A103 Exam 3
1/94
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Canine Terminology
intact female → BITCH
intact male → STUD DOG
delivery/birth → WHELPING
Canine Terminology
intact female → __
intact male → __
delivery/birth → __
Canine Development
neonatal → 0 - 10 DAYS
infant → 11 DAYS - 3 WEEKS
socialization → 3 - 12 WEEKS
fear → 8 - 12 WEEKS
juvenile → 12 WEEKS to PUBERTY
adolescent → PUBERTY to social MATURITY
Canine Development
__ → __ days
__ → __ days - __ weeks
__ → __ weeks
__ → __ weeks
__ → __ weeks to __
__ → __ to social __
1. Canine Development - Neonatal Period
age → 0 - 10 DAYS
eyelids and external ear canals are CLOSED
4 things to look for in pup after birth
strong suckle
raise head
slide along
vocalize
altricial → BORN IN UNDEVELOPED STATE
dependent of mom for 3 things
food
thermoregulation
stimulation to urinate/defecate
Canine Development - Neonatal Period
age → __ days
eyelids and external ear canals are __
4 things to look for in pup after birth
altricial → __
dependent of mom for 3 things
Canine Development - Infant Period
age → 11 DAYS - 3 WEEKS
puppies develop VISION/HEARING and move a lot
provide a COMPLEX environment to allow for optimal development of the DIGESTIVE SYSTEM and desensitization to “FRIGHTENING” STIMULI
what to look for at:
10 - 16 days → EYELIDS OPEN
full sight → 4 - 8 WEEKS
12 - 14 days → EXTERNAL EAR CANALS OPEN
full hearing → 3 - 6 WEEKS
14 - 21 days → WALK & URINATE/DEFECATE SPONTANEOUSLY
14 days → 1ST DEWORMING
Canine Development - Infant Period
age → __ days - __ weeks
puppies develop __/__ and move a lot
provide a __ environment to allow for optimal development of the __ and desensitization to __
what to look for at:
10 - 16 days → __
12 - 14 days → __
full sight → __
14 - 21 days → __
full hearing → __
14 days → __
Canine Development - Socialization Period
age → 3 - 12 WEEKS
expose puppies to ALL situations they are likely to encounter during life and begin VACCINATIONS
what to look for at:
3 - 6 weeks → BABY TEETH ERUPT
4 - 6 weeks → TESTES DESCEND (if not at birth)
6 - 8 weeks → ADULT POSTURES & MOVEMENTS
first vet visit with VACCINATIONS
WEAN (keep with litter until 8 - 10 WEEKS, if possible)
6 - 12 weeks → SOCIALIZATION with people
learn BITING inhibition
basic training → SIT, STAY, DOWN, COME, CRATE TRAINING, LEASH WALK, ETC.
house training → OUTSIDE AT RIGHT TIMES, SAME PLACE, POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT
regression in training progress NORMAL
Canine Development - Socialization Period
age → __ weeks
expose puppies to __ situations they are likely to encounter during life and begin __
what to look for at:
3 - 6 weeks → __
4 - 6 weeks → __ (if not at birth)
6 - 8 weeks → __
first vet visit with __
__ (keep with litter until __ weeks, if possible)
6 - 12 weeks → __
learn __ inhibition
basic training → __
house training → __
regression in training progress __
Canine Development - Fear Period
age → 8 - 12 WEEKS
occurs during the SOCIALIZATION period (3 - 12 weeks)
period when pups develop TRAUMATIC RESPONSES
traumatic experiences may make a puppy FEARFUL, ANXIOUS, or NEUROTIC
training should be THOUGHTFUL
Canine Development - Fear Period
age → __
occurs during the __ period (3 - 12 weeks)
period when pups develop __
these experiences may make a puppy __
training should be __
Canine Development - Juvenile Period
age → 4 MONTHS to PUBERTY (6 - 14 MONTHS)
RAPID physical development
INCREASED independence
CONTINUED training
fear periods (lasting 3 WEEKS)
Canine Development - Juvenile Period
age → __ months to __ ( __ months)
__ physical development
__ independence
__ training
fear periods (lasting __ weeks)
Canine Adolescent Period
age → PUBERTY to SOCIAL maturity
degree of social maturity VARIES BY breed
Canine Adolescent Period
age → __ to __ maturity
degree of social maturity __ breed
Deworming Puppies
MOST, NOT ALL, puppies are born with worms
even if pups are born 100% worm-free, they are AT RISK once born
FREQUENT deworming of puppies is often recommended
deworming at 2, 4, 6, and 8 WEEKS of age ± monthly until 6 MONTHS
worm pathogeny cycle
dog ingests TOXOCARA larva/egg or dog ingests TRANSPORT host
infected dog passes egg in FECES, MILK, and IN UTERO
egg is passed in DOG FECES
larva (inside egg) develops in the ENVIRONMENT
Deworming Puppies
__ puppies are born with worms
even if pups are born 100% worm-free, they are __ once born
__ deworming of puppies is often recommended
deworming at __, __, __, and __ weeks of age ± xmonthly until __ months
worm pathogeny cycle
dog ingests __ larva/egg or dog ingests __ host
infected dog passes egg in __, __, and __
egg is passed in __
larva (inside egg) develops in __
Castrations & Ovariohysterectomies for Canines
castration → NEUTER (removal of TESTES)
ovariohysterectomy → SPAY
2 commonly used acronyms
OHE
OVH
Castrations & Ovariohysterectomies for Canines
castration → __ (removal of __)
ovariohysterectomy → __
2 commonly used acronyms
Benefits of Ovariohysterectomies for Canines
no unplanned PREGNANCIES
no ESTRUS behavior
decreased risk of UTERINE dz
decreased risk of OVARIAN dz
decreased risk of MAMMARY tumors
intact females have 4× greater risk of benign and malignant tumors in dogs than spayed females
Risk of Ovariohysterectomies for Canines
SURGICAL risk
ANESTHETIC risk
urinary INCONTINENCE (3%)
lack of muscle control results in UNCONTROLLED urinating
treat with LIFETIME estrogen supplements
weight GAIN
permanent
Benefits of Ovariohysterectomies for Canines
no unplanned __
no __ behavior
decreased risk of u__ dz
decreased risk of o__ dz
decreased risk of __ tumors
intact females have __ times greater risk of benign and malignant tumors in dogs than spayed females
Risk of Ovariohysterectomies
s__ risk
a__ risk
urinary __ (3%)
lack of muscle control results in __ urinating
treat with __ estrogen supplements
weight __
permanent
Risks of Early Neutering
JOINT DISORDERS → hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia, &/or cranial cruciate ligament tear
CANCERS → lymphosarcoma, mast cell tumor, hemangiosarcoma, or osteosarcoma
Recommended Time for Neutering
breed and size-specific (> 40 LBS)
delay castration/OHE to 1 OR 2 YEARS
there ISN’T a one-size-fits-all recommendation
the best may depend on a dog’s BEHAVIORAL tendencies (roaming, marking, aggression), environmental ENVIRONMENTAL factors (housing, fencing, space), JOB (working dog vs pet), and the LEGAL requirements of a city/town.
Risks of Early Neutering
__ → hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia, &/or cranial cruciate ligament tear
__ → lymphosarcoma, mast cell tumor, hemangiosarcoma, or osteosarcoma
Recommended Time for Neutering
breed and size-specific (> __)
delay castration/OHE to __ years
there __ a one-size-fits-all recommendation
the best may depend on a dog’s __ tendencies (roaming, marking, aggression), environmental __ factors (housing, fencing, space), __ (working dog vs pet), and the __ requirements of a city/town.
Canine Estrous Cycle
puberty (breed-dependent) → @ 4-9 MONTHS to 2 YRS
non-seasonal MONOESTROUS
list the 4 phases and their durations
PROESTRUS - 9 days (0-28d)
ESTRUS - 9 days (1-24d)
DIESTRUS - 2 months
ANESTRUS - 3-5 months (< 3 months = subfertile)
time between cycles → 4-13 MONTHS (avg 7 months)
Canine Estrous Cycle
puberty (breed-dependent)
non-seasonal __
list the 4 phases and their durations
time between cycles
Canine Estrous - Proestrus
female attracts male but RESISTS BREEDING
ENLARGED vulva
BLOOD-TINGED uterine discharge
2 hormones involved
estrogen → INCREASES THROUGHOUT AND PEAKS JUST BEFORE ONSET OF STANDING HEAT
progesterone → AT BASAL LEVELS
Canine Estrous - Proestrus
female attracts male but __
__ vulva
__ uterine discharge
2 hormones involved
estrogen
progesterone
Canine Estrous - Estrus
seeks male, FLAGS tail, STANDS for mating
PINK-STRAW colored discharge
2 hormones involved
estrogen → DROPS
progesterone → (P4) RISES
1.5 to 2.5 ng/ml → LH SURGE
4 to 10 ng/ml → OVULATION (occurs 1-2 DAYS after LH surge)
Canine Estrous - Estrus
seeks male, __ tail, __ for mating
__ colored discharge
2 hormones involved
estrogen → __
progesterone → __
1.5 to 2.5 ng/ml → __
4 to 10 ng/ml → __ (occurs __ days after LH surge)
Canine Estrous - Diestrus
WON’T STAND for mating
LITTLE TO NO discharge
3 hormones involved
estrogen → BASELINE
progesterone → peaks @ 15 TO 80 ng/ml @ 15-30 DAYS then drops to < 2 ng/ml by end of DIESTRUS
prolactin → causes MAMMARY GLAND DEVELOPMENT
Canine Estrous - Diestrus
__ for mating
__ discharge
3 hormones involved
estrogen → __
progesterone → peaks @ __ ng/ml @ __ then drops to < __ ng/ml by end of __
prolactin → causes __
Canine Estrous - Anestrus
duration → 3 - 5 MONTHS
behavioral signs → NONE
2 hormones involved
estrogen → FLUCTUATES
progesterone → LOW
Canine Estrous - Anestrus
duration → __
behavioral signs → __
2 hormones involved
estrogen → __
progesterone → __
Bitch - Gestation Length
from LH peak → 65 ± 1 DAY
from breeding → 63 ± 8 DAYS (55 - 71)
Bitch - Gestation Length
from LH peak → __ day
from breeding → __ days
Normal Whelping
stage 1 → PREPARATION
duration → 6 - 24 HOURS
INCREASED fetal cortisol
INCREASED placenta and uterine PGF2a
DECREASED P4 levels
cervical DILATION and uterine MYOMETRIAL CONTRACTIONS
NESTING/hiding, restless, shivering, increased HR/RR
stage 2 → delivery of PUPPIES
UTERINE and ABDOMINAL contractions
~30 min to 1 hour → ACTIVE STRAINING = puppy
~15 min to 3 hours → BETWEEN PUPPIES
stage 3 → delivery of PLACENTA
passed after PUPPY or after 2 TO 3 PUPS
count PLACENTA and don’t let the mom EAT them
Normal Whelping
stage 1 → p__
duration → __
__ fetal cortisol
__ placenta and uterine PGF2a
__ P4 levels
cervical __ and uterine __ contractions
__/hiding, restless, shivering, increased __/RR
stage 2 → delivery of __
__ and __ contractions
~30 min to 1 hour
~15 min to 3 hours
stage 3 → delivery of __
passed after __ or after __
count __ and don’t let the mom __ them
Canine Dystocia
stage 2 lasts > 30 MIN without puppy delivery
> 2 HOURS between delivery of puppies
mom shows signs of ILNESS or DISTRESS
stage 1 or 2 never BEGINS
prominent BLOOD-TINGED discharge
GREEN-TINGED discharge without delivery
Canine Dystocia
stage 2 lasts > __ without puppy delivery
> __ between delivery of puppies
mom shows signs of __ or __
stage 1 or 2 never __
prominent __ discharge
__ discharge without delivery
Canine Puppy Resuscitation
4 things to check
WARMTH
AIRWAY
BREATHING
CIRCULATION
break the AMNION
suction NOSE and MOUTH with BULB SYRINGE
keep head and neck EXTENDED
vigorously RUB dry
monitor 4 things
BREATHING
VOCALIZING
MOVING
HEART BEATING
provide OXYGEN
Canine Puppy Resuscitation
4 things to check
break the __
suction __ and __ with __
keep head and neck __
vigorously __ dry
monitor 4 things
provide __
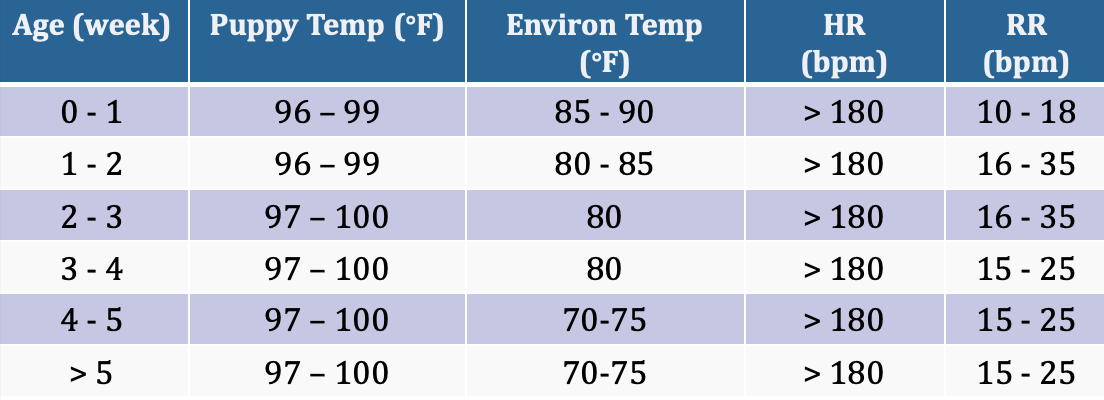
Canine Neonate Care
> 50% of all deaths in puppies occur in the first 3 days
