Bot-Lab (Sem-1) - Chapter 15: Flowers and Types of Inflorescence
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
flowers
the reproductive organs of angiosperms; produce the necessary cells (egg and sperm) to produce a zygote; determinate stem with crowded appendages, and with internodes much shortened or obliterated
produce offspring genetically identical to parents; produce offspring genetically different to parents
two major functions of plant reproduction
fruit
a developed and ripened ovary/ovaries, sometimes with other floral organs and other plant parts
seed
the enlarged and mature ovule with its enclosed embryo and consists usually of supply of stored food; typically dry, dormant, and very resistant to environmental stress
complete
flowers that have all four parts: sepals, petals, stamens and pistils
incomplete
flowers that lack one or more of four parts: sepals, petals, stamens and pistils
perfect
bisexual flowers; flowers with both male and female reproductive parts (pistil and stamen)
imperfect
unisexual flowers: flowers with only one male or female reproductive part (pistil or stamen)
monoecious
having both female and male flowers in one plant
dioecious
having separate plants for male and female flowers
regular symmetry
actinomorphic flower; parts (whorls) of a regular flower, i.e., the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium, are arranged symmetrically around the floral axis
irregular symmetry
the petals and sepals are not uniform in shape and they are arranged around the floral axis in an irregular fashion, i.e., asymmetrically
polypetalous
having separate petals
polysepalous
having separate sepals
polytepalous
having separate tepals
gamopetalous
having fused petals
gamosepalous
having fused sepals
gamotepalous
having fused tepals
superior
an ovary attached above other floral parts
inferior
an ovary which lies below the attachment of other floral parts
epigynous
inferior ovary; having the ovary enclosed in the receptacle, with the stamens and other floral parts situated above
perigynous
sub-inferior ovary; ovary is surrounded by the fused bases of flower parts (calyx, corolla, androecium) that surround the ovary
hypogynous
superior ovary; the gynoecium at the top of the flower, while the rest of the parts are located lower down
simple pistil
composed of one carpel
compound pistil
composed of two or more carpels
anatropous
one in which curvature during development results in displacement of the micropyle to a position adjacent to the funiculus base; this is the most common ovule type of the angiosperms and is presumed to be ancestral
orthotropous
a type of ovule in which no curvature takes place during development; the micropyle is positioned opposite the funiculus base
campylotropous
