
New cards
Define transverse:
fibers run at a right angle to the midline (perpendicular to the midline)
71
New cards
Define major:
large
72
New cards
Define minor:
small
73
New cards
Define minimus:
smallest
74
New cards
Define medius:
medium-sized
75
New cards
Define maximus:
largest
76
New cards
Define longus:
longest
77
New cards
Define brevis:
shortest
78
New cards
Location:
bone names often reflect associated skeletal components
79
New cards
Frontalis (a muscle of facial expression):
elevates eyebrows
80
New cards
Temporalis (a muscle of mastication):
elevates the mandible
81
New cards
Masseter:
elevates the mandible during mastication
82
New cards
Orbicularis oculi (a muscle of facial expression):
closes the eye
83
New cards
Zygomaticus (a muscle of facial):
elevates the upper lip
84
New cards
Sternomastoid (sternocleidomastoid) -
rotates the head
85
New cards
Pectoralis major-
medially rotates humerus, adducts humerus
86
New cards
Abdominal muscles (external oblique, internal oblique, rectus abdominis, transversus abdominis) –
compress & flex the abdomen
87
New cards
Deltoid:
abducts the humerus
88
New cards
Biceps brachii
flexes the elbow
89
New cards
Flexors located in the anteriorly in the forearm:
flex wrist
90
New cards
Sartorius:
laterally rotates the thigh
91
New cards
Adductor longus:
adducts the femur
92
New cards
Gracilis:
adducts the thigh
93
New cards
Quadriceps femoris:
extend the knee
94
New cards
Tibialis anterior:
dorsiflexes the foot
95
New cards
Trapezius:
extends/ hyperextends the head
96
New cards
Infraspinatus:
adducts the humerus
97
New cards
Triceps brachii-
extends the elbow
98
New cards
Extensors located posteriorly in the forearm:
extend wrist or phalanges
99
New cards
Gluteus maximus:
extend & rotate the femur
100
New cards
Gluteus medius:
rotates the femur