fill in the chart
Canine Neonate Care
>__% of all deaths in puppies occur in the first 3 days
fill in the chart
Post Whelping Care
once the puppies are stable (ABC) and active…
tie off the UMBILICUS
dip the umbilicus in IODINE
check for DEFECTS and nursing
± collar
weigh (in GRAMS)
warm
by 10 days, puppies should DOUBLE their birthweight
puppy birthweight = 300 g (0.66 lb)
make sure mom is comfortable and puppies are VIGOROUS and nursing
puppies receive ~10% of their immunoglobulins transplacentally
kittens receive ~25% of their immunoglobulins transplacentally
Post Whelping Care
once the puppies are stable (__) and active…
tie off the __
dip the umbilicus in __
check for __ and nursing
± collar
weigh (in __)
warm
by 10 days, puppies should __ their birthweight
puppy birthweight = __ g (__ lb)
make sure mom is comfortable and puppies are __ and nursing
puppies receive ~__% of their immunoglobulins transplacentally
kittens receive ~__% of their immunoglobulins transplacentally
Canine Core Vaccines
DA2LPP or DHLPP
puppy
visit @ 6 - 8 WEEKS
visit @ 10 - 12 WEEKS
visit @ 14 - 16 WEEKS
visit @ 20 WEEKS (canine parvovirus)
adult → booster in 1 YEAR, then every 3 YEARS
rabies → STATE/LOCAL laws apply
puppy @ 3 - 4 MONTHS
adult → booster in 1 YEAR, then every 1 - 3 YEARS
Canine Core Vaccines
DA2LPP or DHLPP
puppy
visit @ __ weeks
visit @ __ weeks
visit @ __ weeks
visit @ __ weeks (canine parvovirus)
adult → booster in __ yr then every __ yr
rabies → __ laws apply
puppy @
adult → booster in __ yr then every __ yr
Canine Core Vaccine - Rabies
pathogen → RABIES VIRUS
transmission
through SALIVA (bites)
clinical signs
ANXIOUS to VAGUE behavioral changes
difficulty SWALLOWING
sensitivity to LIGHT
paralysis
death
treatment
STATE/LOCAL laws apply
Canine Core Vaccine - Rabies
pathogen → __
transmission
through __ (bites)
clinical signs
__ to __ behavioral changes
difficulty __
sensitivity to __
paralysis
death
treatment
__/__ laws apply
Canine Core Vaccine - DA2LPP or DHLPP
Distemper virus → CANINE DISTEMPER
Adenovirus 2 → INFECTIOUS TRACHEOBRONCHITIS
Adenovirus 1 → CANINE INFECTIOUS HEPATISIS
Leptospirosis → SPIROCHETE (bacteria)
Parainfluenza → INFECTIOUS TRACHEOBRONCHITIS
Parvovirus → CANINE PARVOVIRUS
Canine Core Vaccine - DA2LPP or DHLPP
Distemper virus → __
Adenovirus 2 → __
Adenovirus 1 → __
Leptospirosis → __ (bacteria)
Parainfluenza → __
Parvovirus → __
Canine Core Vaccine - Canine Distemper Virus (CDV)
pathogen → CONTAGIOUS PARAMYXOVIRUS
transmission
primarily AEROSOLIZED droplets
DO NOT live well outside host
pathogenesis
1 day → MULTIPLIES IN MACROPHAGES and CARRIED TO LOCAL LYMPH NODES
few days → PROLIFERATES IN LYMPHOID ORGANS
8 - 9 days → VIREMIA (epithelial cells of skin, eyes, respir, GI and UG tracts, CNS)
clinical signs
viremia → FEVER (104˚F)
gastrointestinal → VOMITING, DIARRHEA, LETHARGY
respiratory and eye → NASAL/OCULAR DISCHARGE, PNEUMONIA
dermatologic → THICKENED FOOT PADS or NASAL PLANUM
neurologic → CIRCLING, HEAD TILT, PARESIS, PARALYSIS, FOCAL or GENERALIZED SEIZURES (chewing fits)
diagnosis
fever and MULTISYSTEMIC disease
virus ISOLATION (ex. RT-PCR)
treatment → symptomatic and supportive
prognosis
asymptomatic or mild disease in OLDER dogs with GOOD immunity
severe disease in YOUNGER dogs (PUPPIES) or host with POOR immunity
cases with neurological signs yield a GUARDED or POOR prognosis
range of hosts distributed WORLDWIDE (domestic and wild canids, marine mammals, felids, procyonids and ursids, nonhuman primates)
genus MORBILLIVIRUS, family PARAMYXOVIRIDAE
Canine Core Vaccine - Canine Distemper Virus (CDV)
pathogen → __
transmission
primarily __ droplets
__ live well outside host
pathogenesis
1 day → __
few days → __
8 - 9 days → __ (epithelial cells of skin, eyes, respir, GI and UG tracts, CNS)
clinical signs
viremia → __
gastrointestinal → __
respiratory and eye → __
dermatologic → __
neurologic → __
diagnosis
fever and __ disease
virus __ (ex. RT-PCR)
treatment → symptomatic and supportive
prognosis
asymptomatic or mild disease in __ dogs with __ immunity
severe disease in __ dogs (__) or host with __ immunity
cases with neurological signs yield a __ or __ prognosis
range of hosts distributed __ (domestic and wild canids, marine mammals, felids, procyonids and ursids, nonhuman primates)
genus __, family __
Canine Core Vaccine - Infectious Canine Hepatitis (Adenovirus 1 (CAV-1))
pathogen → CANINE ADENOVIRUS 1 (dog, wolf, coyote, bear, pinnipeds)
transmission
ORONASAL exposure in infected saliva, urine, or feces
CAN live well outside host or fomites for WEEKS to MONTHS
killed by BLEACH
clinical signs
viremia → FEVER (104˚F)
non-specific signs of LETHARGY, THIRST, or ANOREXIA
eyes and nose → CONJUNCTIVITIS, RUNNY NOSE/EYES, BLUE EYES/CORNEAL EDEMA/OPACITY (may be the only clinical sign or appear after recovery)
GI → ABDOMINAL PAIN, VOMITING, DIARRHEA
coagulopathy or vasculitis → CLOTTING PROBLEMS, HEMORRPHAGE, DIC
liver → HEPATITIS (decreased clotting factors)
kidneys
central nervous system → INCOORDINATION, PARESIS, CENTRAL BLINDNESS, SEIZURES
mortality → 10 - 30% (highest for YOUNG animals)
diagnosis → FEVER, CUTE MULTISYSTEMIC DISEASE, BLEEDING TESTS (ELISA, Serology, and PCR)
treatment → SUPPORTIVE
provide FLUID and NUTRITIONAL support
address coagulopathy (PLASMA or WHOLE BLOOD transfusions)
antibiotics to limit SECONDARY BACTERIAL INVASION
Canine Core Vaccine - Infectious Canine Hepatitis (Adenovirus 1 (CAV-1))
pathogen → __ (dog, wolf, coyote, bear, pinnipeds)
transmission
__ exposure in infected saliva, urine, or feces
__ live well outside host or fomites for __
killed by __
clinical signs
viremia → __
non-specific signs of __, thirst, or __
eyes and nose → __ (may be the only clinical sign or appear after recovery)
GI → __
coagulopathy or vasculitis → __
liver → __ (decreased clotting factors)
kidneys
central nervous system → __
mortality → __% (highest for __ animals)
diagnosis → __
treatment → __
provide __ and __ support
address coagulopathy (__ or __ transfusions)
antibiotics to limit __
Canine Core Vaccine - Infectious Tracheobronchitis (Canine Adenovirus 2 (CAV-2))
clinical signs
usually mild, self-limiting RESPIRATORY infection
pneuomonia
tracheobronchitis (ACUTE or CHRONIC inflammation of the TRACHEA and BRONCHIAL airways)
Canine Core Vaccine - Infectious Tracheobronchitis (Canine Adenovirus 2 (CAV-2))
clinical signs
usually mild, self-limiting __ infection
pneuomonia
tracheobronchitis (__ or __ inflammation of the __ and __ airways)
Canine Core Vaccine - Leptospirosis (DHLPP)
pathogen → SPIROCHETE (leptospira)
transmission → ORONASAL
direct contact with infected URINE
BITE wounds
ingested infected TISSUES
indirect contact with infected WATER, SOIL, FOOD, or BEDDING
clinical signs
after infection, the bacteria multiplies rapidly in the BLOODSTREAM and TISSUES
kidneys → ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
liver → HEPATIC INJURY and VASCULITIS
pancreatitis
gastroenteritis
eye → UVEITIS
PULMONARY HEMORRHAGE SYNDROME or LPHS
lethargy, anorexia, vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, increased thirst and urination, reluctance to move, respiratory difficulty
diagnosis
clinical signs
detect LEPTO in urine or infected tissue
detect a FOUR-FOLD RISE in antibody titer over a 1 to 2 week interval
treatment → ANTIBIOTICS and SUPPORTIVE CARE
prevention
KILLED or PURIFIED subunit vaccines starting @ 12 WEEKS
booster in 3 - 4 WEEKS, then repeated ANNUALLY
Canine Core Vaccine - Leptospirosis (DHLPP)
pathogen → __ (leptospira)
transmission
direct contact with infected __
__ wounds
ingested infected __
indirect contact with infected __
clinical signs
after infection, the bacteria multiplies rapidly in the __ and __
kidneys → __
liver → __
pancreatitis
gastroenteritis
eye → __ or LPHS
lethargy, anorexia, vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, increased thirst and urination, reluctance to move, respiratory difficulty
diagnosis
clinical signs
detect __ in urine or infected tissue
detect a __ in antibody titer over a 1 to 2 week interval
treatment → __
prevention
__ subunit vaccines starting @ __ weeks
booster in __ weeks, then repeated __
Canine Core Vaccine - Canine Parvovirus (CPV)
clinical signs
preferentially infects and destroys RAPIDLY DIVIDING cells
small intestine epithelium → BLOODY DIARRHEA
LYMPHOPOIETIC tissue
bone marrow
heart → MYOCARDITIS
diagnosis
clinical signs
detect ANTIGEN in feces using ELISA, PCR, electron microscopy, or virus isolation
treatment
ISOLATE (1 part bleach : 30 parts water, kills virus in the environment)
supportive care
restore FLUID, ELECTROLYTE, and PROTEIN BALANCE
prevent SECOND BACTERIAL infection
mortality
survival rates can reach 90% with treatment
most deaths occur 2 - 3 DAYS following onset clinical signs
Canine Core Vaccine - Canine Parvovirus (CPV)
clinical signs
preferentially infects and destroys __ cells
small intestine epithelium → __
__ tissue
bone marrow
heart → __
diagnosis
clinical signs
detect __ in feces using ELISA, PCR, electron microscopy, or virus isolation
treatment
__ (1 part bleach : 30 parts water, kills virus in the environment)
supportive care
restore __
prevent __ infection
mortality
survival rates can reach __% with treatment
most deaths occur __ days following onset clinical signs
Canine Core Vaccine - Canine Parainfluenza (CPIV)
pathogen → PARAINFLUENZA VIRUS
transmission → CONTAGIOUS
clinical signs
range from mild, SELF-LIMITING disease to fatal BRONCHOPNEUM in puppies to chronic BRONCHITIS in debilitated adult or old dogs
TRACHEOBRONCHITIS (kennel cough)
Bronchopneumonia
death
diagnosis
clinical signs
treatment → symptomatic and supportive ISOLATION, COUGH SUPPRESSANT, ANTIBIOTICS (if secondary bacterial pneumonia)
Canine Core Vaccine - Canine Parainfluenza (CPIV)
pathogen → __
transmission → __
clinical signs
range from mild, __ disease to fatal __ in puppies to chronic __ in debilitated adult or old dogs
__ (kennel cough)
Bronchopneumonia
death
diagnosis
clinical signs
treatment → symptomatic and supportive __
Feline Terminology
immature male or female → KITTEN
mature female → QUEEN
mature, intact male → TOM
process of giving birth → QUEENING
Feline Terminology
immature male or female → __
mature female → __
mature, intact male → __
process of giving birth → __
Feline Core Vaccines
FVRCP (series of immunizations every 3 WEEKS)
kitten
@ 6 - 9 WEEKS
@ 10 - 12 WEEKS
@ 14 - 16 WEEKS
@ 16 - 20 WEEKS
adult → booster every 1 YEAR
rabies
kitten → @ 3 - 6 MONTHS
adult → booster in 1 YEAR, then every 3 YEARS
Feline Core Vaccines
FVRCP (series of immunizations every __ weeks)
kitten
@ __ weeks
@ __ weeks
@ __ weeks
@ __ weeks
adult → booster every __ yr
rabies
kitten → @ __ months
adult → booster in __ yr, then every __ yr
Feline Core Vaccine - FVR-C-P
Feline Herpesvirus I (Viral Rhinotracheitis)
Feline Calicivirus
Feline Panleukopenia Virus
± Feline Leukemia Virus (for KITTENS < 1 YEAR)
