Ecology IB Bio SL
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
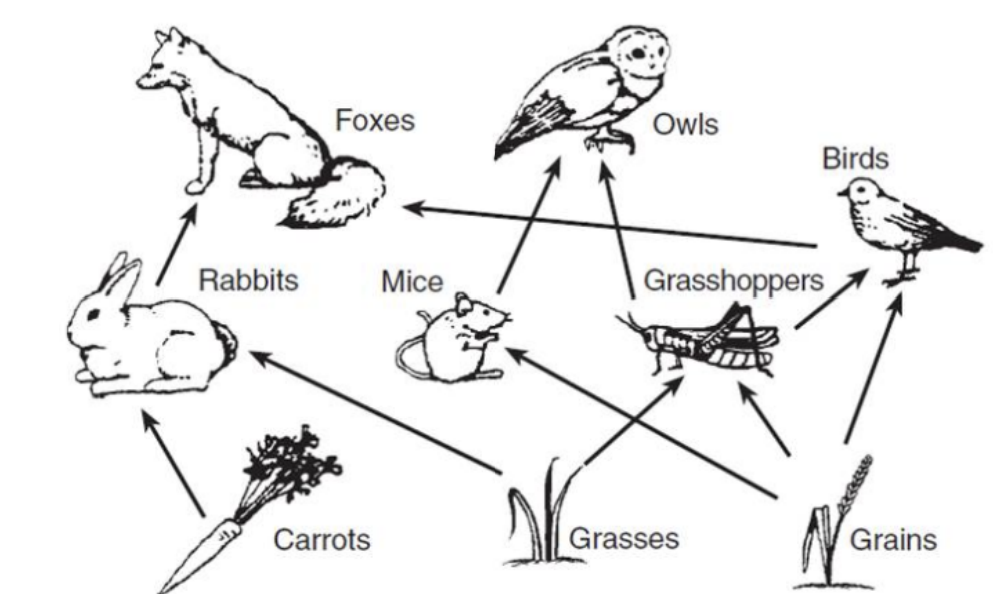
Identify the trophic level for each organism in the food web below
Producers: carrots, grasses, grains
Primary consumers: rabbit, mice, grasshopper, bird
Secondary consumers: fox, owl, bird
Tertiary consumer: fox
What impact does the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere have on the ocean?
The ocean absorbs carbon dioxide which makes the ocean more acidic. This causes coral to deposit less calcium in their bodies causing coral bleaching
Describe peat
Partially decomposed plant material
Can be used as a fossil fuel
Waterlogged soil
How does climate change impact natural selection?
Some organisms are adapted for variation in climate and changes in the climate
Organisms that are able to adapt to changes in food chains will survive better → reproduce and pass on their genes
Organisms not adapted to climate changes will die/disappear over time
Changes in a species may occur or new species may appear
Distinguish between saprotrophs and detritivores.
Saprotrophs: digest organic matter then absorb it and live on/in organic matter
Detritivores: eat (ingest) dead leaves, feces, and carcasses (organic matter)
Why don’t food chains contain more than four or five trophic levels?
90% of energy is not transferred to the next trophic level
Energy is lost through respiration, heat loss, waste (feces and urine)
How did pollution impact the light and dark moths and their ability to camouflage?
Pollution made the bark of trees darker so the light colored moths were no longer able to blend in with the bark so their population decreased.
Describe how energy flows through an ecosystem.
Energy from the sun captured by plants and other autotrophs Sunlight energy converted in photosynthesis
Energy is passed to animals or other consumers
Energy is lost at each trophic level
Only about 10% of the energy is passed to the next trophic level
Some energy is left for decomposers
Draw an example of a food chain.
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
What impact does methane have on climate change?
Methane is a greenhouse gas (GHG) that causes an increase in temperature in the atmosphere; most powerful GHG but has a much shorter lifespan than CO2
What is the role of bacteria in the carbon cycle?
Decomposes dead material causing formation of CO2 from respiration
Saprotrophic bacteria partially decomposes dead material in waterlogged soil resulting in peat formation
Photosynthetic bacteria fixes CO2 during photosynthesis
Describe carbon sinks
Reservoirs that absorb and store CO2 from the atmosphere. In the ocean, photosynthesis will increase the size of the carbon sink
Define community, population, and ecosystem
Population: group of the same species
Community: multiple populations interacting with each other
Ecosystem: community plus the abiotic factors