Chromosomes, Alleles and Genes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
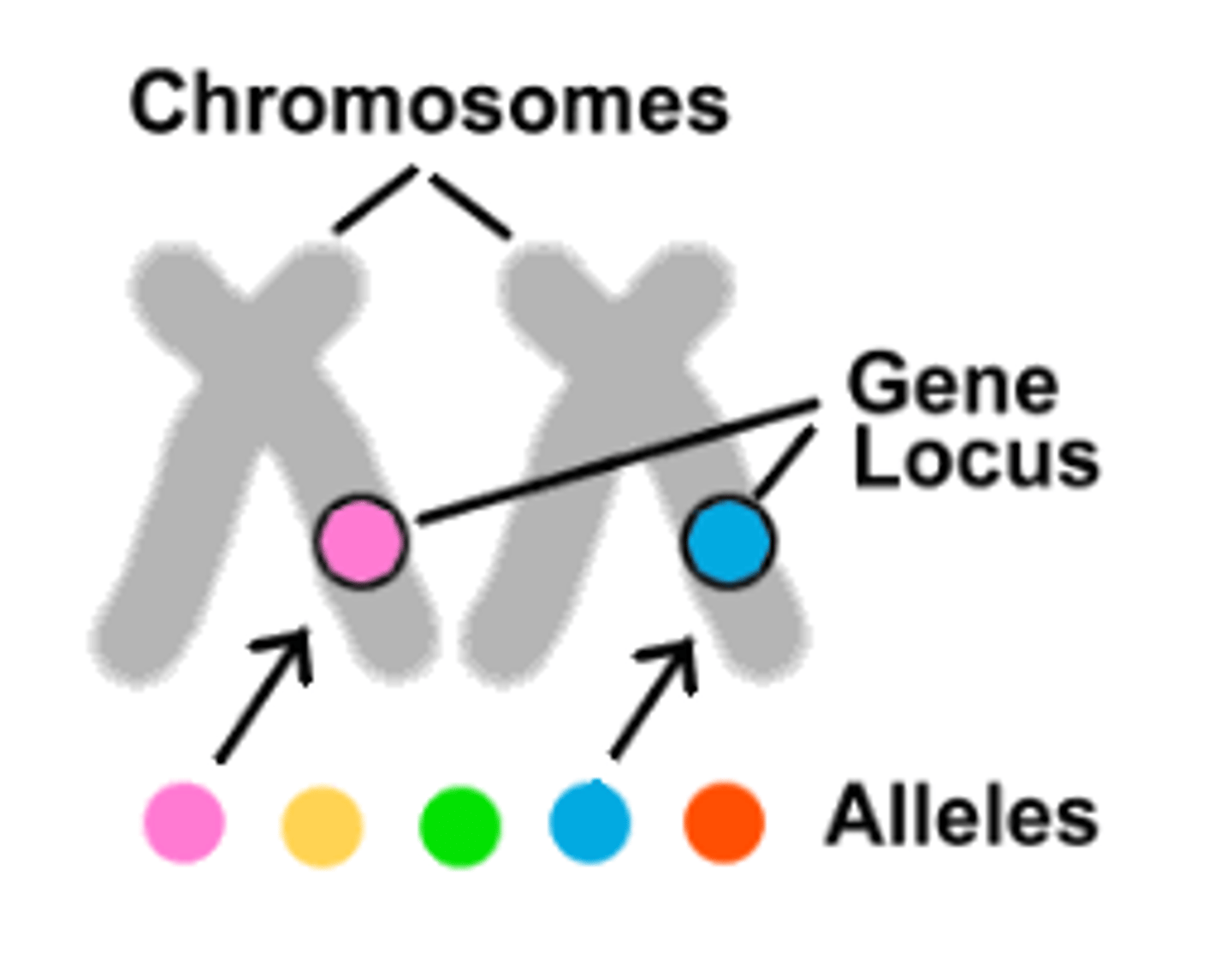
Allele
The different forms of a particular gene
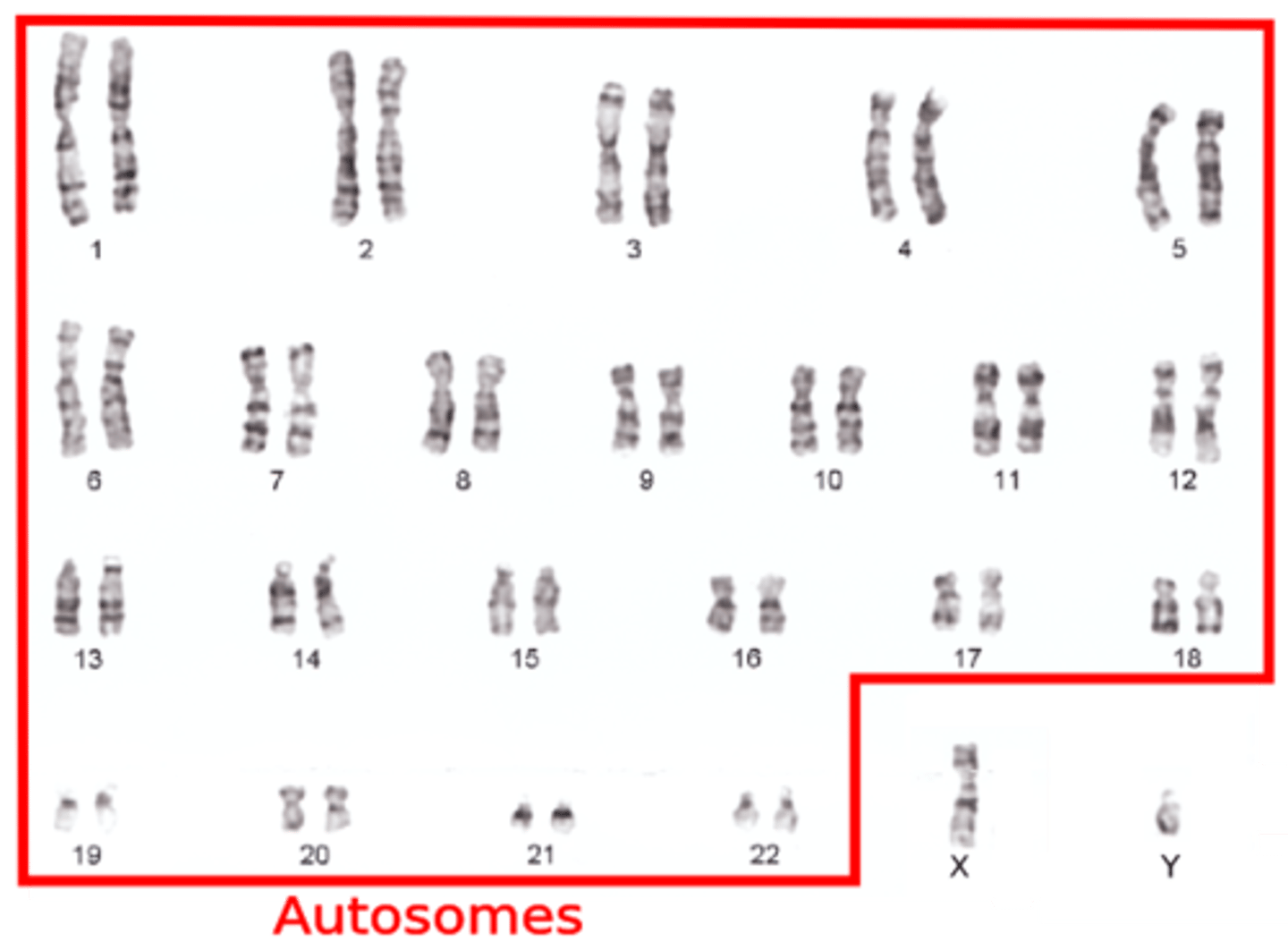
Autosome
Any pair of non-sex homologous chromosomes that are identical in appearance in males and females of a species
Loci
The location of a genes DNA sequence
Genome
the sum total of an organism's DNA measured in the number of base pairs contained in a haploid set of chromosomes
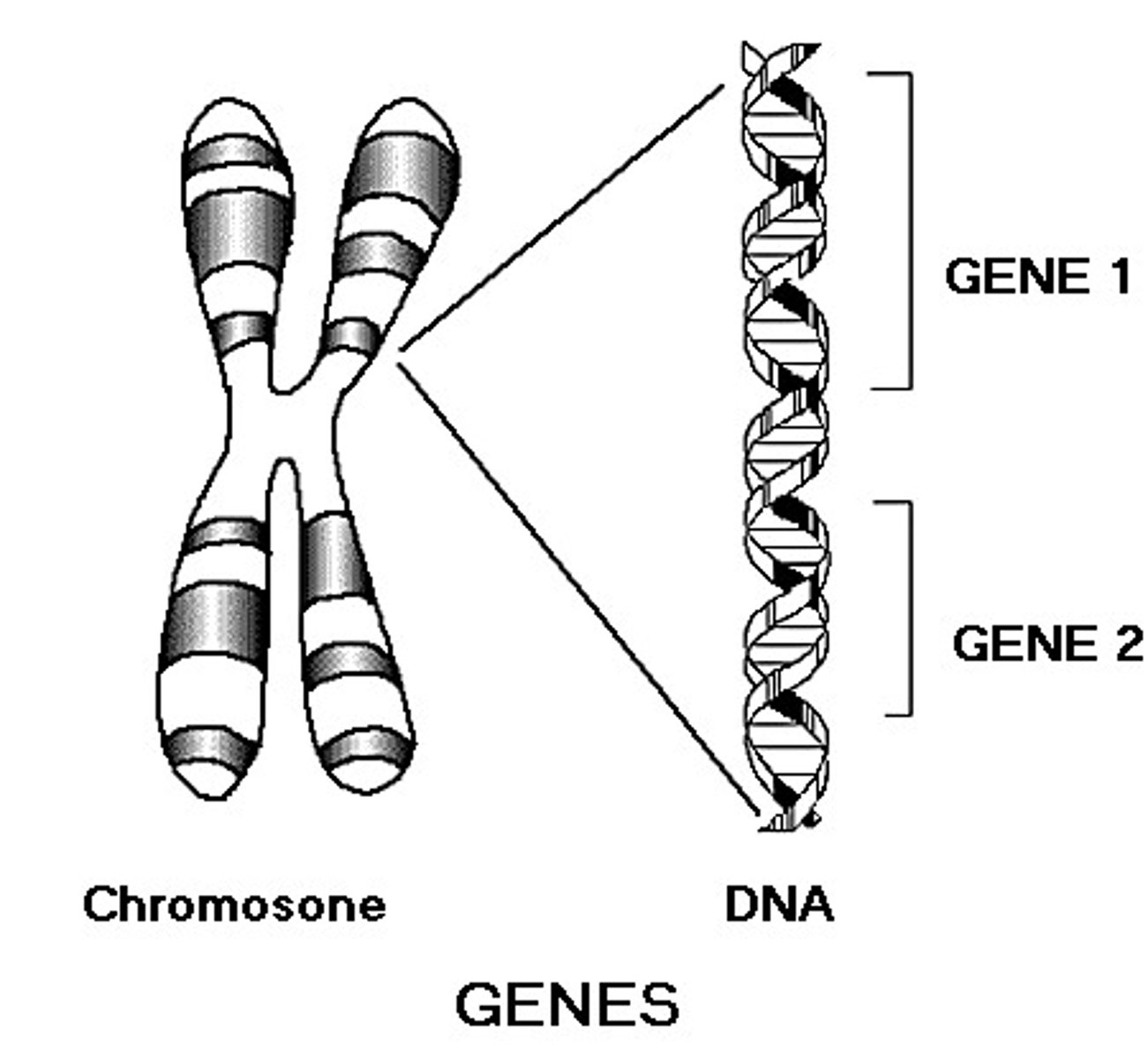
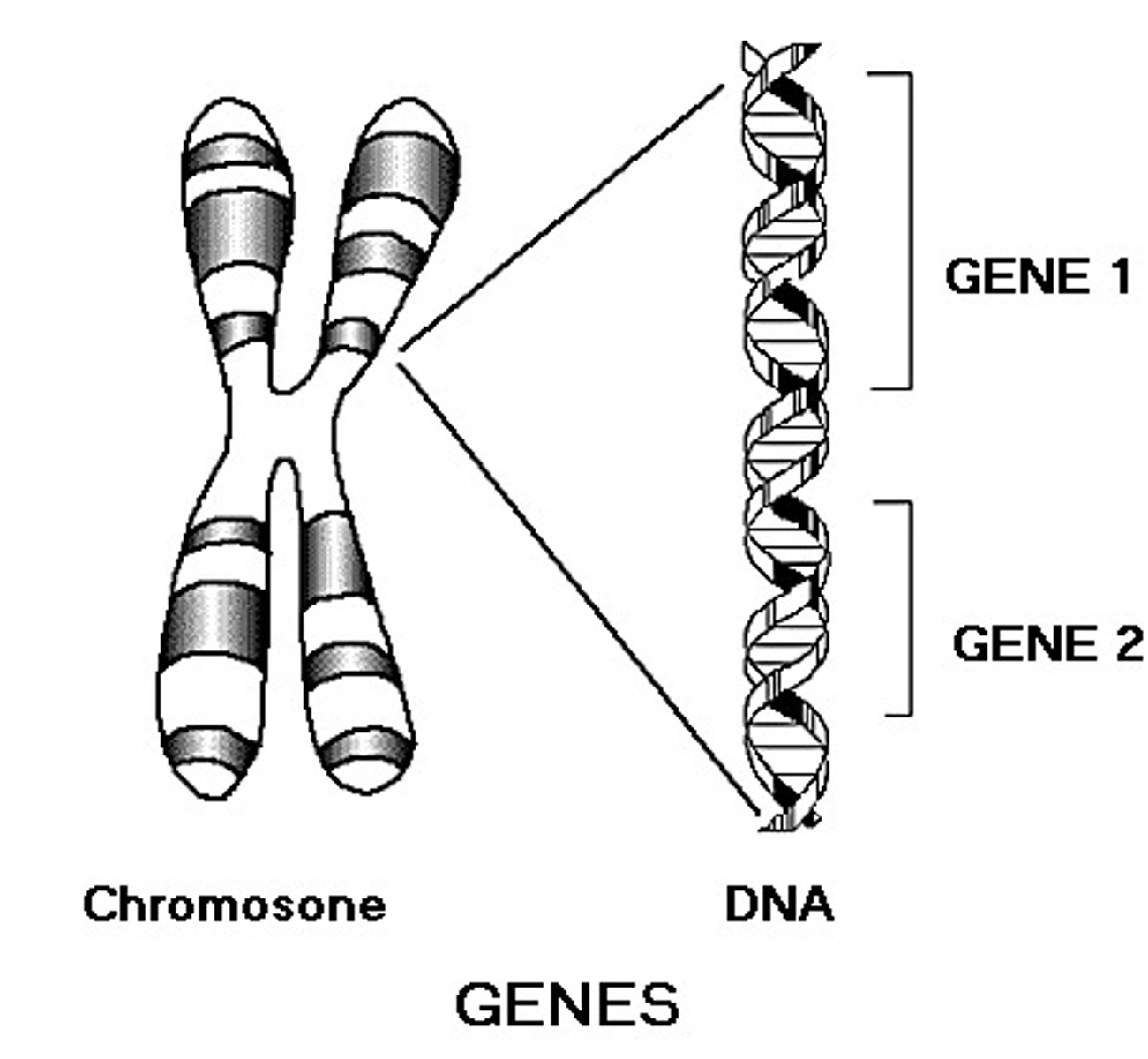
