Health Science "EOC" terms and questions
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
1
New cards
Assessment
The evaluation or estimation of the nature, quality, or ability of someone or something
2
New cards
Signs
changes in a body that can be measured or observed as a result of disease
3
New cards
Symptoms
Subjective characteristics of disease felt only by the patient, tell a doctor what is wrong
4
New cards
complementary medicine
Alternative medicine when used simultaneously with, rather than instead of, standard Western medicine. Ex: acupuncture and chiropractic, meds and acupuncture complement each other, a more narrow field than integrative medicine is
5
New cards
palliative care
Care designed not to treat an illness but to provide physical and emotional comfort to the patient and support and guidance to his or her family. Ex: Hospice
6
New cards
Assisted living residence; ALR
Facility that provides housing, meals, and personal care to individuals who need help with daily living activities but do not need daily nursing care; may also be referred to as supportive housing, residential long -term care facilities, adult residential care facilities, board-and-care, and rest homes.
7
New cards
Cardiac Care Unit (CCU)
An intensive-care unit devoted to patients with acute or critical cardiac disease.
8
New cards
continuing care community
Provides a variety of living arrangements that support lifestyles as they change from independent living to the need for regular medical and nursing care
9
New cards
emergency room (ER)
also called an emergency department, focuses on diagnosing and treating life-threatening emergency medical conditions
10
New cards
General Unit
provides care for patients who are seriously ill but do not need a high level of specialized equipment and continuous nursing care
11
New cards
Hospice
a home providing care for the sick, especially the terminally ill.
12
New cards
intensive care unit (ICU)
area where patients are more critically ill, require additional monitoring, and are more susceptible to infections
13
New cards
intermediate care facility
A facility that provides health-related care and services to individuals who do not require the degree of care or treatment that a hospital or a skilled nursing facility provides but who still require medical care and services because of their physical or mental condition
14
New cards
Transitional Care Unit (TCU)
Hospital-based skilled nursing facility, Daily doctors, nurses, rehab, Patients often discharged home, assisted living or skilled nursing facilities
15
New cards
Psychiatric hospital
A facility that offers treatment to individuals with mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders
16
New cards
Rehabilitation unit
Therapies to regain physical and mental function
17
New cards
hospital
a place where sick or injured people are given care or treatment and where babies are often born
18
New cards
Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF)
a facility that provides 24-hour room, board, and skilled nursing care and treatment to at least three residents. Skilled nursing care and treatment services are those performed by or under the supervision of a registered nurse for individuals requiring 24-hour-a-day care by licensed nursing personnel and under the direction of a licensed doctor.
19
New cards
acupuncture
the practice of inserting fine needles through the skin at specific points to cure disease or relieve pain (Originally a Chinese practice)
20
New cards
chiropractic medicine
system of therapy based on the theory that disease is caused by pressure on nerves, aka science that investigates the relationship between the structure (the spine) and function (mainly the nervous system) of the human body to restore and preserve health
21
New cards
holistic medicine
an approach to health care that emphasizes prevention of illness and takes into account a person's entire physical and social environment ex: Naturopathy, Homeopathy, and Acupuncture.
22
New cards
Homeopathy (homeopathic medicine)
embraces a holistic, natural approach holistic treats the person as a whole, rather than focusing on a diseased part or a labeled sickness. natural because its remedies are produced according to the U.S. FDA-recognized Homeopathic Pharmacopoeia of the United States from natural sources, whether vegetable, mineral, or animal in nature.
23
New cards
massage therapy
manipulation of soft tissues by rubbing or kneading to achieve health benefits
24
New cards
osteopathy
bone disease
25
New cards
Reflexology
A unique method of applying pressure with thumb and index fingers to the hands and feet, and it has demonstrated health benefits.
26
New cards
therapeutic touch
an alternative therapy that involves using one's hands to consciously direct an energy exchange from the practitioner to the patient to facilitate healing or pain relief
27
New cards
Ethical dilemmas are:
problems about which more than one choice can be made and the choice made is influenced by the values and beliefs of the decision
28
New cards
professional code of ethics
A set of guidelines describing how members of a particular profession will pursue their common ideal so that each does his or her best to serve clients or patients, contribute to the good reputation of the field, and avoid pressures to engage in unethical behavior.
29
New cards
euthanasia
the act of painlessly killing a suffering person or animal; mercy killing
30
New cards
Patient's autonomy
the right of competent adults to make informed decisions about their own medical care.
31
New cards
Implied consent
Type of consent in which a patient who is unable to give consent is given treatment under the legal assumption that he or she would want treatment.
