Building Blocks of the Rock Cycle: Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What is a rock?
A naturally occurring solid aggregate of one or more minerals, mineraloids, or organic matter.

What are the three main types of rocks?
Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic.
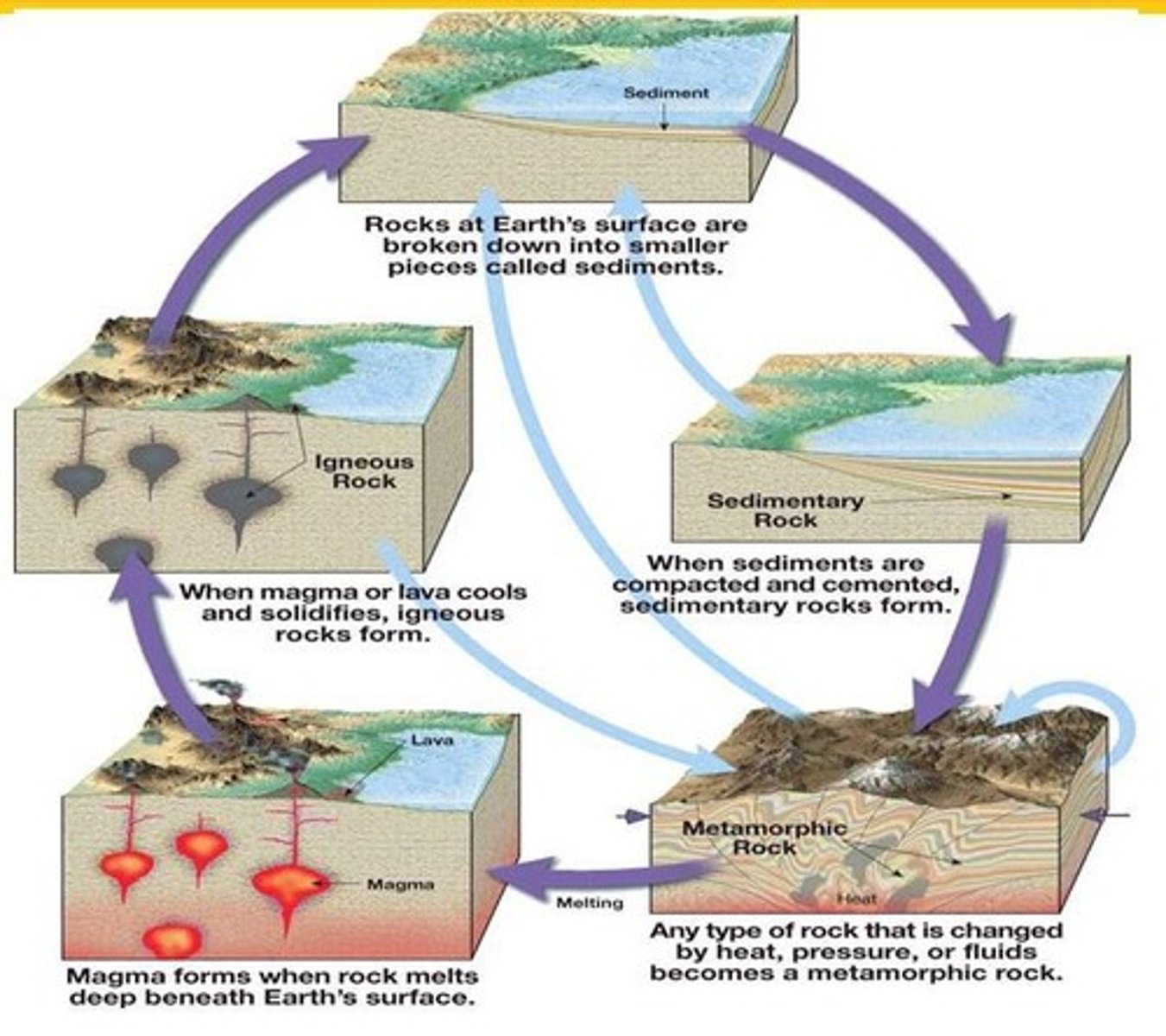
How are igneous rocks formed?
