Textiles - Specialist technical principles
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
What should a designer consider when selecting materials?
functionality, aesthetics, environmental factors, availability, cost, social factors, cultural factors, ethical factors
Examples of strengthening materials:
using interfacing on a skirt/trouser waistband or a neckline to stop the fabric stretching, using interfacing in a collar or cuffs to stiffen them and hold their shape, using interfacing behind buttons and button holes and pockets to strengthen the fabric or using a tightly woven fabric such as webbing from synthetic fibres.
Why are fabrics reinforced?
to be strengthened so they don't lose their shape or break during use
What is interfacing?
a woven or non-woven fabric used as an extra layer to give additional strength and help to keep the shape of a textile product
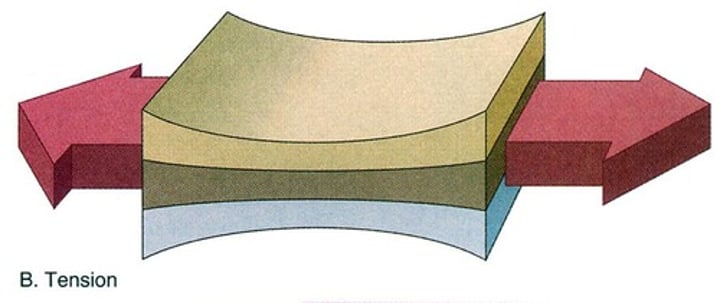
What is tension?
pulling or stretching force
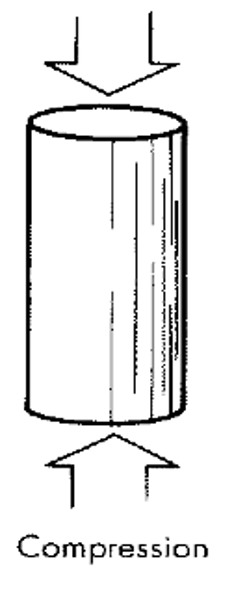
What is compression?
pushing forces that squeeze an object
What is shear?
force directed parallel to a surface

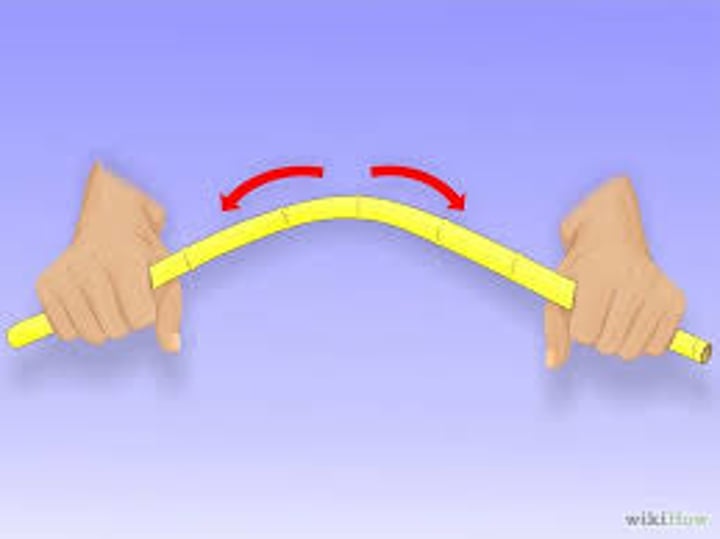
What is bending?
act on an angle to an object and makes it bend
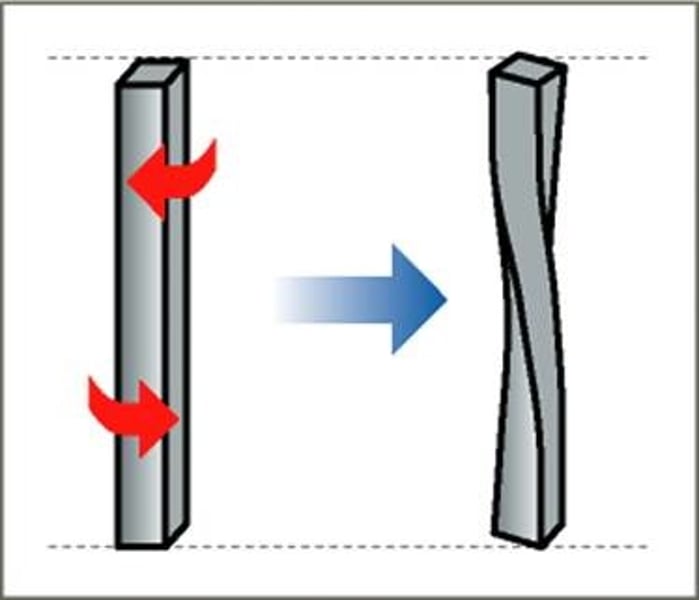
What is torsion?
