CHAP 29 - HUMAN DEVELOPMENT AND AGING
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
The primary germ layers include the mesoderm, the endoderm and the ___
ectoderm
After ejaculation and during sperm migration, what occurs that allows a sperm to penetrate an egg?
Capacitation
Following fertilization, the genetic material of each gamete is contained within which of the following?
Pronucleus
Match each stage of the gestational period to its time frame.
Fetal Stage
Preembryonic stage
Embryonic Stage
Fetal Stage - week 8 to week 38
Preembryonic stage - day 0 to day 16
Embryonic Stage - day 16 to week 18
The first 16 days of development is called which stage?
Preembryonic
What are the three primary germ layers?
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Ethryderm
Myoderm
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Mesoderm
What is the correct order of development during the preembryonic stage?
Zygote, morula, blastocyst
During sperm migration, the membrane of the sperm head becomes more fragile. This change is part of a process called
capacitation
What are the cells formed by the first cleavage of the fertilized egg called?
Blastomeres
What is a zygote?
A fertilized egg
In which embryonic stage is an offspring during the third trimester?
Fetal
During which prenatal stage do cleavage and implantation occur?
Preembryonic stage
The process by which a blastocyst attaches to the lining of the uterus is called
implantation
The ____ stage of development comprises the first 16 days of pregnancy.
preembryonic
What is the cell division that occurs in the earliest stages of zygote development called?
Cleavage
A single-celled, fertilized egg is known as a(n)
zygote
Which developmental stage is complete once the blastomeres arrange to form the three primary germ layers?
Embryogenesis
What is the process in which cells migrate to form the three primary germ layers called?
Gastrulation
When does implantation normally occur?
Day 6 after ovulation
What is the outermost germ layer?
Ectoderm
Which prenatal stage occurs between fertilization and implantation?
Preembryonic
The term ____ refers to the mitotic divisions that occur in the first three days after fertilization.
Cleavage
In which process do the germ layers differentiate into organs and organ systems?
Organogenesis
What is embryogenesis?
The arrangement of a blastomere into 3 primary germ layers
During the embryonic stage, what forms on the uterine wall?
Placenta
The ____ is the germ layer that will form, among other structures, the inner layer of the digestive tract.
endoderm
The folding of the lateral margins of the embryonic disc around the sides of the yolk sac encloses a longitudinal channel known as the primitive ____
gut
Choose all that are functions of amniotic fluid.
-To allow development of the lungs
-To protect the fetus from temperature fluctuations
-To protect the fetus from trauma
-To produce blood during the early stages of development
-To allow development of the lungs
-To protect the fetus from temperature fluctuations
-To protect the fetus from trauma
The process of ____ is the differentiation of the primary germ layers into organ and organ systems.
organogenesis
The ____ sac arises from cells of the hypoblast and produces the first blood cells.
yolk
When does the embryonic stage of development begin?
When the three germ layers are first present, at about 16 days
What are the endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm?
Primary germ layers
The folding of the lateral margins of the embryonic disc around the sides of the yolk sac encloses a longitudinal channel known as which of the following?
Primitive gut
Which structure is attached to the uterine wall and provides nutrients to the developing fetus?
Placenta
At term, how much amniotic fluid is in the amniotic cavity?
700 to 1000 mL
Which forms the foundation for the umbilical cord and the part of the urinary bladder?
Allantois
Placental nutrition reaches the developing conceptus via a tube of blood vessels called the ____ cord
umbilical
During the embryonic stage, what forms on the uterine wall?
Placenta
At about 8 weeks and once all organs system are present, a conceptus is then called a(n)
Fetus
Decidual cells of the endometrium play what role during early development?
They nourish the conceptus.;
After implantation the conceptus receives trophoblastic nutrition consisting of decidual cells of the endometrium.
The ____ is a disc-shaped organ attached to the uterine wall that provides nutrition to the fetus via the umbilical cord.
placenta
In the developing fetus, blood from the umbilical vein bypasses the liver and empties directly into the vena cava by way of a vessel called the ductus
____
venosus
The function of ____ fluid is to protect the embryo from infection, trauma, and temperature fluctuations, allow freedom of movement, and allow development of the lungs.