Gene
Inherited instruction carried on a chromosome; specific segment of DNA carrying an instruction encoded in its base sequence for a specific protein product
Genomics
Study of the entire genetic make-up or genome of a species
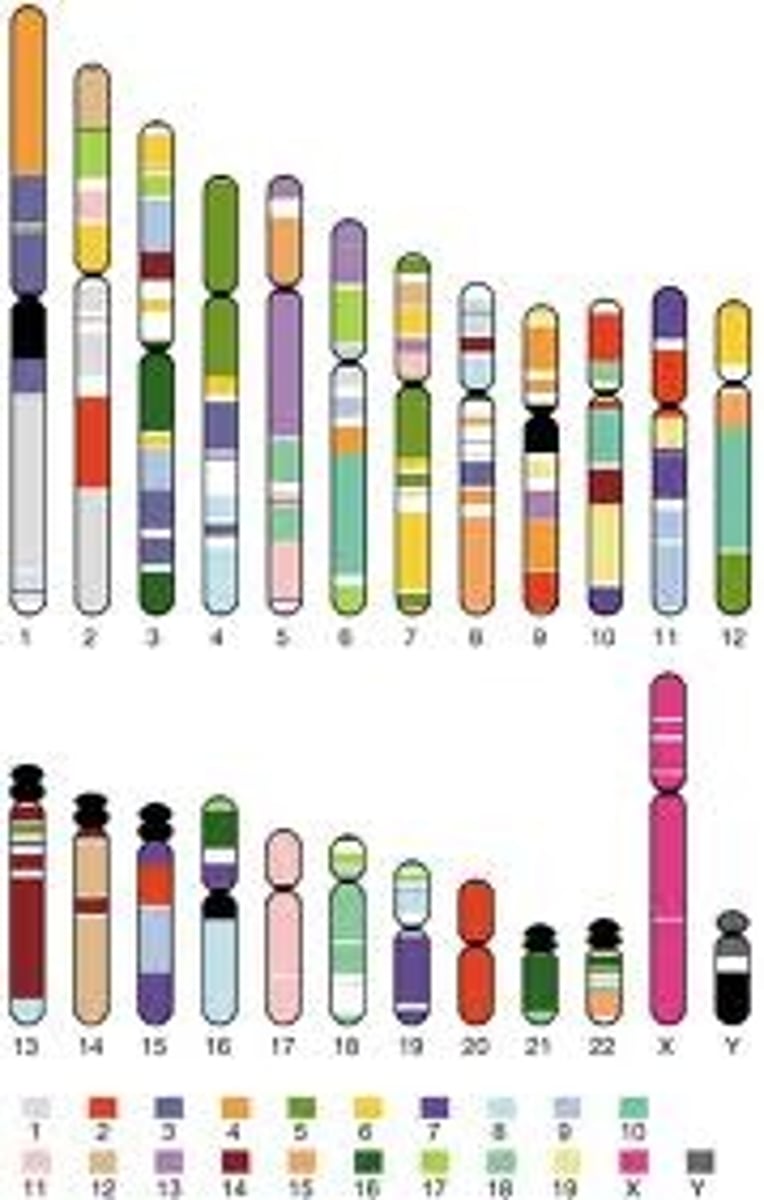
Human Genome Project
International project directed at the identification of the sequence of the more than three billion bases in the human genome

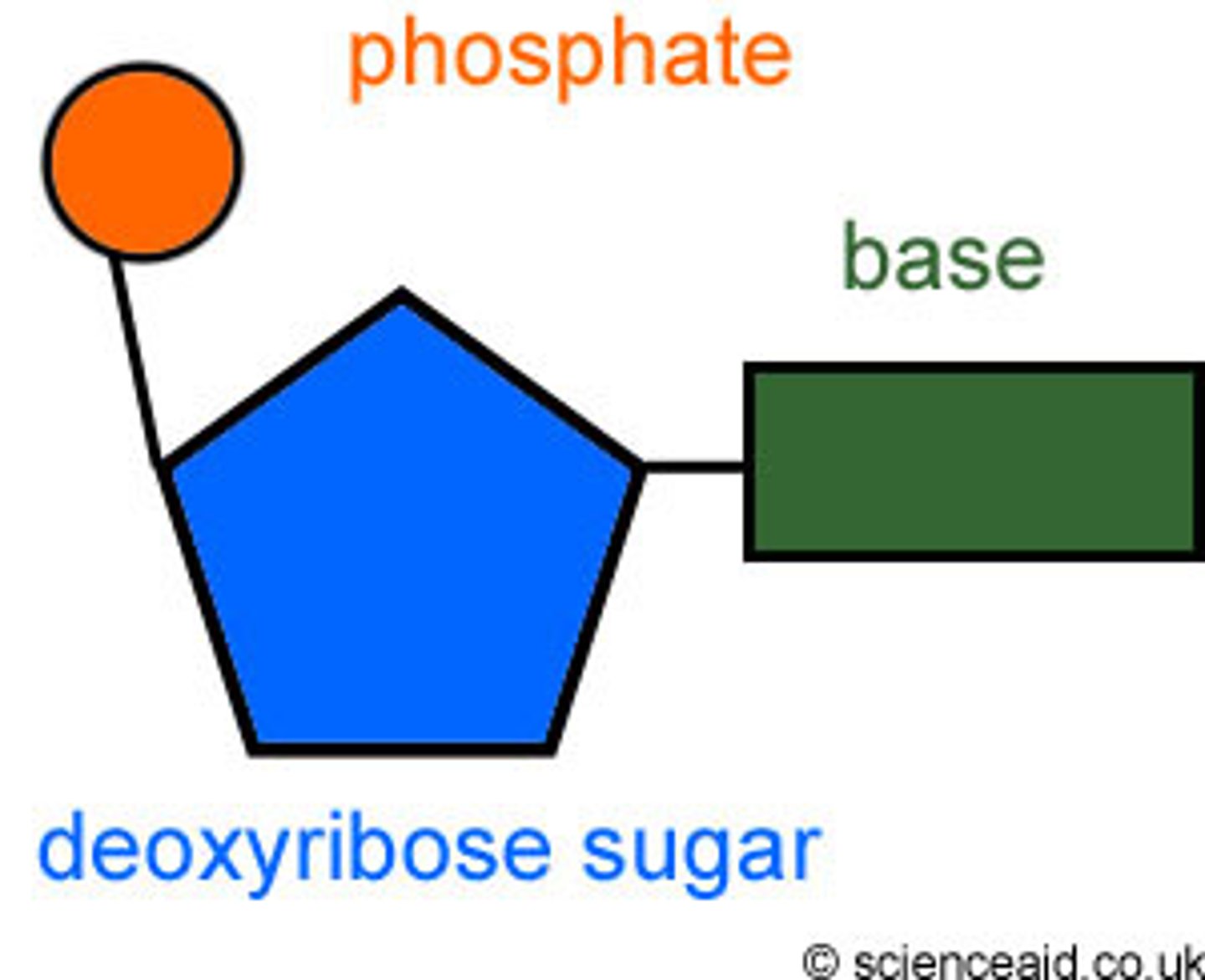
Nucleotide
Basic building blocks or sub-units of DNA and RNA and consisting of a phosphate group, a base and a sugar; the sugar in DNA is deoxyribose and that in RNA is ribose
