Climate and biomes
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
climate
the typical atmospheric conditions that occur throughout the year, measured over many years
weather
the variation in temperature and precipitation over periods of hours or days
earth’s energy budget
the ratio of incoming and outgoing radiation
what kind of energy drives Earth’s climate
incoming ultraviolet, visible and infrared energy (shortwave radiation)
Visible light and UV light coming in goes back out as what in earths energy balance
reflected light (during daytime)
infrared radiation (heat) coming in goes out as what in earth’s energy budget
radiated heat (day- and nighttime)
how is some solar radiation reflected back into outer space?
by gases in our atmosphere and by earths surface
the solar radiation that is reflected back to outer space is in what for
light
how is some solar radiation absorbed
by gases in our atmosphere, as heat
how is most solar radiation absorbed
as heat, by Earth’s surface
earth re-radiates heat, which goes where?
some of the heat escapes the gasses in our atmosphere and goes into outer space
what happens to most re-radiagted solar radiation
re-absorbed (as heat) by Earth’s surface
how do greenhouse hasses contribute to this phenomenon
heat gets trapped by greenhouse gases and causes the heat to be redirected back toward the Earth’s surface
what are greenhouse gases (GHGs)
molecules in Earth’s atmosphere that absorb and re-emit infrared radiation (heat).
t/f: the concentration of GHGs in the atmosphere has large impacts on Earth’s climate
true
what percentage of gasses in the atmosphere are NOT GHGs
99%
what three factors affect solar radiation received at different latitudes
the distance that sunlight must travel through Earth’s atmosphere
the angle at which sunlight lights the Earth
the reflectivity of the Earth’s surface
how does the distance the sunlight must travel through earth’s atmosphere affect solar radiation received at different latitudes
shorter distance at equator causes less solar energy reflected by atmosphere
how does the angle at which sunlight hits earth affect solar radiation received at different latitudes
solar energy is spread over smaller area at equator (more concentrated)
how does the reflectivity of the earth’s surface affect solar radiation received at different latitudes
low albedo of dark forests at equator absorb more solar energy than ice at poles
t/f: earth’s tilt causes seasonal temperatures
true
when will the northern hemisphere receive more sunlight
between March 20 and September 22
when will the souther hemisphere receive more sunlight
between September 24 and march 18
when is march equinox
3/19
when is September equinox
9/23
can warm air or cool air hold more water vapor?
warm air
during march and September, where is precipitation most concentrated
over the equator
where is precipitation most concentrated in January
south of the equator
where is precipitation concentrated during June
north of the equator
what is the inter-tropical convergence zone (ITCZ)
the region that receives high levels of sunlight and rainfall
when is the ITCZ around the equator
in march and september
when is the ITCZ north of the equator
June