a twisting force
What is mining?
Extracting ore or minerals from the ground
Positives of mining
employment, income, cheap materials
negatives of mining
pollutes water supplies and threatens indigenous populations
What is deforestation?
the action of clearing a wide area of trees.
what is land dredging?
miners digging at high pressures into the ground
what is river dredging?
moving along a river using a suction hose to collect gravel and mud
What is drilling?
The process of boring down into the earths crust to extract oil or gas
effects of drilling
distruption to the wildlife, chemicals are disposed into sea and ruin marine life
problems with growing cotton
they need a lot of chemical fertilisers and insecticides and can harm workers health, they use large quantities of water that can be used as drinking water
problems of farming
leads to deforestation of land for cotton crops and causes changes to the landscape and destroys habitats
effect of transporting textile materials
products from where they are made are transported to the country where they are sold uses fuel and puts pressure on transport systems
effects of textile waste
takes up a lot of landfill waste and toxic chemicals can leech out into surrounding land and waterways
problems with colouring processes
use a lot of chemicals and water - they're effluent and can pollute waterways
effects of the use of chemical finishes
flame retardancy can cause pollution of waterways and land if waste is not disposed of properly
6 Rs
Repair, reuse, recycle, rethink, reduce and refuse
How are synthetic fibers made?
made from petrochemicals from non renewable sources
why are polyester fibres more sustainable than synthetic fibres?
synthetic fibres take many years to decompose and polyester fibres can be recycled or made from recycled plastic bottles
What is Ingeo?
a biodegradable fibre that can replace polyester made from corn starch
benefits of organic cotton
better for the environment and has less impact on workers lives and health but is more expensive
fibres to replace cotton
regenerated fibres such as tencel and modal
how can we reduce carbon emissions?
reducing transport miles - products are made closer to were they are sold and use more sustainable forms of transport/ fuel
how can we reduce the water and chemicals in colouring cotton?
growing cotton fibres already coloured, newer and disperse dyes use little water and don't wash out in laundry
what are regenerated fibres
Fibres manufactured from the cellulose, for example from spruce trees or cotton linters
What is cotton?
natural cellulose from cotton plant
what is wool
natural protein from sheep or other animals
what is silk
natural protein made from cocoon of a silk caterpillar
what is polyester, polyamide and elastane
made from petrochemicals from coal or oil
what fibre type is cotton?
staple
what fibre type is wool?
staple
what fibre type is silk
filament
what fibre type is polyester, polyamide and elastane
filament
what's a filament fibre?
long continous lengths
whats a staple fibre
a shorter length fibre
what is the manufacture of cotton?
flat, ribbon like fibres are cleaned and twisted together
what is the manufacture of wool?
sheep are sheared and fibres are cleaned and twisted together
what is the manufacture of silk?
two triangular shaped filaments are held together with natural gum from the caterpillar
what is the manufacture of polyester, polyamide and elastane?
chemicals are made into a polymer which is melted then spun into smooth continuous fibres
What do fibres need before they can be made into woven or knitted fabrics?
they need to be spun into yarns
how are staple fibres formed?
carded so they lie in the same direction before they are spun into yarn
how are filament fibres formed?
lightly twisted to make a yarn
what's the effect of spinning?
holds the fibres together and adds strength
what happens when fibres are tightly twisted together?
the yarn will be strong and smooth but trap less air so are less insulating than loosely twisted fibres
what happens to filament fibres to be blended with staple fibres?