Sex Chromosome
The pair of chromosomes that differ in males and females of a species
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
A molecule that carries the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses
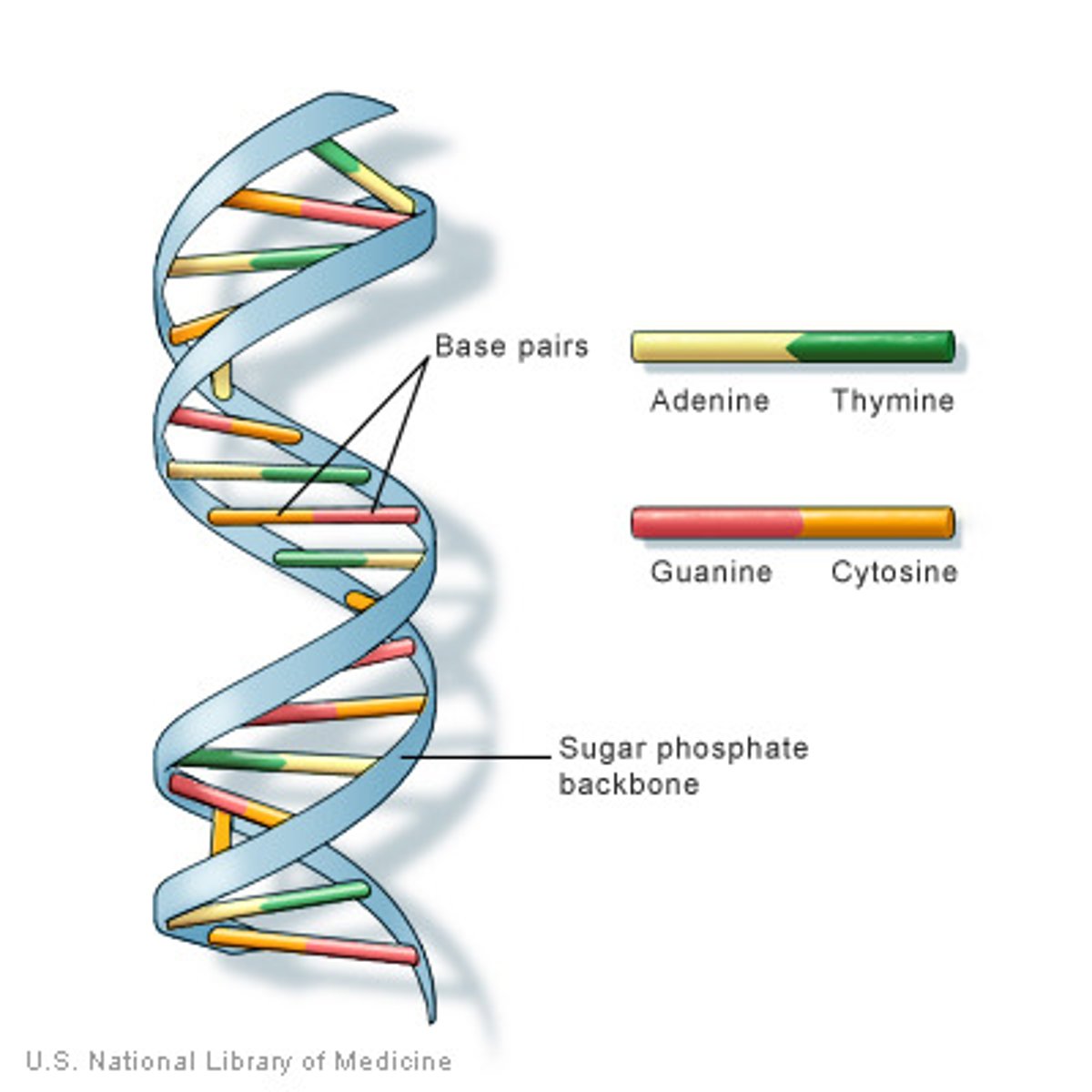
Chromosome
A thread-like structure of DNA and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes
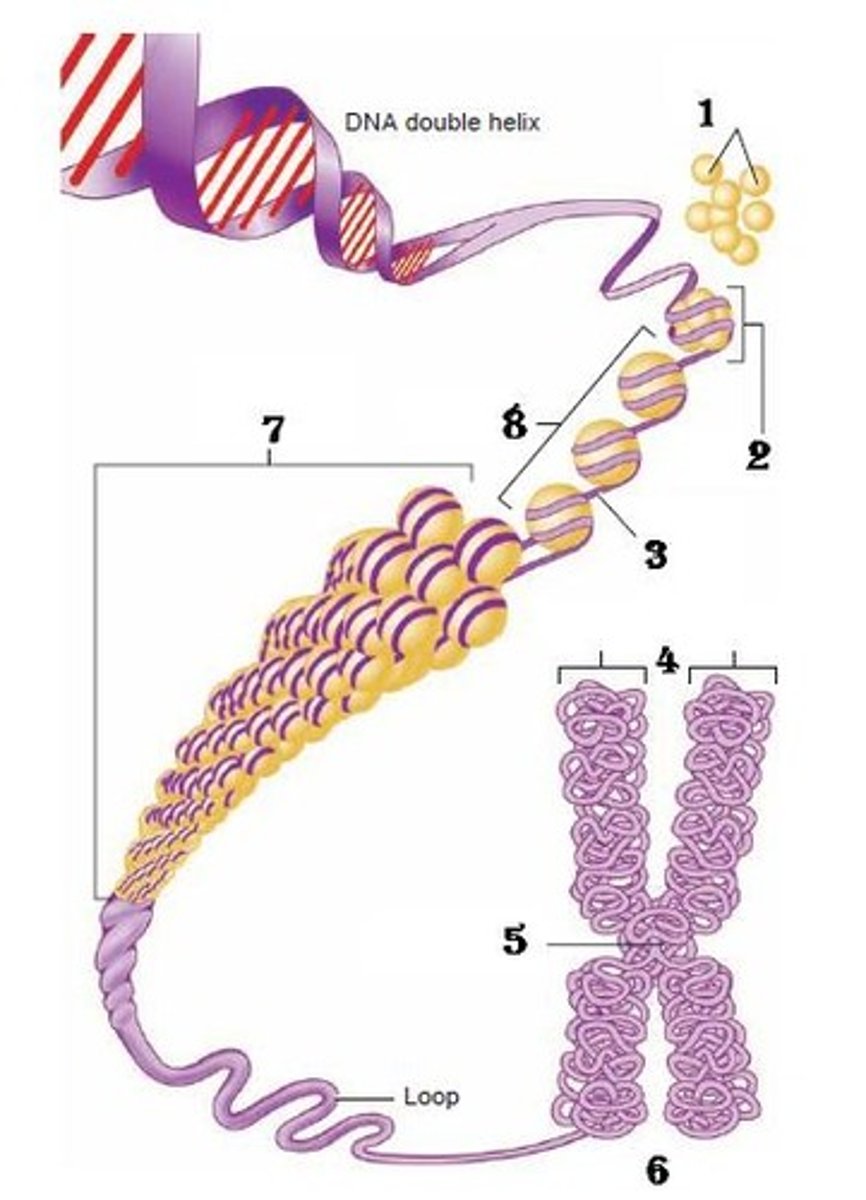
Chromatin
The material of which the chromosomes are composed, consisting of histone proteins and DNA.