From cooling magma or lava through volcanic processes.

What processes lead to the formation of sedimentary rocks?
Accumulation and lithification of sediment or precipitation from solution at normal surface temperatures.
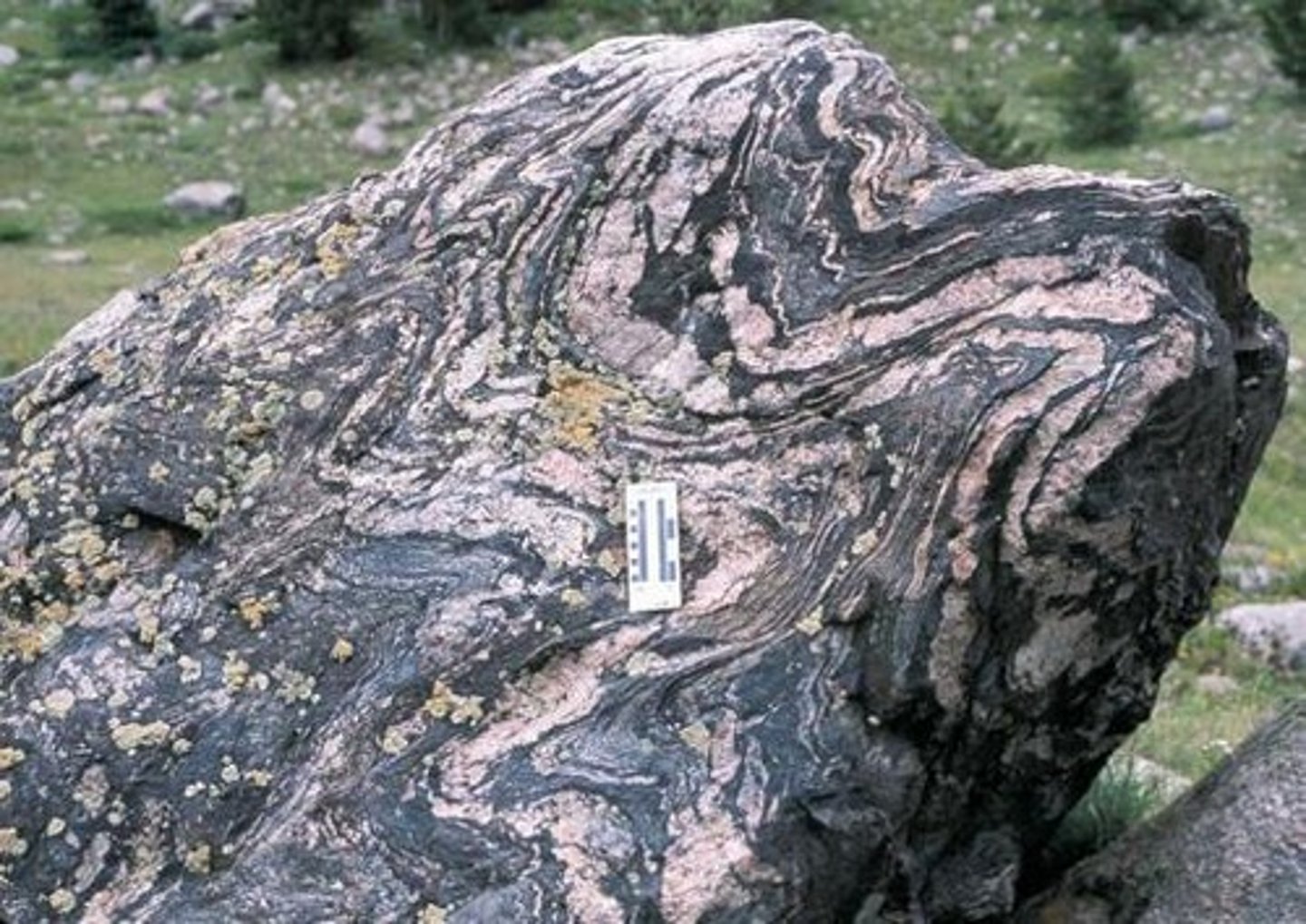
What causes metamorphic rocks to form?