cut down into staple form
what are seedpods of the plant?
bolls that can burst and become fluffy
What type of fibre is cotton?
staple
what type of specialised fabrics are used in sportswear?
elastane - gives stretch, polartec fleece for lightweight thermal insulating garments, lightweight, breathable fabrics made from polyester or polyamide microfibres, moisutre management fabrics - coolmax, breathable and windproof, waterproof fabrics - goretex for outdoor sports
types of specialised fabrics used for furnishings:
fabrics with flame retardant finishes for upholstery and curtains, water-repellent fabrics, fabrics with a sanitised finish - hospital bedding, light-resistant fabrics and PVC-coated fabrics for tablecloths
chemicals that give flame retardancy:
proban and pyrovatex from cellulosic fibres that forms an insoluble cross-linked polymer so it wont wash out.
the effect of flame retardant synthetic fibres:
can cause serious burns when they melt
uses of flame retardancy:
important children's nightwear or furnishing fabrics
heat resistant fabrics
kevlar and Nomex in protective clothing for motorcycle and racing car driverss
What is neoprene?
synthetic rubber used in wetsuits, hoses, laptops/tablet covers, etc.
what are microencapsulated fibres?
contain insect and odor repellents
use of interactive fabrics:
contains conductive fibres such as carbon, silver and steel allow fabrics to have wearable electronics such as GPS, solar panels and performance monitors
Define fabric
a flat, sheet-form material and needs to be cut and shaped into products
what should u make sure a fabric is before use?
crease free and clean
Define template
a pattern shape, usually made from paper or card, used to cut out fabric to the size or shape required
What is the grainline?
marking on the pattern template that is placed on the straight grain of the fabric otherwise it won't hang properly in the finished product - must be checked with a tape measure for accuracy
Describe the process of cutting
both slevedges must be placed exactly on top of each other to keep the grain accurate when making double layer, the fabric must be pinned flat to the fabric at regular intervals to stop it moving
How to transfer markings on a template to the fabric?
using tailor's chalk, a tracing wheel and tracing paper or tailor's tack
What is tacking?
a temporary stitching to hold fabrics together until it's ready to be sewn permanently
Things to consider before making a seam:
they must be appropriate for the fabric, type of product and where its hidden or a decorative function
describe a plain seam
its flat and not seen on the outside of the product but the seam edges will need to be neatened to stop fraying.
describe a french seam
sewn twice so all the edges are enclosed and it is not visible on the outside of the product. Its a strong seam useful for fine fabrics as the turnings are hidden but it's bulky on thicker fabrics
describe a double-stitched seam
strong and flat with all the turnings enclosed. it's visible on the outside of the product so is often used as a decorative feature
How do you make a plain seam?
Put your two pieces of fabric with right sides together and the raw edges even.
Stitch along the seam allowance line. Common seam ⅜ inch (1cm), 1/2 or 1/4 of an inch. Always check your sewing instructions as these will vary by designer.
Neaten the raw edges. The edges may be pressed open and finished separately or pressed to one side and finished together
How do you make a french seam?
place fabrics wrong sides together and stitch on seamline. Press seam open and trim one seam allowance to 5mm. fold over seamline. stitch folded edge over
Hoe do you make a double-stitched seam?
Stitch a 5/8" standard seam with the right sides of the fabric together.2. Stitch again about 1/8" from the seam line in the seam allowance. A narrow zigzag stitch may be used for this second row of stitching.3. Trim the seam allowances close to the stitching.