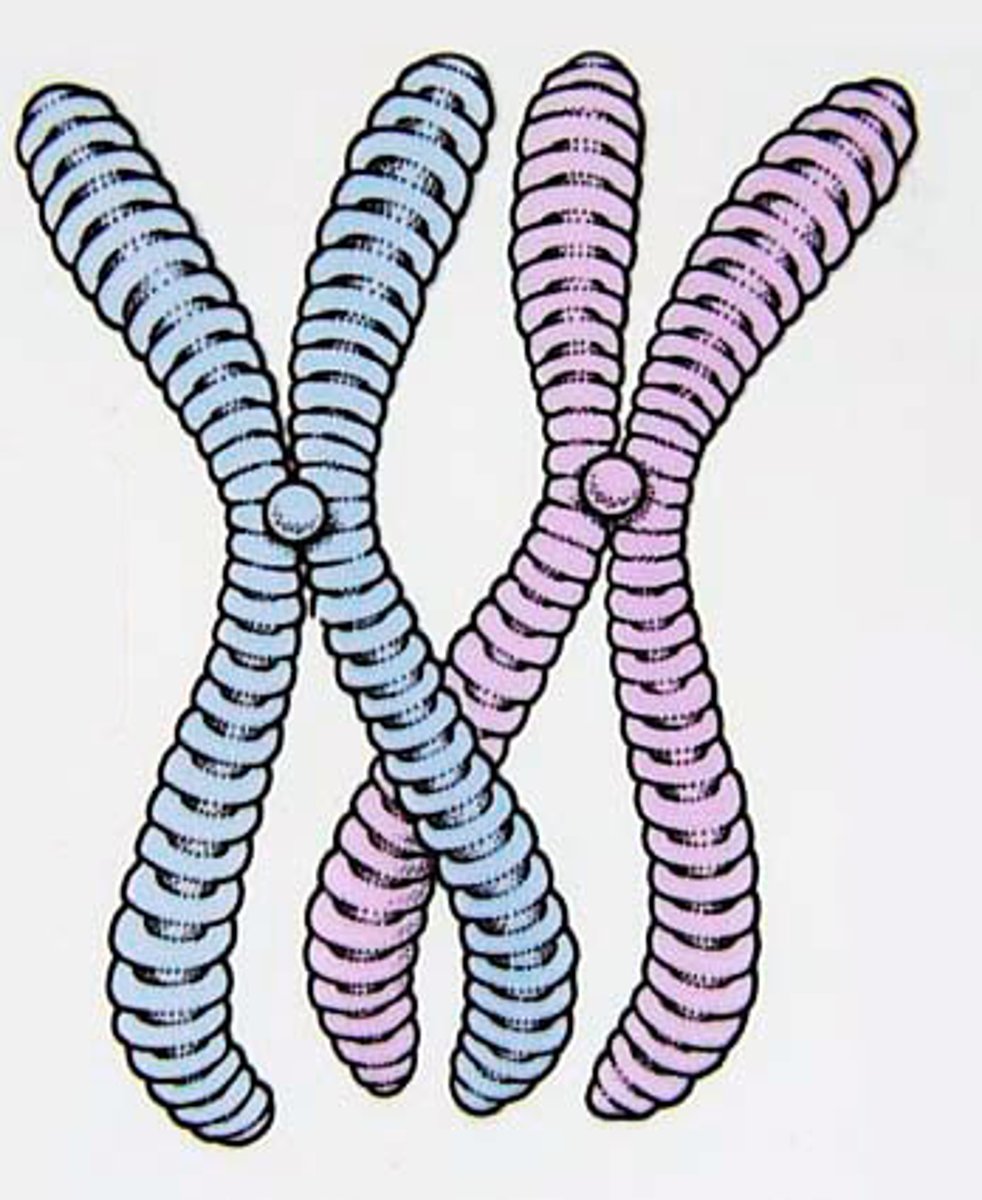
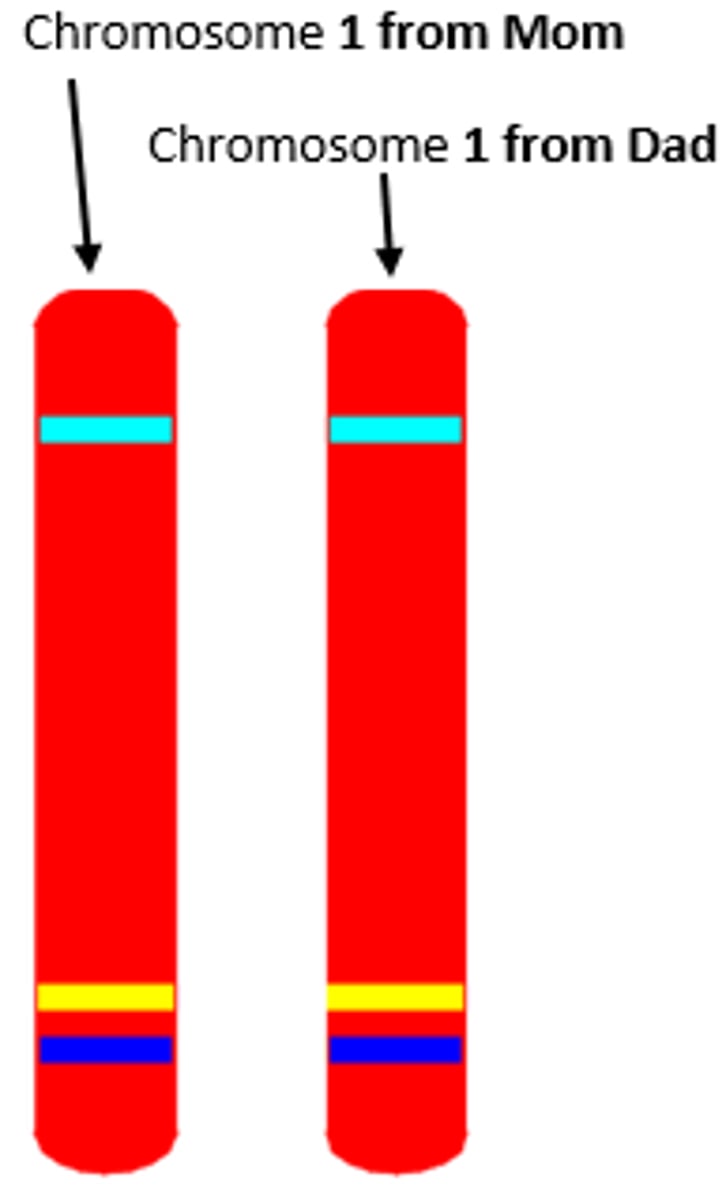
Homologous Chromosomes
Matching pairs of chromosomes that have the same size and shape and carry the same gene loci.
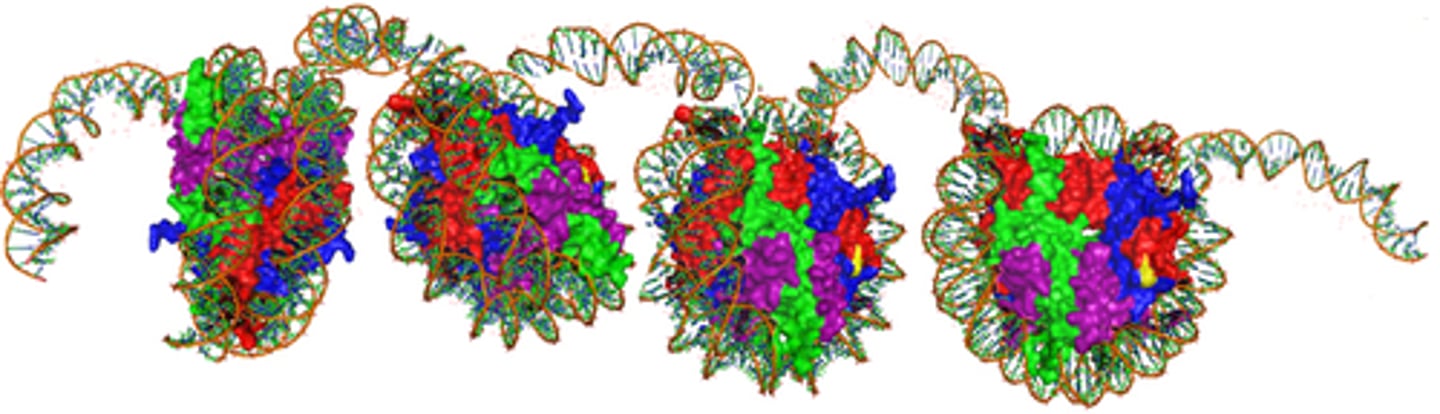
Nucleosomes
A structural unit of a eukaryotic chromosome, consisting of a length of DNA coiled around a core of histones.
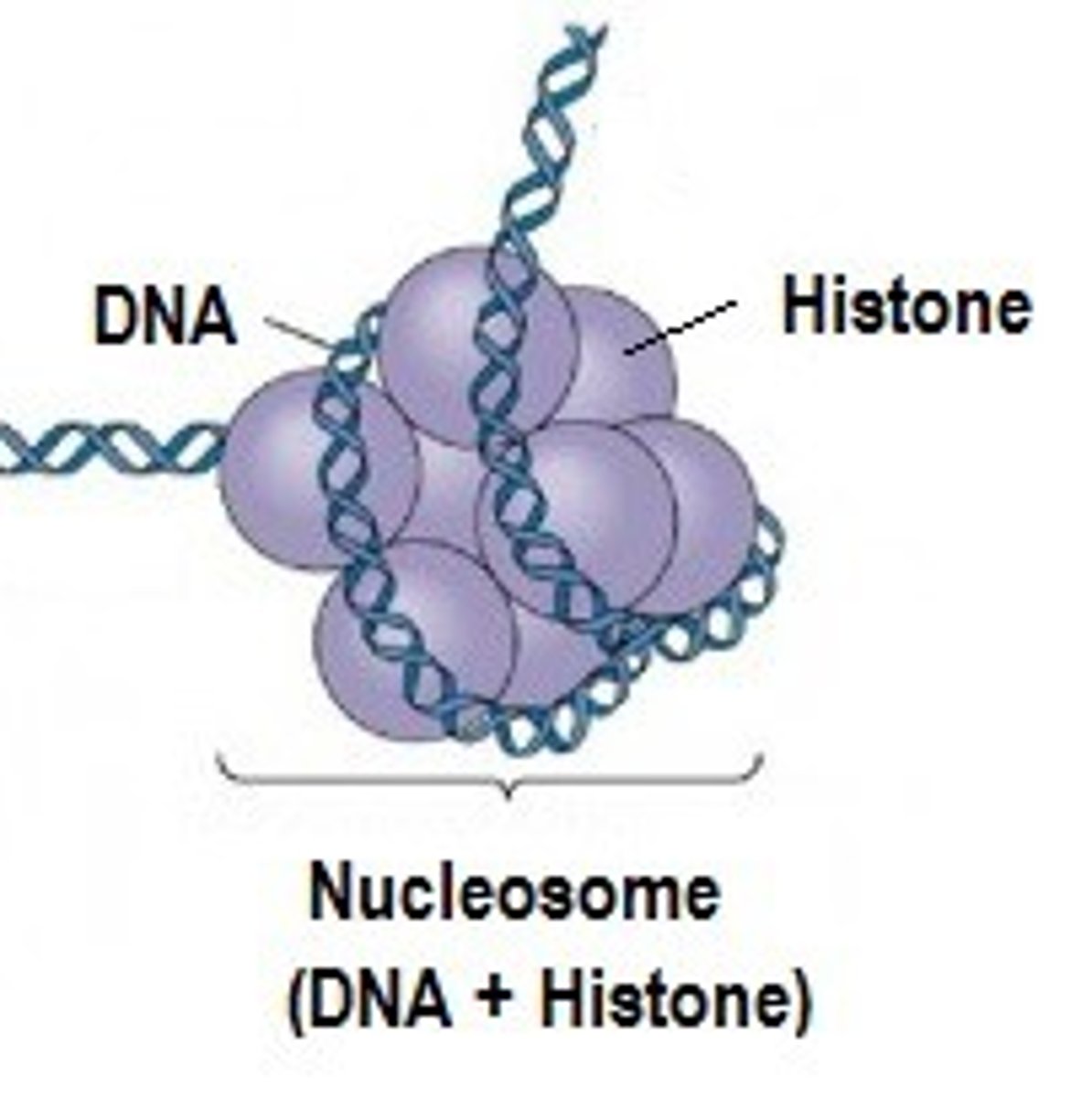
Supercoiling
a double helix (as of DNA) that has undergone additional twisting to create the chromosome.