Feline Core Vaccine - FVR-C-P
Feline Herpesvirus I (Viral Rhinotracheitis)
Feline Calicivirus
Feline Panleukopenia Virus
± Feline Leukemia Virus (for __ < __ yr)
Feline Core Vaccine - Feline Herpesvirus I (FHV-1) or Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis (FVR)
etiology → FHV-1 or FVR (feline rhinotracheitis virus)
transmission
viral contamination of MUCOUS MEMBRANES (eyes, mouth) or INHALES
virus survives on fomites as long as they stay MOIST (ex. water bowl, cat toy), otherwise drying up and dying within a few hours
incubation period → 2 - 6 DAYS
clinical signs
fever and anorexia, oculonasal discharge, sneezing ± salivation, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, INFLAMED/CLOUDY cornea
illness usually lasts 10 - 14 DAYS
may cause ABORTION or fetal resorption
diagnosis
clinical signs
cytology, PCR, immunofluorescence, or virus isolation
treatment
supportive care (treat as an OUT-patient)
keep eyes and nose clean / HUMIDIFY air
maintain HYDRATION
OPHTHALMIC medications
ANTIVIRALS (topical or oral)
mortality
usually LOW
infection is LIFELONG
cats may become ill and recover, but they will be CARRIERS for life, experiencing RECURRENT OUTBREAKS when stressed and shed
infection can be LATENT (hidden, inactive, dormant)
it is often impossible to differentiate between FCV and FHV-1 and infection might be concurrent
FHV-1 tends to affect the CONJUNCTIVAE AND NASAL PASSAGES
Feline Core Vaccine - Feline Herpesvirus I (FHV-1) or Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis (FVR)
etiology → __ (feline rhinotracheitis virus)
transmission
viral contamination of __ (eyes, mouth) or __
virus survives on fomites as long as they stay __ (ex. water bowl, cat toy), otherwise drying up and dying within a few hours
incubation period → __ days
clinical signs
fever and anorexia, oculonasal discharge, sneezing ± salivation, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, __ cornea
illness usually lasts __ days
may cause __ or fetal resorption
diagnosis
clinical signs
cytology, PCR, immunofluorescence, or virus isolation
treatment
supportive care (treat as an __-patient)
keep eyes and nose clean / __ air
maintain __
__ medications
__ (topical or oral)
mortality
usually __
infection is __
cats may become ill and recover, but they will be CARRIERS for life, experiencing __ when stressed and shed
infection can be __ (hidden, inactive, dormant)
it is often impossible to differentiate between FCV and FHV-1 and infection might be concurrent
FHV-1 tends to affect the __
Feline Core Vaccine - Calicivirus (FCV)
etiology → FELINE CALCIVIRUS
transmission
direct, indirect, or in utero
HARDY in environment
incubation period → 2 - 6 DAYS before clinical signs
clinical signs
lethargy, fever, anorexia
OCULONASAL discharge
ORAL MUCOSAL ULCERS (difficulty eating)
up to 70% of infected cats
sneezing, dyspnea
pneumonia
POLYARTHRITIS → limping kitty syndrome (8 - 12 WEEKS of age)
usually resolves without treatment
diagnosis
clinical signs
PCR, virus isolation, paired serology / rising titer
treatment
supportive care
keep eyes and nose clean / HUMIDIFY air
maintain HYDRATION
antibiotics (SYSTEMIC and OPHTHALMIC)
carrier state
50% of infected cats following apparent recovery
continue to shed viral particles intermittently or constantly
may last for MONTHS or FOR LIFE
queens can pass virus to newborn kittens
it is often impossible to differentiate between FCV and FHV-1 and infection might be concurrent
FCV tends to affect the ORAL MUCOSA and LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT
Feline Core Vaccine - Calicivirus (FCV)
etiology → __
transmission
direct, indirect, or in utero
__ in environment
incubation period → __ days before clinical signs
clinical signs
lethargy, fever, anorexia
__ discharge
__ (difficulty eating)
up to __% of infected cats
sneezing, dyspnea
pneumonia
__ → limping kitty syndrome (__ weeks of age)
usually resolves without treatment
diagnosis
clinical signs
PCR, virus isolation, paired serology / rising titer
treatment
supportive care
keep eyes and nose clean / __ air
maintain __
antibiotics (__)
carrier state
__% of infected cats following apparent recovery
continue to shed viral particles intermittently or constantly
may last for __ or FOR LIFE
queens can pass virus to newborn kittens
it is often impossible to differentiate between FCV and FHV-1 and infection might be concurrent
FCV tends to affect the __
Feline Core Vaccine - Feline Panleukopenia (FPV)
entiology → FELINE PARVOVIRUS
domestic and big cats, raccoons, ferrets (not candids)
transmission
contact with infected CATS, FECES, SECRETIONS, or FOMITES
pathogens can live up to 1 YEAR in environment
incubation period → 3 - 5 DAYS
clinical signs
infects and destroys RAPIDLY DIVIDING cells
surpressed IMMUNE SYSTEM (fever 104˚F - 107˚F)
small intestines → VOMITING, HEMORRHAGIC DIARRHEA
bone marrow → PANLEUKOPENIA
lymphoid tissue
infection of pregnant queen → RESORPTION, STILLBORN, or ABORTION
cerebellum → ATAXIA and TREMORS with NORMAL mentation
retina → BLINDNESS
sudden death of KITTEN
diagnostics
clinical signs
kitten with FEVER, VOMIT, ABDOMINAL PAIN, and LEUKOPENIA
detect FPV in FECES
paired serology → RISING ANTIBODY TITER
treatment
ISOLATE (even recovered cats shed for another 6 WEEKS)
SUPPORTIVE CARE → restore fluid and electrolytes
prevent SECONDARY BACTERIAL INFECTION
antiemetic
prevention
most adult cats develop immunity, so they don’t become sick or they experience a self-limiting illness (5 - 7 DAYS)
mortality → highest in YOUNG KITTENS (< 5 MONTHS OLD)
Feline Core Vaccine - Feline Panleukopenia (FPV)
entiology → __
domestic and big cats, raccoons, ferrets (not candids)
transmission
contact with infected __
pathogens can live up to __ yr in environment
incubation period → __ days
clinical signs
infects and destroys __ cells
surpressed __ (fever __˚F - __˚F)
small intestines → __
bone marrow → __
lymphoid tissue
infection of pregnant queen → __
cerebellum → __ with __ mentation
retina → __
sudden death of __
diagnostics
clinical signs
kitten with __
detect FPV in __
paired serology → __
treatment
__ (even recovered cats shed for another __ weeks)
__ → restore fluid and electrolytes
prevent __
antiemetic
prevention
most adult cats develop immunity, so they don’t become sick or they experience a self-limiting illness (__ days)
mortality → highest in __ (< __ months old)
Feline Core Vaccine - Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)
etiology → RETROVIRUS (CAT-specific)
transmission
BITES → infected blood, saliva, and cerebrospinal fluid
IN UTERO → pregnant queens to kittens and through milk when nursing
pathogen WON’T survive in the environment
clinical signs
FIV attacks WHITE BLOOD COUNT (immunosuppression) eventually
most infected cats mount an immune response to FIV, leading to decreased VIRUS REPLICATION, but not ELIMINATION of infection
cats often remain ASYMPTOMATIC for many years
clinical signs usually develop due to SECONDARY INFECTIONS and CHRONIC DEGENERATIVE CONDITIONS
INFLAMMATORY disease (ex, ocular, oral, etc)
anemia
diarrhea
pneumonia
skin diseases
neurological diseases
neoplasia
diagnostics
no test is 100% accurate under all conditions
positives should be confirmed by another test method
detect ANTIBODIES in blood for routine screening
testing is confused by VACCINES AGAINST FIV and CONSUMPTION OF ANTIBIOTICS IN COLOSTRUM
wait to test kittens until 6 MONTHS OF AGE
ELISA → identifies antibodies in blood
if negative → re-test in 60 DAYS
if positive → test by IFA to identify antigen within infected WBC’s and platelets or test by PCR
treatment
DO NOT euthanize
nothing specific, infected for LIFE
treat SECONDARY ILLNESSES
control
infected cats should be SPAYED/NEUTERED and kept INDOORS to minimize the risk of infecting other cats and decrease exposure to possible infectious agents
vaccination
commercially available
contains inactivated whole body virus ISOLATES from clades A and D, with INFECTED cells and an ADJUVANT
one independent study showed vaccine WASN’T able to to protect cats when they were challenged by a SUBTYPE A field strain from the UNITED KINGDOM
current testing methods can’t reliably distinguish NATURALLY INFECTED cats from VACCINATED cats
NON-CORE but perhaps recommended for cats at HIGH-RISK of exposure (outdoor or cats living with infected)
TEST and MICROCHIP or COLLAR before vx
Feline Core Vaccine - Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)
etiology → __ (__-specific)
transmission
__ → infected blood, saliva, and cerebrospinal fluid
__ → pregnant queens to kittens and through milk when nursing
pathogen __ survive in the environment
clinical signs
FIV attacks __ (immunosuppression) eventually
most infected cats mount an immune response to FIV, leading to decreased __, but not __ of infection
cats often remain __ for many years
clinical signs usually develop due to __
__ disease (ex, ocular, oral, etc)
anemia
diarrhea
pneumonia
skin diseases
neurological diseases
neoplasia
diagnostics
no test is 100% accurate under all conditions
positives should be confirmed by another test method
detect __ in blood for routine screening
testing is confused by __
wait to test kittens until __ months of age
__ → identifies antibodies in blood
if negative → re-test in __ days
if positive → test by __ to identify antigen within infected WBC’s and platelets or test by __
treatment
__ euthanize
nothing specific, infected for __
treat __
control
infected cats should be __ and kept __ to minimize the risk of infecting other cats and decrease exposure to possible infectious agents
vaccination
commercially available
contains inactivated whole body virus __ from clades __, with __ cells and an __
one independent study showed vaccine __ able to to protect cats when they were challenged by a __ field strain from the __
current testing methods can’t reliably distinguish __ cats from __ cats
__ but perhaps recommended for cats at __ of exposure (outdoor or cats living with infected)
__ before vx
Feline Core Vaccine - Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV)
etiology → RETROVIRUS
transmission
in → SALIVA, FECES, MILK, URINE, BLOOD
spread by → BITING, MUTUAL GROOMING, LICKING, SHARING DISHES, TRANSFUSING, NURSING, and/or PREGNANCY
pathogen survival rate → LOW (only hours) IN THE ENVIRONMENT
CLOSE, CAT-TO-CAT contact is required to transmit the disease
prognosis
most susceptible at < 6 MONTHS OF AGE (young cats)
IMMUNE SYSTEM is not fully mature
resistant WITH AGE (adults develop)
virus exposure sufficient to infect 100% of young kittens will infect < 30% of adults
pathogenesis
following exposure, about 30% of adult cats show MILD symptoms (fever and lethargy), but mount an immune system response and ELIMINATE the virus
if immune system of cat is INSUFFICIENT to control virus, cat will become PERMANENTLY infected and enter an ASYMPTOMATIC state that can last months to years.
