tools and methods of psych (6-9)
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
participant observation
occurs when a researcher takes an active, insider role in what they are studying.
Systematic observation
refers to the careful observation of one or more specific behaviors in a particular setting.
Coding system
a set of rules used to categorize observations
Reactivity
the possibility that the presence of the observer will affect people’s behaviors
Experience sampling method(ESM)
used to alert participants to complete a data collection procedure at that moment in time.
Day reconstruction method(DRM)
method of obtaining self-reports of daily activities, moods, and emotions. Asks participants to think about the previous day and write about distinct episodes that occurred
Psychobiography
type of case study in which a researcher applies psychological theory to explain the life of an individual
Archival research
involves using previously compiled information to answer research questions
Content analysis
the systematic analysis of existing document
Response set
a tendency to respond to survey questions from a particular perspective rather than to give anwer directly related to the questions.
Social desirability response set
the tendency to answer questions in the way that would reflect most favorably on the respondent
Yea-saying
the tendency to agree consistently
Nay saying
the tendency to disagree consistently
Close-ended questions
a limited number of response alternatives are given
Open-ended questions
respondents are free to answer any way they lik
Rating scales
which assign scores along some numerical dimension; are very common in many areas of research
Graphic rating scale
requires a mark along a continuous line
Semantic differential line
is a measure of the meaning of concepts—rating them on a series of bipolar adjectives
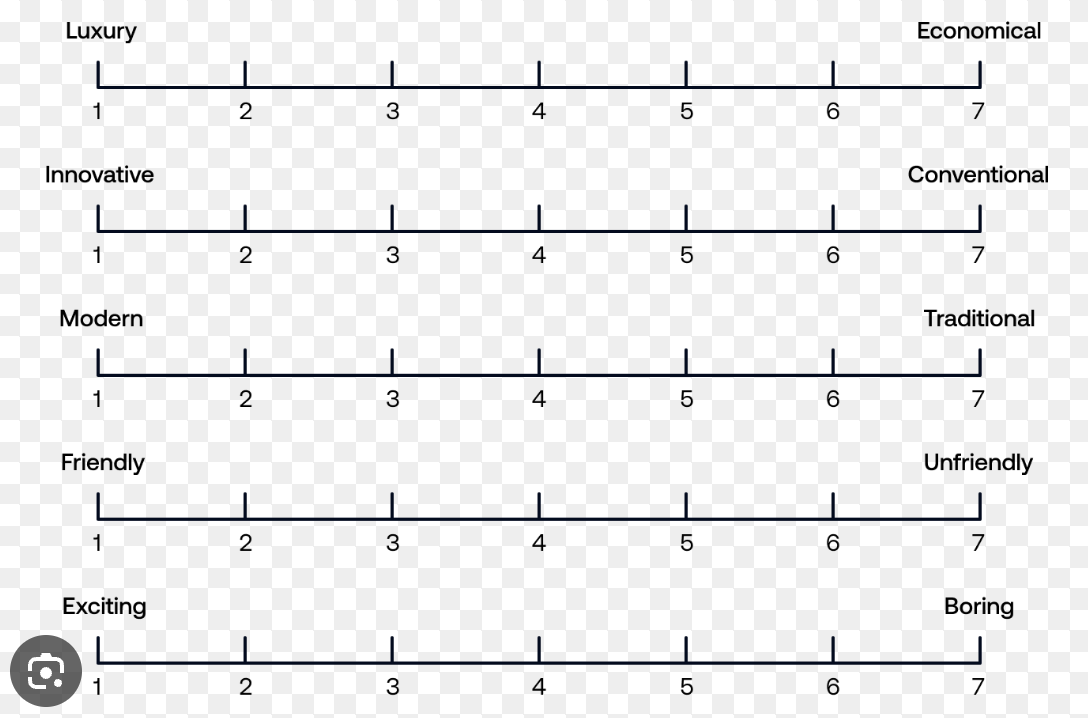
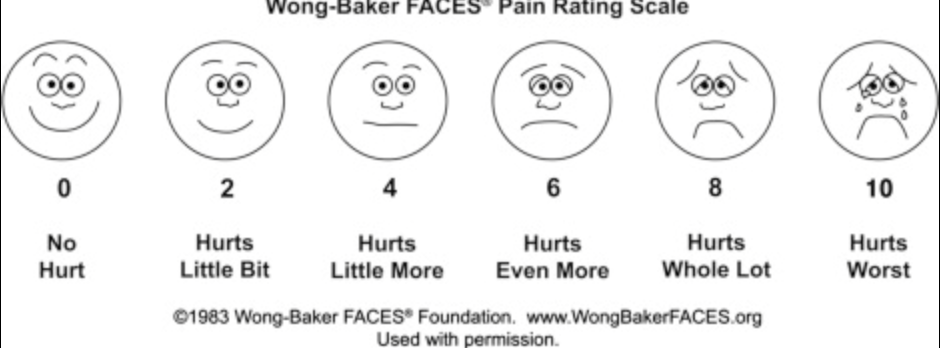
Pictorial scales
appropriate for populations such as children who can have trouble understanding other scales
Interview bias
the interviewer can inadvertently show approval or disapproval of certain answers
face to face interviews
interviewer and respondent meet to conduct the intervie
Focus group
an interview with a group of about 6 to 10 individuals brought together for 2-3 hours.