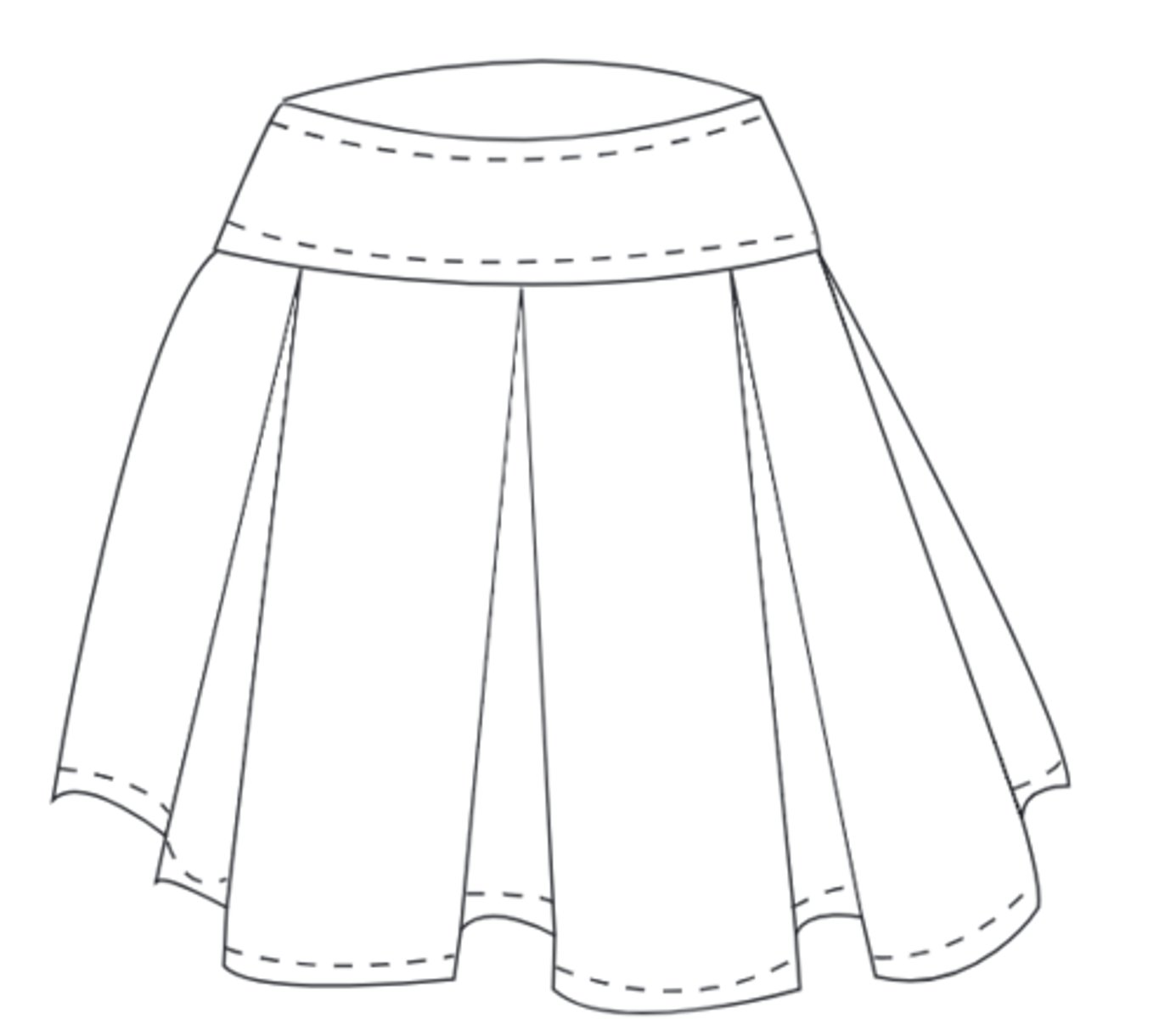
what are pleats?
folds in fabric that are stitched and pressed in place that allow for movement in clothing, add texture and a decorative effect
How are knife pleats made?