3 associated diseases
NEOPLASIA (like lymphoma or leukemia)
DEGENERATIVE DISEASES (such as anemia, liver disease, intestinal disease, and reproductive problems)
IMMUNE DEFICIENCY (increased susceptibility to infectious agents, chronic respiratory infections, chronic gingivitis, and stomatitis, poor healing of wounds, abscesses, and other infections)
clinical signs
loss of APPETITE (fever)
progressive WEIGHT loss (poor coat)
enlarged LYMPH NODES (diarrhea)
PALE gums and other mucus membranes
INFLAMMATION of the skin, urinary bladder, and upper respiratory tract
seizures, behavior changes, and other neurological disorders
a variety of EYE conditions
ABORTION of kittens or other reproductive failures
incidence
2 - 3% of cats in the US are infected
rates RISE significantly (13% or more)
diagnostics
screening relies on detecting the CORE VIRAL ANTIGEN p27 circulating in the blood, which is produced abundantly in most infected cats
ELISA → (ENZYME-LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY) in-clinic test
IFA → (INDIRECT IMMUNOFLUORESCENT ANTIBODY ASSAY) sent to a laboratory
PCR and Virus Isolation
sick cats should be tests even if THEY HAVE TESTED NEGATIVE IN THE PAST
cats and kittens should be tested when they are FIRST ACQUIRED
cats with known exposure to a retrovirus-infected cat or to a cat with unknown status, particularly via a bite wound, should be tested IMMEDIATELY and again in 30 DAYS
treatment
nothing specific
treatment for secondary illnesses
although many cats die within 3 - 4 YEARS of diagnosis, others remain CLINICALLY HEALTH for many years
control
FeLV-positive cats should be evaluated by a vet TWICE PER YEAR (PE, CBC, Chem, UA)
vaccination
several vaccines for FeLV are available, including WHOLE INACTIVATED VIRUS, GENETICALLY ENGINEERED SUBUNIT or RECOMBINANT CANARYPOX VECTOR VACCINES
efficacy of commercially available vaccines is DIFFICULT TO ACCESS
most published efficacy trials were conducted by the Vx manufacturer, and most studies do not evaluate more than one vaccine
recommended for ALL KITTENS (cats < 1 YR) due to increased susceptibility to the virus and permanent nature of infection
NON-CORE for cats after their 1 year booster unless they are AT RISK (outdoor cats, cats living with FeLV-infected cats, multicat environments where FeLV status of all cats is unknown)
Feline Core Vaccine - Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV)
etiology
transmission
in
spread by
pathogen survival rate
__ contact is required to transmit the disease
prognosis
most susceptible at < __ months of age
__ is not fully mature
resistant __
virus exposure sufficient to infect 100% of young kittens will infect < __% of adults
pathogenesis
ollowing exposure, about __% of adult cats show __ symptoms (fever and lethargy), but mount an immune system response and __ the virus
if immune system of cat is __ to control virus, cat will become __ infected and enter an __ state that can last months to years.
3 associated diseases
__ (like lymphoma or leukemia)
__ (such as anemia, liver disease, intestinal disease, and reproductive problems)
__ (increased susceptibility to infectious agents, chronic respiratory infections, chronic gingivitis, and stomatitis, poor healing of wounds, abscesses, and other infections)
clinical signs
loss of __ (fever)
progressive __ loss (poor coat)
enlarged __ (diarrhea)
__ gums and other mucus membranes
__ of the skin, urinary bladder, and upper respiratory tract
seizures, behavior changes, and other neurological disorders
a variety of __ conditions
__ of kittens or other reproductive failures
incidence
__% of cats in the US are infected
rates __ significantly (__% or more)
diagnostics
screening relies on detecting the __ circulating in the blood, which is produced abundantly in most infected cats
ELISA → (__) in-clinic test
IFA → (__) sent to a laboratory
PCR and Virus Isolation
sick cats should be tests even if __
cats and kittens should be tested when they are __
cats with known exposure to a retrovirus-infected cat or to a cat with unknown status, particularly via a bite wound, should be tested __ and again in __ days
treatment
nothing specific
treatment for secondary illnesses
although many cats die within __ yr of diagnosis, others remain __ for many years
control
FeLV-positive cats should be evaluated by a vet __ (PE, CBC, Chem, UA)
vaccination
several vaccines for FeLV are available, including __
efficacy of commercially available vaccines is __
most published efficacy trials were conducted by the Vx manufacturer, and most studies do not evaluate more than one vaccine
recommended for __ (cats < __ yr) due to increased susceptibility to the virus and permanent nature of infection
__ for cats after their 1 year booster unless they are __ (outdoor cats, cats living with FeLV-infected cats, multicat environments where FeLV status of all cats is unknown)
Beef Production Terminology
cattle > 1 year of age → BEEF
calves < 3 months of age → VEAL
Beef Production Terminology
cattle > 1 year of age →
calves < 3 months of age →
World Cattle Numbers & Beef Production, 2025F
top cattle inventory and beef producers
India → 307 MILLION total cattle and 4.9 METRIC TONS beef
Brazil → 234 MILLION total cattle and 11.9 METRIC TONS beef
China → 108 MILLION total cattle and 7.8 METRIC TONS beef
USA → 87 MILLION total cattle and 12.3 METRIC TONS beef
~9.5% of world’s cattle
produce ~20% of world’s beef and veal
EU → 74 MILLION total cattle and 6.6 METRIC TONS beef
Argentina → 54 MILLION total cattle and 3.2 METRIC TONS beef
US Cash Receipts by Commodity, 2025F
total animals & animal products → $275 BILLION
beef: cattle and calves → $108 BILLION
Beef Industry in USA
2024 → 58 LBS of beef consumed per person
2025
total cattle inventory
beef cows
World Cattle Numbers & Beef Production, 2025F
top cattle inventory and beef producers
India → __ mil total cattle and __ metric tons beef
Brazil → __ mil
China → __ mil total cattle and __ metric tons beef
USA → __ mil total cattle and __ metric tons beef
~__% of world’s cattle
produce ~__% of world’s beef and veal
EU → __ mil total cattle and __ metric tons beef
Argentina → __ mil total cattle and __ metric tons beef
US Cash Receipts by Commodity, 2025F
total animals & animal products → $__ billion
beef: cattle and calves → $__ billion
Beef Industry in USA
2024 → __ lbs of beef consumed per person
2025
total cattle inventory
beef cows
Beef Industry Trends
changes are based on 5 aspects
DEMAND (domestic and exports)
BEEF prices
cost of PRODUCTION (feed)
WEATHER (drought vs flood)
LAND prices
Beef Industry Trends
changes are based on 5 aspects
__ (domestic and exports)
b__ prices
cost of __ (feed)
__ (drought vs flood)
l__ prices
Cattle Feeding Areas
southern and central region of the GREAT PLAINS
top cattle states (list ≥ 5)
TEXAS
NEBRASKA
KANSAS
CALIFORNIA
OKLAHOMA
MONTANA
IOWA
SOUTH DAKOTA
WISCONSIN
Cattle Feeding Areas
southern and central region of the __
top cattle states (list ≥ 5)
Segmented Beef Cattle Industry
cow-calf operation
HEIFER BREEDING → CALVING/NURSING → COW RE-BREEDING → WEANING
goal → birth 6 - 10 MONTHS @ 400 - 750 LBS
weanlings light → sell → STOCKER
weanlings heavy → sell → FINISHING
weanlings undesirable → retain ownership → SLAUGHTER
stocker/yearling operation
goal → wean to 600 - 900 LBS @ 12 - 16 MONTHS
finishing/feedlot
CAFO → CONCENTRATED ANIMAL FEEDING OPERATION
goal → grow to 900 - 1450 LBS @ 18 - 24 MONTHS
processing/slaughter
industrial or small-scale
market/retail
wholesale, grocery, restaurant
Segmented Beef Cattle Industry
cow-calf operation
heifer-__ → c__/n__ → cow-__ → w__
goal → birth __ mo @ __ lbs
weanlings light → sell → __
weanlings heavy → sell → __
weanlings undesirable → retain ownership → __
stocker/yearling operation
goal → wean to __ lbs @ __ mo
finishing/feedlot
CAFO → __
goal → grow to __ lbs @ __ mo
processing/slaughter
industrial or small-scale
market/retail
wholesale, grocery, restaurant
US Beef Cow Farms
2025 trends
number of small farm operations → 80%
herd size between 1 - 49 heads (28%) or 100 - 500 heads (38%)
a cow’s role on a beef farm
CONCEIVE EARLY → at beginning of season (first 40 days)
DELIVER → at least one live calf each year
RE-BREED ON SCHEDULE → 40 - 90 days after calving
wean a BIG calf
yield a POSITIVE RETURN on investment
US Beef Cow Farms
2025 trends
number of small farm operations → __%
herd size between 1 - 49 heads (__%) or 100 - 500 heads (__%)
a cow’s role on a beef farm
__ → at beginning of season (first 40 days)
__ → at least one live calf each year
__ → 40 - 90 days after calving
wean a __ calf
yield a __ on investment
Beef Production - Breeding
estrous cycle → NONSEASONALLY POLYESTROUS
18 - 24 DAY cycle (avg 21 days)
PE - E - ME - DE
NATURAL SERVICE (bull-bred) → fertile and healthy bull at right stocking density
young bull → 20 - 25 cows
mature bull → 25 - 40 cows
range → 4 bulls : 100 cows
exposure time ≤ 60 DAYS
ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION → heat detect or synchronize estrus and/or ovulation
4 advantages
GENETIC IMPROVEMENT
MAXIMIZE USE OF BULL
SAFER WITHOUT BULL
LIMIT SPREAD OF DISEASES
5 disadvantages
COSTLY
TRAINED-LABOR
TIME-CONSUMING
SPECIAL HANDLING FACILITIES
EQUIPMENT
Beef Production - Breeding
estrous cycle → __
__ d cycle (avg 21 days)
PE - E - ME - DE
__ (bull-bred) → fertile and healthy bull at right stocking density
young bull → __ cows
mature bull → __ cows
range → __ bulls : __ cows
exposure time ≤ __ d
__ → heat detect or synchronize estrus and/or ovulation
4 advantages
5 disadvantages
Beef Production - Cow-Calf Cycle
1st breeding → MAY to JUN
caving/nursing → FEB to MAY
weaning → OCT to NOV
breeding heifers
SIZE → at 65% of projected adult weight and height
breed-DEPENDENT, but usually 700 - 850 LBS
AGE → by 15 months for first-time calving @ 2 YEARS
DATE → early in the season so they calve 20 - 30 days before cows
allows more time for 1st calf heifers to return to estrous cyclicity post-calving
check for pregnancy 40 - 90 DAYS after removal of bull by PALPATION PER RECTUM or ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION PER RECTUM
Beef Production - Cow-Calf Cycle
1st breeding → __
caving/nursing → __
weaning → __
breeding heifers
__ → at 65% of projected adult weight and height
breed-__, but usually __ lbs
__ → by 15 months for first-time calving @ __ yr
__ → early in the season so they calve 20 - 30 days before cows
allows more time for 1st calf heifers to return to estrous cyclicity post-calving
check for pregnancy __ d after removal of bull by __
Beef Production - Calving Goals
calving season → 40 - 90 DAYS in the SPRING (Mar to Jun) or FALL (Sept to Oct)
CLEAN, SAFE environment
FREQUENT observation
provide ASSISTANCE to heifers when needed
SAVE calves
mortality rate → < 30%
keep RECORDS
Beef Production - Calving Goals
calving season → __ days in the __ (Mar to Jun) or __ (Sept to Oct)
__ environment
__ observation
provide __ to heifers when needed
__ calves
mortality rate → < __%
keep __
Beef Production - Calf Processing
