04.2 Consumption Function and Theories
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Consumption Function
C = f (Yd)
where C= Personal Consumption and Yd=Disposable Income
Disposable Income
Expenditure after taxes
Consumption is?
positively correlated by disposable income
Purpose of Consumption Function
Consumption expenditure depends on, varies with, is influenced by, or is explained or affected by disposable income
Main Determinants of Consumption
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
Average Propensity to Consume (APC)
Savings
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
Marginal Propensity to Consume Formula
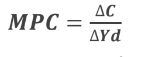
Purpose of MPC
measures change in consumption with respect to change in disposable income
slope of the consumption function or curve
Average Propensity to Consume Formula
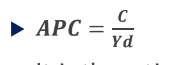
Average Propensity to Consume, Definition
ratio of consumption to income
Savings
Portion of income that is not spent or the difference of disposable income and consumption
Marginal Propensity to Save
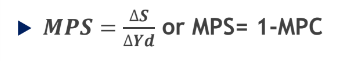
Marginal Propensity to Save, Definition
ratio of the change in savings to the change in disposable income.
Measures by how much savings change when income changes
Other determinants of Consumption
Wealth
Expected Income
Expected Price Level
Actual Price Level
Interest Rates
Age of Household Head
Attitude Toward Thrift, and etc.
Consumption Theories
Current Income Hypothesis
Permanent Income Hypothesis
Relative Income Hypothesis
Life Cycle Hypothesis
Current Income Hypothesis
Proposed by John Maynard Keynes
C = f(Yd)
Consumption depends on current Disposable Income
Permanent Income Hypothesis
Proposed by Milton Friedman
Consumption depends on permanent income, rather than transitory income
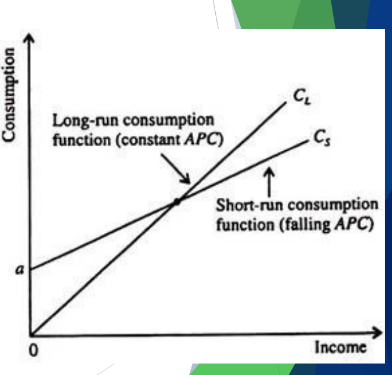
Relative Income Hypothesis
Proposed by James Duesenberry
2 explanation of consumption behavior of individuals:
Consumption of goods is greatly influenced by imitating neighbors spending
Households will try to maintain the highest standard of living in the past
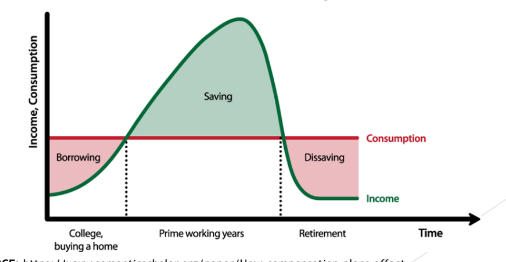
Life Cycle Hypothesis
Proposed by Albert Ando, Richard Brumberg, Franco Modigliani
Views that individuals plan their consumption and saving behavior over long periods with intention of allocating their income over lifetime