BIOCHEM
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Common Monosaccharides
Aldose and Ketose (CH2O)n
Aldose
Carbonyl group at the end of Carbon chain
Ketose
Carbonyl group at any other position
Glucose Structure
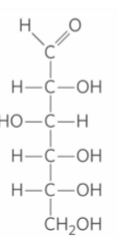
D- Fructose
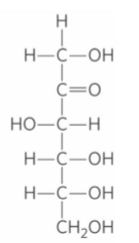
All monocaccharides (except dihydroxyacetone) contain
1+ chiral carbon atom
Reference Carbon
Chiral center most distant from the carbonyl carbon (determine D or L)
D-isomer
configuration at reference carbon is the same as D-Glyceraldehyde.
Epimers
Two sugars that differonly in the configuration around one carbon atom
Aldehydes and Ketones react with H2O to form
Hydrates

Aldehyde and Ketone + 1x alcohol
Hemi-acetal
Aldehyde and Ketone + 2x alcohol
Acetal / Ketal
Acetal
Very stable and stay as acetal
Hemi-acetal
Highly reactive species
Intramolecular hemiacetal formation
Bulky group in eq position for it to stay in cyclic formation
In Aq solution
aldotetroses and monosaccharides with 5+ backbone carbon atoms occur as cyclic structures
Two cyclic forms of D-Glucose
alpha and beta
anomers
isomeric forms of monosaccharides that differ in their configuration about the hemiacetal/hemiketal carbon atom
anomeric carbon
carbonyl carbon atom
Haworth Persective Formula
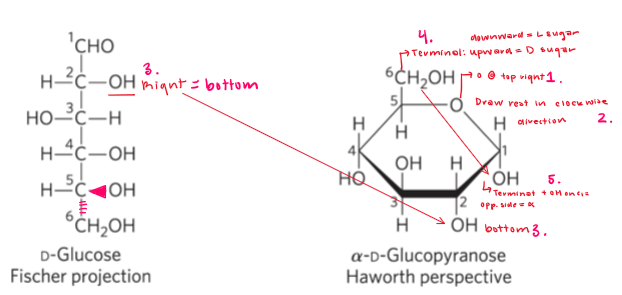
Nomenclature for cyclics sugars
Pyranose and furanose
D-glucose formation
Favor pyranose.furanose because angle strain
Reducing sugars
Aldoses and suagrs that can form aldehydes
Red precipitate
Reducing sugar undergos a redox reaction where free aldehyde groups convert Cu2+ to Cu+
Ketoses = reducing sugar
tautomerize to aldehyde
Copper test assay
Blue = soluble
O-glycosidic bond
Covalent linkage joining two monosaccharides through condensation and hydrolysis and might form non-reducing sugar
Reducing end (hemi-acetal)
end of disaccharide or polysaccharide chain with a free anomeric carbon
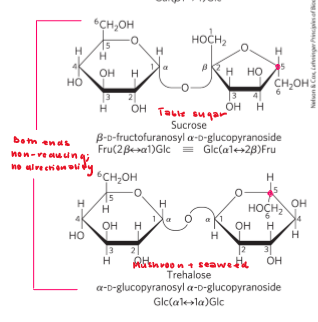
Common disaccharides
Lactose = reducing
Sucrose = nonreducing
Trehalose = nonreducing
reducing sugar
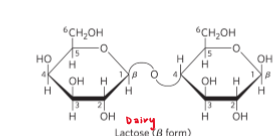
nonreducing sugars
more stable = longer shelf life
Polysaccharide
glycan
oligo«poly
Mr > 20,000 without a defined length because enzyme will continusly link monosaccharides and not know when to stop polymerization. ( dependent on Temp, pH and number of monomers)
Homopolysaccaharide
Sinlge monomerric sugar species
Heteropolysaccharide
2+ kinds of monomers
Glycogen
Energy storange molecular in animals
Liver cells
excess sugar (glucose→ glycogen)
alpha 1→4
alpha1→6 branches
Starch
Energy storage molecule in plants
contains:
amylose = long, unbranched chains of D-glucose connected by alpha 1→ 4
amylopectin = larger polymer of alpha 1→ 4 and alpha 1→ 6
alpha 1→ 4 structure
6 residue turn helix
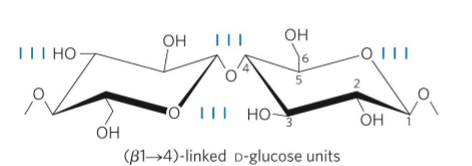
Cellulose
tough, fibrous, water-insoluble, stable
cell wall from plants
linear
unbranched
homopolysaccharide
D-glucose
Beta 1 → 4 (animals dont have enxyme to hydrolyze) (most stable linear structure)
Each chair is turned 180.