folds of the fabric over in one direction facing the same way
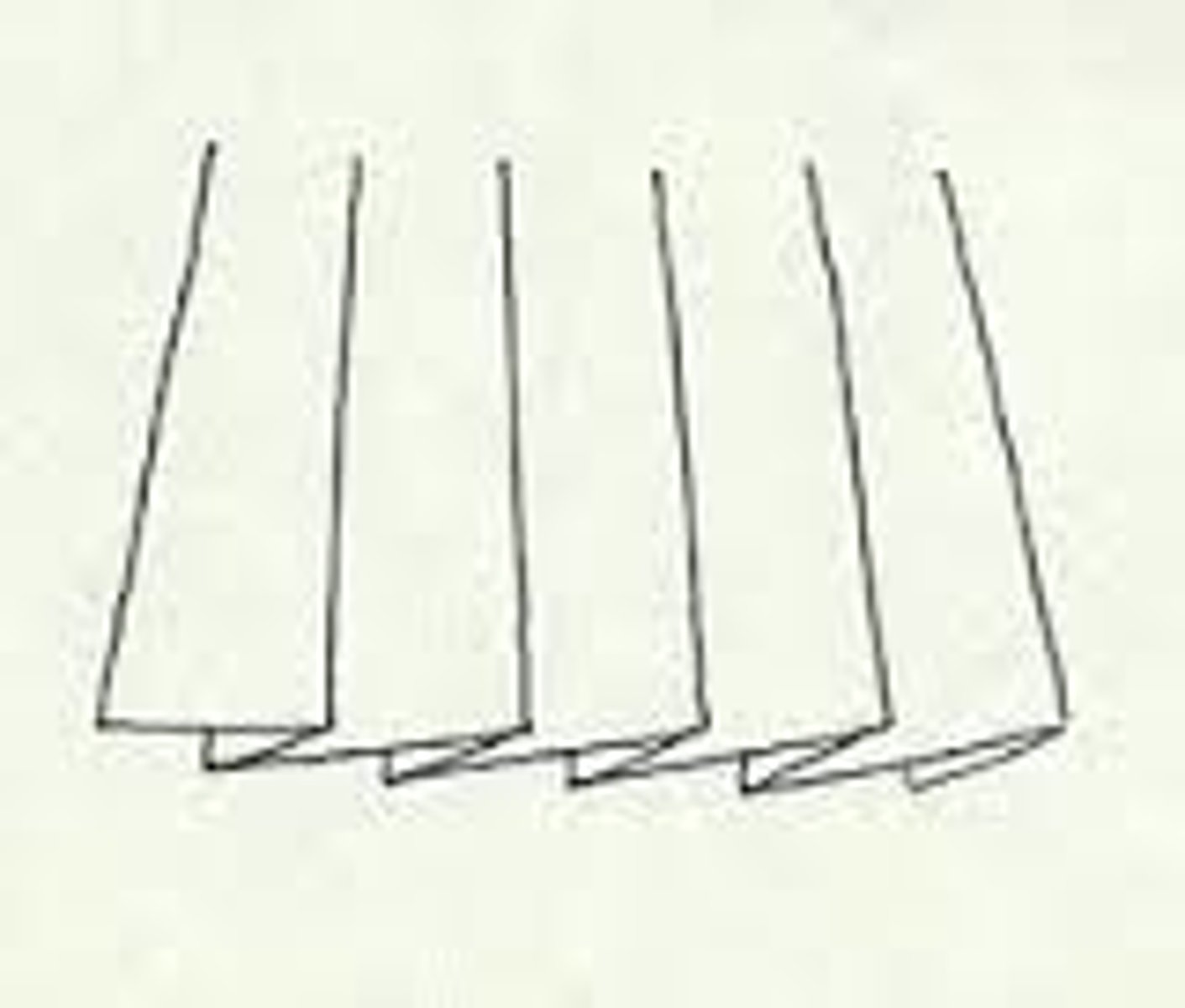
How are inverted pleats made?