EAR tag
determine SEX
disBUD (before ~8 weeks when horn attaches to skull) and deHORN (the YOUNGER, the better; avoid using POLLED genetics)
NERVE block (lidocaine ± sedation; NSAID) before operating
< 2 weeks → SHAVE hair and apply CAUSTIC PASTE
< 8 weeks → TUBE dehorner or HEAT dehorner
< 6 months → BARNES dehorner
young adult → GIGLI wire
tattoo
BRAND → letters 4 inches tall, 3/8 to 1 inch wide
use a HOT IRON or FREEZE BRAND
CASTRATE → bull to steer
ideally < 2 MONTHS old
SHAGGY → > 8 months
use ELASTRATOR BAND or BURDIZZO or EMASCULOTOME
Beef Production - Calf Processing
__ tag
determine __
dis-__ (before ~8 weeks when horn attaches to skull) and de-__ (the __, the better; avoid using __ genetics)
__ block (lidocaine ± sedation; NSAID) before operating
< 2 weeks → __ hair and apply __
< 8 weeks → __ dehorner or __ dehorner
< 6 months → __ dehorner
young adult → __ wire
tattoo
__ → letters 4 inches tall, 3/8 to 1 inch wide
use __
__ → bull to steer
ideally < __ mo old
__ → > 8 months
use __
Beef Production - Weaning
@ 6 - 10 MONTHS
although calves are born over range of 40 - 60 DAYS, most calves in the herd will be weaned at THE SAME time
500 LBS → ideal weaning weight (400 - 580 LBS)
7 factors affecting weaning weights
calving date (COW’S FERTILITY)
available FORAGE
creep FEED
disease or illness
GENETIC selection
CROSSBREEDING → 10% - 30% increase in pounds of calf weaned per cow bred
GROWTH STIMULANTS → Zeranol (synthetic estrogen), Synovex C (progesterone and testosterone), Compudose (estradiol)
Beef Production - Weaning
@ __ mo
although calves are born over range of __ days, most calves in the herd will be weaned at __ time
__ lbs → ideal weaning weight (__ lbs)
7 factors affecting weaning weights
calving date (__)
available __
creep __
disease or illness
__ selection
__ → 10% - 30% increase in pounds of calf weaned per cow bred
__ → Zeranol (synthetic estrogen), Synovex C (progesterone and testosterone), Compudose (estradiol)
Beef Production - Growth Stimulants
work with an animal’s ENDOCRINE system to partition NUTRIENTS to support more MUSCLE growth for INCREASED WEIGHT GAIN, IMPROVED FEED EFFICIENCY, and a LEANER CARCASS
NATURAL hormones → estradiol, progesterone, testosterone
SYNTHETIC hormones → zeranol, trenbolone acetate, melengestrol acetate
RALGRO (zeranol) → stimulates the PITUITARY GLAND of the animal to produce increased amounts of SOMATOTROPIN, the animal’s own natural growth-promoting agent
Beef Production - Growth Stimulants
work with an animal’s __ system to partition __ to support more __ growth for __
__ hormones → estradiol, progesterone, testosterone
__ hormones → zeranol, trenbolone acetate, melengestrol acetate
__ (zeranol) → stimulates the __ of the animal to produce increased amounts of __, the animal’s own natural growth-promoting agent
Beef Production - Implants
why use implants
GROWTH promotants
improves GROWTH rate
improves FEED efficiency
generate LEANER carcass
make ECONOMIC SENSE to producers (10 : 1 return)
if the beef production practices from 1955 were used together, more than 165 MILLION ACRES of land would be needed to sustain today’s beef production
who uses implants
9% - 30% → COW/CALF PRODUCERS
34% - 90% → feedlots with < 1000 HEAD use at least once during the finishing phase
78% - 99% → feedlots with > 1000 HEAD use at least once during the finishing phase
who doesn’t use implants
USDA → ORGANIC meat comes from cattle that ARE NOT given any antibiotics or growth hormones
organic food is produced WITHOUT USING most conventional PESTICIDES (fertilizers made with synthetic ingredients or sewage sludge), BIOENGINEERING, or IONIZING RADIATION
before a product can be labeled “organic,” a GOVERNMENT-APPROVED CERTIFIER inspects the farm where the food is grown to make sure the farm is following all the rules necessary to meet USDA organic standards.
Beef Production - Implants
why use implants
__ promotants
improves __ rate
improves __ efficiency
generate __ carcass
make __ to producers (__ : __ return)
if the beef production practices from 1955 were used together, more than __ mil acres of land would be needed to sustain today’s beef production
who uses implants
9% - 30% → __
34% - 90% → feedlots with < __ head use at least once during the finishing phase
78% - 99% → feedlots with > __ head use at least once during the finishing phase
who doesn’t use implants
USDA → __ meat comes from cattle that __ given any antibiotics or growth hormones
organic food is produced __ most conventional __
before a product can be labeled “organic,” a __ inspects the farm where the food is grown to make sure the farm is following all the rules necessary to meet USDA organic standards.
Rabbit Terminology
male → BUCK
female → DOE
< 6 months of age → JUNIOR
> 6 months of age → SENIOR
6 - 8 months of age → INTERMEDIATE or 6/8 (most common for larger breeds)
baby → KIT
birthing → KINDLING
Rabbit Terminology
male → __
female → __
< 6 months of age → __
> 6 months of age → __
6 - 8 months of age → __ or 6/8 (most common for larger breeds)
baby → __
birthing → __
Rabbit Production - Market
pets
~2.2 MILLION in 1.5 MILLION households
show/youth programs (4-H and FFA)
meat
LOW-fat, LOW-calorie, LOW-cholesterol, HIGH-protein, RED meat
more common in countries like ITALY, SPAIN, and FRANCE
processed as “FRYERS” at live weight of 3 - 6 lbs @ 8 - 12 weeks of age
retail dressed rabbits/carcass weight from $6.59 PER POUND to $18 PER POUND
lab animals
300,000 PER YEAR
wool
ANGORA breed
8 - 10 INCHES or 12 - 16 OUNCES PER YEAR
skin
fur or glue
☆ the exact number of rabbits in various US industries is unknown
Rabbit Production - Market
pets
~__ mil in __ mil households
show/youth programs (__)
meat
__-fat, __-calorie, __-cholesterol, __-protein, __ meat
more common in countries like __
processed as “__” at live weight of 3 - 6 lbs @ 8 - 12 weeks of age
retail dressed rabbits/carcass weight from $__/lb to $__/lb
lab animals
__ thousand per year
wool
__ breed
__ in or __ oz/yr
skin
fur or glue
☆ the exact number of rabbits in various US industries is unknown
Rabbit Production - Breeds
angora
size → MEDIUM
mature weight → 9 - 12 LBS
use → WOOL, MEAT
californians
size → MEDIUM
mature weight → 9 - 12 LBS
use → MEAT
new zealand white
size → MEDIUM
mature weight → 9 - 12 LBS
use → MEAT
dutch
size → SMALL
mature weight → 3 - 6 LBS
use → LAB
flemish giants
size → LARGE
mature weight → 14 - 16 LBS
use → MEAT
Rabbit Production - Breeds
angora
size → __
mature weight → __ lb
use → __
californians
size → __
mature weight → __ lb
use → __
new zealand white
size → __
mature weight → __ lb
use → __
dutch
size → __
mature weight → __ lb
use → __
flemish giants
size → __
mature weight → __ lb
use → __
Rabbit Production - Housing
lighting → 12 HOURS light and 12 HOURS dark for YEAR-ROUND breeding
ventilation
temperature control → rabbits are TEMPERATURE SENSITIVE (50 - 70˚F)
HUTCHES / CAGES → many types; wire mesh; hangings
manure management → frequent CLEANING, COMPOSTING, AND RAISING WORMS
Rabbit Production - Housing
lighting → __ hr light and __ hr dark for __ breeding
ventilation
temperature control → rabbits are __ (50 - 70˚F)
__ → many types; wire mesh; hangings
manure management → frequent __
Rabbit Breeding
puberty
females EARLIER than males
light-weight breeds → 4 - 5 MONTHS
medium-weight breeds → 5 - 8 MONTHS
large-weight breeds → 8 - 10 MONTHS
NO WELL-DEFINED estrous cycle
waves of FOLLICLES grow over 7 - 10 days with eventual SEXUAL RECEPTIVITY
INDUCED ovulator (not SPONTANEOUS ovulators)
ovulate ~10-12 hours AFTER breeding
breeding ratio → 1 buck : 10 does
move DOES to BUCK for breeding
gestation → 30 - 31 DAYS (range of 28 - 35 DAYS )
pregnancy evaluation → ABDOMINAL palpation @ 12 - 14 DAYS
production
does may be re-bred WHILE nursing a litter if they are in good condition (or wait until WEANING to breed)
4 litters/year → if does are bred 8 weeks post-kindling
5 litters/year → if does are bred 6 weeks post-kindling
breeding does in COMMERICAL rabbitries are productive for 2.5 - 3 YEARS
Rabbit Breeding
puberty
females __ than males
light-weight breeds → __ mo
medium-weight breeds → __ mo
large-weight breeds → __ mo
__ estrous cycle
waves of __ grow over 7 - 10 days with eventual __
__ ovulator (not __ ovulators)
ovulate ~10-12 hours __ breeding
breeding ratio → __ buck[s] : __ doe[s]
move __ for breeding
gestation → __ d (range of __ d)
pregnancy evaluation → __ palpation @ __ d
production
does may be re-bred __ nursing a litter if they are in good condition (or wait until __ to breed)
__ litters/year → if does are bred 8 weeks post-kindling
__ litters/year → if does are bred 6 weeks post-kindling
breeding does in __ rabbitries are productive for __ yr
Rabbit Production - Kindling
provide a NESTING box with bedding 27 - 28 DAYS after breeding
does will PULL OUT THEIR OWN FUR to create a nest
examine the litter within 24 HOURS of kindling to make sure kits are alive
remove UNDERSIZED kits
monitor for HYPOTHERMIA or STARVATION due to low milk production
don’t STRESS the doe
CANNIBALISM is rare, but possible
average litter size → 8 - 10 kits
post-kindling
7 - 10 days → OPEN EYES
19 - 20 days → START TO EAT SOLID FOOD
5 - 10 weeks → WEAN (based on BREED and MARKET)
Rabbit Production - Kindling
provide a __ box with bedding __ d after breeding
does will __ to create a nest
examine the litter within __ hr of kindling to make sure kits are alive
remove __ kits
monitor for __ due to low milk production
don’t __ the doe
__ is rare, but possible
average litter size → __ kits
post-kindling
7 - 10 days → __
19 - 20 days → __
5 - 10 weeks → __ (based on __)
Rabbit Sex Determination
at WEANING → separate bucks and does
hold rabbit on its BACK
pinch the TAIL between your middle and index fingers, and place your thumb on the fur in the VENT area
pull out the tail gently but firmly, and press down in front of the GENITAL region with your thumb
male
protruding, ROUNDED urethral opening
SCROTUM is not always obvious, especially in young bucks
bucks have open INGUINAL RINGS, which allow the testicles to retract into the ABDOMEN
female → SLIT-LIKE vulva
Rabbit Sex Determination
at __ → separate bucks and does
hold rabbit on its __
pinch the __ between your middle and index fingers, and place your thumb on the fur in the __ area
pull out the tail gently but firmly, and press down in front of the __ region with your thumb
male
protruding, __ urethral opening
__ is not always obvious, especially in young bucks
bucks have open __, which allow the testicles to retract into the __
female → __ vulva
Rabbit Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT)
stomach chambers → MONOGRASTRIC
digestion → HINDGUT FERMENTERS
diet → HERBIVORES
pathway of food
TEETH → SALIVARY GLAND → ESOPHAGUS → LIVER → STOMACH → PANCREAS → LARGE INTESTINE → CAECUM → SMALL INTESTINE → RECTUM → ANUS
antibodies that are safe to use in rabbits are LIMITED compared to other species
ORAL administration of many antibiotics (that would be effective against bacteria causing respiratory infections) will also kill bacteria necessary to keep the intestines healthy and functioning