Stabilized by H-bonds
Chitin
Linear
homopolysaccharide
N-acetylglucosamine
Beta 1→4
Acetylated amino groups = hydrophobic bc OH on regilar sugar are hydrophillic
Bacterial cell wall
Gram (+) = 1 plasma membrane + 3 layers of peptidoglycan
Gram (-) = 2 plsama membranes + 1 layer of peptidoglycan
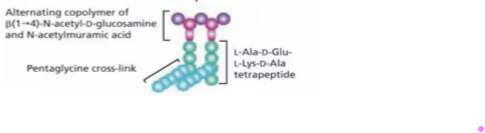
Peptidoglycan
Polysaccharide cross-link = alternating copolymer of Beta 1→4- N -acetyl-D-glucosamine + N-acetylmuramic acid
Peptide links L-Ala-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala tetrapeptide
Pentaglycine Cross-link by short peptides
Glycosaminoglycan
Animal Cell composition
Heteropolysaccharide in ECM (densely negative hydrophylic surface and attract Na+, growth factors and H2O) of cells
Viscosicty, adhesiveness, tensile strength
linear polyer of repeating disaccharide units linked through electrostatic interactions
Types of Glycosaminoglycans
Hyaluranon (GlcA + GlcNAc)
Keratan sulfate (Gal + GlcNAc65)
Chondroitin 4-sulfate (GlcA + GalNAc4S)
Heparin ( IdoA2S+ GlcNS3S6S) ( most negative charge)
One monosaccharide is always either N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine and the other is usually glucuronic acid or iduronic acid
Contains sulfate groups
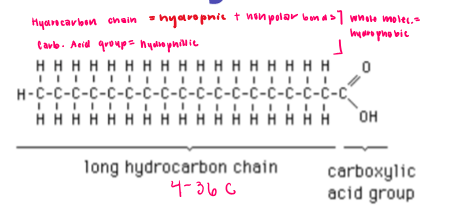
Fatty acid
Carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chains from 4-36 carbons long
Building block of fats
Oxidation of Fatty Acids
to CO2 and H2O is highly exergonic because hydrocarbon is highly reduced
Nomenclature for Unbranched Fatty Acids
18:1(delta9)
chain length : double bonds (location)
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
PUFA
Contaons more than one = in their backbone
PUFAs and Humans
must obtain alpha-linolenic acid (ALA;18:3(delta9,12,15)) from diet
humans use ALA to synthesize:
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; 20:5(delta5,8,11,14,17))
docosahexaenoic acid (DHA;22:6(delta 4,7,10,13,16,19))
Melting Point of Fatty Acids
@ room Temp:
Saturated fatty acids = solid
Unsaturated fatty acids are liquid
Triacylglycerols = fats = triglyceride
Fatty acid esters of glycerol
3 FA, each ester linkage with a single glycerol
simple ( one kind of FA)
Mixed ( 2/3 different FA)
Non-polar, Hydrophobic
Store Energy and Insulation
adipocyte + seeds with lipases
Biological waxes
esters of long-chain saturated and unsaturated FA + long = chain alcohols
Energy storage
Biological Membranes