Subjecting preexisting rocks to high heat, high pressure, or hot mineral-rich fluids.

What is lithification?
The process of compaction and cementation that transforms sediment into sedimentary rock.
What is physical weathering?
The disintegration or physical breakup of rocks without changing their chemical composition.

What is chemical weathering?
The decomposition of rocks through chemical reactions, such as dissolution or oxidation.
What is erosion?
The movement of breakdown products due to weathering processes.
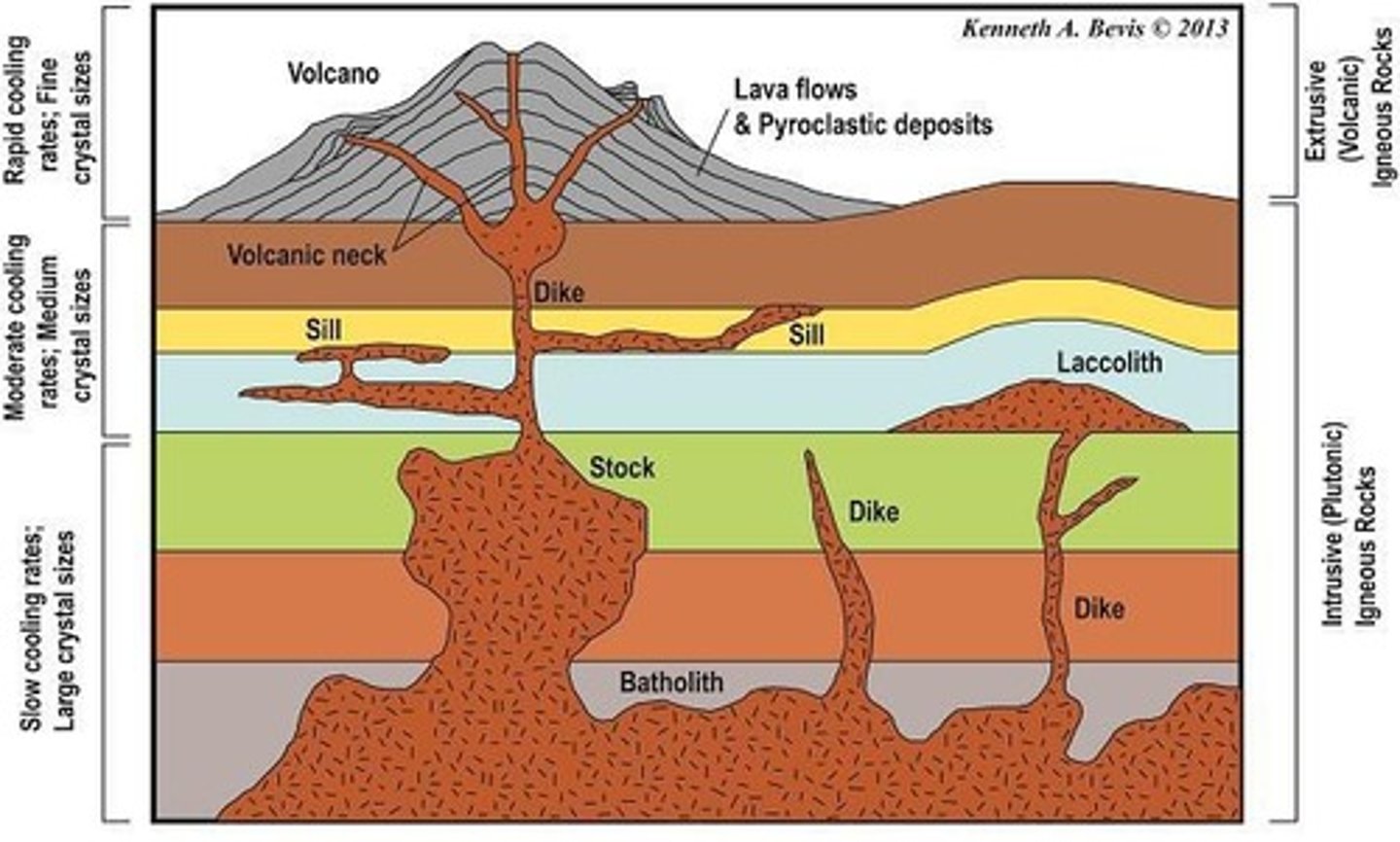
What are extrusive igneous rocks?