32
New cards
HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, a federal law protecting the privacy of patient-holistic treats the person as a whole, rather than focusing on a diseased part or a labeled sickness
33
New cards
advanced directive (living will)
document specifying the type of care wanted by the maker in the event of an incapacitating or terminal illness
34
New cards
assault
threat or attempt to injure; an attack
35
New cards
breach of contract
the nonperformance of a contractual duty. You didn't do what you signed you were gonna do.
36
New cards
contract
a binding agreement between two or more persons that is enforceable by law
37
New cards
Durable power of attorney for health care
document that designates a health care proxy, who is authorized make health care decisions for a client who is unable
38
New cards
False imprisonment
unlawful restraint or restriction of a person's freedom of movement
39
New cards
Libel
A written defamation of a person's character, reputation, business, or property rights.
40
New cards
Slander
the action or crime of making a false spoken statement damaging to a person's reputation.
41
New cards
agent
a person who acts or does business for another
42
New cards
Battery
unlawful touching of another person without consent
43
New cards
Confidentiality
Respecting the privacy of both parties and keeping details secret
44
New cards
defamation of character
Wrongfully hurting a person's good reputation. The law imposes a general duty on all persons to refrain from making false, defamatory statements about others.
45
New cards
express consent
an oral or written agreement
46
New cards
fraud
A deliberate deception intended to secure an unfair or unlawful gain
47
New cards
informed consent
an ethical principle that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
48
New cards
living will
A document that indicates what medical intervention an individual wants if he or she becomes incapable of expressing those wishes.
49
New cards
Human Development
the scientific study of the changes that occur in people as they age from conception until death
50
New cards
Ergonomics
the study of the human factors that affect the design and operation of tools and the work environment
51
New cards
Parasites
Organisms that grow, feed, and shelter on or in another organism (referred to as the host), while contributing nothing to the survival of that organism. Parasites must have a host to survive.
52
New cards
Pathogen
A disease causing agent
53
New cards
normal flora
Microorganisms that reside in or on the body without causing disease
54
New cards
Opportunistic infection
Infections that occur when the body's defenses are weakened
55
New cards
Aerobic
requires oxygen
56
New cards
antiseptic
a clean, sterile substance that prevents infection
57
New cards
disinfectant
any chemical agent used to destroy or inhibit the growth of harmful organisms
58
New cards
Sterilization
The process of destroying all microbes usually using high, concentrated, heat.
59
New cards
nosocomial infection
a disease acquired in a hospital or clinical setting
60
New cards
Stress
the reaction of the body and mind to everyday challenges and demands
61
New cards
Culture
Beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of people.
62
New cards
Medical Charting
is a complete record of a patient's key clinical data and medical history, such as demographics, vital signs, diagnoses, etc. Could be a whiteboard in the patient's room.
63
New cards
Dyspnea
difficulty breathing
64
New cards
Tachycardia
fast heart rate
65
New cards
hyper-
over, excessive
66
New cards
Cheyne-Stokes
abnormal breathing pattern; periods of dyspnea and apnea (difficult and stopped breathing)
67
New cards
Exhalation
breathing out
68
New cards
ADLs
Activities of Daily Living such as eating, dressing, bathing.
69
New cards
apical pulse
pulse taken with a stethoscope and near the apex of the heart
70
New cards
Afebrile
the absence of fever
71
New cards
bradypnea
abnormally slow breathing
72
New cards
sphygmomanometer
instrument to measure blood pressure, attaches to a cuff
73
New cards
Fee-for-service (for determining medical costs)v
A payment model where healthcare providers are paid for each service they provide to a patient.
* How it works: Providers bill for each service, and the payer (usually an insurance company) reimburses them based on a predetermined fee schedule.
* Pros: Encourages providers to offer more services, allows patients to choose their providers, and provides a clear payment structure.
* Cons: Can lead to overuse of services, may incentivize providers to prioritize quantity over quality of care, and can be expensive for patients without insurance.
* Examples: Medicare, Medicaid, and many private insurance plans use fee-for-service payment models.
* How it works: Providers bill for each service, and the payer (usually an insurance company) reimburses them based on a predetermined fee schedule.
* Pros: Encourages providers to offer more services, allows patients to choose their providers, and provides a clear payment structure.
* Cons: Can lead to overuse of services, may incentivize providers to prioritize quantity over quality of care, and can be expensive for patients without insurance.
* Examples: Medicare, Medicaid, and many private insurance plans use fee-for-service payment models.
