c) To measure the melting point of pure and impure benzoic acid and compare them
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Theory
• The melting point of the benzoic acid crystals previously obtained and recrystallised is found
• As comparison the melting point of impure benzoic acid crystals not recrystallised is also found
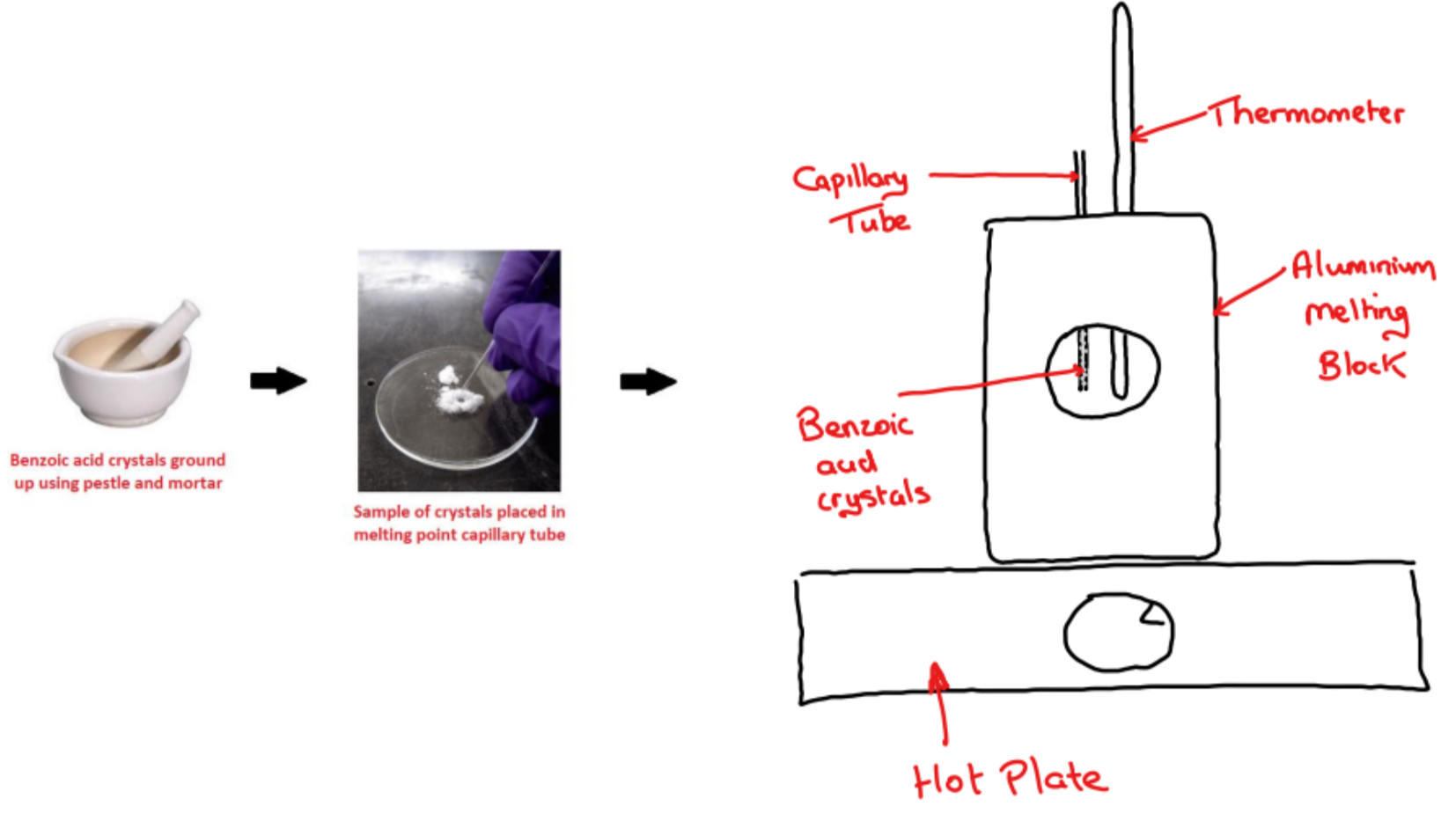
Procedure:
➢ The benzoic acid crystals are ground up using a pestle and mortar
➢ The crystals are placed in a melting point capillary tube which is placed into an aluminium melting block
➢ The aluminium melting block is heated slowly using a hot plate while observing the crystals
➢ The melting point range of the benzoic acid crystals is recorded using a thermometer
i.e. the temperature is recorded when:
a) The benzoic acid crystals begin to melt
b) The benzoic acid crystals have finished melting
• The two temperatures recorded gives the melting point range of benzoic acid
What is the melting point range of pure benzoic acid?
• 121°C - 122°C
• The closer the benzoic acid crystals used are to this range, the more pure they are
Give two differences noted when determining the melting point of impure benzoic acid
(1) The melting point obtained will be lower than 121°C - 122°C
(2) The crystals will melt over a wider range of temperature E.g. 116°C-119°C i.e. pure crystals melt over a sharper range
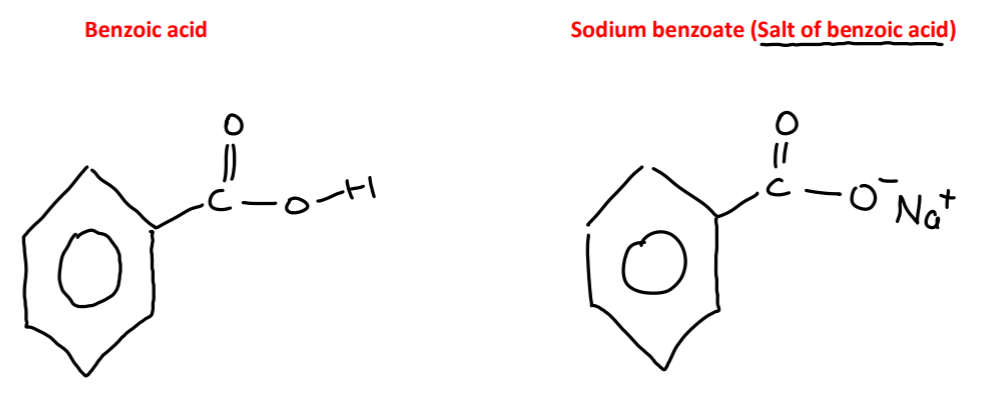
Give a common use of benzoic acid or of its salts
Benzoic acid and salts of benzoic acid Example: Sodium benzoate are commonly used as food preservatives
Benzoic acid and its salts formation
To make a salt the H+of the acid is replaced by a metal ion eg. Na+