u1 apwh test review (before 1200) (copy)
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
paleolithic societies
hominins grouped together in small societies such as bands and subsisted by gathering plants, fishing, and hunting or scavenging wild animals.
Neolithic societies
lived in densely built settlements and numbered 50-300 individuals. During the Pre-Pottery, Early and Middle ___, the basic unit of society was the clan or extended family that consisted of parents, children, grandparents and other close kinship.
imperial administration
rule by an emperor or empress; new emperors are passed down through generation or through conquest
stratification
the arrangement or classification of something into different groups.
"wealth is the main symbol of social stratification"
social hierarchy
religion
this shaped society as a whole, along with social hierarchies, conflicts, trade, alliances, the joining of two states, etc.
primary sources
a piece of evidence that was created from that timeline
e.g., the Declaration of Independence, or a copy of of the Declaration of Independence to preserve the document.
The Vedas
secondary sources
any documents that are based off of primary sources
e.g., textbooks, history websites
analyzing a picture and writing text/annotating
contextualization
using historical context to understand a source better
methods of state building from the classical states
marriage alliances -- unifying power & trust
tribute — paying goods or wealth to the stronger power to keep them away
e.g., Xiongnu empire paying in silk or grains to the Chinese empire for peace and to prevent invasion.
religious authority
rulers, often considered divine
Byzantine empire
east side of Roman empire
does not consist of Mediterranean culture
mirrored the political system of late imperial Rome
unique culture thrived
Judaism
monotheistic
beliefs became codified into the Torah
Capture from the Babylonians lead to some degree of culture assimilation
monotheistic
belief in one God
e.g., Christianity, Islam, Judaism, Buddhism
polytheistic
belief in multiple Gods
e.g., Ancient Greek religions, Hinduism
Hinduism
Based off of the writings of the Vedas and the Upanishads
oldest religion in the world
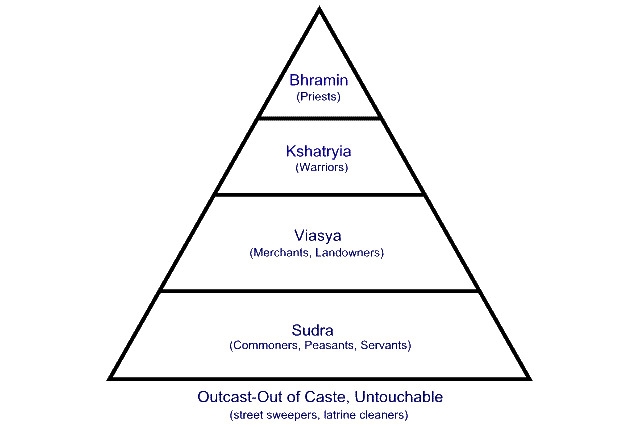
Caste System
based off of Hindu culture
Vedas
sacred texts combined to explain rituals, ceremonies, coming of age, retirement, marriages, cremation, sacrifices, stories, values, hymns, etc.
Upanishads
focuses more on life’s meaning and how man & universe is related
added ideas to the Vedas, such as karma, reincarnation, atman, etc.
dharma
role in society/life based on your stature in the caste system
samsara
cycle of passions/suffering.