amniotic
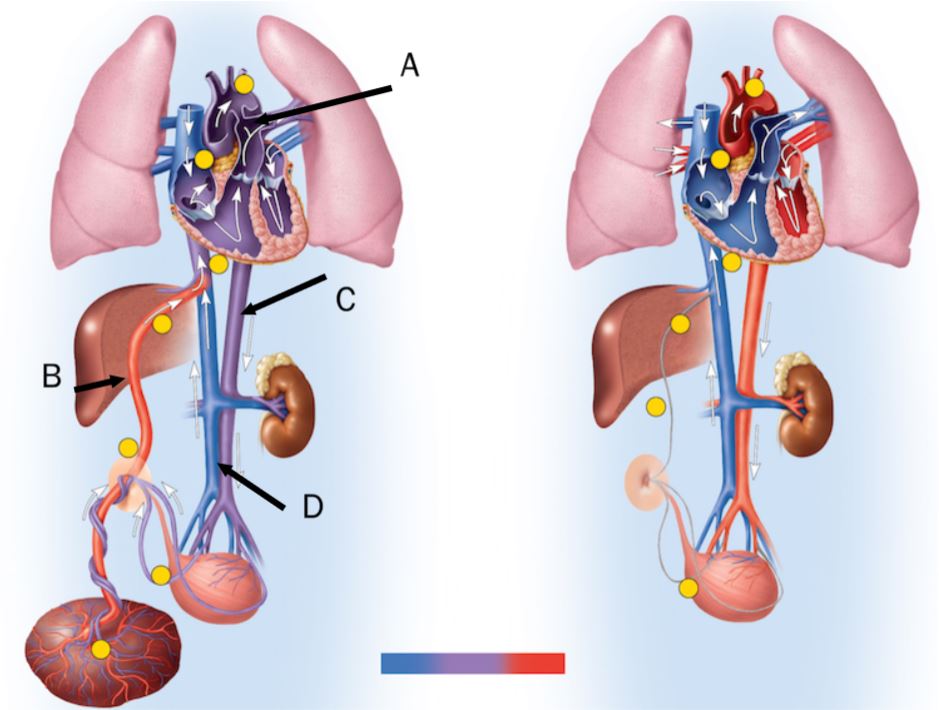
In the figure, the ductus venosus is labeled ____
B
The blood vessels within the umbilical cord include two umbilical ____ and one ____.
arteries, vein
An infant up to 4 weeks old is classified as a(n)
neonate
During development, an individual is known as what from the beginning of the ninth week through birth?
Fetus
For the first 8 weeks after implantation, the conceptus is nourished by which type of nutrition?
Trophoblastic
A neonate's first breath requires a large effort to inflate its collapsed alveoli.
True;
Because the lungs are non-functioning in utero, the alveoli in a fullterm neonate are collapsed. It does require significant effort to expand them.
During fetal development, blood from the umbilical cord flows directly into the vena cava bypassing the liver via which vessel?
Ductus venosus
The proximal part of each umbilical artery becomes what after birth?
Superior vesical artery
In the figure, the umbilical artery is labeled
D
What is an infant up to 6 weeks old called?
Neonate
An infant weighing under 2.5 kg (5.5 lbs) is considered __________
premature
What is a fetus?
A conceptus after 8 weeks of development
In the first two weeks following birth, about how many breaths per minute does a neonate take?
45
In some neonates, the foramen ovale does not close to form the fossa ovalis. This is an example of which of the following?
Congenital anomaly;
A congenital anomaly is the abnormal structure or position of an organ at birth.
Why does the pathway of circulation change after birth?