Rocks formed from magma that cools and solidifies on the Earth's surface.
What are intrusive igneous rocks?
Rocks formed from magma that cools and solidifies within the Earth's crust.
What is the role of sediment in the rock cycle?
Sediment is formed from weathered rocks and can eventually lithify into sedimentary rocks.
What is the significance of the rock cycle?
It illustrates the continuous transformation of rocks through various geological processes.
What is metamorphism?
The transition of one rock into another by changes in temperature and pressure.
What are the four types of metamorphic rock formation?
Regional, Dynamic, Contact, and Hydrothermal.
What is frost wedging?
A type of physical weathering where water seeps into cracks, freezes, and expands, breaking the rock apart.
What is plant (root) wedging?
A form of physical weathering where plant roots grow into cracks in rocks, causing them to break apart.
What is thermal expansion in the context of weathering?
The physical weathering process where rocks expand when heated and contract when cooled, leading to fractures.
What are clastic rocks?
Sedimentary rocks formed from the accumulation of fragments of preexisting rocks.
What are chemical rocks?
Sedimentary rocks formed from the precipitation of minerals from solution.

What is an example of a clastic sedimentary rock?
Sandstone.

What is an example of a chemical sedimentary rock?
Limestone.

What is the process of lithification?
The process of converting sediment into sedimentary rock through compaction and cementation.
What are the main types of rocks in the rock cycle?
Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
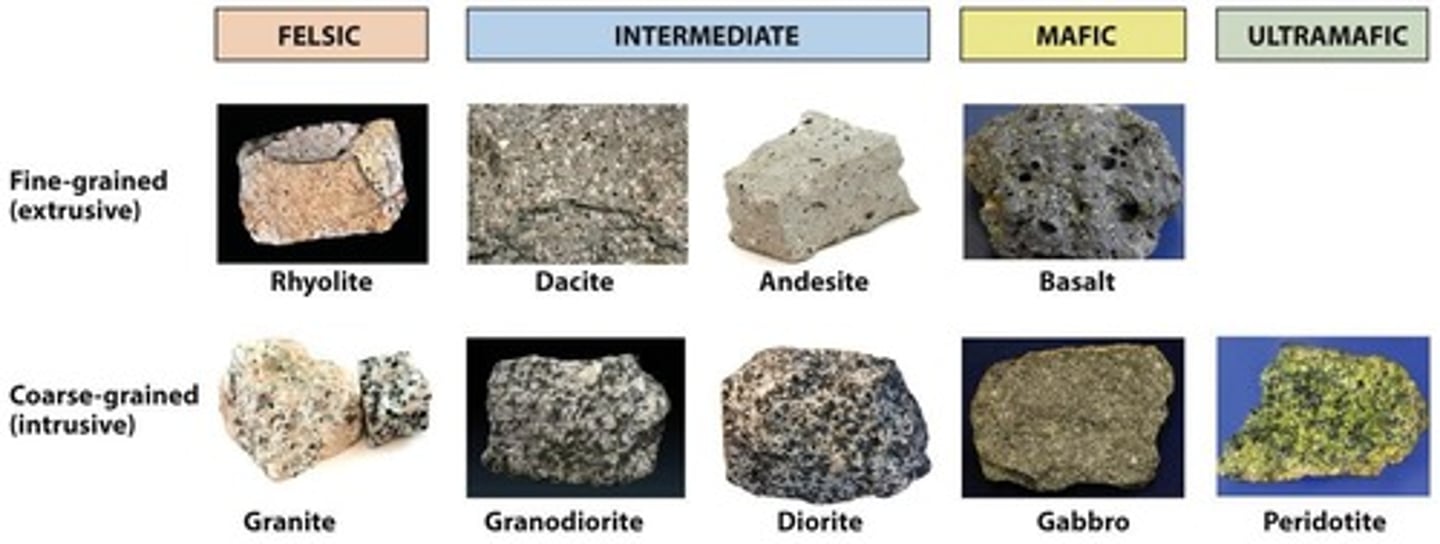
What distinguishes plutonic igneous rocks from volcanic igneous rocks?