two knife pleats facing each other
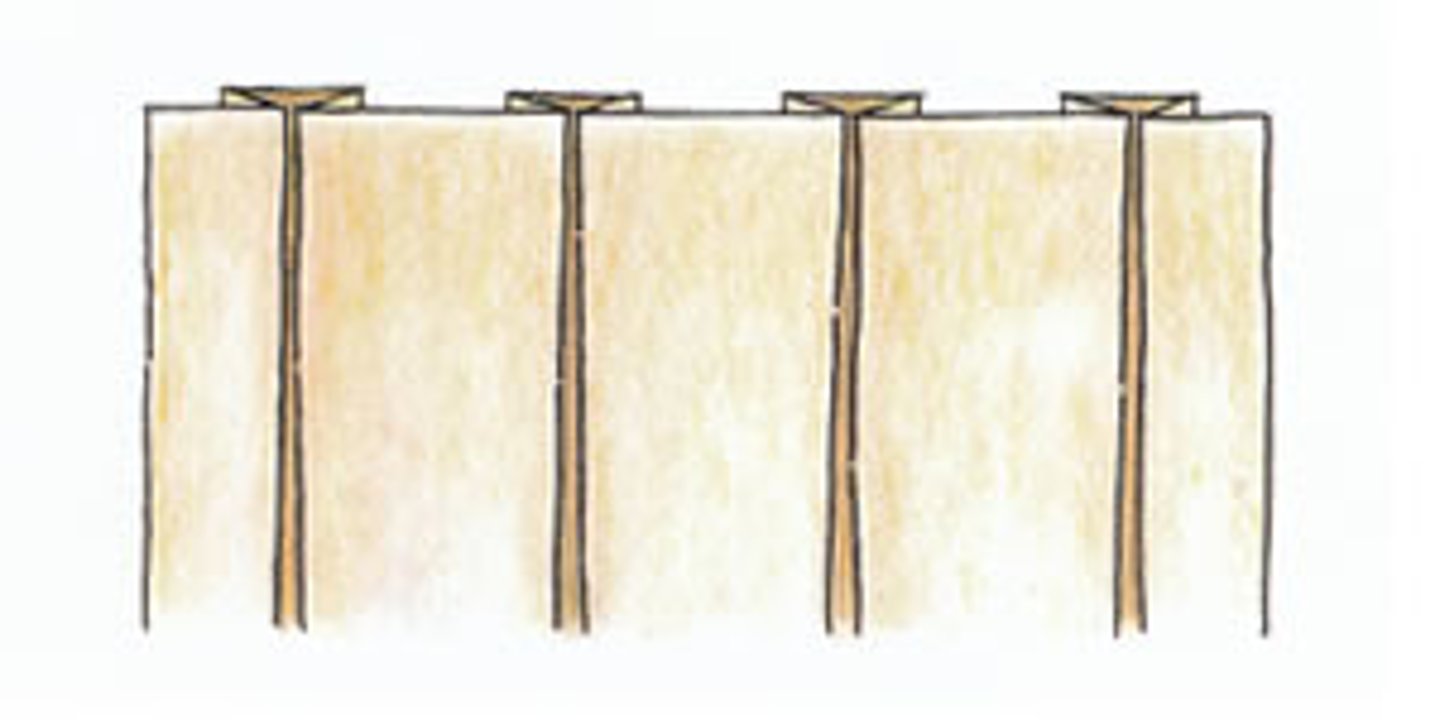
How are box pleats made?
two knife pleats facing away from each other
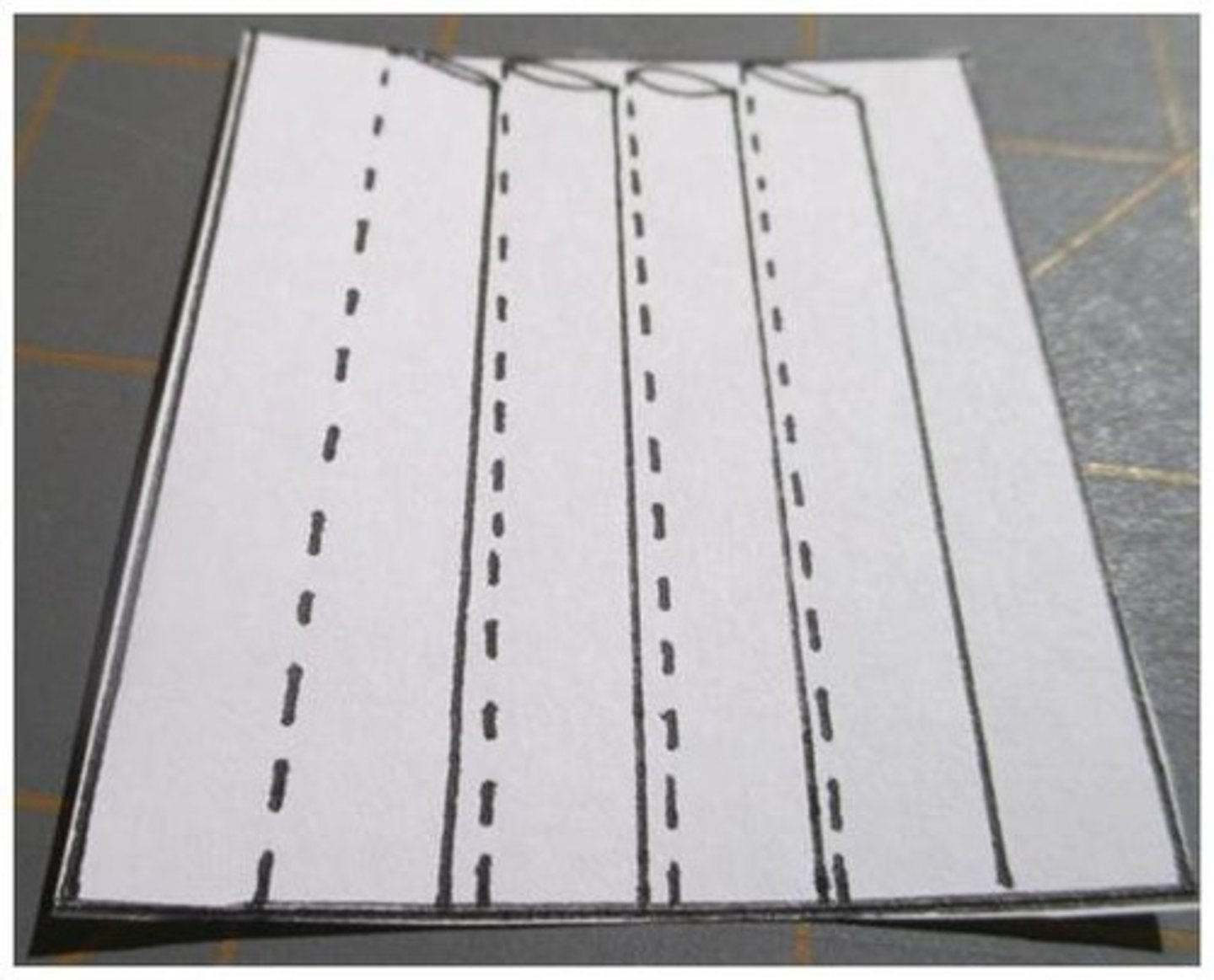
What are tucks?
narrow and stitched along their length - decorative feature
What is gathering?
fabric is drawn up using thread to reduce the length of the fabric
Uses of gathers?
to shape fabric, add ease and movement in clothing and as a decorative effect
Effect of quilting
adds texture and decoration of a product
process of quilting
consists of layers of wadding sandwiched between two layers of fabric and sewn in a decorative pattern
uses of quilting
to add warmth as the trapped air in wadding acts as an insulator
What is piping?
defines and strengthens an edge and can add decoration
How is piping made?
enclosing a cord in a strip of bias-cut fabric before stitching it into a seam
How are yarns made?
Yarns are made by spinning and twisting fibres together.
What is plying?
yarns twisted with other yarns to make them stronger so they can be used for many purposes
What is a ply of a yarn?
number of single strands in the yarn
What does the fabric width determine?
the amount needed to make a product - the wider, the less needed
what are general purpose threads made out of?
polyester fibres
How are embroidery threads made?
from different fibres and some are designed to make special effects
types of fastenings:
zips, buttons, velcro, poppers, press studs, and hook and eyes
What is one-off production?
A single unique product made by skilled workers such as wedding dresses or made-to-measure suits
What are bespoke/ one off products and examples?
> Tailor made to specific user needs
> Suits and dresses, Artwork, ceramics and jewellery, Architecture
What is batch production?
> Specific quantity of a product is made
> They can be repeated
> Machinery and workforce are flexible and could change to make a different batch
> Uses jigs, moulds and cheaper products
What aids manufacturing systems to change a new product quickly?
computer control is used to track what's made according to consumer's demand