Chapter 3_Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins (print)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Amino Acids
The building blocks of proteins.
Peptides
Small condensation products of amino acids.
Proteins
Linear heteropolymers of α-amino acids.
Ionization
The process of gaining or losing protons.
Main agents of Protein Biological Function
Catalysis
Transport
Structure
Motion
Amino Acid Properties well suited to carry biological function (4)
capacity to polymerize (join together)
useful acid-base properties
varied physical properties
varied chemical functionality
A
Alanine
R
Arginine
N
Asparagine
D
Aspartic Acid
Asp
Aspartic Acid
Asn
Asparagine
C
Cysteine
E
Glutamic Acid
Glu
Glutamic acid
Glutamine
Gln
Q
Glutamine
Gly
Glycine
G
Glycine
H
Histidine
His
Histidine
Isoleucine
Ile
I
Isoleucine
Lys
Lysine
K
Lysine
Met
Methionine
Phe
Phenylalanine
F
Phenylalanine
P
Proline
S
Serine
T
Threonine
Thr
Threonine
Tryptophan
Trp
W
Tryptophan
Tyrosine
Y
Tyr
Tyrosine
V
Valine
pKa
The measure of acidity or basicity of a molecule.
Isoelectric Point (pI)
The pH at which an amino acid carries no net charge.
Buffers
Substances that resist changes in pH.
Polymerize
The process of joining amino acids together to form peptides.
N-terminal
The starting point of numbering and naming peptides.
Cofactors
Non-amino acid components of proteins.
Coenzymes
Organic cofactors of proteins.
Prosthetic groups
Covalently attached cofactors of proteins.
Posttranslational modifications
Changes made to proteins after they are synthesized.
Uncommon amino acids
Amino acids not typically incorporated by ribosomes.
Reversible modifications
Changes to amino acids that can be reversed.
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
Residues
The individual amino acids in a protein or polypeptide chain.
Polypeptide chains
The individual chains that make up a protein.
Conjugated proteins
Proteins that are covalently bound to a nonprotein entity, such as a lipid or carbohydrate.
Prosthetic group
covalently attached cofactors
heme in myoglobin
The nonprotein entity that is covalently bound to a cofactor conjugated protein.
Sequence
The order of amino acids in a protein or polypeptide chain.
Three-dimensional structure
The spatial arrangement of atoms in a protein.
Native fold
The natural, functional conformation of a protein.
Biochemical role
The specific function or activity that a protein performs in a biological system.
Function regulation
The mechanisms by which a protein's activity is controlled or modulated.
Physico-chemical properties
The physical and chemical characteristics of a protein, such as solubility, charge, and hydrophobicity.
Purification
The process of isolating a protein from a mixture.
Chromatography
A technique used to separate and analyze mixtures based on differences in physical and chemical properties.
Column chromatography
A type of chromatography that uses a column packed with a solid phase to separate proteins.
Ion exchange
A type of chromatography that separates proteins based on their charge.
Size exclusion
A type of chromatography that separates proteins based on their size.
Affinity
A type of chromatography that separates proteins based on their specific binding interactions.
Electrophoresis
A technique used to separate and analyze proteins based on their charge and size.
SDS-PAGE
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, a method for separating proteins based on their molecular weight.
SDS PAGE GEL: Ingredients and Function in Buffer
SDS: detergent denatures into linear shape and coats protein in negative charge
2-Mercaptoethanol: reduces disulfide bonds to denature protein
Glycerol: To weigh the sample down when you load the sample to fall into the well
Tris HCL: Ensures proper pH
to help pull the proteins along the gel. The negative charge of the Cl ions means they move faster through the gel than the proteins.
Bromophenol Dye: Able to see the protein’s movement
What makes SDS PAGE GEL separates only by
When proteins all have the same charge and shape the only thing that the structure can be separated by is by mass only
Molecular weight
The mass of a protein or polypeptide chain, calculated by summing the atomic weights of its constituent amino acids.
At low pH, the amino acid exists in a _____ charged form
positively (cation)
At high pH, the amino acid exists in a ____ charged form
negatively (anion)
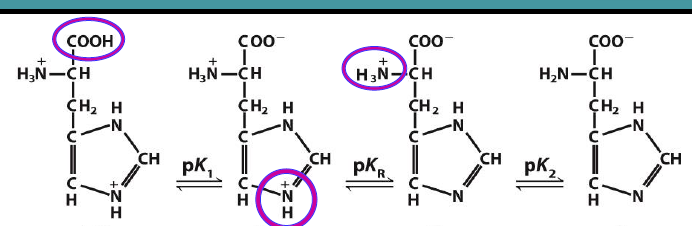
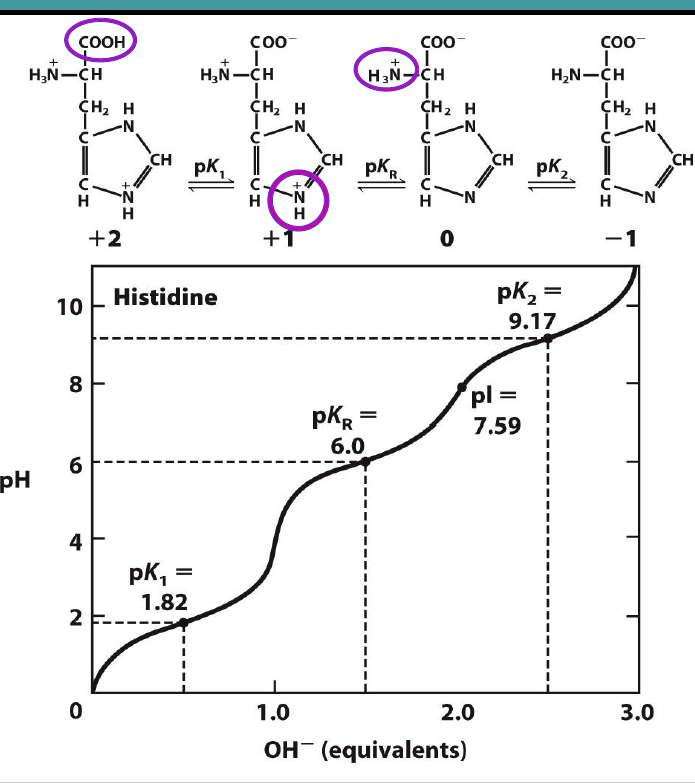
Draw this molecule’s titration curves
Isoelectric focusing
A technique used to separate proteins based on their isoelectric point.
pI (isoelectric point)
The pH at which a protein has no net charge.
2D electrophoresis
A combination of isoelectric focusing and SDS-PAGE used to separate proteins in two dimensions.
UV-visible spectrophotometry
A method used to measure the concentration of proteins and peptides based on their absorbance of UV or visible light.
Specific activity
The ratio of a protein's activity to its total protein concentration, used to assess the purity of the protein.
Protein sequencing
Determining the order of amino acids in a protein or polypeptide chain.
native fold
the folded shape of a protein is most often referred to as its native "conformation" or "structure
Edman degradation procedure
Amino acid sequence is determined by breaking disulfide bonds, cleaving the protein into small fragments
Purifies protein by removing one residue at a time