Plutonic rocks cool slowly underground and have coarse grains, while volcanic rocks cool rapidly at the surface and have fine or glassy textures.
What are the compositional types of igneous rocks?
Felsic (high SiO₂, light-colored), Intermediate, and Mafic (low SiO₂, dark).

What is the role of weathering and erosion in the rock cycle?
They break down rocks into sediments, which can then be transported and deposited to form sedimentary rocks.
What are the two main types of metamorphic rocks?
Foliated (layered or banded) and Non-foliated (recrystallized without layering).
What is the significance of index minerals in metamorphic rocks?
They indicate the conditions of temperature and pressure under which the rock formed.
What gases are commonly emitted from volcanoes during eruptions?
Water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
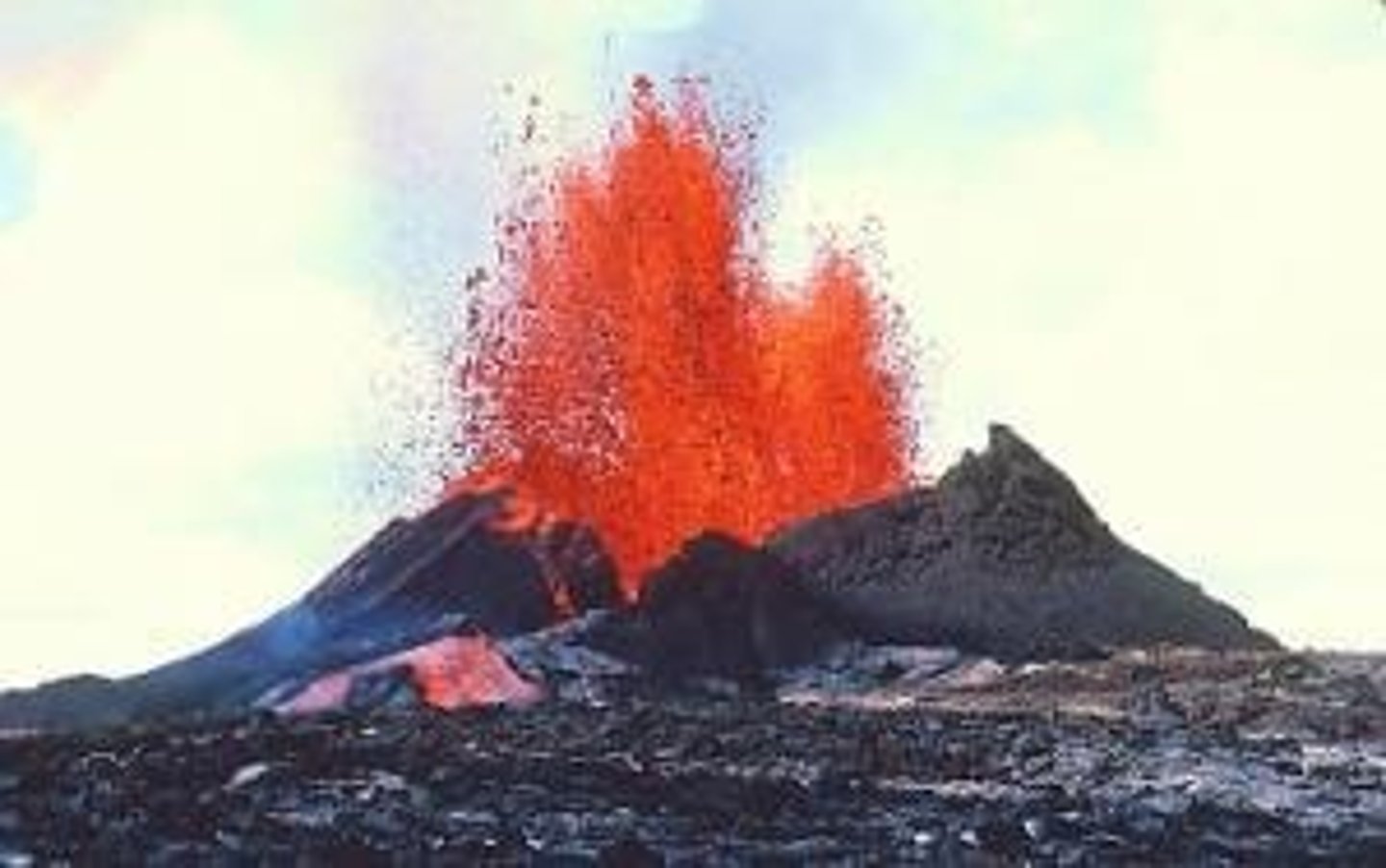

What was the significance of the 1991 Pinatubo eruption?
It was the second-largest volcanic eruption of the 20th century, significantly affecting atmospheric conditions.
How do volcanic CO2 emissions compare to anthropogenic CO2 emissions?
Volcanic emissions are much lower; anthropogenic activities emit significantly more CO2.
What is the process of cooling and crystallization in the rock cycle?
The process where magma or lava cools and solidifies to form igneous rocks.
What are clastic sedimentary rocks?
Rocks formed from fragments of other rocks, such as shale, sandstone, and conglomerate.
What are chemical sedimentary rocks?
Rocks formed from the precipitation of minerals from solution, such as halite and gypsum.
What is the role of sorting and grain size in sedimentary rocks?