Rabbit Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT)
stomach chambers → __
digestion → __
diet → __
pathway of food → __
antibodies that are safe to use in rabbits are __ compared to other species
__ administration of many antibiotics (that would be effective against bacteria causing respiratory infections) will also kill bacteria necessary to keep the intestines healthy and functioning
Rabbit Production - Diet
feeding → HERBIVORE, SINGLE-STOMACH, HINDGUT FERMENTER
water → CONSTANT, FREE ACCESS
feed efficiency → 3 LB FEED : 1 LB MEAT (3:1)
Rabbit Production - Diet
DRY forage (hay) → 40% - 80% of rabbit’s diet
DAILY diet → mostly hay, a small amount of fresh vegetables, and a specified amount of pellets based on BODY WEIGHT
unlimited, high-quality GRASS HAY (ex. timothy, orchard, or brome) should make up the bulk of rabbit’s diet
grass hay is high in FIBER
hay allows rabbit to use a NORMAL GRINDING MOTION of the cheek teeth, which keeps them in proper alignment
YOUNG, GROWING rabbits can eat any type of hay, including alfafa
alfalfa hay is fed with caution to ADULT rabbits (> 7 MONTHS of age) because it is rich in PROTEIN and high in CALCIUM
pellets → ALL-GRAIN PELLETS (fed with hay) or COMPLETE PELLETS (all forage)
ex. for adult rabbits, timothy pellets should be offered at approx 1/8 to ¼ cup per 5 lb of body weight
over-feeding pellets to adult rabbits is a common cause of obesity and SOFT STOOL because pellets are generally low in LONG-STRAND fiber and high in CARBOHYDRATES, and can cause an overgrowth of ABNORMAL BACTERIA in the gastrointestinal tract
supplement with ¼ - ½ cup of LEAFY GREEN VEGETABLES per day
ex. romain lettuce, bok choy, mustard greens, carrot tops, cilantro, watercress, basil, kohlrabi, beet greens, broccoli greens
CAUTION: some leafy greens (collard and dandelion greens, parsley, kale, swiss chard, and escarole) should be fed in limited quantities because they’re high in CALCIUM and may cause Ca-BASED BLADDER STONES
ROOT CROPS → carrots, sweet potatoes, turnips, beets
CAUTION: carrots are high in CARBOHYDRATES and should not be offered DAILY
introduce new vegetables slowly, in small quantities, and monitor for DIARRHEA or GAS pain
Rabbit Production - Diet
feeding → __
water → __
feed efficiency → __ lb __ : __ lb __ (__:__)
__ forage (hay) → __% of rabbit’s diet
__ diet → mostly hay, a small amount of fresh vegetables, and a specified amount of pellets based on __
unlimited, high-quality __ (ex. timothy, orchard, or brome) should make up the bulk of rabbit’s diet
grass hay is high in __
hay allows rabbit to use a __ of the cheek teeth, which keeps them in proper alignment
__ rabbits can eat any type of hay, including alfafa
alfalfa hay is fed with caution to __ rabbits (__ mo of age) because it is rich in __ and high in __
pellets → __ (fed with hay) or __ (all forage)
ex. for adult rabbits, timothy pellets should be offered at approx 1/8 to ¼ cup per 5 lb of body weight
over-feeding pellets to adult rabbits is a common cause of obesity and __ because pellets are generally low in __ fiber and high in __, and can cause an overgrowth of __ in the gastrointestinal tract
supplement with ¼ - ½ cup of __ per day
ex. romain lettuce, bok choy, mustard greens, carrot tops, cilantro, watercress, basil, kohlrabi, beet greens, broccoli greens
CAUTION: some leafy greens (collard and dandelion greens, parsley, kale, swiss chard, and escarole) should be fed in limited quantities because they’re high in __ and may cause __
__ → carrots, sweet potatoes, turnips, beets
CAUTION: carrots are high in __ and should not be offered __
introduce new vegetables slowly, in small quantities, and monitor for __ or __ pain

Rabbit Health - Feces
two kinds of feces
ROUND, FIRM pellets
CECOTROPES (NIGHT feces) → very soft and covered with a thick mucus
rabbits ingest them as a normal part of their digestive process to RECYCLE PROTEIN, WATER, AND VITAMINS
COPROPHAY → eating fecal matter
common in rodents and rabbits, although only rabbits produce a special STOOL for this purpose
Rabbit Health - Feces
two kinds of feces
__ pellets
__ (__ feces) → very soft and covered with a thick mucus
rabbits ingest them as a normal part of their digestive process to __
__ → eating fecal matter
common in rodents and rabbits, although only rabbits produce a special __ for this purpose
Rabbit Restraint
handling → generally DOCILE and EASY
risks → SCRATCHES and BITES
support the HINDLEGS
rabbits have very strong LEGS and very little BONE MASS
when they KICK, it is easy for them to suffer serious injury to their SPINE
Rabbit Restraint
handling → generally __
risks → __
support the __
rabbits have very strong __ and very little __
when they __, it is easy for them to suffer serious injury to their __
Bison
family → BOVIDAE
weight → 1000 - 2200 LBS
height → 5 - 6.5 FEET
length → 7 - 12 FEET
speed → 40 MPH
lifespan → 12 - 20+ YEARS
defense → 2 FEET CURVED HORNS (male and female)
HARDY → survive blizzards and extreme heat
VERY EFFICIENT grazers → prefer a TOTAL GRASS diet with grains of 2 POUNDS PER DAY
Bison
family → __
weight → __ lb
height → __ ft
length → __ ft
speed → __ mph
lifespan → __ yr
defense → __
__ → survive blizzards and extreme heat
__ grazers → prefer a __ diet with grains of __ lb/day
Bison Production - History
20,000 - 30,000 years ago → crossed the BEIRING STRAIT land bridge from ASIA to NORTH AMERICA
1700s → 30 - 60 MILLION bison in North America
1900 → 300 bison (ENDANGERED)
2010 - 2020s → 200,000 - 500,000 bison
5,400 in national parks
20,500 in conservation herds
420,000 in private ranches
Bison Production - History
20,000 - 30,000 years ago → bison crossed the __ land bridge from __ to __
1700s → __ mil bison in North America
1900 → __ bison (__)
2010 - 2020s → __ bison
__ in national parks
__ in conservation herds
__ in private ranches
Bison Production - Market
BREEDING stock
HOBBY/EXHIBITION animals
meat → (RED meat, lower in FAT, CHOLESTEROL, AND CALORIES than beef, pork, and skinless chicken)
least → most grams of fat
BISON (2.42) → CHICKEN → BEEF → PORK
least → most kcal of calories
BISON (143) → CHICKEN → BEEF → PORK
least → most mg chloresterol
BISON (82) → BEEF → PORK → CHICKEN
Bison Production - Market
__ stock
__ animals
meat → (__ meat, lower in __ than beef, pork, and skinless chicken)
least → most grams of fat
least → most kcal of calories
least → most mg chloresterol

Bison Production - Meat and Meat Safety
smaller producer → 25 - 100
medium producer → 100 - 250
large ranch → 100s - 1000s
2020 → 57,300 processed at. USDA inspected plants
SINGLE-PRODUCER or SEGMENTED (cow-calf and feedlot) plan
FEDERAL MEAT INSPECTION ACT (FMIA)
AMENABLE LIVESTOCK SPECIES → cattle, swine, goats, sheep, horses
POULTRY PRODUCTS INSPECTION ACT (PPIA)
AMENABLE POULTRY → chickens, turkey, ducks, geese, guinea fowl, and ratites
to legally sell meat and meat products, animal(s) must be slaughtered in a FACILITY INSPECTED by the USDA’s FOOD SAFETY INSPECTION SERVICE, FSIS, and meat products from the inspected carcasses must. be handled in a facility inspected by COUNTY, STATE, OR USDA INSPECTORS
non-amenable species
WILD LAND MAMMALS → antelope, deer, elk, moose, bison, water buffalo, bear, caribou, and reindeer
GAME BIRDS → wild turkeys, wild geese, wild ducks, grouse, quail, pheasant, and other non-domesticated species of fowl
rabbits
poultry (fewer than 20,000)
no mandatory USDA FSIS inspection for non-amenable species → no FEDERAL TAX DOLLARS for inspection
AGRICULTURAL MARKETING ACT of 1946 → gave FSIS the authority to perform voluntary inspection service of non-amenable animals if meat and poultry products must bear a USDA mark of inspection
exotics passed under voluntary FSIS inspection received a TRIANGULAR USDA MARK
producers must investigate FEDERAL and STATE-SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS (state fish & wildlife agency, state heath department, and state department of ag)
farmers must PAY A CERTIFIED USDA FSIS INSPECTOR to inspect non-amenable species
2024 rate → $72 per hour and $88 over time
USDA federally inspected plant must first APPLY FOR AND RECEIVE APPROVAL to process “exotic” animals OR USDA FSIS has granted SPECIAL PROVISIONS to allow on-farm harvesting if farms have a SEPARATE AREA in which to present the live animal(s) to a licensed vet or USDA inspector, before being killed, followed by FAST TRANSPORT to a USDA-inspected plant
products from animals not amenable to the FMIA and PPIA, including those inspected and passed under VOLUNTARY FSIS inspection, are subject to FEDERAL REGULATION by the Us Department Of Human Health And Human Services’ (HHS) FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION (FDA) as “food” under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic act.
bison sold in the COMMERCIAL MARKETPLACE must be processed in a FDA-APPROVED FACILITY
these facilities are required to comply with all FDA regulations, as well as with the FSIS regulations regarding SANITATION
some STATE MEAT Inspection Acts
LOCAL HEALTH CODES → may prohibit sale of un-inspected bison in markets and restaurants
Bison Production - Meat and Meat Safety
smaller producer → __
medium producer → __
large ranch → __
2020 → __ processed at. USDA inspected plants
__ or __ (cow-calf and feedlot) plan
__ (FMIA)
__ → cattle, swine, goats, sheep, horses
__ (PPIA)
__ → chickens, turkey, ducks, geese, guinea fowl, and ratites
to legally sell meat and meat products, animal(s) must be slaughtered in a __ by the USDA’s __, FSIS, and meat products from the inspected carcasses must. be handled in a facility inspected by __
non-amenable species
__ → antelope, deer, elk, moose, bison, water buffalo, bear, caribou, and reindeer
__ → wild turkeys, wild geese, wild ducks, grouse, quail, pheasant, and other non-domesticated species of fowl
rabbits
poultry (fewer than 20,000)
no mandatory USDA FSIS inspection for non-amenable species → no __ for inspection
__ → gave FSIS the authority to perform voluntary inspection service of non-amenable animals if meat and poultry products must bear a USDA mark of inspection
exotics passed under voluntary FSIS inspection received a __ of inspection
producers must investigate __ (state fish & wildlife agency, state heath department, and state department of ag)
farmers must __ to inspect non-amenable species
2024 rate → $__ per hour and $__ over time
USDA federally inspected plant must first __ to process “exotic” animals OR USDA FSIS has granted __ to allow on-farm harvesting if farms have a __ in which to present the live animal(s) to a licensed vet or USDA inspector, before being killed, followed by __ to a USDA-inspected plant
products from animals not amenable to the FMIA and PPIA, including those inspected and passed under __ inspection, are subject to __ by the Us Department Of Human Health And Human Services’ (HHS) __ as “food” under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic act.