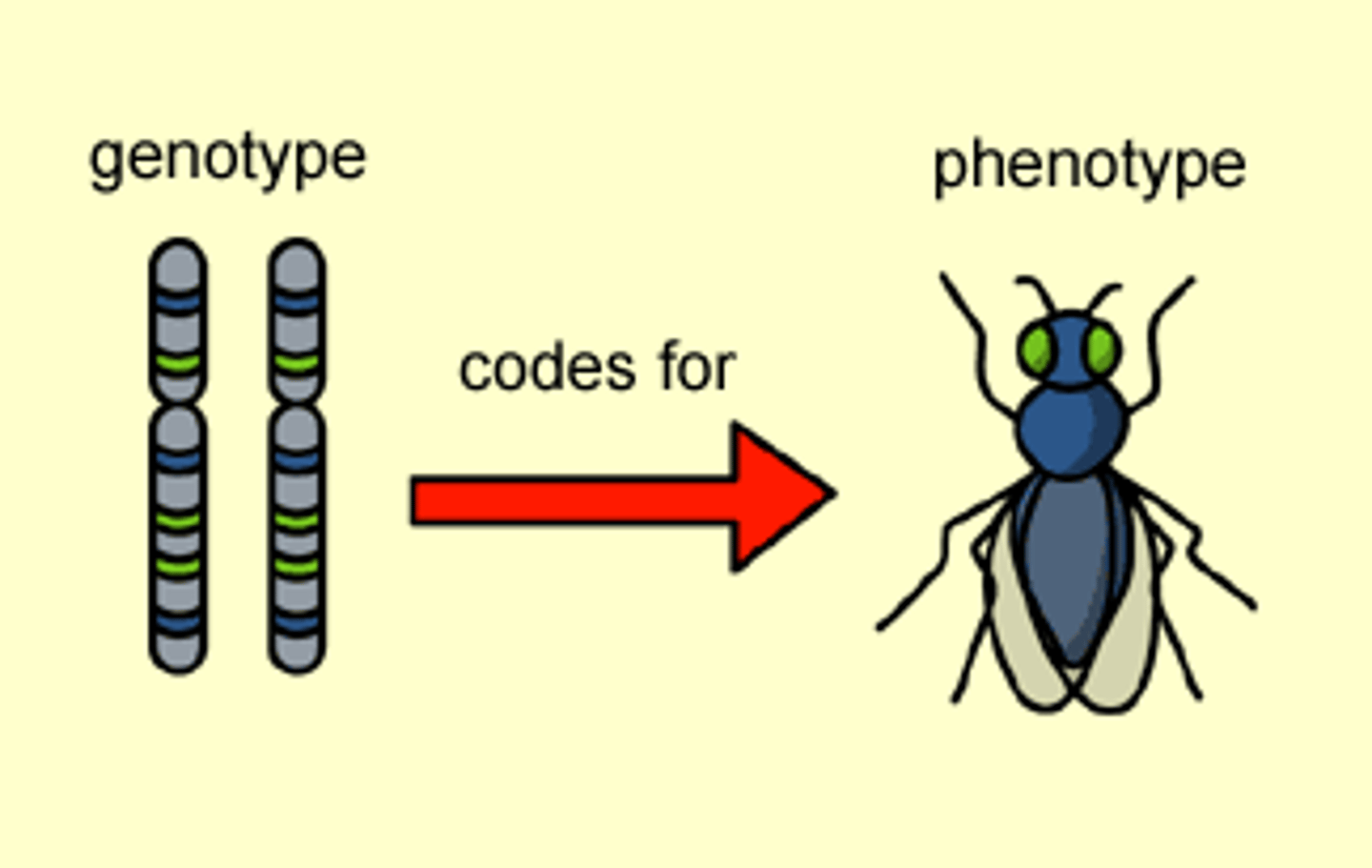
Phenotype
Physical expression of a genotype. Physical appearance.
Dominant allele
One allele when present that will be expressed in the phenotype and may mask the presence of another allele

Recessive allele
An allele that will only be expressed when two alleles are present.
Genotype
The combination of alleles for a gene location
Mutation
is a hereditable random change in the DNA or genetic material
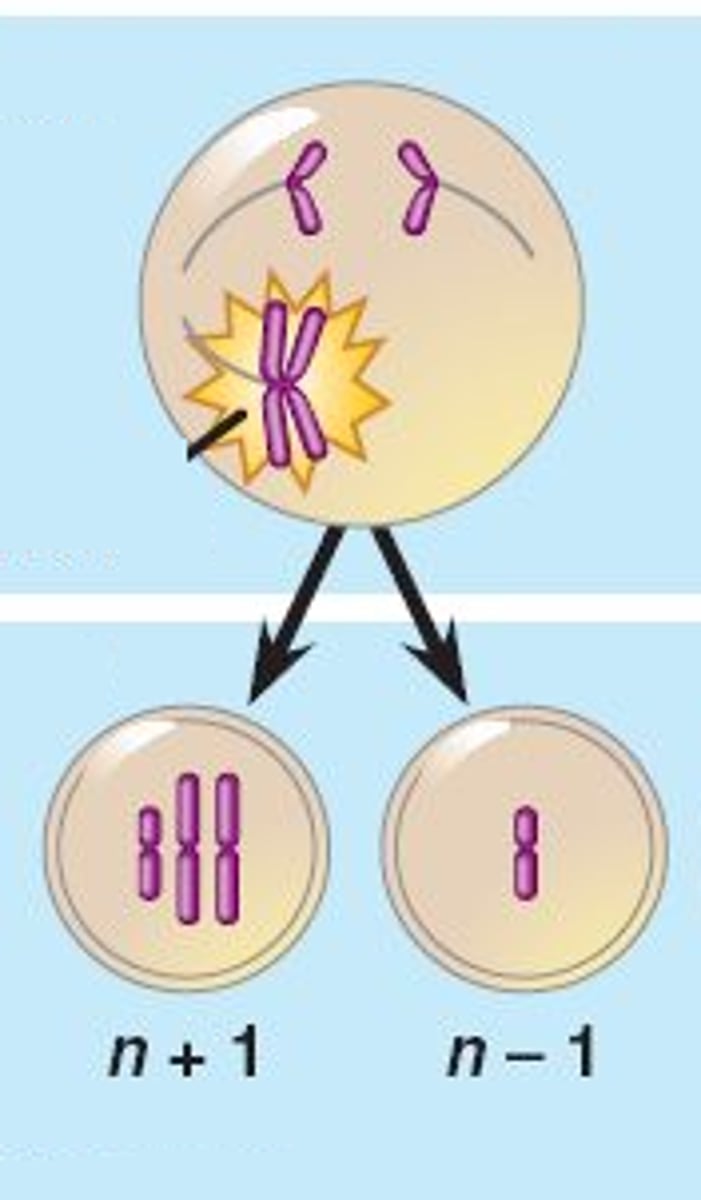
Non-disjunction
failure of one or more homologous chromosomes to separate during sexual cell division
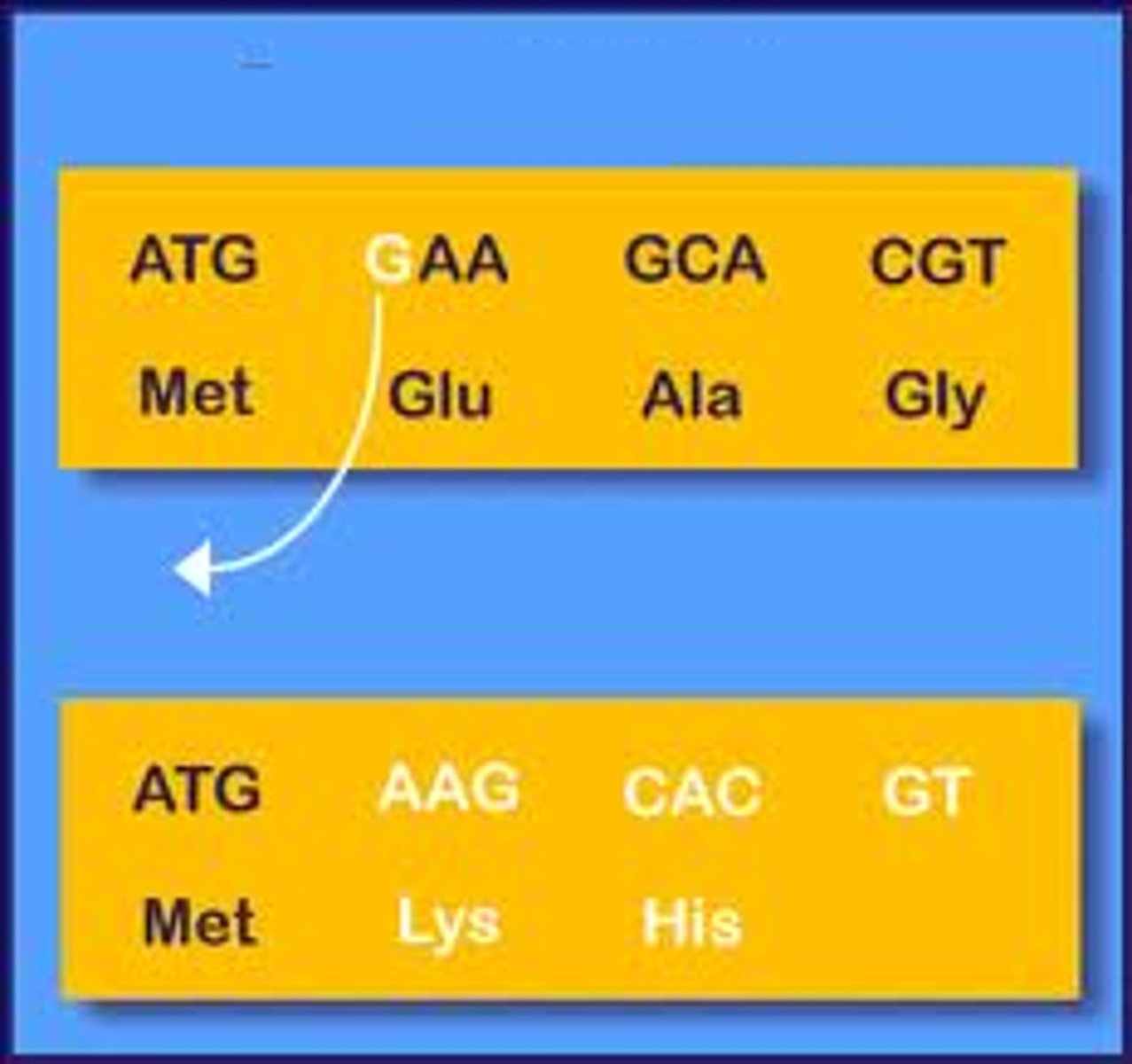
Linked Genes
genes that are located on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together
Heredity
is the study of heritable traits (genes) and their transmission from parents to offspring.