They reveal the energy of the transporting environment; fine grains indicate low energy, while coarse grains indicate high energy.
What is the significance of the carbon cycle in relation to the rock cycle?
The carbon cycle involves the movement of carbon through the atmosphere, biosphere, and geosphere, influencing rock formation and transformation.
What happens to carbon in plants during decomposition?
It becomes part of the soil, contributing to the nutrient cycle.
How does the rock cycle connect to climate change?
Processes like weathering and volcanic eruptions release gases that can influence atmospheric conditions and climate.
What is the role of plate tectonics in the rock cycle?
Plate tectonics drives the movement and transformation of rocks between different types through geological processes.
Define weathering.
The physical and chemical breakdown of rock.
What is deposition in the context of geology?
The dropping of rock fragments.
How do weathering and erosion contribute to soil formation?
They accelerate mass wasting and facilitate the formation of soils.
List the agents of erosion.
Gravity, running water, waves, glaciers, and humans.
What is mass wasting?
The movement of regolith (soil, sand, and rock) when a slope is too steep to remain stable.

What is regolith?
The loose material, including soil, sand, and rock, that can move during mass wasting events.
What are the learning goals of the lecture on weathering and soil formation?
To explain components of physical and chemical weathering, define soil, discuss soil formation factors, and address soil problems related to climate change.
What gases are emitted from volcanoes during an eruption?
Water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
What was significant about the 1991 Pinatubo eruption?