desires, such as food, sex, & pleasure
Moksha
escape from samsara
Buddhism: can achieve this in one lifetime
Hinduism: can take generations to achieve
Hindu life cycle
student: learn basic Hinduism
Householder: make a family
hermit: spiritual practice, volunteering, reading scripture, pilgrimage
renunciation: free obligation, work on spiritual self, perhaps with a Guru
pilgrimage
journey to a holy place in one’s culture/religion
Buddhism
Began in 6th century BCE
Siddhartha Guatama/Enlightened One/Buddha
4 Noble Truths
Demoted caste systems & called everyone equal since anyone can become enlightened
Siddhartha Guatama
Enlightened One, or the Buddha
Did not find meaning in Hinduism, left home and became an ascetic (wandering holy man)
his Enlightenment came underneath a tree
4 Noble Truths
Buddhismn
life is suffering/samsara
suffering is caused by false desires/things that do not bring satisfaction
suffering can be relieved by removing desire/samsara
to remove samsara follow the Eight Fold Path
path to Enlightenment/Nirvana
Confucianism
inner virtue, morality, and respect for the community and its values
civil exams to achieve a high stature are based off of these beliefs; anyone can take the civil exams and achieve a high stature
created social hierarchy and gave men more status
5 basic relationships
more of a philosophy rather than a religion
accepting of society’s endless cycle of inequality
Daoism
religion
to be in a natural order of the universe; the cosmos are a natural and unchanging principle that governs all of the workings of the world.
not good or bad, but just is.
learn to “live with it”
Yin & Yang
reflective & introspective
5 basic relationships in Confucianism
Emperor & subject: the Emperor has responsibility to take care of his subjects, and the subjects obey their emperor.
older brother & younger brother: the older brother takes care of younger brother and the younger brother obeys the older brother
husband & wife: husband takes care of wife and wife obeys husband
friend & friend: mutual care and obedience
a superior man in Confucianism exhibits
ren - kindness
li - sense of property
Xiao - filial peity/loyalty to family
Christianity
originated from a Jewish belief of a Messiah
its founder, Jesus, was viewed as a Messiah
born and raised a Jew
during his lifetime, the area he lived in was controlled by Rome
assured life after death to ALL followers, so it did not follow a caste system or social hierarchy
love, charity, humility
Final judgement day where righteous are granted immortality and sinners are sent to hell
Jesus was executed by Roman officials bc. he was seen as a rebel against Judaism
After his death, his teachings were spread, but not w/o conflict
Hellenism
Culture of Ancient Greece
Mainly spread by Alexander the Great
no caste system in this culture
formed out of curiosity and theories, but were never acted upon. their questions and theories were milestones later contributed to the scientific methods
Symmetry, proportion, and the pursuit of the ideal
e.g., Greek statues have identical proportions (6x the foot is the height, hence our measurements today)
Became more cosmopolitan through the expanding empire of Alexander the Great
Alexander purposefully spread this culture by introducing marriages b/w different cultures (methods of state-building)
belief systems
generally force social structures, while offering roles and status to men and women (gender roles in society)
what agricultural surplus lead to
___ lead to higher developed society, with gender roles, caste systems, and social hierarchy.
patriarchal religions/cultures
___ religions or cultural examples include Confucianism, Christianity, and Hinduism
asceticism
extreme rejection of the materialistic values of the world, such as pleasure of desire.
Moksha
monasticism
lifestyle of living as monks in a monastery
eliminated the caste system by giving women and the poor to level up in society by becoming a monk
Buddhism
Shamanism
not a religion
set of practices to manipulate the natural world through rites and ceremonies performed by shamans.
found within people who can’t read, therefore eliminates caste system
animism
objects are inhabited by spirits or God
found within people who can’t read, therefore eliminates caste system
ancestors communicated with the living using oracle bones
raised importance of having a script and people who can read
oracle bones that survive today provide information on early Chinese civilizations
the importance of oracle bones in Chinese society
Roman Empire
very organized
including division of states and their military
led to Western Latin Empire and eastern Greek portion, plus the Byzantine Empire
their civil laws apply to all cultures
Jus Gentium and Jus Civile
Persian Empire
1st Persian Empire: Achaemenid
reached peak under Cyrus the Great
at its peak, conquered many countries, mainly in the Arabian Peninsula
disagreement between the Greeks and the Romans caused Alexander the Great to expand Persian Empire
the last Persian Empire was the Sassanid Empire. Its unravel is one of the primary factors for the spread of Islam
centralized
power with one individual or group of individuals
target of blame falls upon that individual or group of individuals when weakness falls upon the people
decentralized
decisions made at a local scale
devolution can lead to separation of regions
difficulty uniting during times of crises
The Period of Warring States
occurred after the fall of the Zhou Dynasty
period of conflict, confusion, instability, chaos
caused regenration
questions like “what is the best form of government?” or “what is the nature of a man"?”