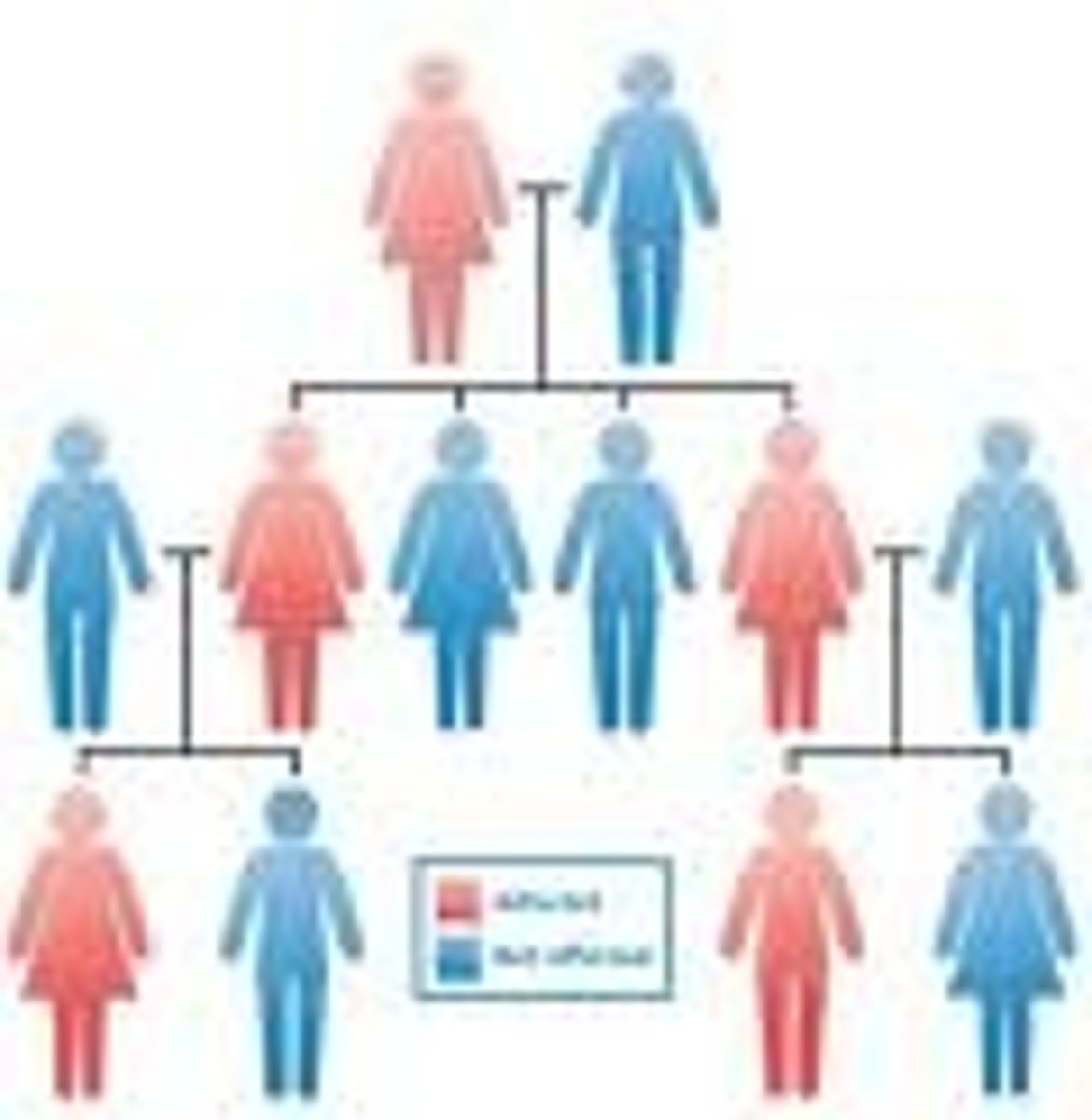
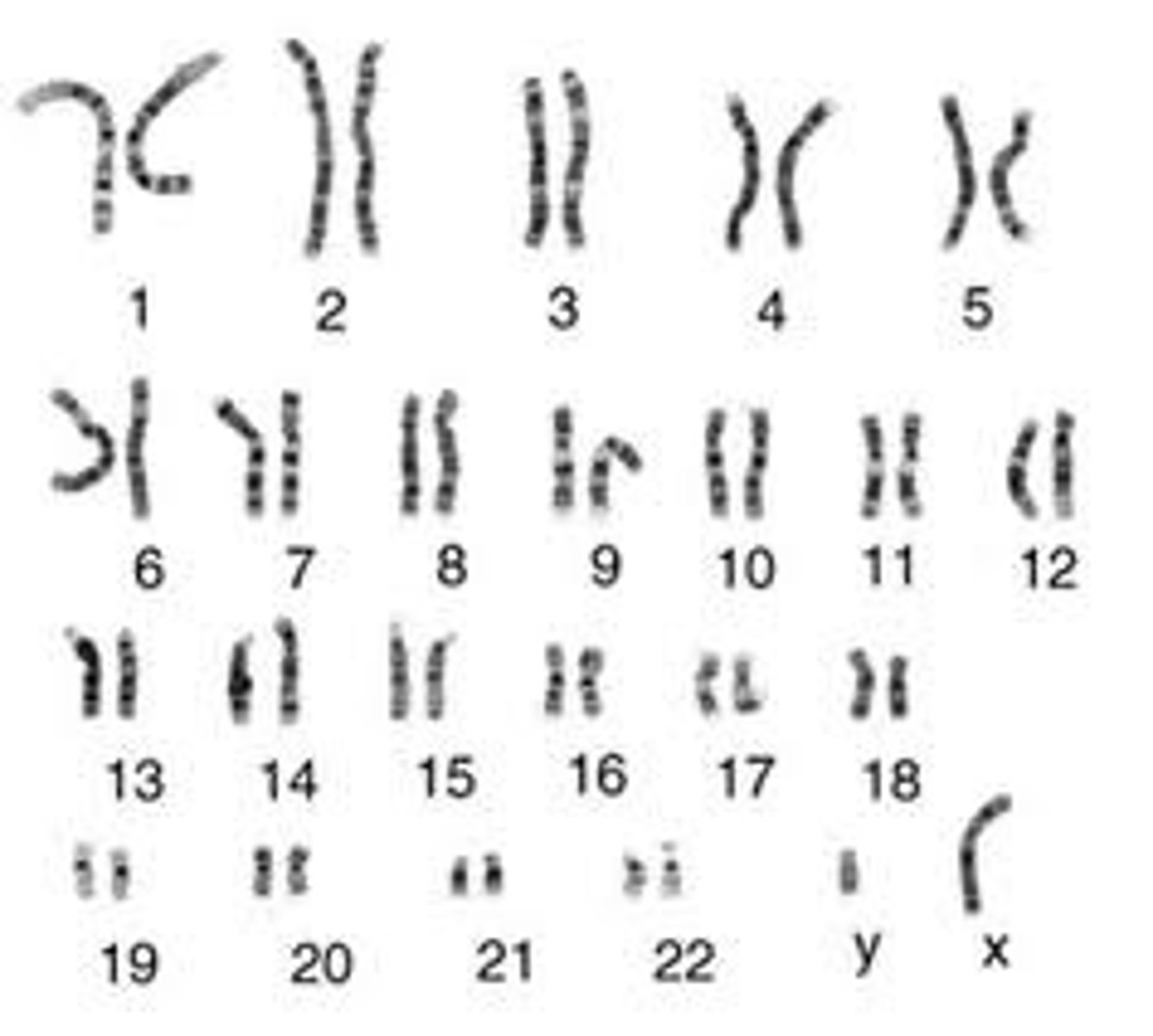
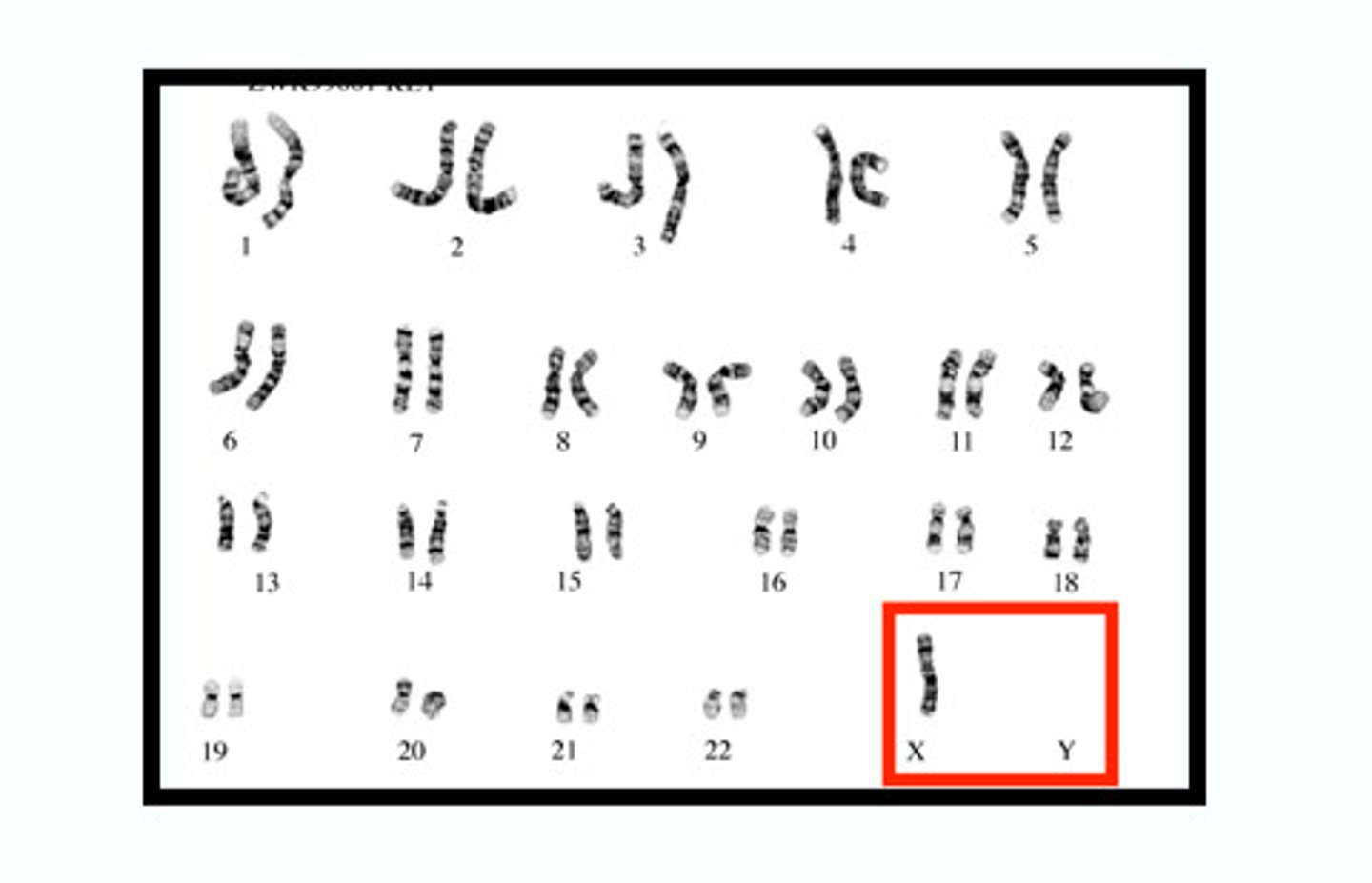
Karyotype
is a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells. It reveals extra or missing chromosomes, or abnormal positions of chromosome segments.
Sex-linked genes
these are genes found on the Sex chromosomes. In humans it refers to genes on the X-chromosome.