To allow gas exchange to occur in the new environment
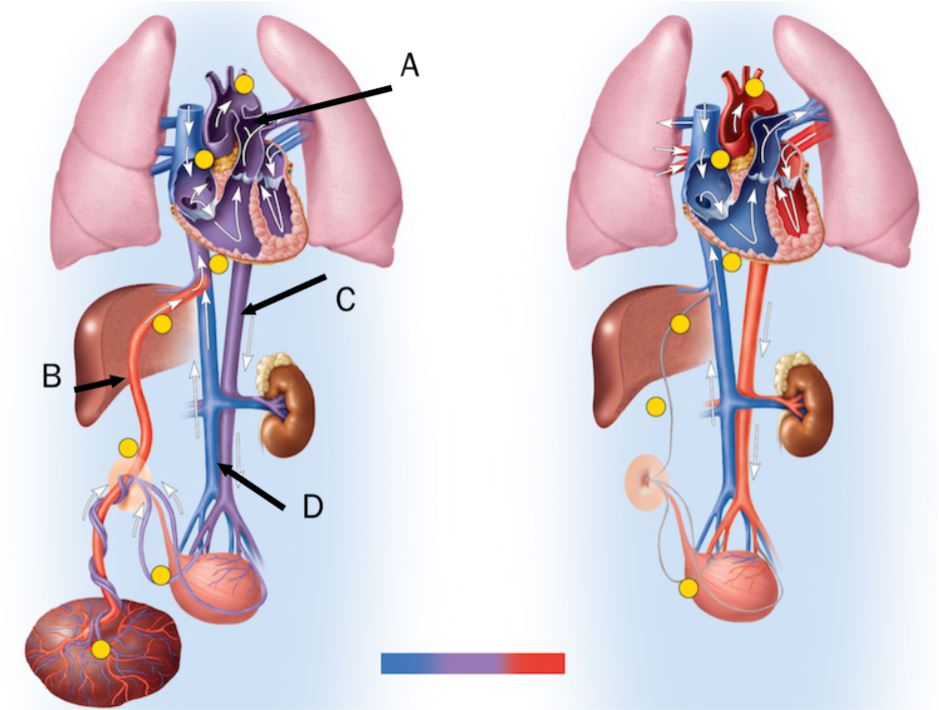
In the figure, the ductus venosus is labeled
b
An infant is considered premature if they are under which weight?
2.5 kg (5.5 lbs)
The study of birth defects is known as
teratology
During development, an individual is known as what from the beginning of the ninth week through birth?
Fetus
Agents that cause anatomical deformities in the fetus are called
teratogen
A congenital anomaly is also called what?
A birth defect
The substance that causes more birth defects than any other drug is
alcohol
The proximal part of each umbilical artery becomes what after birth?
Choose four signs of fetal alcohol syndrome.
Webbed toes
Small head
Hyperactivity
Poor attention span
Malformed facial features
Gigantism
Small head
Hyperactivity
Poor attention span
Malformed facial features
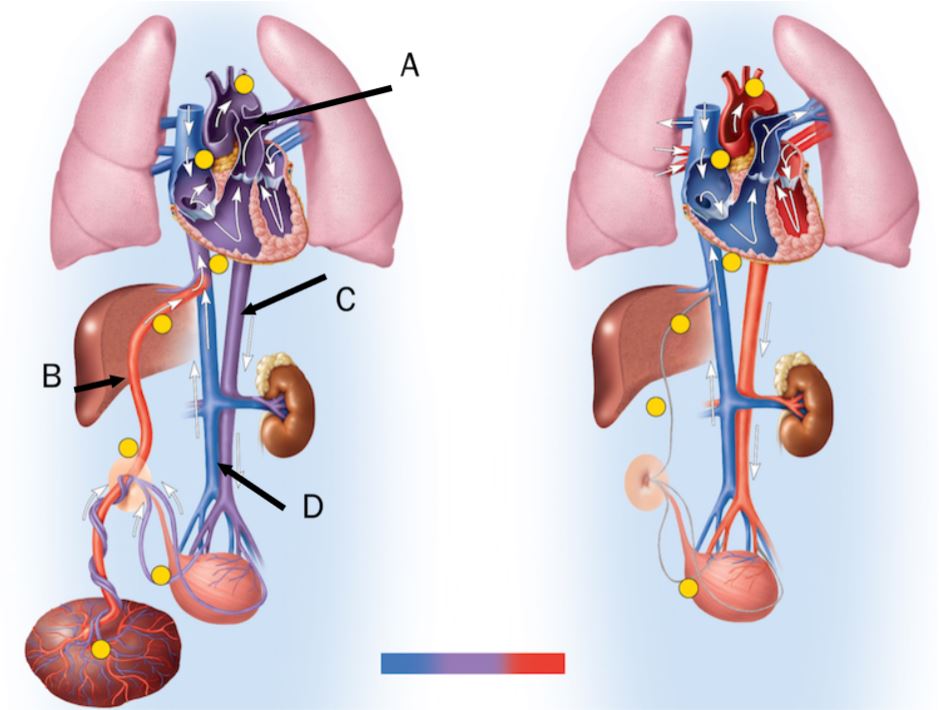
In the figure, the umbilical vein is labeled
C
What does teratology study?
Birth defects
Environmental agents that cause mutations are called what?
Mutagens
What is a teratogen?
What is a teratogen?
What causes more birth defects than any other drug?
Alcohol
The failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis is known as
Nondisjunction
Which disorder is characterized by a small head, cleft palate, cardiac and central nervous system defects, malformed facial features, and behavioral signs including hyperactivity, and poor attention span?
