Concept 14.4: Many human traits follow Mendelian patterns of inheritance
1/15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Human genetics
Based around basic Mendelian genetics even with the limitations of human subjects for genetic research
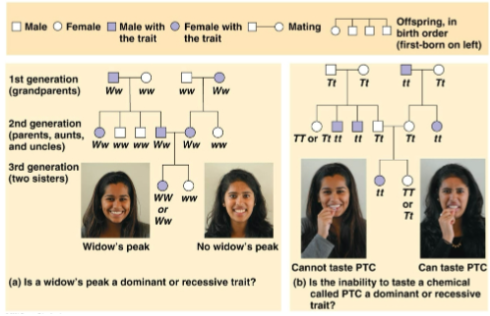
Pedigree
A family tree that describes the inheritance of a trait across generations
Used to analyze the results of human matings that have already occurred to make future offspring predictions
Recessive disorders
Disorders that range from relatively mild to life-threatening that only show up with individuals homozygous for the allele
Always born to carrier or affected parents
Carriers
Heterozygous individuals who carry the recessive allele but are phenotypically normal
Rarity reduces likelihood of meeting and mating
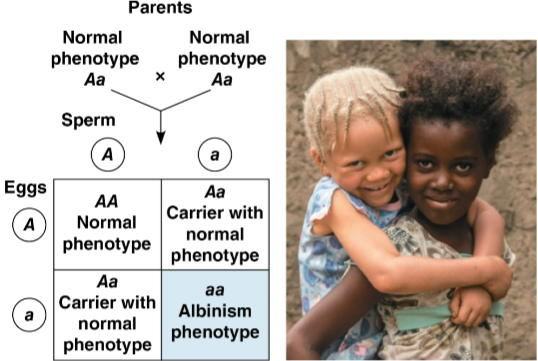
Albinism
A recessive condition characterized by a lack of pigmentation in skin and hair
Consanguineous matings
Matings between close relatives that increase the chance that both parents of a child carry the same rare allele
Often outlawed or taboo in many societies and cultures
Cystic fibrosis
The most common lethal genetic disease in the United States
Results in defective chloride transport ions in plasma membranes, leading to a buildup of chloride ions outside the cell
Mucus buildup and abnormal nutrient absorption in the small intestine are common symptoms
Can cause death by the age of 5; requires antibiotics and physical therapies to prolong life usually up to one’s 40s
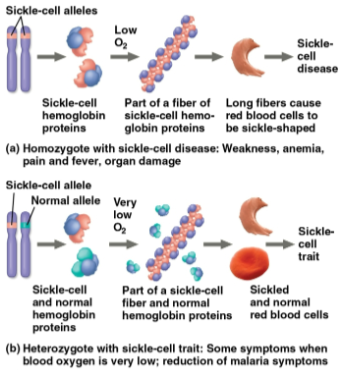
Sickle-cell disease
A disease that affects 1 out of 400 African-Americans
Caused by the substitution of a single amino acid in the hemoglobin protein in red blood cells, leading to abnormally shaped cells in homozygotes
However, heterozygote carriers are typically healthy and are less susceptible to the malaria parasite
Symptoms include physical weakness, pain, organ damage, and even paralysis
Dominant disorders
Disorders that are caused by dominant alleles
Those that cause lethal diseases are rare and arise by mutation
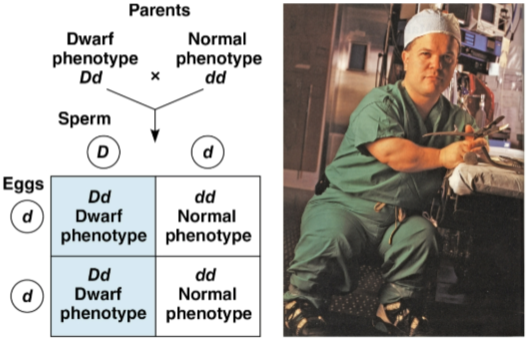
Achondroplasia
A form of dwarfism caused by a rare dominant allele
Huntington’s disease
A degenerative disease of the nervous system with no obvious phenotypic effects until the individual is about 35 to 40 years of age
Nervous system deterioration, when started, is irreversible and fatal
Can be tested for within an individual’s genome, up to personal choice
Lifestyle
A major factor on an individual’s phenotype regardless of the genotype
Genetic counselors
Professionals that provide information to prospective parents concerned about a family history for a specific disease
Help determine the risk of a child with a specific disease for decisions about having children
Fetal and newborn testing can also reveal genetic disorders
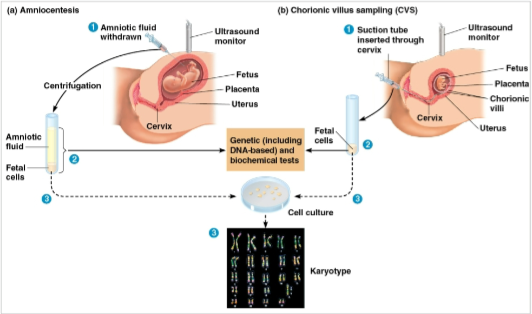
Amniocentesis
Sampling the liquid that bathes the fetus for the removal and testing of genetic disorders

Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
Using a sample of the placenta for the removal and testing of genetic disorders
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
A recessively inherited disorder that occurs in 1 of every 10,000 to 15,000 births in the United States
Routinely tested for at birth in most American hospitals alongside several other conditions