when is the ITCZ south of the equator
in December
what is a biome
a large community characterized by its climate and unique assemblage of plants and animals
what biome type is near the equator
tropical rainforests
what biome type is in the subtropics
deserts and tropical grasslands (savannas
what biome type is in the mid-latitudes (30° to 60°)
temperate forests and grasslands
what biome type is at high latitudes (60° to 70°)
taiga and tundra
what is taiga
cold forest
what is tundra
treeless, frozen soil
how are Hadley cells made
the sun heats the moist tropical air, causing it to rise
the rising air begins to cool, which causes water vapor to condense into rain and fall back to earth
after rising more than 10km into the atmosphere, the now cool, dry air circulates back to earth at approximately 30°N and 30°S latitudes
the cool dry air sinks and begins to warm. it reaches earth’s surface as warm, dry air and flows back toward the equator
how do Hadley cells explain why deserts are located at about 30°N and S
since the air and moisture being circulated in the Hadley cells curves towards the ITCZ ends at 30°N and S, the dry hot air is located at these latitudes
t/f:the ITCZ location changes throughout the year
true
what kind of precipitation patterns are seen between 0° and 23.5°N or S
wet and dry seasons, rather than fall/winter/summer/spring
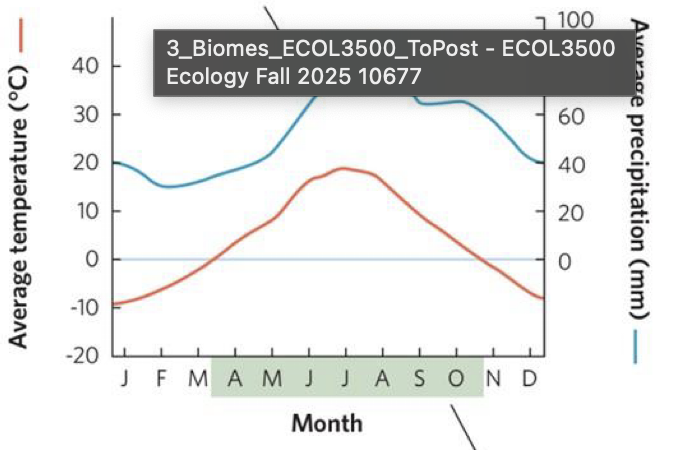
what does it mean when the precipitation line is above the temperature line on a climate diagram
plant growth is limited by temperature
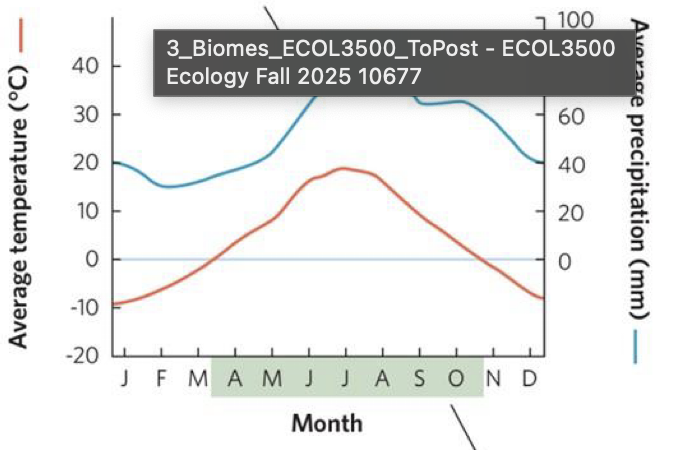
what does the green shaded region indicate
the growing season, when temperatures are above 0°C
what does it mean when the precipitation line is below the temperature line
plant growth is limited by precipitation
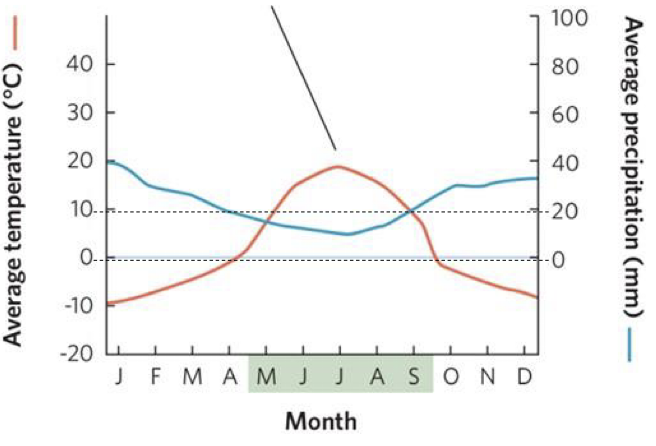
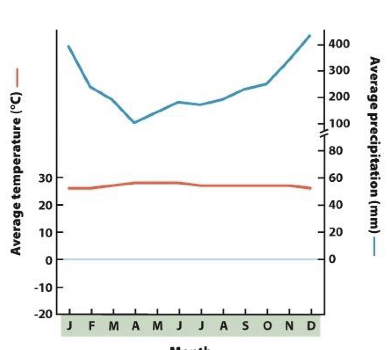
what biome does this chart represent
tundra
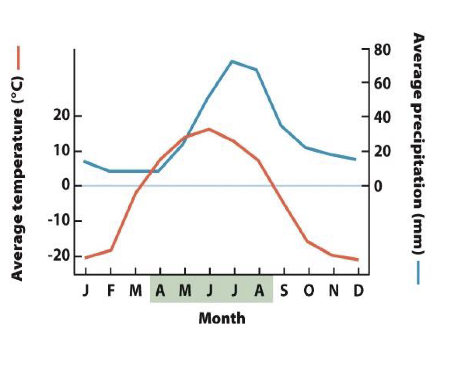
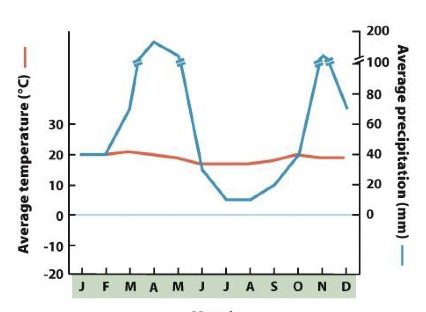
what biome does this graph represent and where is it located
tropical rainforest; near the equator
what is the climate like in tundra
a very cold desert', limited solar radiation and rainfall 6-10'“ per year (most precipitation is snow, unusable to plants), permafrost
how much is carbon is stored in the tundra
twice as much than the whole atmosphere
what is permafrost
frozen layer of subsoil
what is the climate like in the tropical rainforest
hot and lots of rain
what kind of nutrient and energy cycles are in the tropical rainforest
hi-speed, with plenty of water and light (there is a race for light)
what biome has the highest species diversity of plants and animals
tropical rainforest
what biome does this graph represent and where is it located
tropical savanna and between 10-20°N and S
what is the climate of the tropical savanna
warm-climate grassland, scattered trees with wet and dry seasons
other characteristics of the tropical savanna
woodlands/forests when wetter and grazers, rangelands: wild lands used for livestock production
where is the desert typically located
30°N or S
what is the climate of the desert
low rainfall (,25 cm of rain)
plants and animals have what to deal with extreme climate of the desert
adaptations