Fetal alcohol syndrome
The term ____ refers to an abnormal number of chromosomes
Aneuploidy
Any change in the structure of a chromosome or a DNA molecule, often resulting in a change of organismal structure or function is known as a(n)
mutations
If during meiosis II nondisjunction occurred and the resulting zygote had only a single copy of chromosome 14, this would be an example of which of the following?
Monosomy 14
Agents that cause anatomical deformities in the fetus are called
teratogen
The condition of having three copies of a chromosome is known as
trisomy
What is the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis called?
Nondisjunction
Monosomy
Monosomy is when a cell lack a chromosome. It is one potential result of nondisjunction which is the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate.
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy or the presence of an extra chromosome or the lack of a chromosome is the result of nondisjunction which is the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate.
The anomaly that results from when a zygote has 3 X chromosomes is called ____
triplo x syndrome
The presence of an extra chromosome or lack of one is called what?
Aneuploidy
Klinefelter syndrome results from which genotype?
XXY;
XYY results in XYY syndrome, XO results in Turner syndrome and XXX results in triplo-X syndrome.
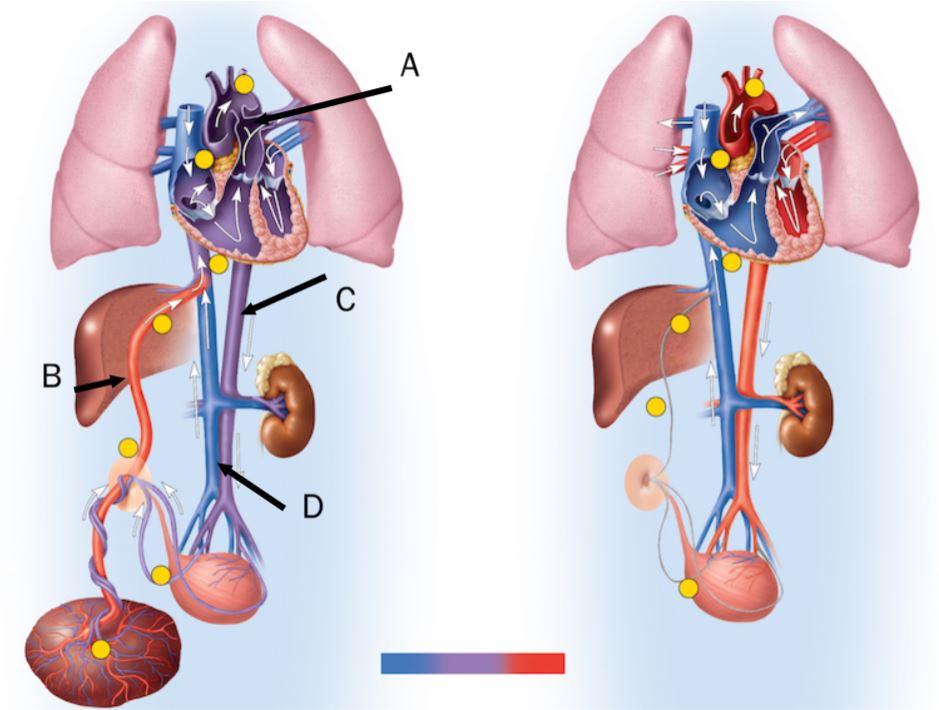
In the figure, the ductus arteriosus is labeled
A
Which disorder results from having three copies of chromosome 21?
Down syndrome
What is monosomy?
The lack of a chromosome
The term ____ refers to the degenerative changes that occur with aging.
senescence
What is trisomy?
The presence of an extra chromosome
Which degenerates at a faster rate?
Glomeruli of kidneys
Which disorder is associated with the presence of three X chromosomes?
trisomy X
The syndrome that results when a zygote has 2 X chromosomes and a Y chromosome is called ____ syndrome
Klinefelter
What is the genotype of someone with Down syndrome?
Trisomy 21
Why does hair turn grey?
Melanocytes die out.
The degeneration that occur in an organ system after its peak functional age is called what?
Senescence
Aging changes that occur naturally over the course of time are called what?
Intrinsic
Which describes the relative senescence of different organ systems?
Organ systems degenerate at different rates.
Bone loss that is severe enough to compromise physical health and activity is known as
Osteoporosis
Which disorder is characterized by the presence of XXY, resulting in a sterile male with underdeveloped testis, abnormal breast development, and unusually long arms and legs?
Klinefelter syndrome