bison sold in the __ must be processed in a __
these facilities are required to comply with all FDA regulations, as well as with the FSIS regulations regarding __
some __ Inspection Acts
__→ may prohibit sale of un-inspected bison in markets and restaurants
Bison Production - Buffalo Cheese
bison → not milked COMMERCIALLY
TRAINABLE, but not DOMESTICATED animals
mozzarella
WATER BUFFALO → produces buffalo cheese
SEPARATE species, UNRElATED to bison
some food companies market products as BUFFALO that are not water buffalo, which may be regarded as DECEPTIVE labeling
NATIONAL BISON ASSOCIATION → filed formal comments with the FSIS and FDA urging that the FOOD STANDARDS AND LABELING POLICY BOOK clarify that products containing water buffalo be required to be labeled with the FULL NAME, rather than just “buffalo”
Bison Production - Buffalo Cheese
bison → not milked __
__, but not __ animals
mozzarella
__ → produces buffalo cheese
__ species, __ to bison
some food companies market products as __ that are not water buffalo, which may be regarded as __ labeling
__ → filed formal comments with the FSIS and FDA urging that the __ clarify that products containing water buffalo be required to be labeled with the __, rather than just “buffalo”
Bison Production - Housing
land ≥ 2 - 3 ACRES per animal
STRONG fencing, corral-chute system (7 - 8 ft tall), and a appropriate squeeze chute
know STATE LIABILITY AND TRESPASS laws
National Bison Association → BUFFALO PRODUCER’S GUIDE to MANAGEMENT and MARKETING
Bison Production - Housing
land ≥ __ acres per animal
__ fencing, corral-chute system (__ ft tall), and a appropriate squeeze chute
know __ laws
National Bison Association → __
Bison Production - Management Goals
health program
good RECORD keeping
vaccination
deworming
observation
feeding
similar to BEEF CATTLE
pasture → ROTATIONAL grazing (land OVER need)
winter → SUPPLEMENTAL hay, protein (11% - 13%), salt, minerals
Bison Production - Management Goals
health program
good __ keeping
vaccination
deworming
observation
feeding
similar to __
pasture → __ grazing (land __ need)
winter → __ hay, protein (__%), salt, minerals
Bison Production - Breeding
puberty → 2 YEARS
breeding season → FALL (Aug to Oct)
1 mature bull : 10 - 12 cows
to limit INTERBREEDING → change bull every 1 - 2 seasons
gestation → 275 - 285 DAYS (9 MONTHS)
calving → SUMMER (mid Apr to Jul)
calf weight → 40 - 50 LBS
post-calving
weaning → @ 8 - 9 MONTHS
castration → BULLS SOLD FOR MEAT BEFORE BREEDING AGE
dehorning → UNLIKELY
ear tagging → YES
Bison Production - Breeding
puberty → __ yr
breeding season → __ (Aug to Oct)
__ mature bull : __ cow
to limit __ → change bull every 1 - 2 seasons
gestation → __ d (__ mo)
calving → __ (mid Apr to Jul)
calf weight → __ lb
post-calving
weaning → @ __ mo
castration → __
dehorning → __
ear tagging → __
Bison Production - Feeding to Finishing
2 segments after weaning
PASTURE
ROUGHAGE in a DRYLOT
FEEDLOT → finishing ration
ex. 10 lb alfafa hay and 7 - 10 lb corn per day
average daily gain → 2 - 3 LBS
processed
live weight → 1000 - 1100 LBS
dressing weight → 620 LBS (62%)
Bison Production - Feeding to Finishing
2 segments after weaning
__ → finishing ration
ex. 10 lb alfafa hay and 7 - 10 lb corn per day
average daily gain → __ lbs
processed
live weight → __ lbs
dressing weight → __ lbs (__%)
Ratites
list five different kinds
OSTRICH
EMU
RHEA
CASSOWARY
KIWI
FLIGHTLESS birds
flat BREASTBONE resembles a raft (Latin ratis)
shape of a raft (Latin ratitus)
Ratites
list five different kinds
FLIGHTLESS birds
flat __ resembles a raft (Latin ratis)
shape of a raft (Latin ratitus)
Ratites - Ostrich
2 toes
LARGEST and HEAVIEST bird
found in AFRICA
height → 7 - 9 FEET
weight → 200 - 350 LBS
speed → 30 - 50 MPH
1-month old chick → 35 MPH
LONG necks, SMALL heads, LARGE eyes
males → BLACK and WHITE feathers
females → GRAY feathers
history
1800s → COMMERCIAL production in South Africa of FEATHERS
late 1940s → market developed for MEAT and LEATHER
maturity → 2 - 4 YEARS
females lay 1 - 5 eggs in a COMMUNAL nest (up to 60 total eggs)
egg incubation period → 40 - 46 DAYS
males and females both incubate eggs and raise young
by 6 MONTHS, chicks are almost __
lifespan
wild → 30 - 40 YEARS
zoo → 70 YEARS
diet → OMNIVORES
Ratites - Ostrich
__ toes
__ and __ bird
found in __
height → __ ft
weight → __ lb
speed → __ mph
1-month old chick → __ mph
__ necks, __ heads, __ eyes
males → __ feathers
females → __ feathers
history
1800s → __ production in South Africa of __
late 1940s → market developed for __
maturity → __ yr
females lay __ eggs in a __ nest (up to 60 total eggs)
egg incubation period → __ d
males and females both incubate eggs and raise young
by __ m, chicks are almost __
lifespan
wild → __ yr
zoo → __ yr
diet → __
Ratites - Emu
3 toes
2ND LARGEST bird
found in AUSTRALIA
height → 5 - 6 FEET
weight → 125 - 150 LBBS
speed → 30 MPH
color appearance
head and neck have GRAYISH BLUE skin
feathers are BLACK on head and MOTTLED BROWN on back
plumage is COURSE and HAIR-LIKE
age of maturity → 1.5 - 3 YEARS
5 - 15 eggs per clutch (up to 3 clutches per season)
incubation period → ~50 DAYS
lifespan
wild → 10 - 20 YEARS
zoo → 35 YEARS
Ratites - Emu
__ toes
__ bird
found in __
height → __ ft
weight → __ lb
speed → __ mph
color appearance
head and neck have __ coat
feathers are __ on head and __ on back
plumage is __
age of maturity → __ yr
__ eggs per clutch (up to __ clutches per season)
incubation period → ~__ d
lifespan
wild → __ yr
zoo → __ yr
Ratites - Rhea
3 toes
found in SOUTH AMERICA
height → 5.5 FEET
weight → 44 - 55 LBS
feathers
pale gray to brown
HEAD and NECK completely feathered
no TAIL feathers
LONG BODY feathers droop over posterior of bird
females → lay 1 egg every other day or every 3 - 4 days for 7 - 10 DAYS
in a GROUND, COMMUNAL nest of the male’s design
males → incubate eggs for 42 DAYS and care for newly hatched young
Ratites - Rhea
__ toes
found in __
height → __ ft
weight → __ lb
feathers
pale gray to brown
__ completely feathered
no __ feathers
__ feathers droop over posterior of bird
females → lay __ egg[s] every other day or every 3 - 4 days for __ d
in a __ nest of the male’s design
males → incubate eggs for __ d and care for newly hatched young
Ratites - Cassowary
3 toes
height → 4 - 6 FEET
speed → 30 MPH
found in AUSTRALIA and MALAY ARCHIPELAGO (forests)
NO plumage on head or neck
skin is bright BLUE, RED, and YELLOW
CASQUE → large bony crest on top of head
brownish-black HAIR-LIKE feathers on body
defense → SHARP TOENAILS ON THEIR INNER TOES
maturity → @ 2.5 - 3 YEARS
GREEN eggs laid (3 - 5 per clutch)
incubation period → 49 - 56 DAYS
males → sit on eggs and rear chicks for 9 MONTHS
lifespan
wild → 12 - 20 YEARS
zoo → 40 YEARS
Ratites - Cassowary
__ toes
height → __ ft
speed → __ mph
found in __ and __ (forests)
__ plumage on head or neck
skin is bright __
__ → large bony crest on top of head
brownish-black __ feathers on body
defense → __
maturity → @ __ yr
__ eggs laid (__ per clutch)
incubation period → __ d
males → sit on eggs and rear chicks for __ mo
lifespan
wild → __ yr
zoo → __ yr
Ratites - Kiwi
5 species
3 toes
height → 1 - 2 FEET
weight → 2 - 11 LBS
found in NEW ZEALAND
feathers → brown or gray, HAIR-like
special feathers around their FACES, similar to whiskers
SOLID bones
VERY STRONG, MUSCULAR legs → 1/3 of their BW
they can outrun humans
SMALL head, NO tail, SLENDER bill with NOSTRILS at the end (PHENOMENAL sense of smell)
diet → OMNIVOROUS (insects, larva, crayfish, roots, berries, and fruit)
activity → NOCTURNAL
maturity
females → 2 - 3 YEARS
males → 14 - 18 MONTHS
eggs laid
1 (rarely 2) per clutch, 1 clutch per year
eggs can weigh up to 25% of mom’s body mass
incubation → 75 - 85 DAYS (males sit on eggs)
lifespan
wild → 30 YEARS
zoo → 50 YEARS
Ratites - Kiwi
__ species
__ toes
height → __ ft
weight → __ lb
found in __
feathers → brown or gray, __-like
special feathers around their __, similar to whiskers
__ bones
__ legs → __ of their BW
they can outrun humans
__ head, __ tail, __ bill with __ at the end (__ sense of smell)
diet → __ (insects, larva, crayfish, roots, berries, and fruit)
activity → __
maturity
females → __ yr
males → __ mo
eggs laid
__ (rarely __ ) per clutch, __ clutch[es] per year
eggs can weigh up to __% of mom’s body mass
incubation → __ d (males sit on eggs)
lifespan
wild → __ yr
zoo → __ yr
Ratites Production - Marketing
meat
LOW-fat, LOW-cholesterol, HIGH-iron RED meat
dressing percentage → 54-57%
ex. $6.75 /LB for ground ostrich and $19.55 /LB for ostrich steak
skin → LEATHER
quill pattern
fat → OIL
cosmetics and pharmaceuticals
feathers
harvested ONCE per year
eggs
shells $15 for art
food $20 - $50 per Ostrich egg (1 - 24 chicken eggs)
Ratites Production - Marketing
meat
__-fat, __-cholesterol, __-iron __ meat
dressing percentage → __%
ex. $__ /lb for ground ostrich and $__ /lb for ostrich steak
skin → __
quill pattern
fat → __
cosmetics and pharmaceuticals
feathers
harvested __ per year
eggs
shells $__ for art
food $__ per Ostrich egg (1 - 24 chicken eggs)
Ratites Production - Facilities
VERY DANGEROUS to handle
fences should be 5 FEET high and FLUSH with ground
HIGH walls and CROWD pens make handling easier
space needed = 0.25 - 3 ACRES per breeding pair
Ratites Production - Facilities
__ to handle
fences should be __ ft high and __ with ground
__ walls and __ pens make handling easier
space needed = __ acres per breeding pair
Ostrich and Emu - Breeding
ostrich
maturity
male → 2.5 YEARS
female → 2 YEARS
mating in MONOGAMOUS or POLYGAMOUS relationships
DRAMATIC mating behavior
MANAGED mating season (Mar to Sept)
breed and begin laying eggs 5 - 10 DAYS later
continue laying EVERY OTHER day with up to 15 - 20 eggs
if eggs are removed, female will continue laying up to 40 - 50 eggs
eggs weigh 3 - 5 LBS
emu
maturity → 1.5 - 3 YEARS
mating in mostly MONOGAMOUS relationships
female DOMINANT/larger
breed and lay an egg every 3 - 4 DAYS
up to 30 eggs in a clutch
eggs weigh 1.5 LBS
MALE incubates nest
Ostrich and Emu - Breeding
ostrich
maturity
male → __ yr
female → __ yr
mating in __ relationships
__ mating behavior
__ mating season (Mar to Sept)
breed and begin laying eggs __ d later
continue laying __ day with up to __ eggs
if eggs are removed, female will continue laying up to __ eggs
eggs weigh __ lb
emu
maturity → __ yr
mating in mostly __ relationships
female __/larger
breed and lay an egg every __ d
up to __ eggs in a clutch
eggs weigh __ lb
__ incubates nest
Ostrich and Emu - Incubation and Hatching
ARTIFICIAL incubation > NATURAL incubation
collect eggs DAILY (be clean)
initially store
@ 55-65˚F
75% humidity