It was the second-largest volcanic eruption of the 20th century.
What is the average residence time of carbon in soil?
160 years, based on a carbon reservoir of 1,600 gigatonnes and annual carbon exchange.
What is plant wedging?
Cracking of rock caused by plant roots and burrowing animals.
Define exfoliation in geological terms.
The cracking of rock due to a decrease in confining pressure when overlying rock is removed.
What is dissolution (salt) in the context of weathering?
A process where groundwater moves into rock pores, and as water evaporates, salt crystals grow and exert pressure on the rock.
What is oxidation in chemical weathering?
Reactions involving oxygen that lead to the breakdown of minerals.
What is carbonation in weathering?
Reactions involving carbon dioxide that can lead to the dissolution of minerals.
How do human activities affect mass movement?
Human activities can destabilize slopes and increase the likelihood of mass wasting.
What is the role of soil in the carbon cycle?
Soil acts as both a source and a sink for carbon through various biological and geological processes.
What is the significance of the rock cycle in relation to climate?
The rock cycle interacts with climate through processes like weathering and erosion, influencing soil formation and carbon storage.
What are clay minerals?
Minerals that are a key component of soil, affecting its properties and formation.
What are soil orders?
Categories that classify soils based on their characteristics and formation processes.
What are some soil problems related to climate change?
Soil degradation, erosion, and changes in soil fertility due to shifting climate conditions.
What is the impact of volcanic eruptions on atmospheric conditions?
Volcanic eruptions can release gases that affect climate and atmospheric chemistry.
How does the process of weathering differ between mechanical and chemical types?
Mechanical weathering physically breaks down rocks without changing their chemical composition, while chemical weathering alters the minerals within the rocks.
What is hydrolysis in the context of chemical reactions?
Reactions involving water.
What is the chemical equation for the formation of carbonic acid from carbon dioxide and water?
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
What does chemical weathering refer to?
The process by which rocks are rotting away due to chemical reactions.
What is carbonation hydrolysis?
A process where carbonic acid reacts with minerals like feldspar to produce clay minerals.
What is the pedosphere?
The entire layer of disintegrated and decomposed rock debris and organic matter at the surface of the Earth.
Define bioturbation.
The disintegration and mixing of organic and mineral matter caused by plant growth in soil and weathered rock.
What is soil?
An internally organized natural body of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that support life.
What are the five factors that determine soil characteristics?
Climate, organic material, relief (topography), parental material, and time (CLORPT).
What is the significance of climate in soil formation?
Climate is the combination of temperature and precipitation that exists over a large area for a long period of time.
What are clay minerals characterized by?
Clay minerals have a negative charge and are not electrically neutral.
What is cation adsorption?
The process where cations dissolve in water and adsorb onto clay minerals.
What is cation exchange capacity?
The ability of soil to hold and exchange cations, which are positively charged ions.
What soil problems can arise in areas of high precipitation?
They may create acidic soil due to the presence of hydrogen ions.
How can acidic soil be neutralized?
By adding powdered calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
What are the soil horizons in undisturbed soil?
O (Organic), A (Alluviation), E (Eluviation), B (Subsoil), C (Parent Material), R (Bedrock).
What is the mnemonic for remembering soil horizons?
Oscar Always Eats Blue Cheese.
What is the residence time of carbon in soil?
Approximately 27 years.
What is the main force driving erosion?
Gravity.
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
Weathering is the breakdown of rocks, while erosion is the movement of those materials.
What is the role of soil in carbon storage?
Soil acts as a sink for carbon by storing organic matter from dead plants and animals.
What characterizes temperate humid climates in terms of soil?
They receive more than ~50 cm of precipitation per year.
What characterizes temperate arid climates in terms of soil?
They receive less than ~50 cm of precipitation per year.
What is the chemical weathering process involving feldspar to make clay minerals?
The carbonation and hydrolysis of feldspar results in the formation of clay minerals such as kaolinite.