answers to these questions lead to the cultures of Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism
Qin Dynasty
only lasted 14 years, but created many aspects of Chinese culture
aspects include creating a bureaucracy
roads, bridges, literacy systems, the Great Wall of China, paper money, standard units of weight
However strict political philosophy generated resentment, lead to revolution after death of emperor.
bureaucracy
a group of people having the most influence over a country
Han Dynasty
came to power after the Qin Dynasty
ruled for 400 years
official adoption of Confucianism and civil service exams of this philosophy caused it to be embedded into Chinese culture
why Romans are the reason that different cultures engage in trade
their basic laws -- jus civile and jus gentium -- applied to all cultures, which created unity
diplomacy
negotiation b/w allies and foes
e.g., in the Gupta Empire, defeated kings from rivalry empires would pay a price to stay in rule, making them indirect subjects to Emperor Samudragupta.
Han taking over the Xiongnu through an alliance
unification
blending of two regions
viae militares
military roads created by the Romans to move troops easily
all governments’ policies to facilitate commercial activities
Romans applying their laws to all cultures (ignorance is not an excuse for a crime) lead to more cultural unity
Qin emperor centralizing China, created infrastructure by collecting tax from the people
helped advance government
over extension of borders
one of the main reasons why an empire would collapse; borders grew so large that they had trouble guarding their territory
high amount of taxation
one of the main reasons of the decline of an empire; this created an imbalance between the rich and the poor.
pattern and settlement in Arabia before Muhammed’s life
Arabia was intensely tribal without any centralized force of government
known as the Nomadic Bedouins, security and protection was given to people in the tribe
trade was bringing in wealth that challenged the tribal system