a type of ovule in which the nucellus is bent only along the lower side
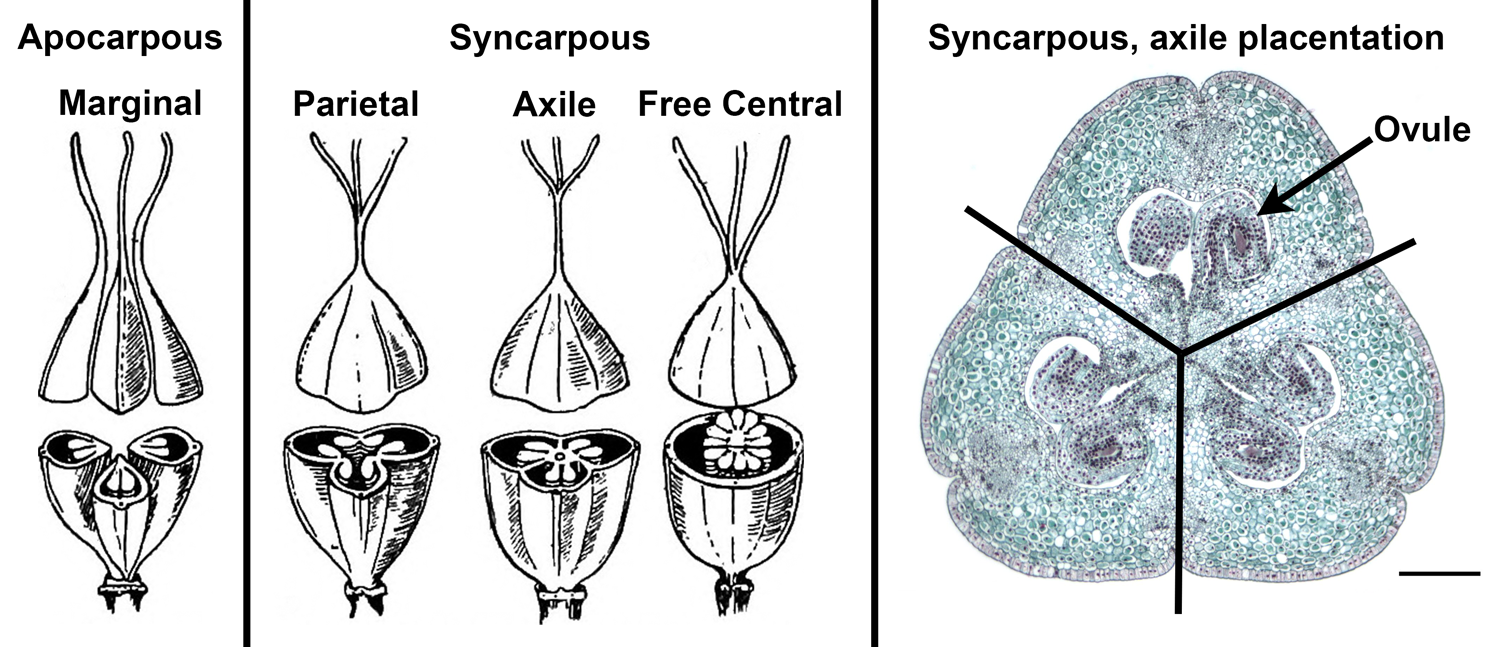
axile placentation
the placentae are located on a central column; partitions from the central column to the ovary wall create chambers (locules) that separate the placentae and attached ovaries from each other
parietal placentation
type of placentation found in compound, unilocular ovaries in which the ovules arise from placentae inserted on the wall of the locule near the sutures
central placentation
resembles axile placentation; however, the column is not connected by partitions to the ovary wall, and thus no locules are formed
basal placentation
one or more ovules are attached to the bottom of the ovary
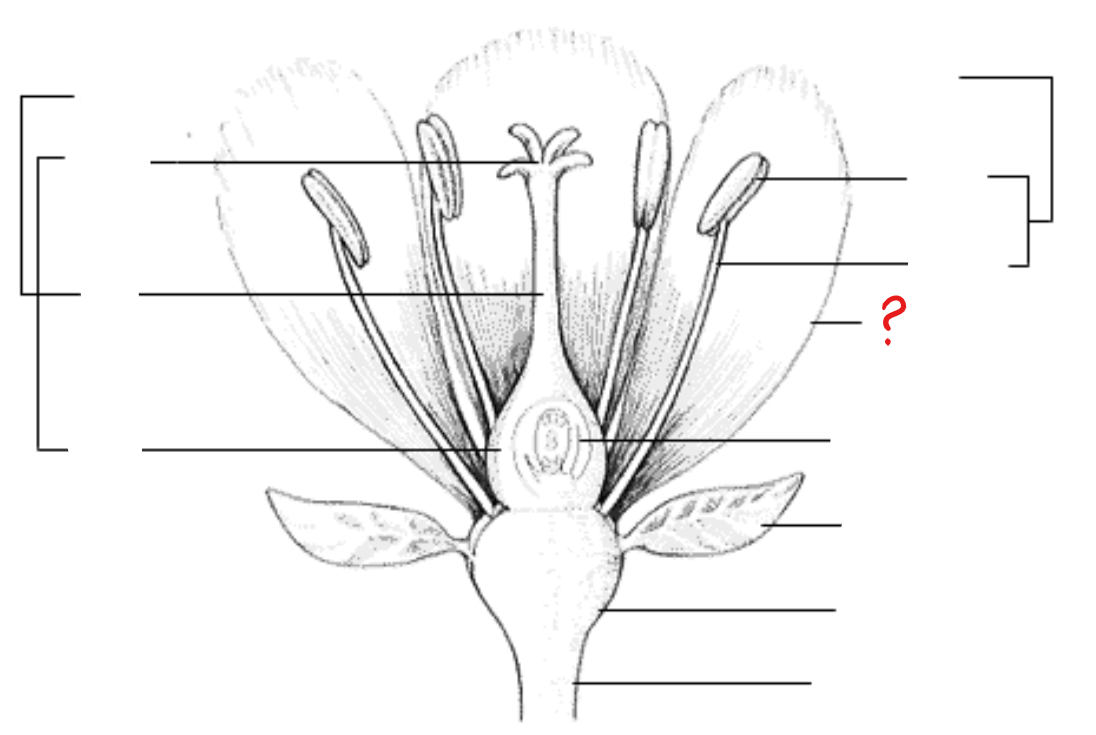
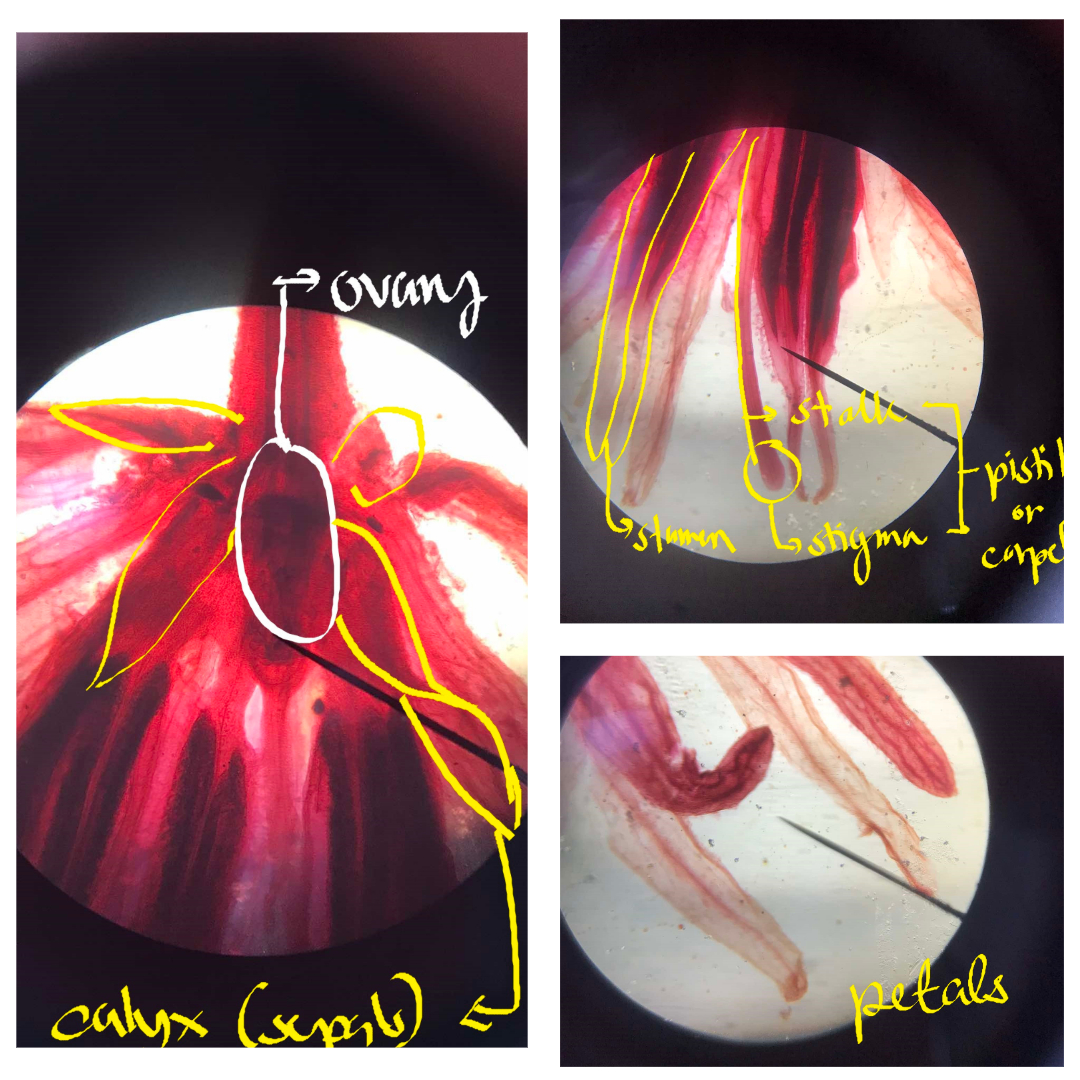
calyx (sepals); corolla (petals); androecium (stamens); gynoecium (carpels/pistils)
basic parts of the flower
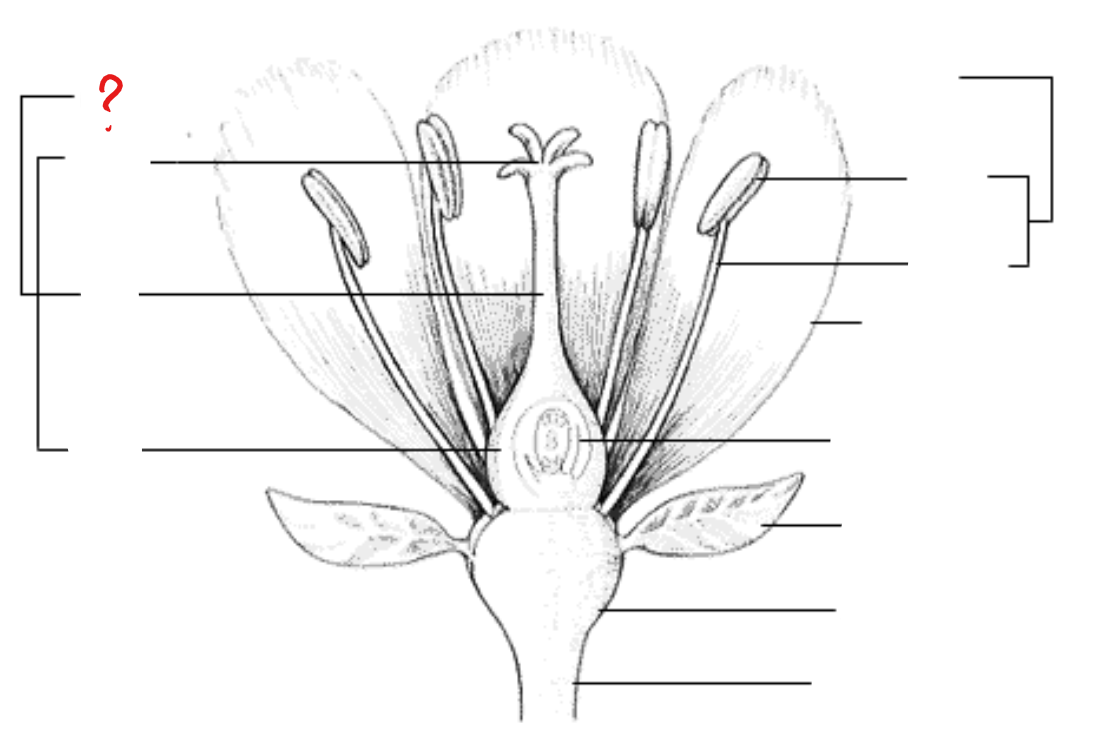
calyx (sepals)
leaf-like parts that form the outer whorl of the entire floral branch; internally similar to leaves: epidermis, mesophyll, and ramified vascular systems; maybe replaced with bracts in some species
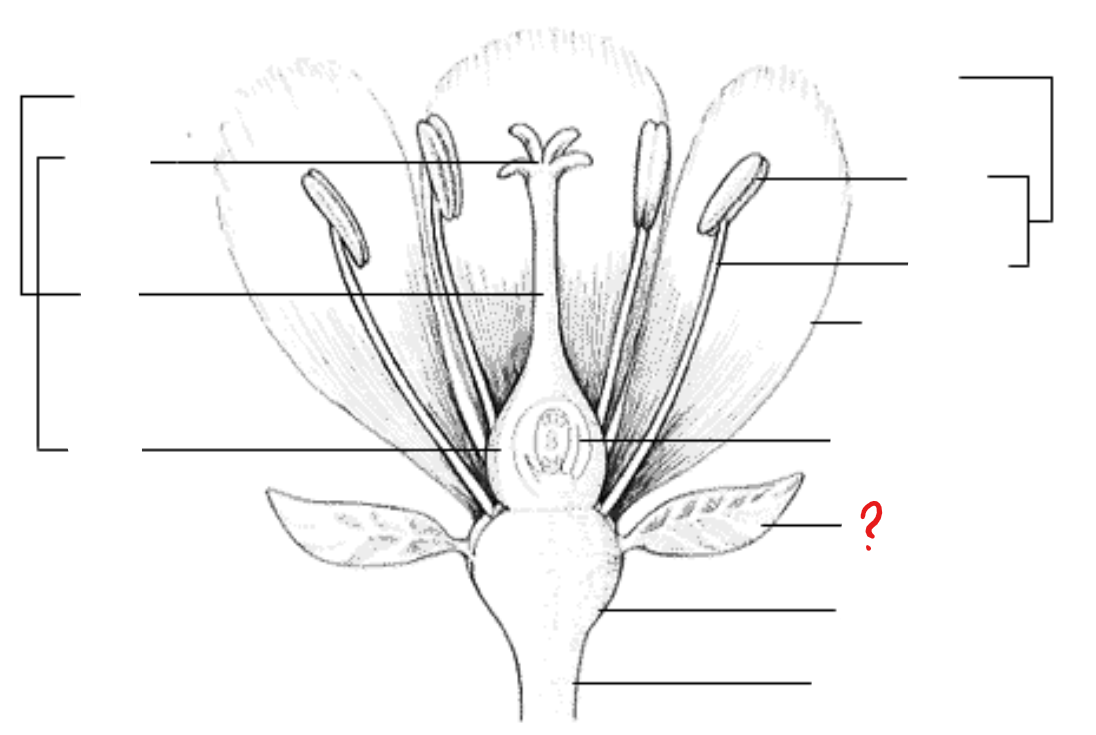
corolla (petals)
leaf-like parts inner to the sepals and usually have other colors apart from green; internally similar in structure as the sepals
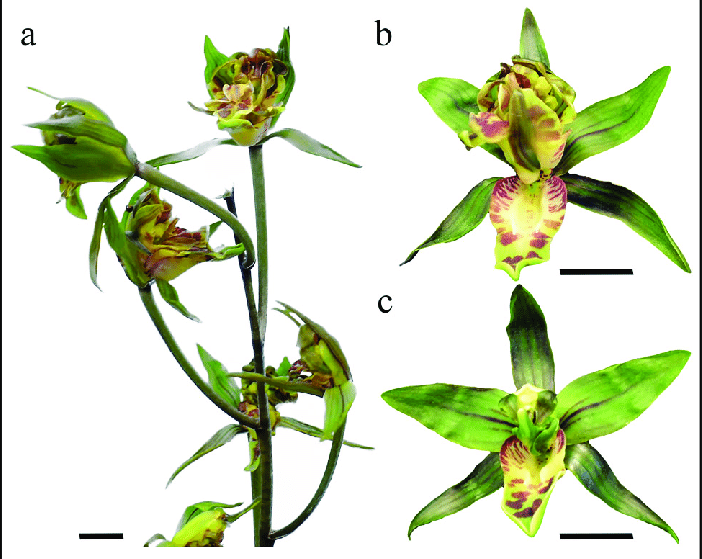