Panel study
the same sample of subjects is studied at two or more points in time.
Sample
the members of a population selected to participate in a research investigation
Population
the defined group of individuals from which a sample is drawn
Confidence interval
an interval of values within which there is a given level of confidence where the population value lies
Sampling error
the potential deviation from the true population value of the value obtained using sample data.
Probability sampling
each member of the population has a specificable probability (chance) of being chosen.
Simple random
every member of the population has an equal probability of being selected
Stratified random sampling
the population is divided into subgroups(strata), and random samples are taken from each strata
Cluster sampling
existing groups or geographic areas, called clusters, are identified; samples are taken from those clusters
Nonprobability sampling
the probability (chance) of any particular member of the population being chosen is unknown
Convenience sampling
“hapazahed” or “take them where you find them” samplin
Purposive sampling:
the sample meets a predetermined criterion
Snowball sampling
sampling procedure in which one or more current research participants recruit others to become part of the sample
Quota sampling
the sample reflects the numerical composition of various subgroups in the population
Sampling frame
the actual population of individuals or clusters from which the sample is drawn
Response rate
the percentage of people sampled who completed the survey
Confounding variable
a variable that varies along with the independent variable
Internal validity
the certainty with which results of an experiment can be attributed to the manipulation of the independent variable rather than to some other, confounding variable.
Posttest- Only Design
A true experimental design in which the dependent variable(posttest) is measured only once, after manipulation of the independent variable.
Selection differences
differences in the type of subjects who make up each group in an experimental design. One way such differences can arise is by allowing participants to choose which group they will be assigned to.
Pretest-Posttest Design
a true experimental design in which the dependent variable is measured both before (pretest) and after (posttest) manipulation of the independent variable
attrition
the loss of subjects who decide to leave an experiment
Mortality
Repeated measures design
an experiment in which the same subjects are assigned to each group. Also known as within-subjects design or within-persons design.
Random assignment
use of random procedure to determine which condition a participant will participate in
Order effect
in a repeated measures design, the effect that the order of introducing treatment has on the dependent variable.
Practice effect (learning effect)
improvement in participant performance with repeated testing
Fatigue effect
deterioration of participant performance with repeated testing
Carryover effect
a problem that may occur in repeated measures designs of the effects on treatment are still present when the next treatment is present
Counterbalancing
a method for controlling order effects in a repeated measures design by either including all orders of treatment presentation or randomly determining the order for each subject.
Latin square
a technique to control for order effects without having all possible orders
Matched pairs design
a method of assigning subjects to groups in which pairs of subjects are matched on some characteristic and then individually assigned randomly to groups.
Straightforward manipulations
manipulation of the independent variable through the use of direct stimulus presentations, types of instructions and other simple procedures.
Staged manipulations (event manipulation)
manipulation of the independent variable, using complex situations, often simulating real-life social interactions.
confederate(accomplice)
a person posing as a participant in an experiment who is actually part of the experiment
Strength of manipulation
the potential amount of impact of the independent variable on the dependent variable
Self reports
measures that require participants to describe themselves
Behavioral measures
measures that require participants to engage in a specific behavior
Psychological measures
measures of psychological activity
Galvanic skin response (GSR)
the electrical conductance of the skin, which changes when sweating occurs.
Electromyogram (EMG)
a measure of the electrical activity of muscles, including muscle tension
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
a measure of the electrical activity of the brain.
Ceiling effect
failure of a measure to detect a difference because it was too easy
Floor effect
failure of a measure to detect a difference because it was too difficult.
Demand characteristics
cues that inform the subject how he or she is expected to behave.
Filler items
items included in a questionnaire measure to help disguise the true purpose of the measure
Placebo group
in drug research, a group given an inert substance to assess the psychological effect of receiving a treatment
Expectancy bias (expectancy effects)
the impact an experimenter’s expectations can have on the outcome of a research study.
Single blind experiment
an experimental method originating in drug research wherein research participants do not know whether they are in the experimental group or the control group.
Double blind experiment
and experimental method originating in drug research wherein both research participants and experiments are unaware of participant status in the experimental or control conditions
Manipulation check
a measure used to determine whether the manipulation of the independent variable has had its intended effect on a subject.
naturalistic observations
a descriptive method in which observations are made in a natural social setting