Aneuploidy
a condition where a person inherits one more or one less chromosome in their somatic cells
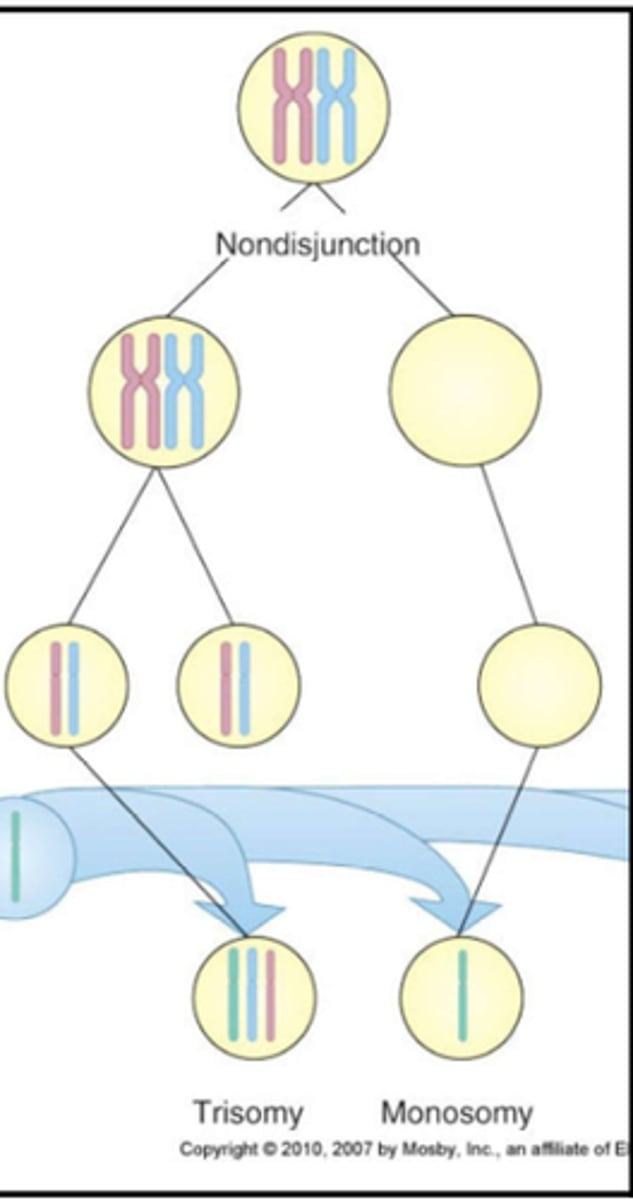
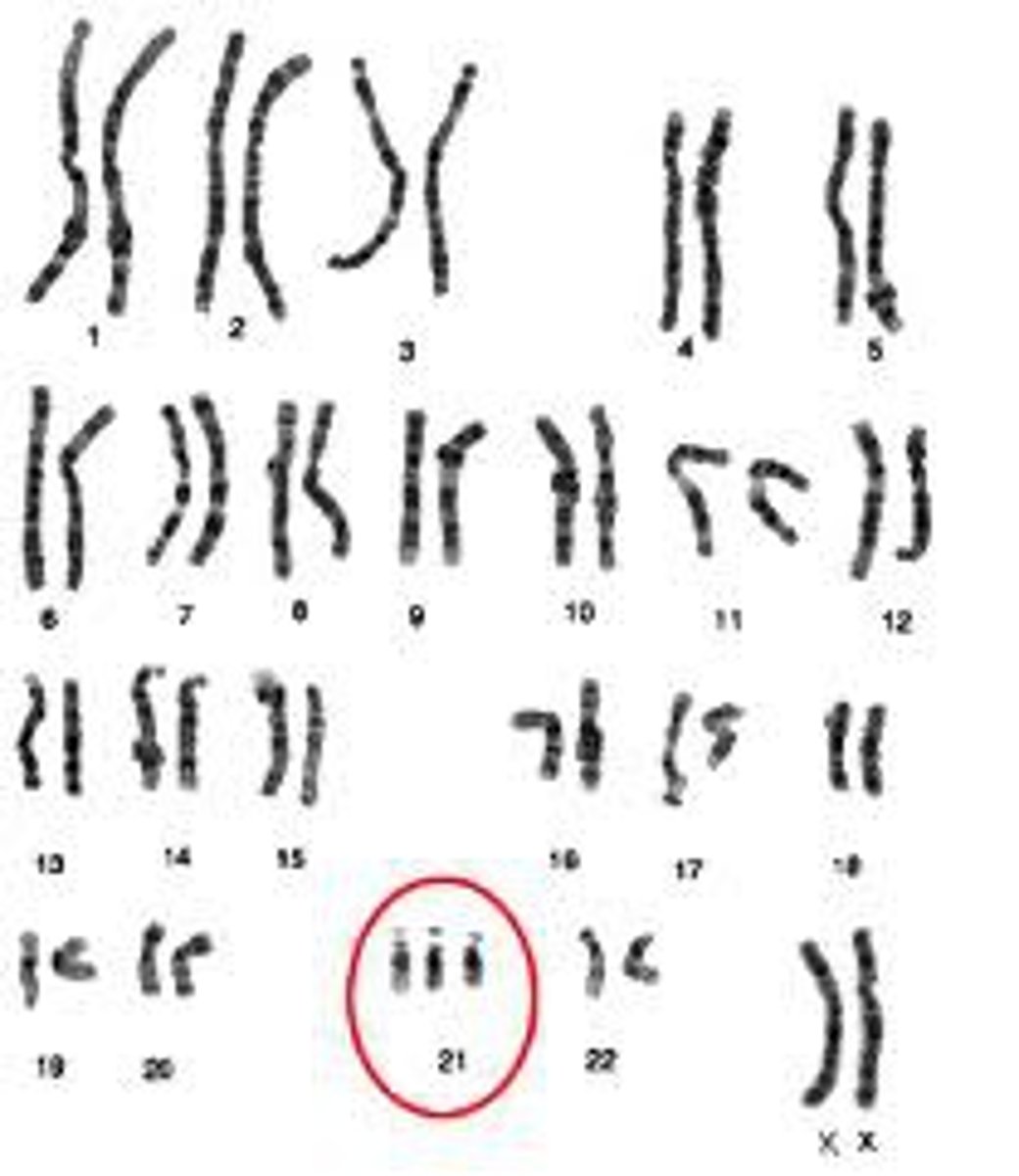
Trisomy
a type of aneuploidy where a person inherits an extra copy of a chromosome resulting in a ploidy number in humans of 2n+1=47
Monosomy
a type of aneuploidy where a person inherits one less chromosome resulting in a ploidy number in humans of 2n-1=45
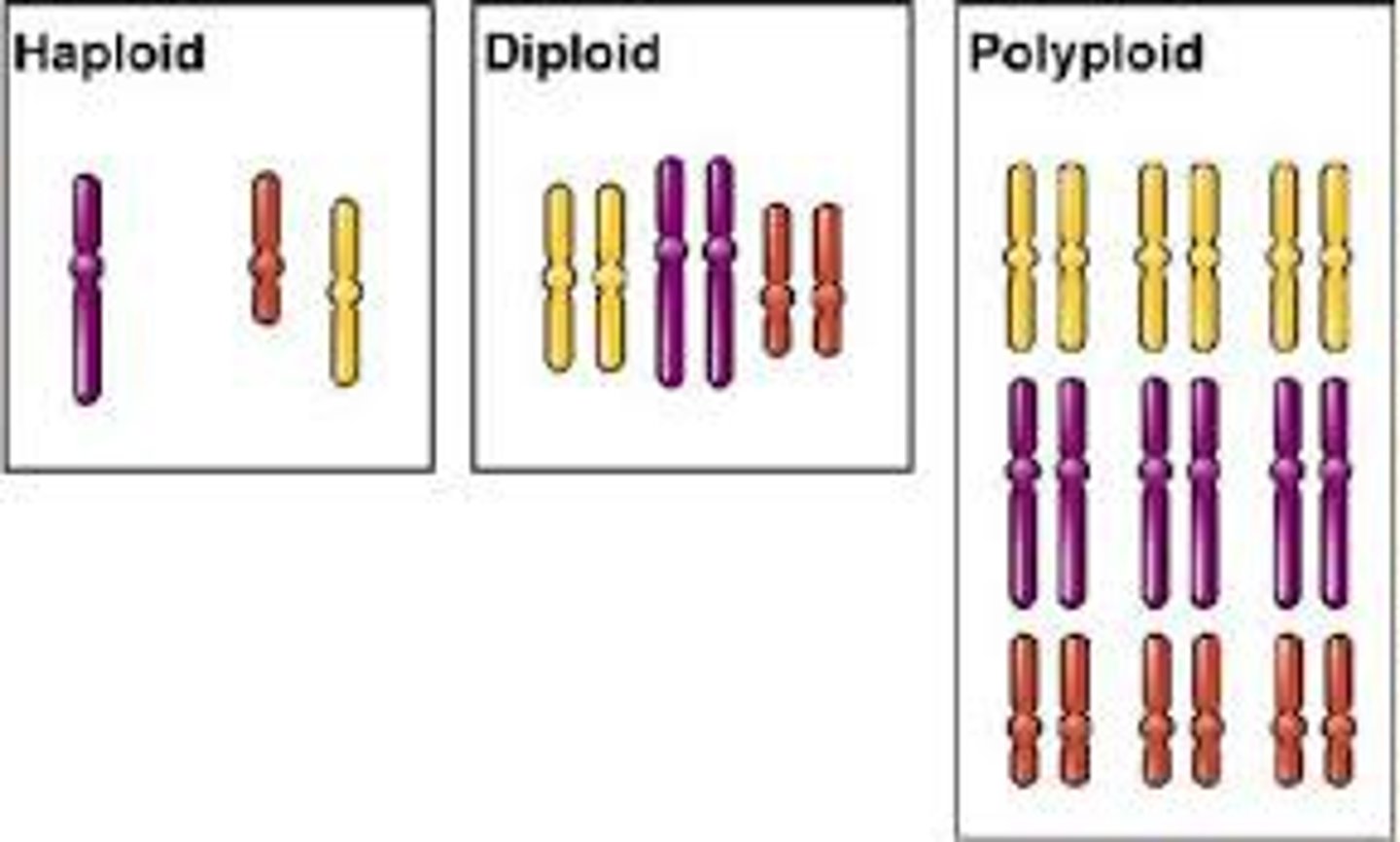
Polyploidy
cells and organisms that contain more than two sets of chromosomes. instead of 2n the organism becomes, 3n or 4n due to non-disjunction of whole sets of chromosomes