tepals
observed in orchids and some basal angiosperms; fusion of sepals and petals; petaloid in structure and function
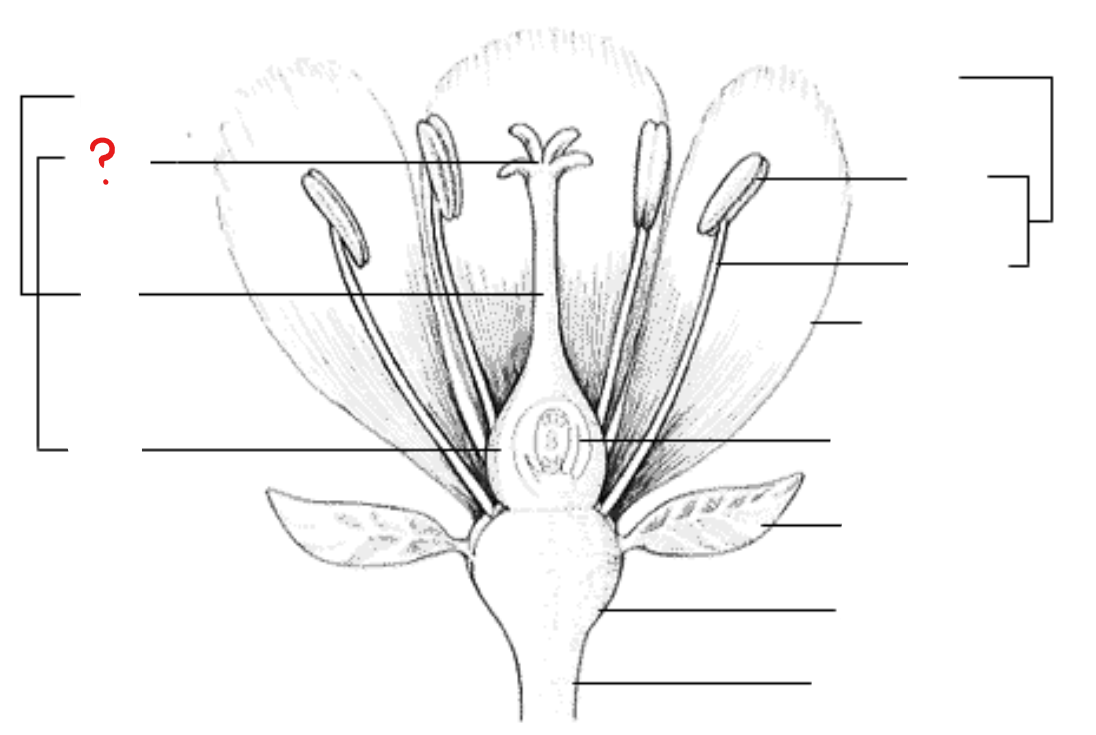
androecium (stamens)
consists of the anther and the stalk and filament; usually contains one vascular bundle
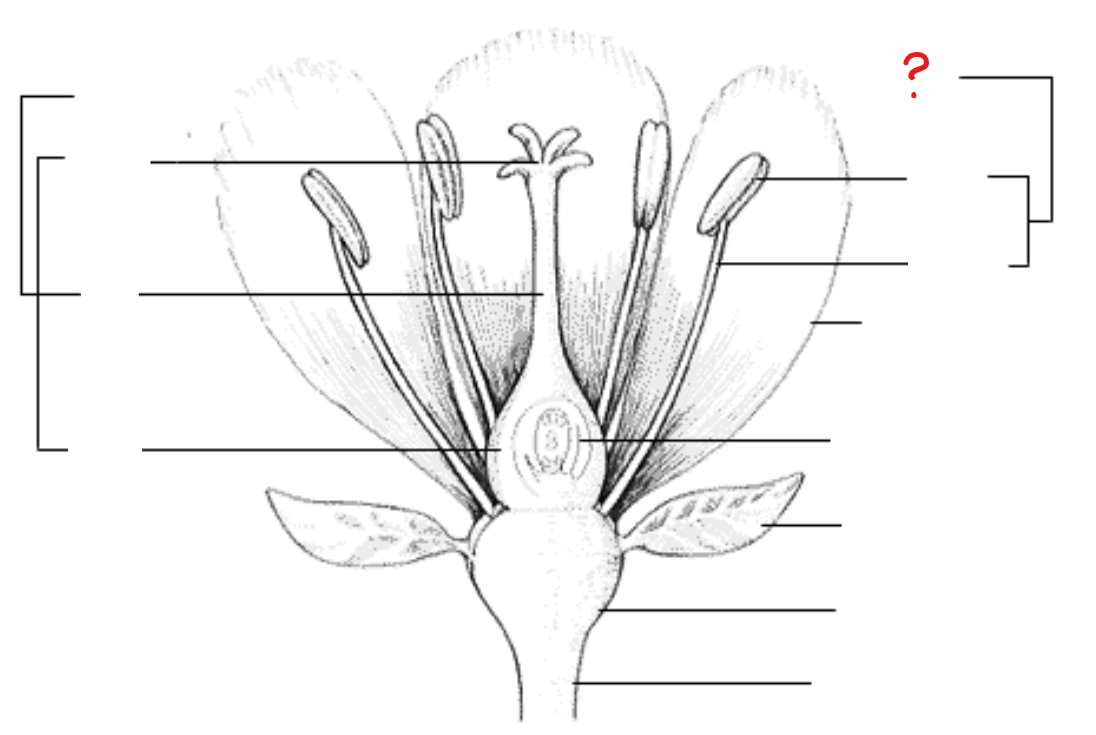
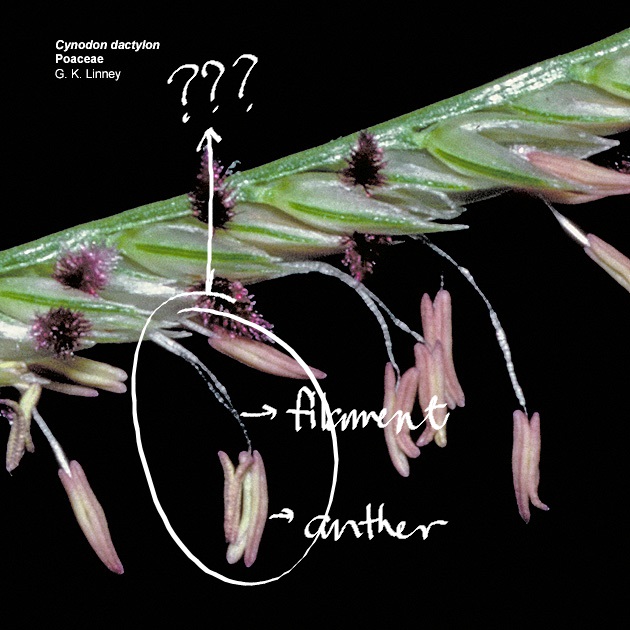
anther
found at the tip of the stamen; divided into two lobes, with each lobe having two pollen sacs with pollen grains, some degree of differentiation of anther walls, and two vascular bundles
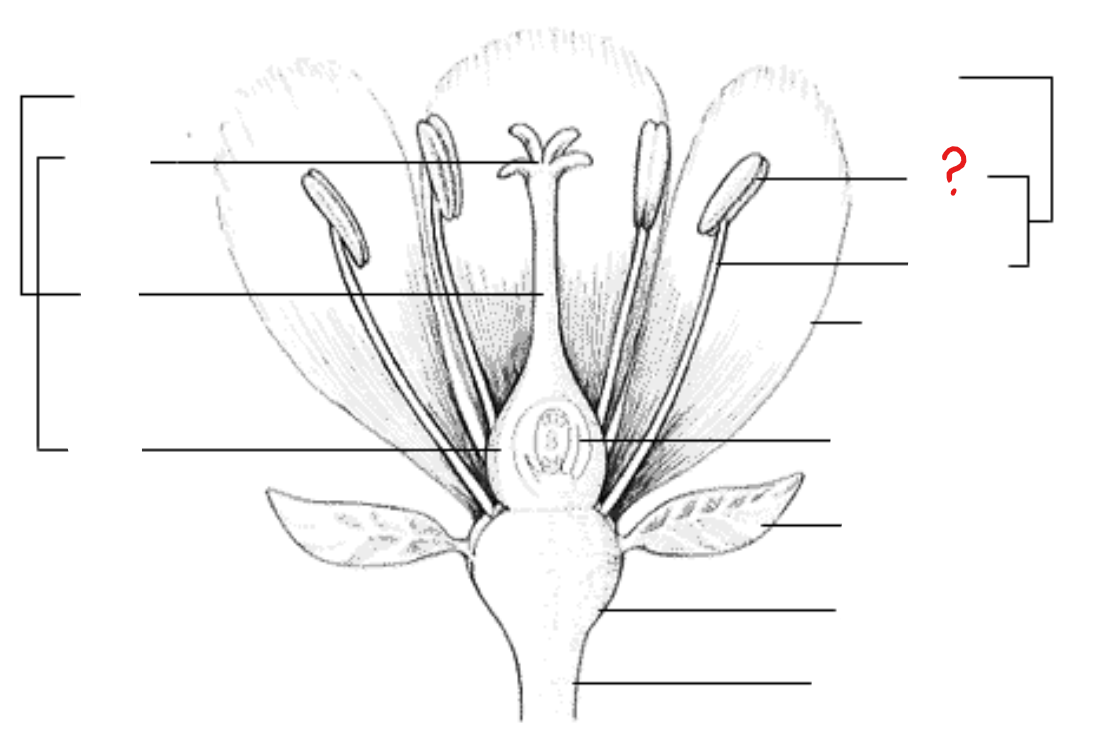
gynoecium (carpels/pistils)
basic unit of the female reproductive organ of the flower; a modified leaf that bears seeds on its surface; parts include: ovary, style, and stigma
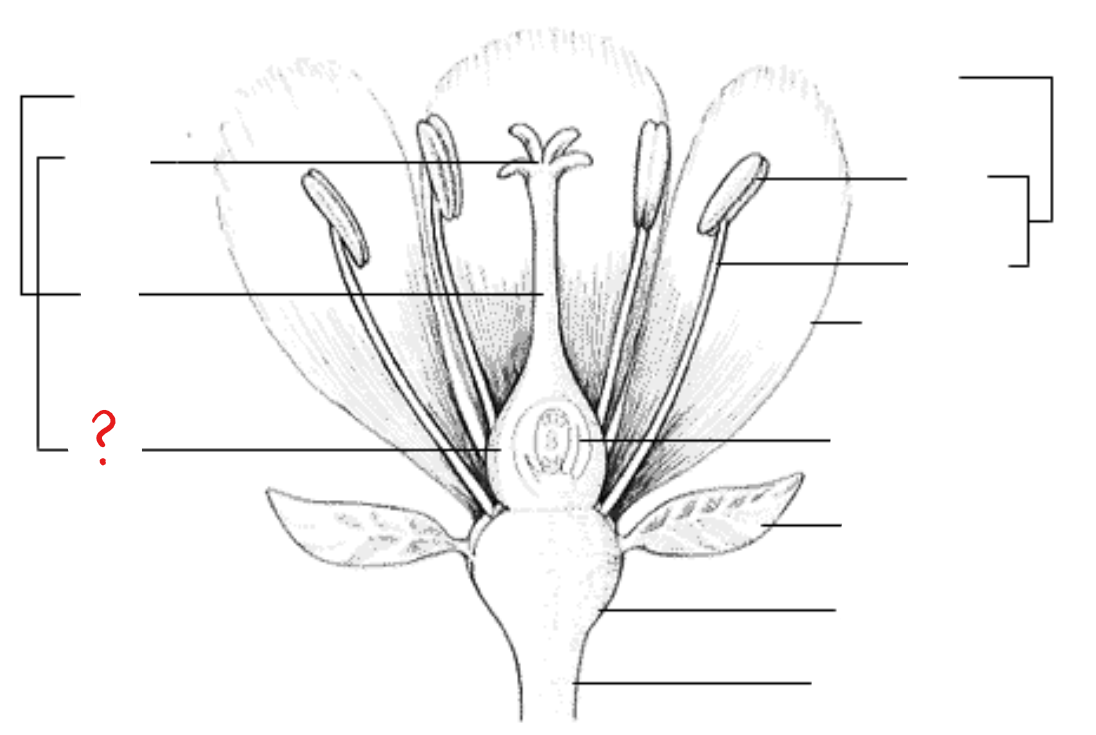
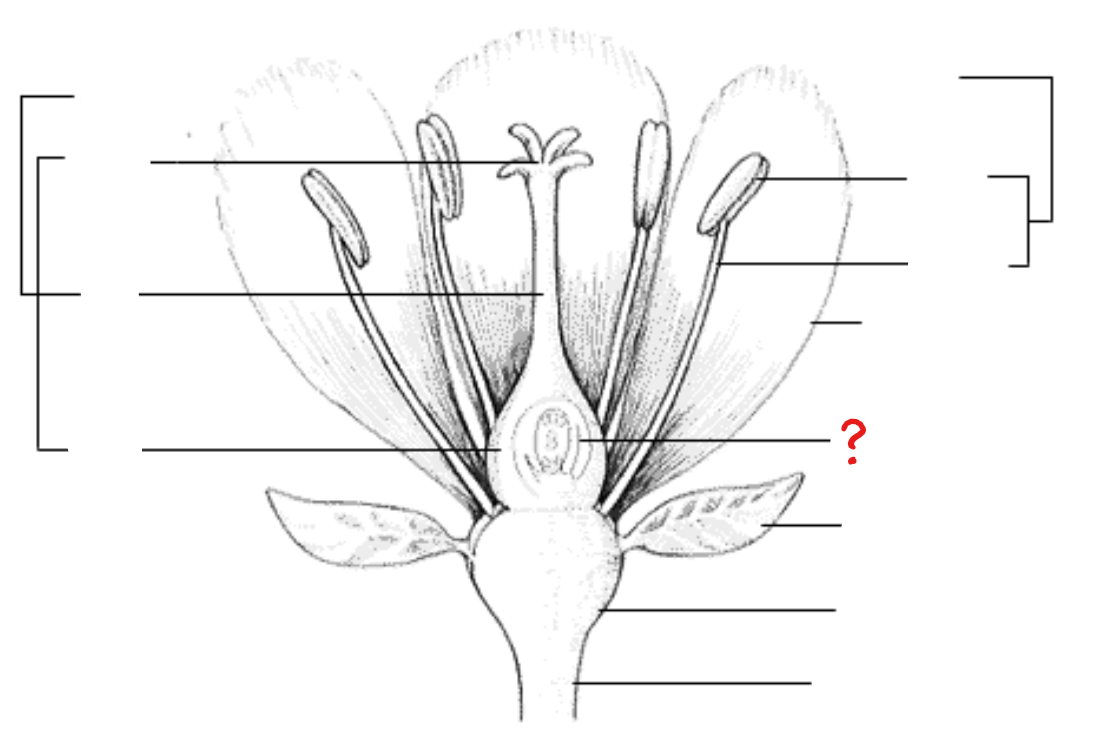
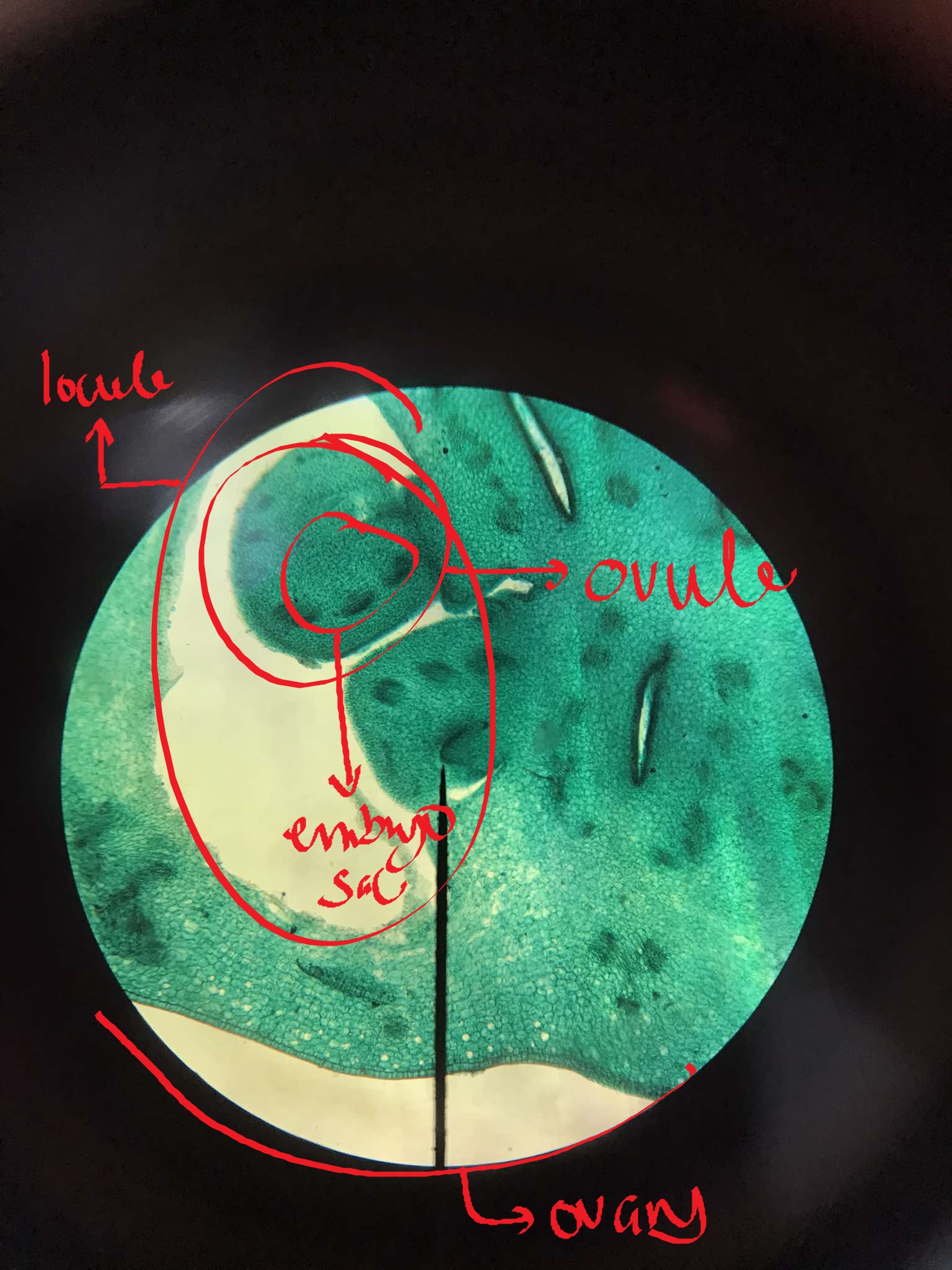
ovary
seed-bearing enclosed organ; anatomic features include the epidermis, ground tissue, and vascular tissues in characteristic position; divided into cavities called locules
locules
cavities within the ovary; houses the ovules attached to the placenta
ovules
develops into the seed; found within the locules of the ovary and attached to the placenta
placentation
the arrangement and attachment of ovules within the plant's ovary; variable among species
style
stalk of the carpel/pistil