where Islam began
Medina; people in Mecca thought of Muhammed’s teachings as a threat to the current polytheistic beliefs of the tribe, so he was kicked out and sent elsewhere. He started his teachings in Medina, where it first popularized.
however, the faith of one God (Allah) later influenced modern society in Arabia by bringing tribes together and creating a sense of unity.
5 pillars
faith/belief in no God but Allah
prayers - 5 times a day facing Mecca (holy place)
alms giving - donating money to the poor
fasting - Ramadan, praying (Ramadan is a cultural practice ADOPTED into Islam)
Muhammed’s return to Mecca, raised an army of 10,000 people to destroy the city and the Gods in Quaba to establish Allah, and restart its beliefs
Khalif
takes place of Muhammed after his death, essentially as a leader of a religious community
mix of religious, military, and political authorities
someone who is given a mandate of power
first four Khalif’s are known as the Rightly Guided Ones
last Khalif’s name is Ali, and debate was to choose between the four Khalifs or Ali
prophet
messenger of God
Suni and Chia tribes
Suni tribe was Muhammed’s tribe
believed that the only legitimate Khalif was the Ali, since he was related to Muhammed and rejected all the other three Khalifs
Shia was a tribe with other Muslim beliefs
all four Khalifs were legitimate
Umayyads
they spread Islam the farthest by conquest
the most influential group of Islam
filled the position of Khalifs for generations
overthrown by the Abbasid because the Abbasids were non-arabian Muslims
Abbasids
non-arabian Muslims
created a new dynasty in 750 CE
overthrew Umayyads
curious for education
Baghdad
became the richest city in Arabia
had the most influence
taken over the Mongols
major trading center
influenced by the Persians; establishment of a bureaucracy
Persian Empire

Qin empire
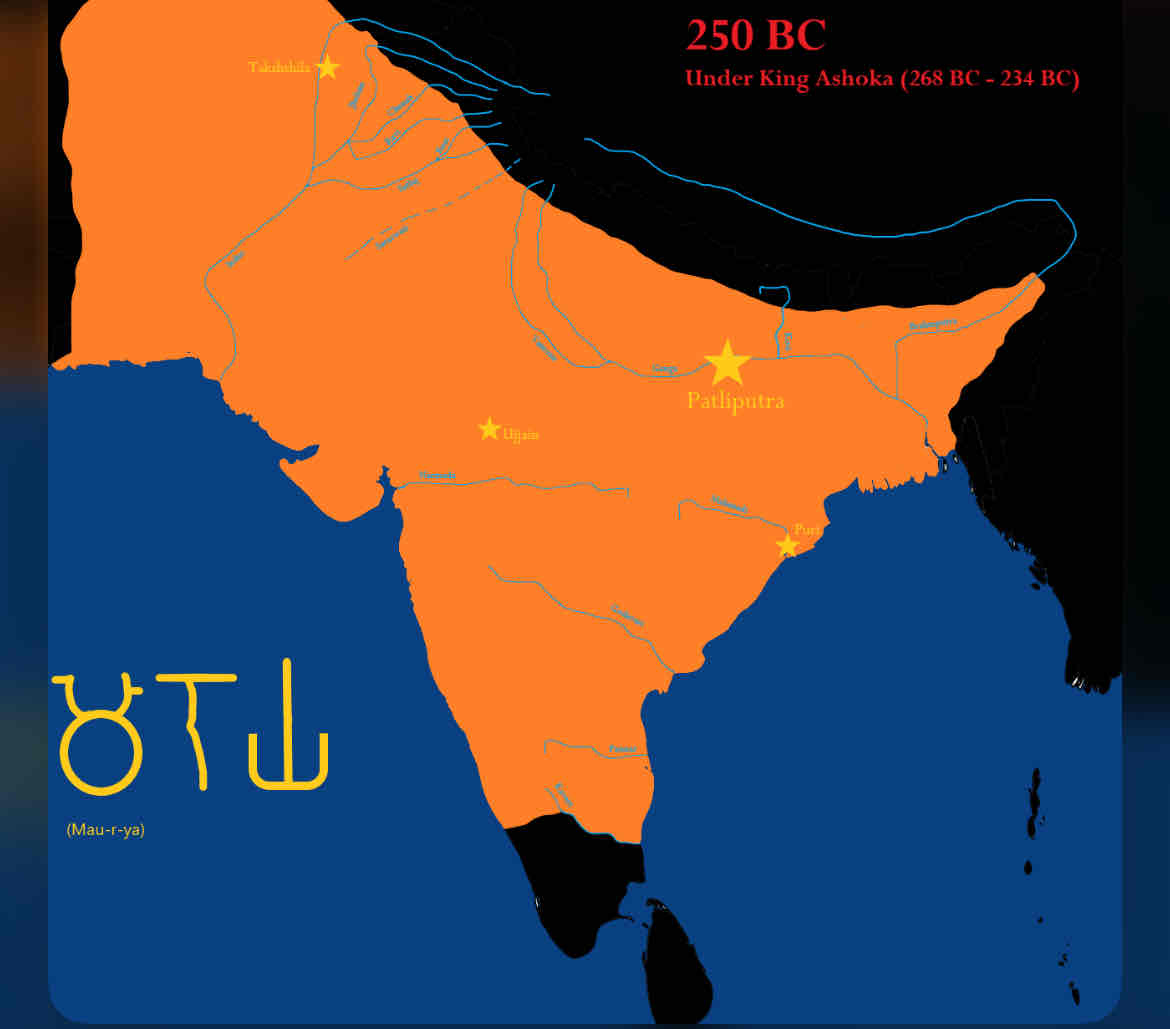
Mauryan Empire
Roman Empire & Phoenicia
Mayan Civilization
Moche civilization
Han Empire
Gupta Empire