air cell UP or egg ON THE SIDE
turn 3× PER DAY
incubate within 7 DAYS of collection
@ 97.5˚F - 99˚F
humidity
ostrich → 35 - 40%
emu → 24 - 35%
weigh WEEKLY
rotate
duration
ostrich → 39 - 59 DAYS (avg 42 days)
emu → 46 - 56 DAYS (avg 50 days)
move to HATCHER 1 - 2 days BEFORE hatching
chick PIPS shell membrane into the AIR CELL
chick will break through the shell and hatch within 12 - 18 HOURS
hatch rate
ostrich eggs → 70%
emu eggs → 50 - 80%
chicks are moved to a BROODER
initial temperature @ 90˚F at FLOOR-LEVEL for 10 - 14 DAYS
water
food
ventilation → CLEAN and DRY
light
litter → bedded with WOOD SHAVINGS, STRAW, RICE HULLS, or CLEAN SAND (nothing slippery or tasty)
DECREASE brooder temperature by 5˚F every 2 WEEKS until supplemental heat is no longer needed
weigh, leg band, microchip, DNA identification, tattoo
determine sex at 1 - 2 MONTHS of age
(DIMORPHOUS plumage occurs at 14 MONTHS )
Ostrich and Emu - Incubation and Hatching
__ incubation > __ incubation
collect eggs __ (be clean)
initially store
@ __˚F
__% humidity
air cell __ or egg __
turn __× per day
incubate within __ d of collection
@ __˚F
humidity
ostrich → __%
emu → __%
weigh __
rotate
duration
ostrich → __ d (avg 42 days)
emu → __ d (avg 50 days)
move to __ 1 - 2 days __ hatching
chick __ shell membrane into the __
chick will break through the shell and hatch within __ hr
hatch rate
ostrich eggs → __%
emu eggs → __%
chicks are moved to a __
initial temperature @ __˚F at __-level for __ d
water
food
ventilation → __
light
litter → bedded with __ (nothing slippery or tasty)
__ brooder temperature by __˚F every __ wk until supplemental heat is no longer needed
weigh, leg band, microchip, DNA identification, tattoo
determine sex at __ mo of age
(__ plumage occurs at __ mo)
Ratites Production - Health Maintenance
establish a relationship with a knowledgeable vet/other farmers
follow a good DISEASE PREVENTION program
ratites are susceptible to similar illnesses and parasites as POULTRY
provide special care for young (HIGH morality rate less than 6 MONTHS of age)
Ratites Production - Health Maintenance
establish a relationship with a knowledgeable vet/other farmers
follow a good __ program
ratites are susceptible to similar illnesses and parasites as __
provide special care for young (__ morality rate less than __ mo of age)
Camelid Evolution
40 million years ago → ORIGINATED IN NORTH AMERICA
3 million years ago → MIGRATED TO ASIA, AFRICA, AND SOUTH AMERICA
10-12,000 years ago → EXTINCT IN NORTH AMERICA
today
list one vicuña species
VICUÑA
list three lama species
GUANACO
ALPACA
LLAMA
list two camelus species
DROMEDARY
BACTRIAN
Camelid Evolution
40 million years ago →
3 million years ago →
10-12,000 years ago →
today
list one vicuña species
list three lama species
list two camelus species
Camelid Classification Terminology
class → MAMMALIA
order → ARTIODACYLA (even-toed)
suborder → TYLOPODA (pad-footed)
family → CAMELIDAE
Camelid Classification Terminology
class →
order → __ (even-toed)
suborder → __ (pad-footed)
family →
Ruminants versus Camelids
ruminants
foot type → FIRM HOOVES and SOLE
red blood cells → ROUND with lifespan of 125 - 160 DAYS
NASAL or ORAL breather
chew CUD
FOREGUT fermenters with 4 stomach chambers
HAS estrous cycle
SPONTANEOUS ovulators
breed STANDING
COTYLEDONARY placenta
artificial insemination COMMON
camelids
foot type → SOFTER FOOTPADS and TOENAILS
red blood cells → ELLIPTICAL with lifespan of > 200 DAYS
PRIMARILY NASAL breather
chew CUD and SPIT
FOREGUT fermenters with 3 stomach chambers
pathway → C1 (largest) to C2 to C3
NO estrous cycle
INDUCED ovulators
breed in STERNAL RECUMBANCY (cush)
DIFFUSE placenta
artificial insemination DIFFICULT
breeding duration → 30 MIN
mating call → MALE ORGLES
Ruminants versus Camelids
ruminants
foot type →
red blood cells → __ with lifespan of __ days
__ breather
chew __
__ fermenters with __ stomach chambers
__ estrous cycle
__ ovulators
breed __
__ placenta
artificial insemination __
camelids
foot type →
red blood cells → __ with lifespan of __ days
__ breather
chew __
__ fermenters with __ stomach chambers
pathway →
__ estrous cycle
__ ovulators
breed __ (cush)
__ placenta
artificial insemination __
breeding duration → __ min
mating call →
Camelids Species - Llama
lifespan → 15 - 25 YEARS
adult weight → 250 - 450 LBS
newborn weight → 18 - 40 LBS
height → 5 - 6 FT @ HEAD
list five marketing using
PACK ANIMAL
FIBER
MEAT
GUARD ANIMAL
FUEL
Camelids Species - Llama
lifespan → __ years
adult weight → __ lbs
newborn weight → __ lbs
height → __ feet @ __
list five marketing using
Camelids Species - Alpaca
lifespan → 15 - 25 YEARS
adult weight → 120 - 200 LBS
newborn weight → 13 - 20 LBS
height → 4.5 FEET @ HEAD
list five marketing using
PACK ANIMAL
FIBER (4 lbs fleece/yr)
MEAT
EXHIBITION
FUEL
2 breeds
huacaya
fiber type → SHORT, DENSE, CRIMPED FIBER
shorn every 1 YEAR
suri
fiber type → LONG, SILKY RINGLETS/DREADLOCKS
short every 2 YEARS
Camelids Species - Alpaca
lifespan → __ years
adult weight → __ lbs
newborn weight → __ lbs
height → __ feet @ __
list five marketing using
2 breeds
huacaya
fiber type →
shorn every __ yr
suri
fiber type →
short every __ yr
Camelids Species - Vicuna
lifespan → 15 - 20 YEARS
adult weight → 99 - 120 LBS
newborn weight → 9 - 13 LBS
height → 3 FEET @ WITHERS
mostly WILD (but farms exist)
labeling system in Peru
created through government-sanctioned CHACU
uses IDENTIFIER garments
vicunas captured, sheared, returned to the wild, and not sheared again for 2 YEARS
150 GRAMS of fine wool/animal/shearing produced
vicuña fleece = marketed/exported ILLEGALLY
Camelids Species - Vicuna
lifespan → __ years
adult weight → __ lbs
newborn weight → __ lbs
height → __ feet @ __
mostly __ (but farms exist)
labeling system in Peru
created through government-sanctioned __
uses __ garments
vicunas captured, sheared, returned to the wild, and not sheared again for __ yr
__ grams of fine wool/animal/shearing produced
vicuña fleece = marketed/exported __
Camelids Species - Guanaco
lifespan → 15 - 25 YEARS
adult weight → 210 - 265 LBS
newborn weight → 18 - 33 LBS
height → 4 FT @ WITHERS
speed → 40 MPH (and swim)
Camelids Species - Guanaco
lifespan → __ years
adult weight → __ lbs
newborn weight → __ lbs
height → __ feet @ __
speed → __ mph (and swim)
US Llama and Alpaca Inventory, 2007-2022
2007 → TIED (~125 thousand)
2012 → ALPACA dominated
2017 → ALPACA dominated
2022 → ALPACA dominated
overall trend
llama inventory → DECREASING
alpaca inventory → SMALL RISE IN 2012, BUT DECREASING
combined inventory → DECREASING
US Llama and Alpaca Inventory, 2007-2022
2007 → __ (~125 thousand)
2012 → __ dominated
2017 → __ dominated
2022 → __ dominated
overall trend
llama inventory →
alpaca inventory →
combined inventory →
Camelid Reproduction
physiology
puberty
females → 6 MONTHS of age
produce OVARIAN HORMONES
males → 7 - 9 MONTHS of age
capable of BREEDING
South America → breed females at 1 YEAR of age if 60% adult BW
North America → breed females at 15 - 24 MONTHS of age and males at 2 - 3 YEARS of age
gestation length (avg. 354 DAYS, or 11 - 12 MONTHS)
alpacas → 325 - 360 DAYS
llamas → 330 - 375 DAYS
gestation and parturition
South America → dictated by PEAK PASTURE GROWTH in the RAINY season
NOV (summer) to APR (fall)
US → birthing season dictated by BREEDERS
over 95% of pregnancies are carried in the LEFT uterine horn
parturition generally occurs DURING THE DAY, particularly in the EARLY MORNING HOURS (6 - 11 am)
approx 70% of females remain standing for cria delivery
baby = CRIA
sternal by 15 MINS
stand by 1 HOUR
nurse by 2 - 4 HOURS
mom’s do not LICK THEIR CRIAS DRY, but instead NUZZLE NOSE-TO-NOSE
epidermal membrane
white, KERATINIZED layer (1 - 2 mm thick) over the cria
attached to cria at 5 areas
LIPS
ANUS
UMBILICUS
CORONET
JUNCTION OF THE SKIN AND FOOTPAD
usually delivered INTACT
will DRY OUT and RUB OFF after birth
placenta/fetal membrane delivery
normal delivery duration → 2 HOURS
retained delivery duration → 6 HOURS
birthing = CRIATION
future observations
COLOSTRUM (Failure of Passive Transfer)
gain ~0.5 LBS/DAY, then 1 LB/DAY
eat solid food by 2 - 3 WEEKS
ruminate by 4 - 6 WEEKS
weaned at 4 - 6 MONTHS
Berserk Male Syndrome → males IMPRINT on humans when young and become extremely AGGRESSIVE/DANGEROUS when mature
Camelid Reproduction
physiology
puberty
females → __ mo of age
produce __
males → __ mo of age
capable of __
South America → breed females at __ yr of age if __% adult BW
North America → breed females at __ mo of age and males at __ yr of age
gestation length (avg. __ d, or __ mo)
alpacas → __ d
llamas → __ d
gestation and parturition
South America → dictated by __ in the __ season
__ (summer) to __ (fall)
US → birthing season dictated by __
over 95% of pregnancies are carried in the __ uterine horn
parturition generally occurs __, particularly in the __ hours (6 - 11 am)
approx __% of females remain standing for cria delivery
baby = __
sternal by __ min
stand by __ hr
nurse by __ hr
mom’s do not __, but instead __
epidermal membrane
white, __ layer (1 - 2 mm thick) over the cria
attached to cria at 5 areas
usually delivered __
will __ and __ after birth
placenta/fetal membrane delivery
normal delivery duration → __ hr
retained delivery duration → __ hr
birthing = __
future observations
__ (Failure of Passive Transfer)
gain ~__ lb/d, then __ lb/d
eat solid food by __ wk
ruminate by __ wk
weaned at __ mo
Berserk Male Syndrome → males __ on humans when young and become extremely __ when mature
Camelid Male Management
SIX fighting teeth
erupt @ 18 - 36
may be filed with a DREMEL and a diamond-bit
females also have SMALL fighting teeth that erupt @ 4 - 6 YEARS
surgical castration is performed ≥ 18 - 24 MONTHS of age to allow for NORMAL CLOSURE of growth plates
avoid tall animals with POST-LEGGED conformation that may predispose to ARTHRITIS and/or PATELLAR LUXATION
Camelid Male Management
__ fighting teeth
erupt @ __ mo
may be filed with a __ and a diamond-bit
females also have __ fighting teeth that erupt @ __ yr
surgical castration is performed ≥ __ mo of age to allow for __ of growth plates
avoid tall animals with __ conformation that may predispose to __ and/or __
Camelid Handling and Restraint
camelids are HERD animals
HALTER → with caution! (do not suffocate)
NECK then CHIN/JAW hold
PHYSICAL STRUCTURES → chute, gates, fences, etc.
EAR hold → no twisting
SPIT rag
cast
sedate
lure with FOOD
☆ avoid EYE CONTACT
Camelid Handling and Restraint
camelids are __ animals
__ → with caution! (do not suffocate)
__ then __ hold
__ → chute, gates, fences, etc.
__ hold → no twisting
__ rag
cast
sedate
lure with __
☆ avoid __