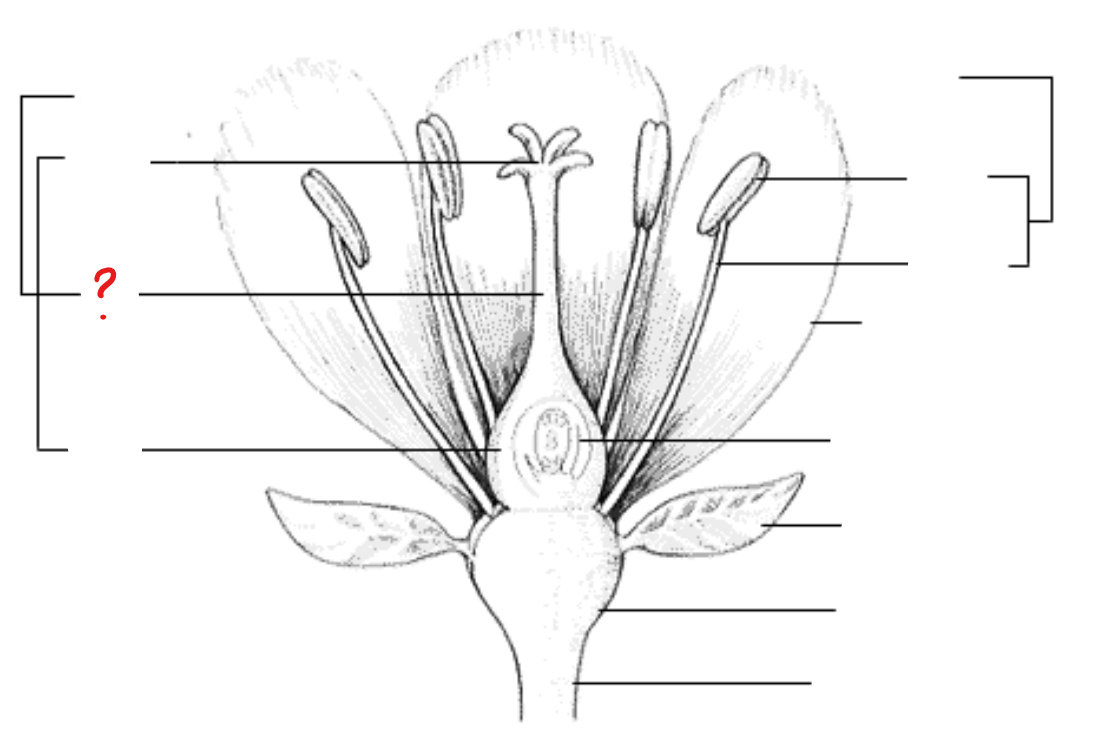
stigma
at the type of the pistil; surface for pollen growth
spikelet
units attached to the rachis of an inflorescence; usually bears one or more florets (depending on the species)

floret
consists of the stamens and the pistil bounded on the outside by lodicules
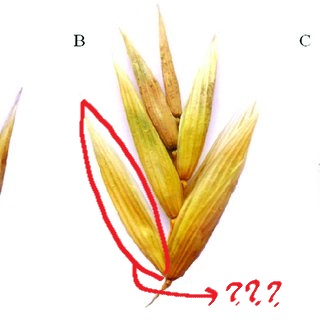
lodicules
small, scale-like perianth segments surround stamens and the pistil in a floret
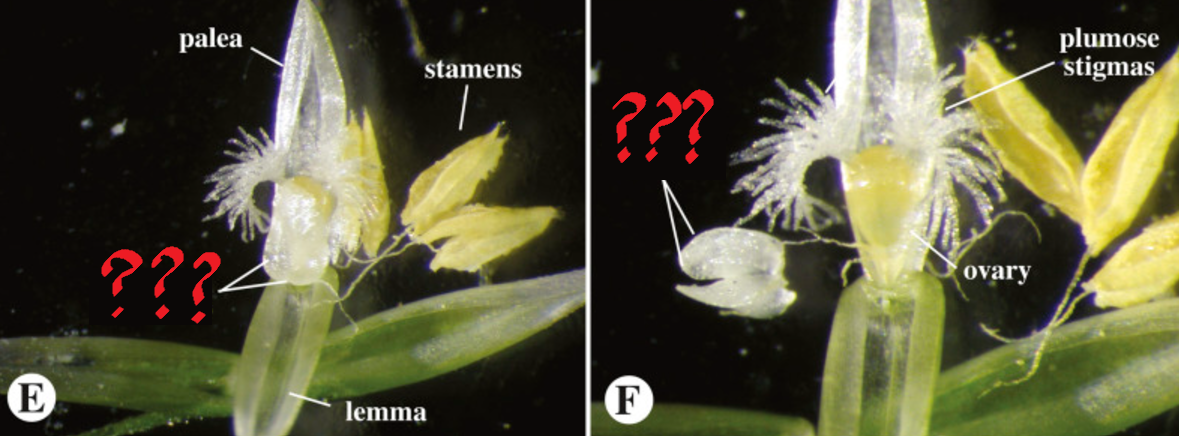

stamens
usually differentiated into a long and slender filament with four-lobed anther
palea and lemma
bract and bracteole respectively; both boat-shaped and surround the whole floret on the outside, with the latter being the outermost
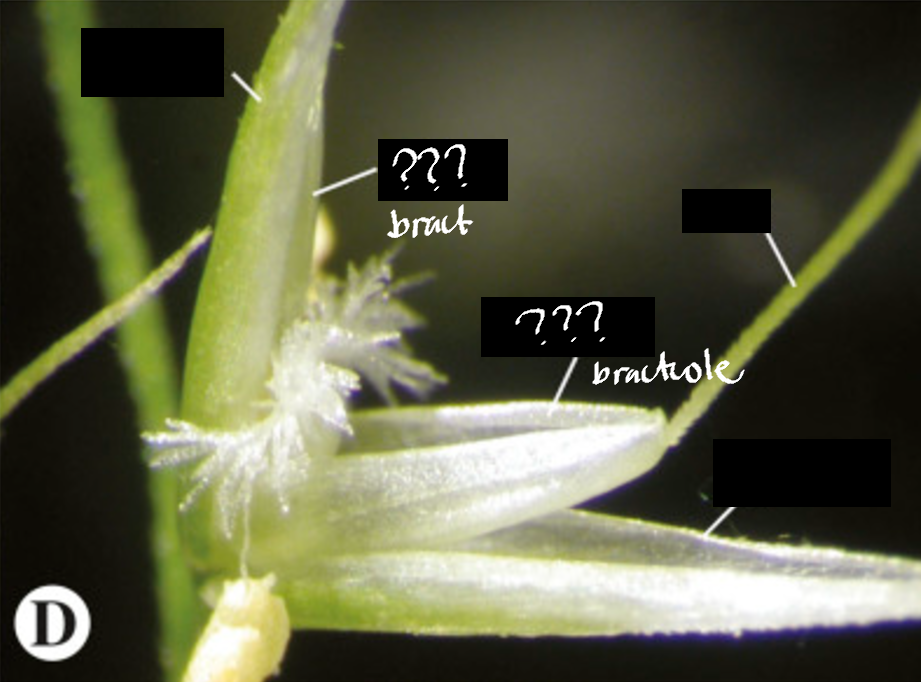

glumes
bract-like scales, usually a pair of them, that are present outside of the palea and lemma; usually empty

caryopsis
the fruit that develops within the floret, bearing a single exalbuminous seed

exalbuminous seed
seeds that have no endosperm or have completely consumed their endosperm during embryo development
pedicel
attaches the flower to the stem; usually subtended by bracts (epicalyx)

epicalyx (bracts)
a whorl of bracts that surrounds the calyx of a flower, forming an extra calyx-like structure; subtends the pedicel

apical meristem
from where the flowers develop; ceases to produce foliage leaves and instead shift from indeterminate to a determinate growth