74
New cards
Pre-existing health problem
is a health condition or disease that is present before a new health coverage starts
75
New cards
Co-pay
the amount of money the patient has to pay that the insurance company will not pay
76
New cards
Co-insurance
Requires the insured individual to pay a fixed percentage of the loss after the deductible has been paid
77
New cards
HMO
A group plan offering prepaid medical care to its members; health maintenance organization
78
New cards
PPO
Preferred provider organization. A prepaid health insurance plan in which providers agree to deliver services for discount fees; patients can go to any provider, but using nonparticipating providers results in higher costs to the patient
79
New cards
Premium
Amount you pay monthly, quarterly, semiannually or annually to purchase different types of insurance
80
New cards
Deductible
Amount you must pay before you begin receiving any benefits from your insurance company
81
New cards
What does it mean when a health care professional obtains a license/certification?
The healthcare professional is qualified enough and legally allowed to practice.
82
New cards
What are the responsibilities of the local health department?
Continuously assess needs and improve capacity to promote better health. Whether assessing community health, implementing quality improvement efforts, or pursuing accreditation, local health departments maximize opportunities to improve public health practice and the public's health.
83
New cards
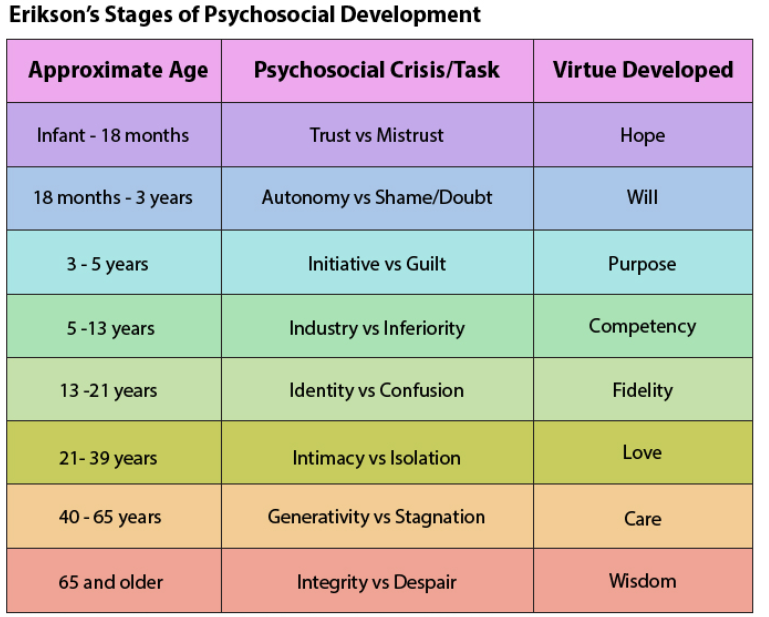
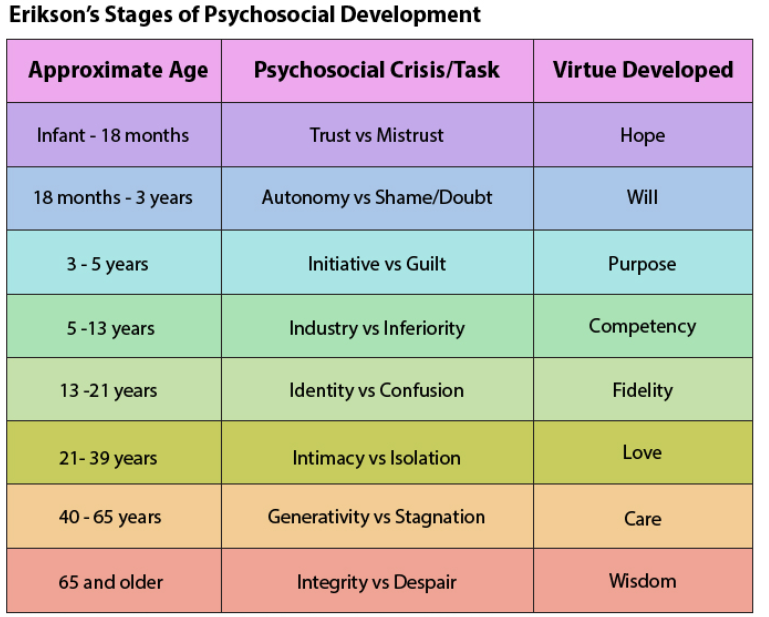
Erikson’s stages of development
84
New cards
Stage 1- Infancy stage Trust vs. Mistrust
* Virtue: Hope, Maldevelopment: Withdrawal
* Concomitant Freudian stage: oral stage
* Example: Secure environment provided by the caregiver, with regular access to affection and food
* Concomitant Freudian stage: oral stage
* Example: Secure environment provided by the caregiver, with regular access to affection and food
85
New cards
Stage 2 – Early Childhood period: Autonomy vs. Shame, doubt
* Virtue: Will, Maldevelopment: Compulsion
* Concomitant Freudian stage: anal stage
* Example: Caregiver promotes self-sufficiency while maintaining a secure environment
* Concomitant Freudian stage: anal stage
* Example: Caregiver promotes self-sufficiency while maintaining a secure environment
86
New cards
Stage 3 – Play Age period: Initiative vs. Guilt
* Virtue: Purpose, Maldevelopment: Inhibition
* Concomitant Freudian stage: genital stage
* Example: Caregiver encourages, supports, and guides the child’s own initiatives and interests
* Concomitant Freudian stage: genital stage
* Example: Caregiver encourages, supports, and guides the child’s own initiatives and interests
87
New cards
Stage 4 – School Age period: Industry vs. Inferiority
* Virtue: Competence, Maldevelopment: Inertia (passivity)
* Concomitant Freudian stage: latency stage
* Example: Reasonable expectations set in school and at home, with praise for their accomplishments
* Concomitant Freudian stage: latency stage
* Example: Reasonable expectations set in school and at home, with praise for their accomplishments
88
New cards
Stage 5 – Adolescence period: Identity vs. Identity confusion
* Virtue: Fidelity, Maldevelopment: Repudiation
* Example: Individual weighs out their previous experiences, societal expectations, and their aspirations in establishing values and ‘finding themselves.’