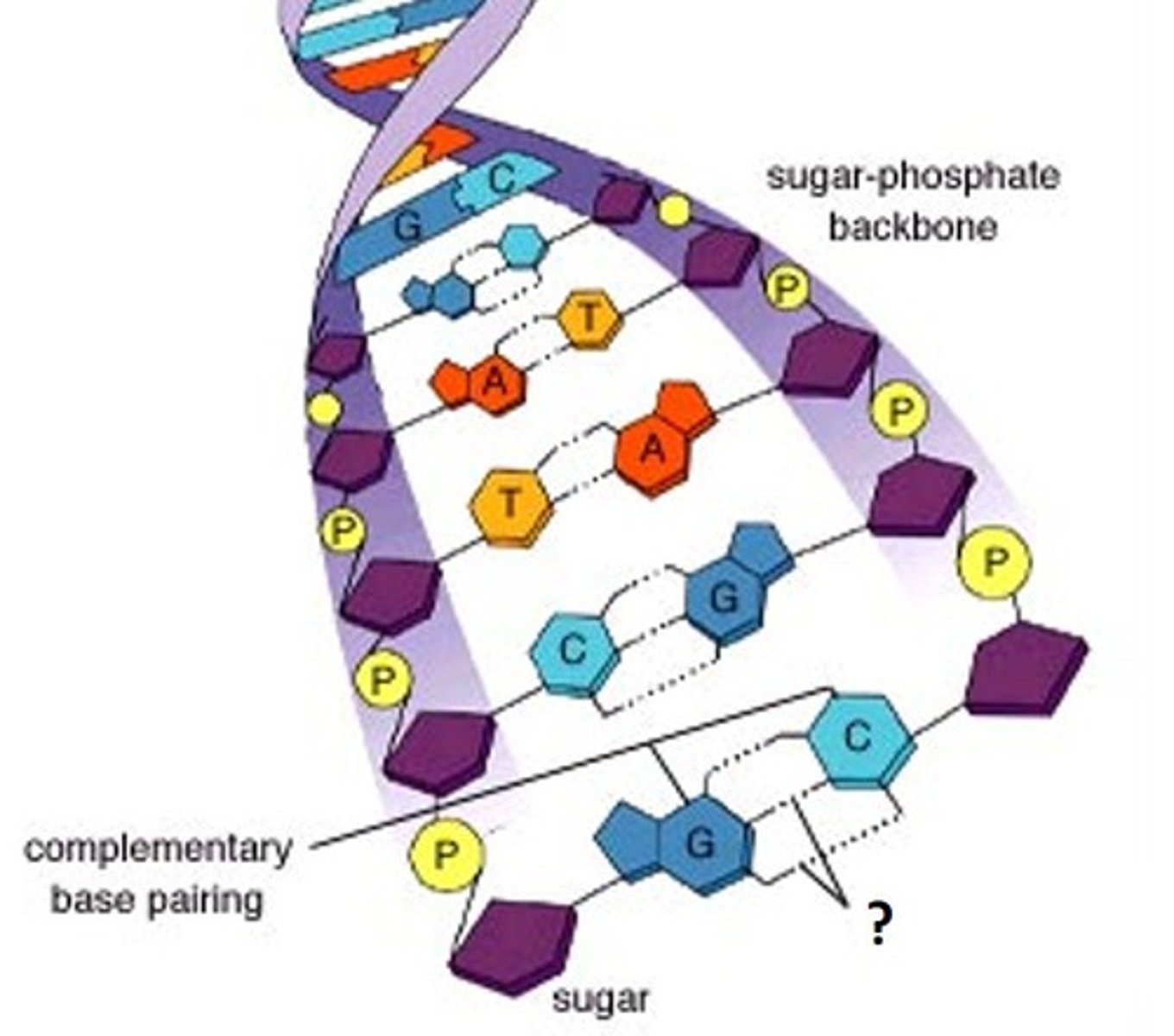
Complementary Base Pairs
the linking of pairs of nitrogenous bases on the DNA molecule. Guanine is the complementary base of cytosine, and adenine is the complementary base of thymine in DNA and of uracil in RNA
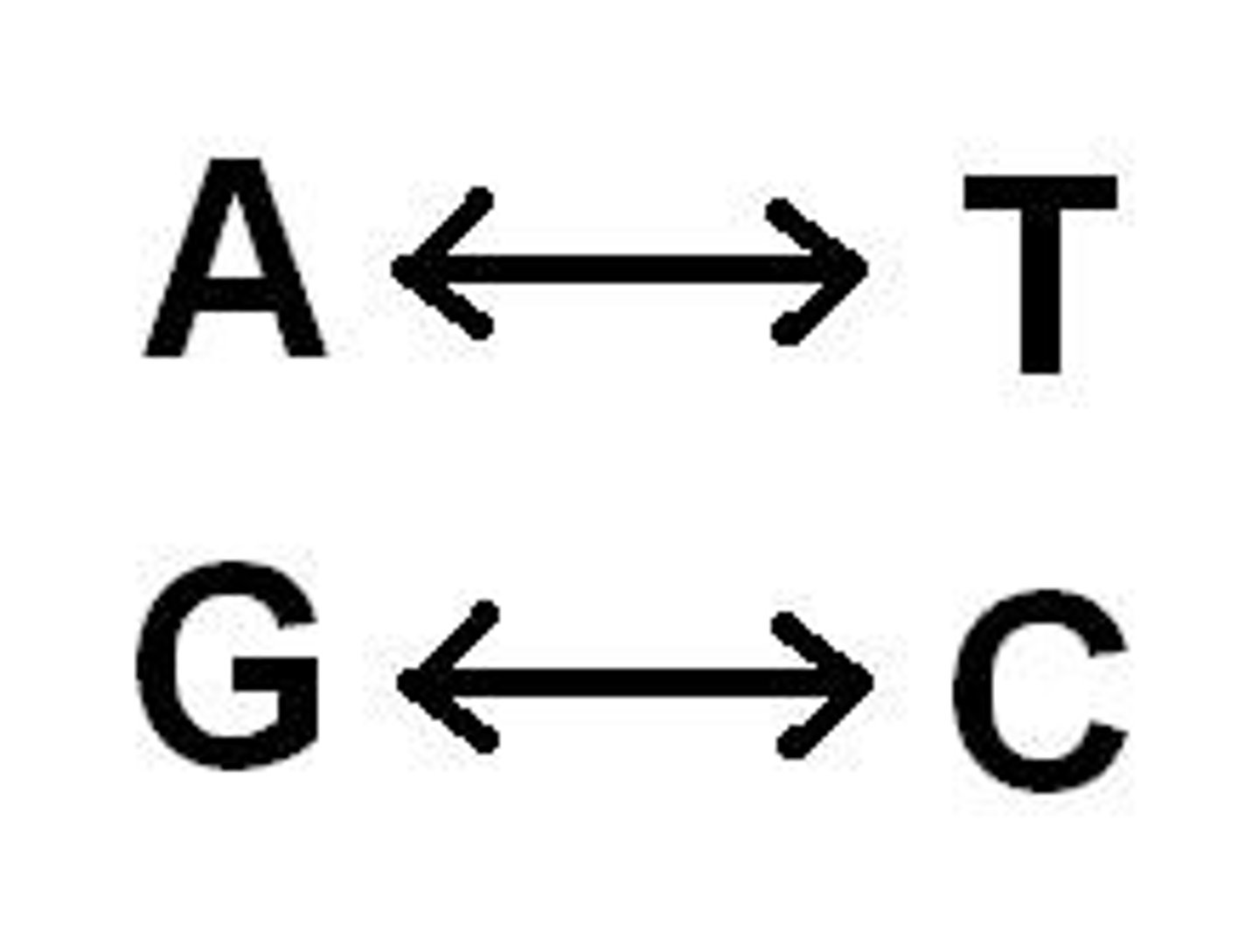
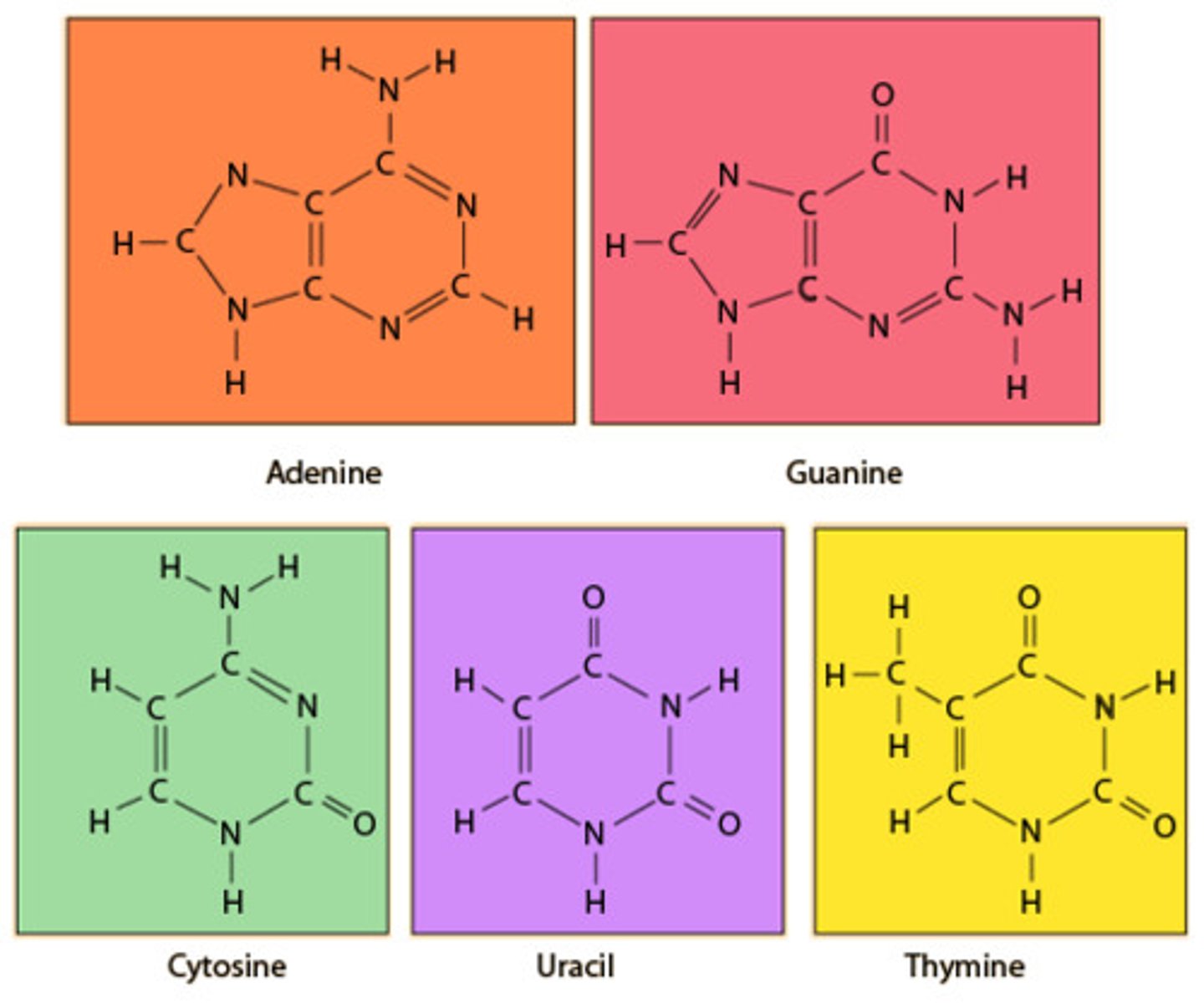
Nitrogenous base
a nitrogen rich component of the DNA molecule and part of the nucleotide building block. 5 types (A,T,C,G and U)
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bonds that form between the base pairs in the DNA and hold the two DNA strands together in the rungs