flower primordium
the formation of small buds at the end of roots, from which a flower will grow or develop; will start from periclinal divisions of the meristematic tissue in shoot apex and later proceed by more divisions (including anticlinal divisions)
w.m. flower Tomato (L. esculentumI)
identify the specimen
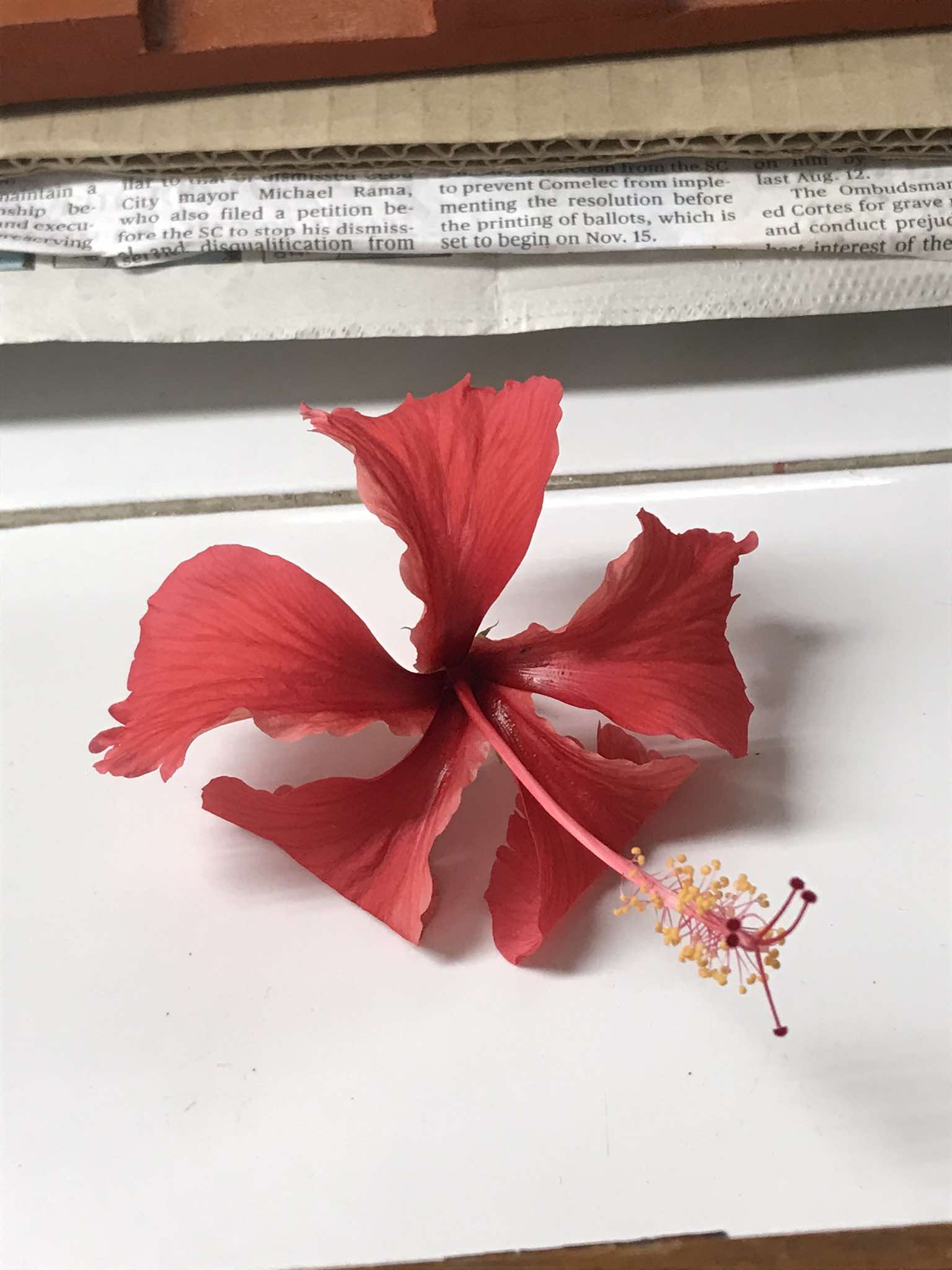
Hibiscus rosa sinensis
Malvaceae; gumamela

Nymphaea nouchali
Nymphaeaceae; water lily

Annona squamosa
Annonaceae; atis/sugar apple

Cosmos caudatus
Asteraceae; cosmos
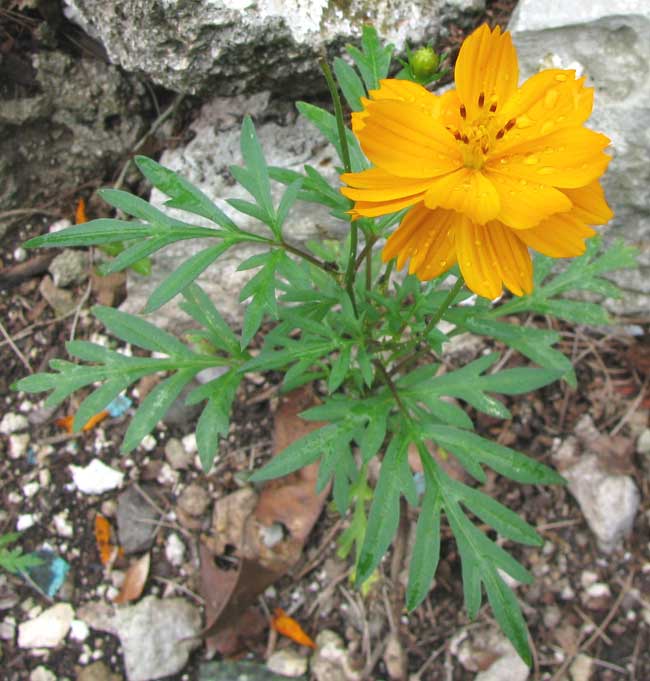

Jatropha pandurifolia
Euphorbiaceae; peregrina/jatropa
Orchidaceae
family of orchids
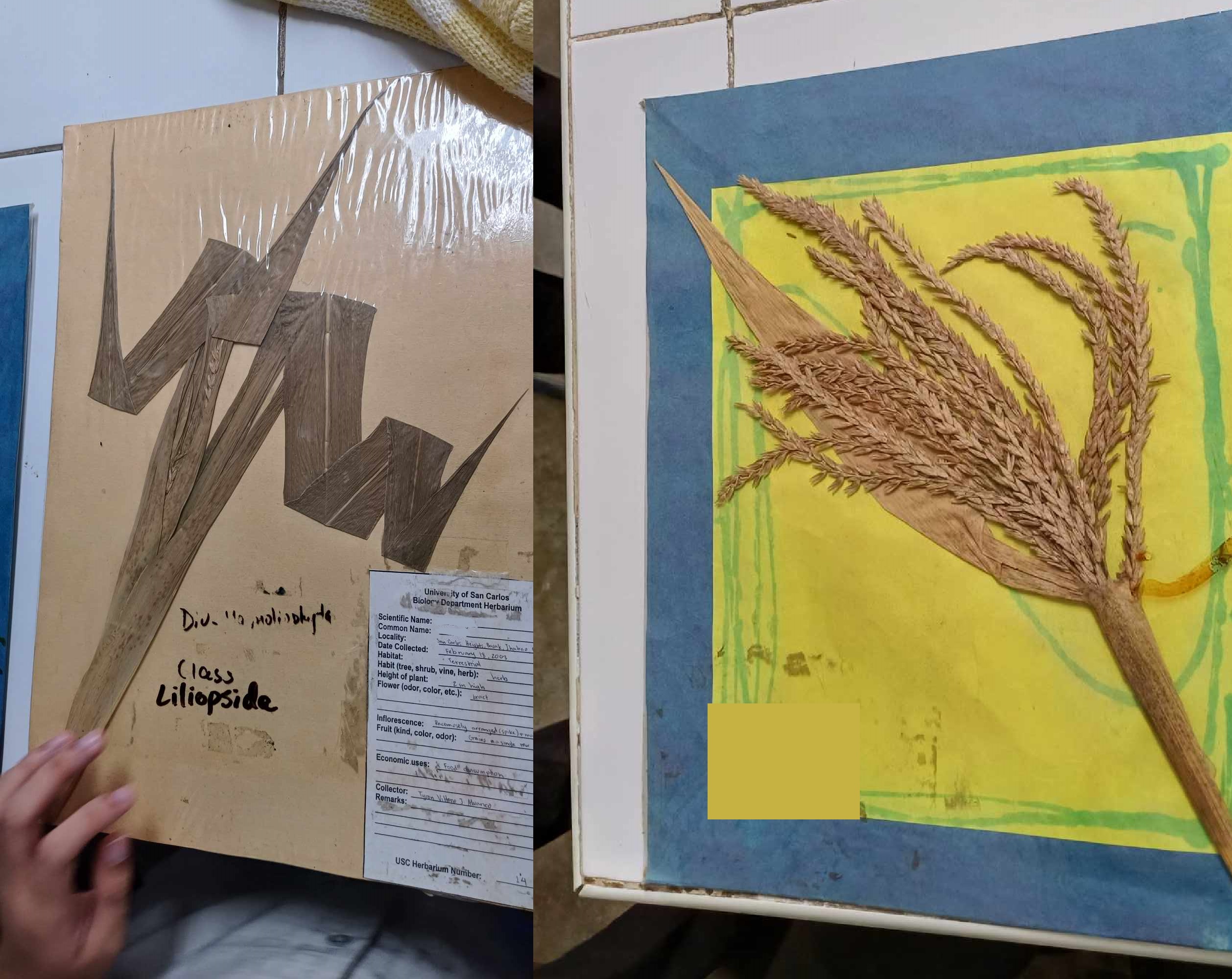
Zea mays
Poaceae; corn

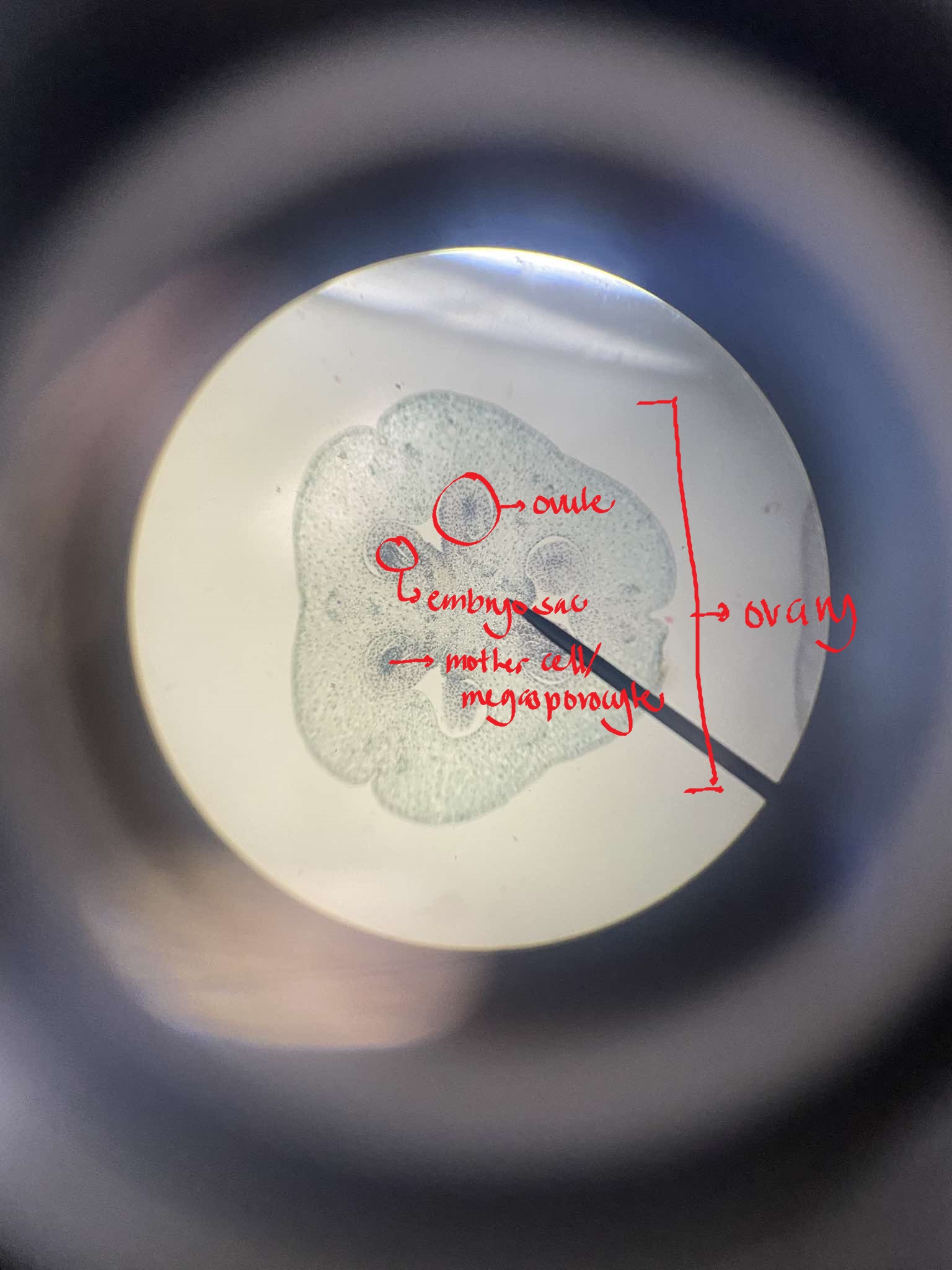
gymnoecium
site of embryo sac development; two major processes: megasporogenesis and megametogenesis
megasporogenesis
the development of megaspores from the megasporocyte, the cell that undergoes meiosis; meiosis of the megasporocyte nucleus results in the formation of four haploid megaspore nuclei
megasporocyte
a diploid cell in plants in which meiosis will occur, resulting in the production of four haploid megaspores
megagametogenesis
the process of maturation of the female gametophyte, or megagametophyte, in plants
megagametophyte
multicellular structures that develop inside the megaspore wall