* Example: Individual weighs out their previous experiences, societal expectations, and their aspirations in establishing values and ‘finding themselves.’
89
New cards
Stage 6 – Young Adulthood period: Intimacy vs. Isolation
* Virtue: Love, Maldevelopment: Distantiation
* Example: Individual forms close friendships or long-term partnership
* Example: Individual forms close friendships or long-term partnership
90
New cards
Stage 7 – Adulthood period: Generativity vs. Stagnation/Self-absorption
* Virtue: Care, Maldevelopment: Rejectivity
* Example: Engagement with the next generation through parenting, coaching, or teaching
* Example: Engagement with the next generation through parenting, coaching, or teaching
91
New cards
Stage 8 – Old Age period: Integrity vs. Despair
* Virtue: Wisdom, Maldevelopment: Disdain
* Example: Contemplation and acknowledgment of personal life accomplishments
* Example: Contemplation and acknowledgment of personal life accomplishments
92
New cards
5 stages of Denial- Elizabeth Kubler-Ross
1. Denial
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. Depression
5. Acceptance
93
New cards
Proper way to lift objects
Bend at hips, use legs, no knees or back
94
New cards
What is the body's immune response?
In an immune response, the immune system recognizes the antigens (usually proteins) on the surface of substances or microorganisms, such as bacteria or viruses, and attacks and destroys, or tries to destroy, them.
95
New cards
Pathogen
disease-causing agents
96
New cards
Opportunistic Infection
occurs when when the immune system is weakened
97
New cards
Normal flora
The regular bacteria that live in your body.
* Normal flora refers to the microorganisms that live on or within the human body without causing disease.
* These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the human body by aiding in digestion, producing vitamins, and preventing the growth of harmful bacteria.
* The composition of normal flora varies depending on the location in the body, with different types of bacteria, fungi, and viruses found in different areas.
* Disruption of normal flora can lead to infections and disease, such as bacterial vaginosis and Clostridium difficile infection.
* Factors that can disrupt normal flora include antibiotic use, poor hygiene, and changes in pH levels.
* Normal flora refers to the microorganisms that live on or within the human body without causing disease.
* These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the human body by aiding in digestion, producing vitamins, and preventing the growth of harmful bacteria.
* The composition of normal flora varies depending on the location in the body, with different types of bacteria, fungi, and viruses found in different areas.
* Disruption of normal flora can lead to infections and disease, such as bacterial vaginosis and Clostridium difficile infection.
* Factors that can disrupt normal flora include antibiotic use, poor hygiene, and changes in pH levels.
98
New cards
How do we treat a virus? What is ineffective?
For most viral infections, treatments can only help with symptoms while you wait for your immune system to fight off the virus. __**Antibiotics do not work for viral infections.**__ There are antiviral medicines to treat some viral infections. Vaccines can help prevent you from getting many viral diseases.
99
New cards
Antiseptic
* Antiseptics are substances that kill or prevent the growth of microorganisms on living tissue.
* They are commonly used to clean wounds and prevent infections.
* Common antiseptics include alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and iodine.
* They are commonly used to clean wounds and prevent infections.
* Common antiseptics include alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and iodine.
100
New cards
Disinfectant
(usually) More powerful than antiseptics EX: sterilization high concentrated heat to kill all bacteria. Only used on objects and surfaces, not people.
* Effectiveness against viruses and bacteria
* Common disinfectants: Lysol, Clorox, Purell
* Effectiveness against viruses and bacteria
* Common disinfectants: Lysol, Clorox, Purell