x-s ovary Lily
identify the specimen
Embryo sac 4-nucleate Lilium
identify the specimen

pollen
develop inside the microsporangium or pollen sacs which enclose the sporogenous tissue which subsequently under meiosis (microsporogenesis) resulting into tetrads
microsporangium
also called pollen sacs; a sporangium that produces microspores that give rise to male gametophytes when they germinate
tetrad
becomes a microspore, which will undergo gametogenesis and transforms into either a binucleate or trinucleate structure that becomes functional pollen
palynology
the study of the external features of the pollen
microscoporogenesis
begins with the cells (microsporocytes/pollen mother cells) making up the sporogenous tissue found inside each pollen sac on the anther of a flower
tapetum cells
surround the microsporocytes; form the inner layer of the pollen sac wall
successive cytokinesis
a type of cytokinesis that occurs in angiosperms, where the cytoplasm is divided after each meiotic division; the cytoplasm is successively partitioned after each meiotic division
simultaneous cytokinesis
no wall is formed after meiosis II, the four daughter cells will be separated by phragmoplasts which will later become part of the pollen wall
microspore
composed of a large nucleus, large vacuole, and some cytoplasmic organelles
tryphine
a structure formed from the condensed cytoplasmic contents of the broken-down tapetum; deposited on the pollen grains as a coat
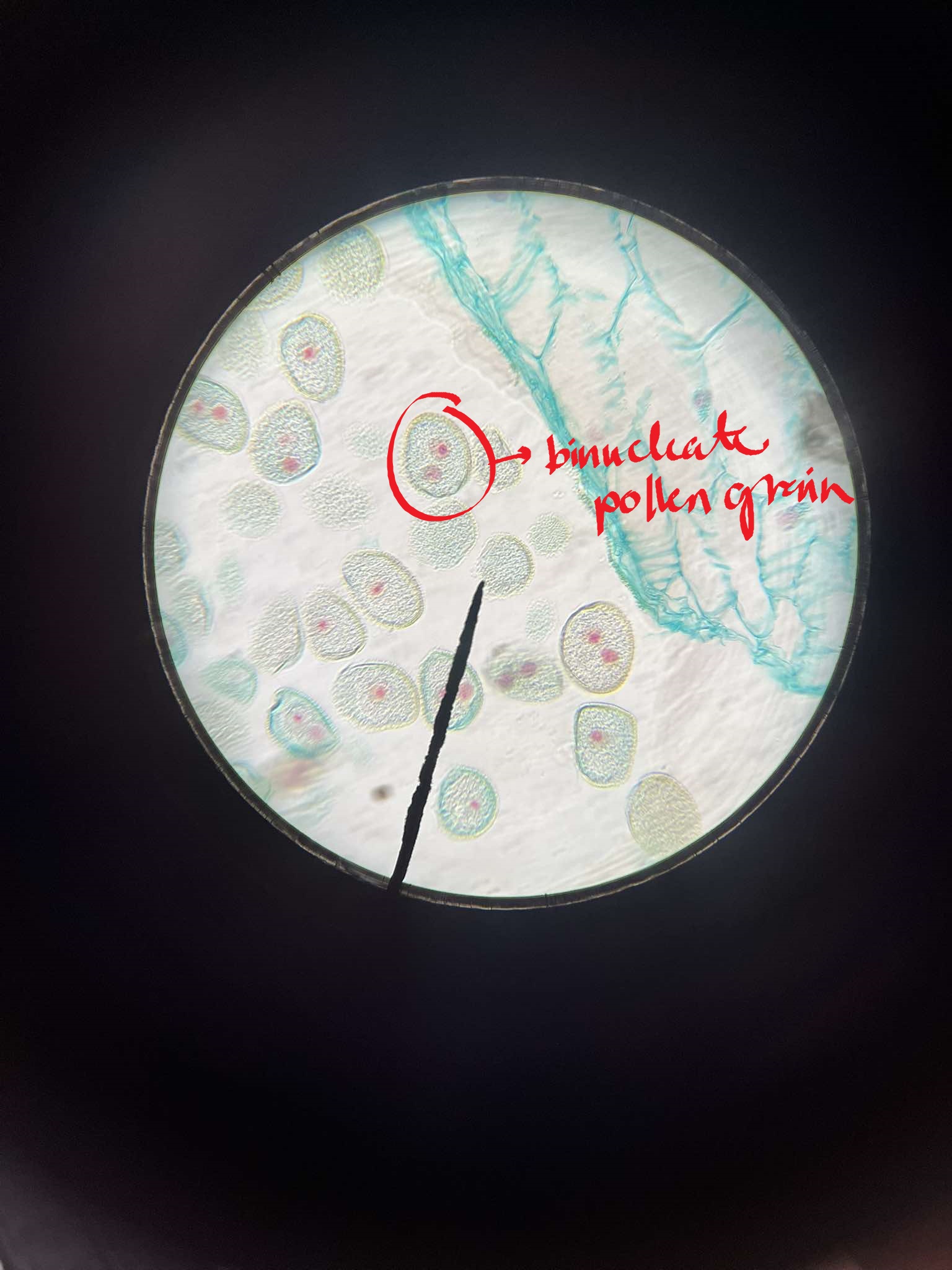
microgametogenesis
the process in plant reproduction where a microgametophyte develops in a pollen grain to the three-celled stage of its development
vegetative nuclei
direct the operations of the growing structure
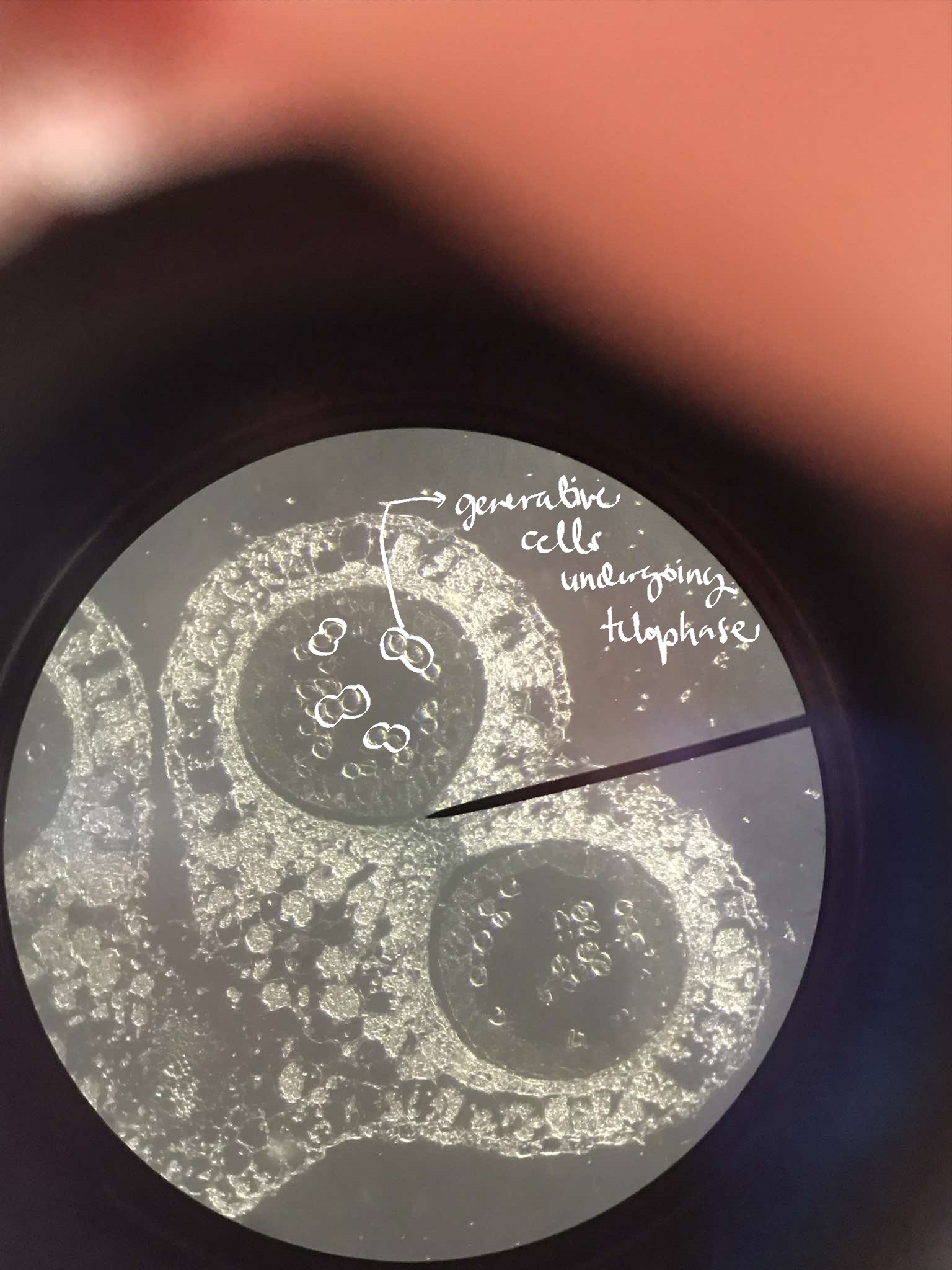
generative nuclei
can be thought of as two nonmotile sperm cells
x-s anther Lily (telophase)
identify the specimen
x-s mature pollen in anther Lilium
identify the specimen
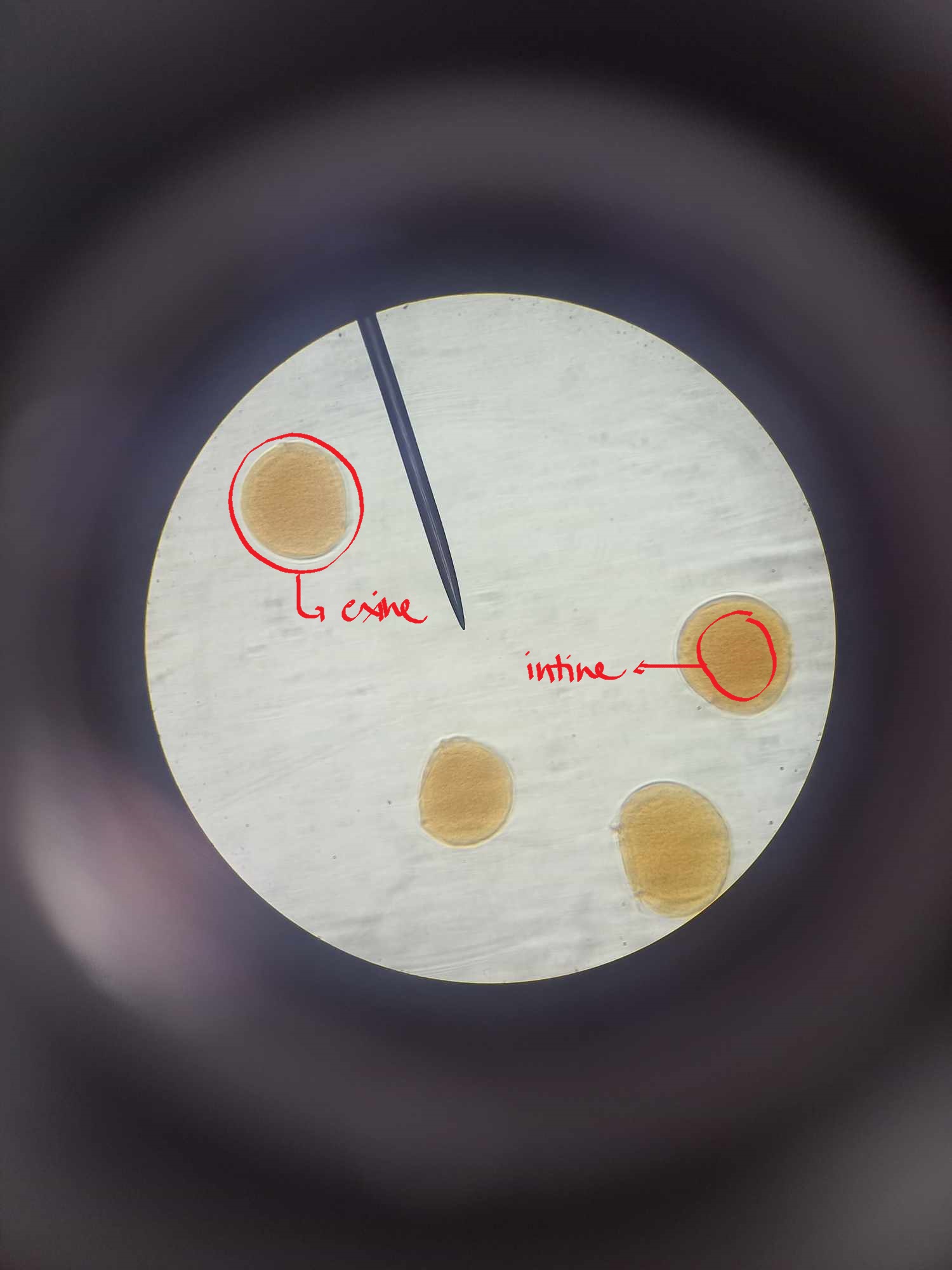
exine
outer wall of a mature pollen grain
intine
inner wall of a mature pollen grain
apertures
pores along the thin areas of the exine
porate
pollen with rounded aperture
colpate
pollen with furrow-like aperture
uniaperturate/monosulcate
pollen with one aperture only; observed in monocots
tricolpate/tricolpate-derived
pollen with three or more apertures; observed in eudicots
w-m pollen grain Corn
identify the specimen
w-m pollen grain Lily
identify the specimen
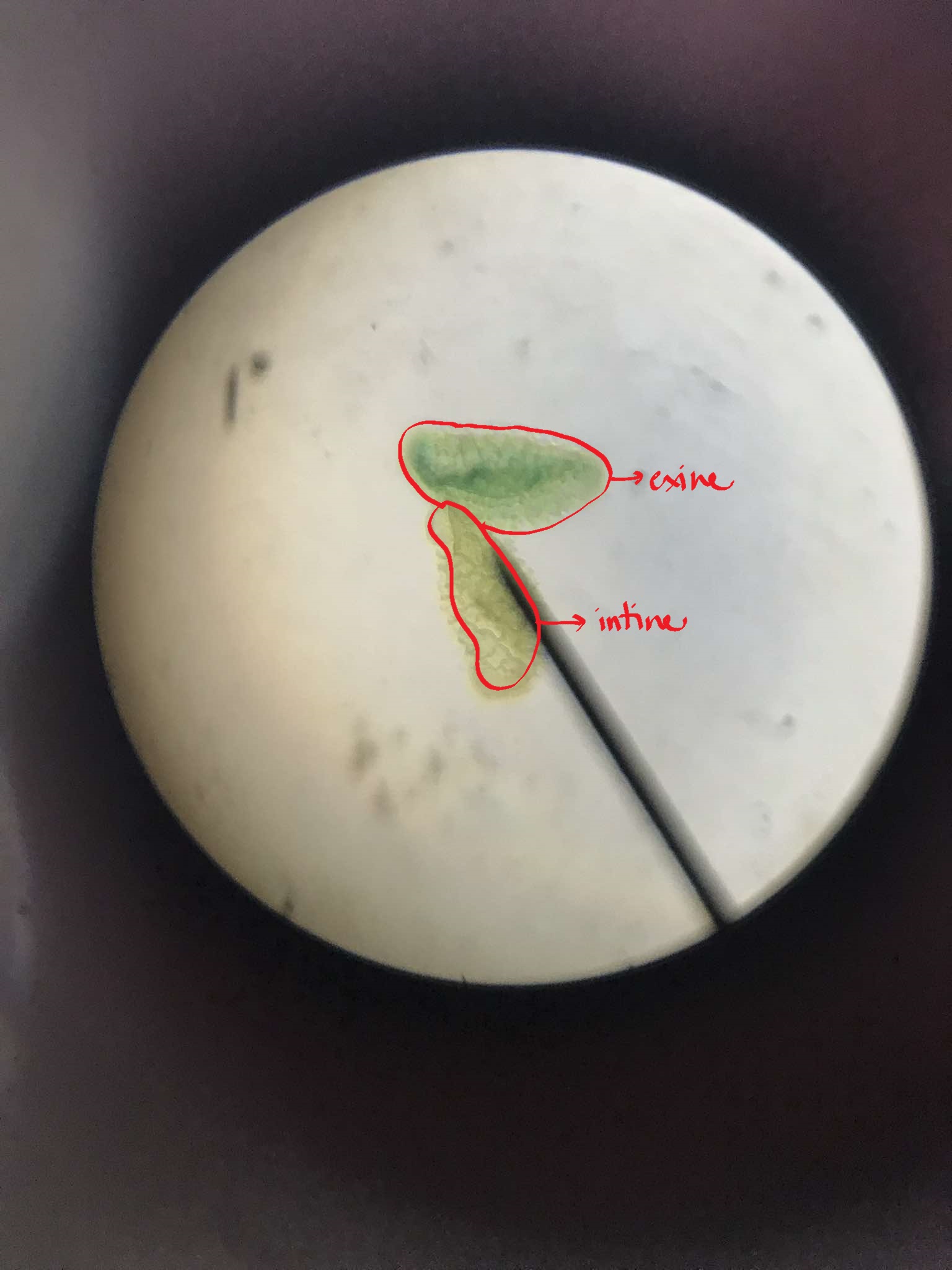
w-m pollen grain Cucurbita pepo
identify the specimen
w-m pollen guava (Psidium guajava)
identify the specimen

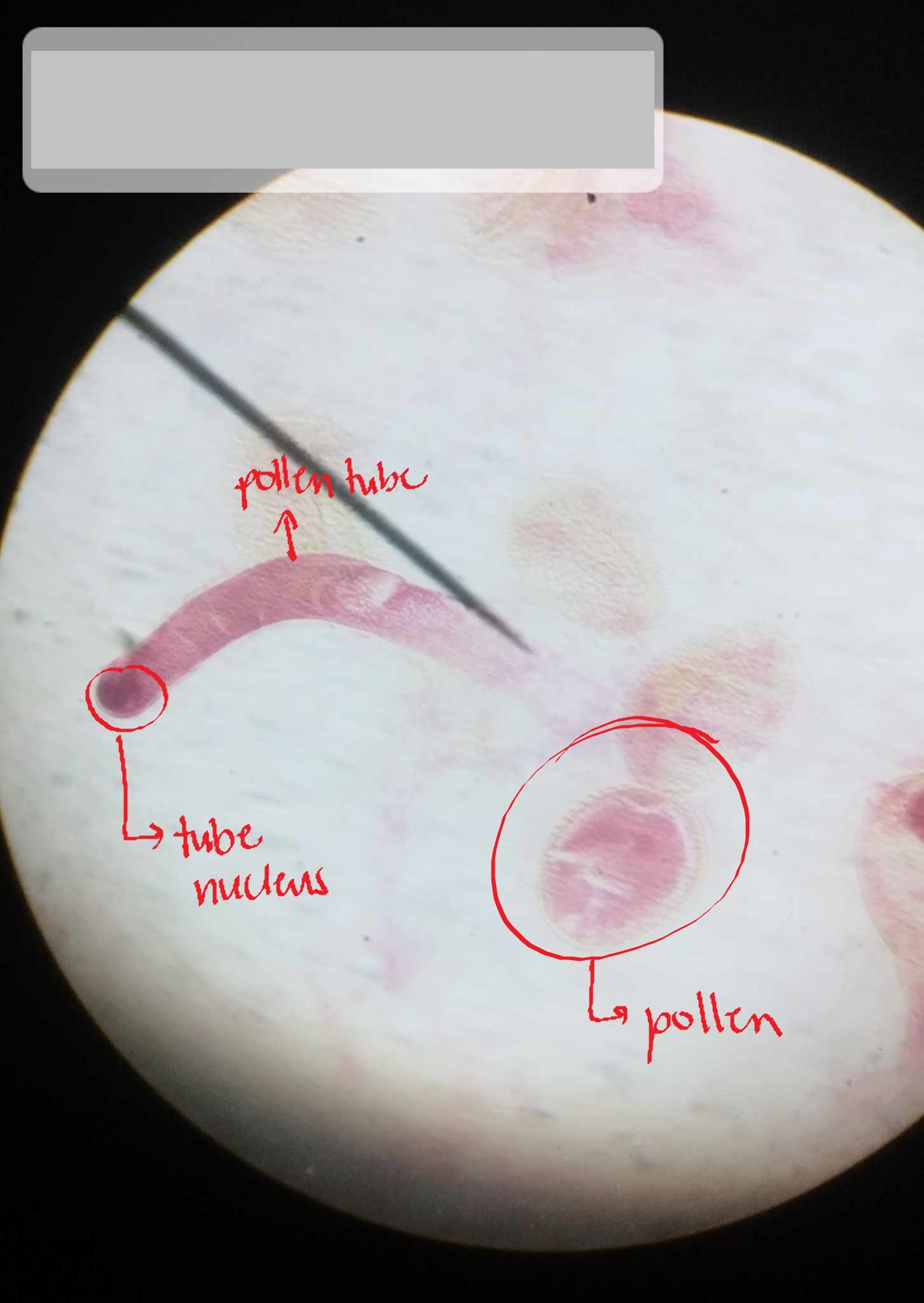
pollen germination
occurs when pollen lands on a compatible stigma
w-m pollen germinating Lilium
identify the specimen