Rheumatology
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Rheumatoid arthritis - antibodies? When would you do XRs? XR findings?
Antibodies – RF 70-80%, Anti-CCP antibody (test for this if suspecting and RF negative)
XR – hands and feet of all pts with suspected RA
- Periarticular osteopenia
- Bony erosions
- Soft tissue swelling
- Joint destruction, loss of joint space
RA - disease activity score? Management - initial, assessing response, flare, 2nd line treatment?
DAS28
Management:
Initially DMARD monotherapy (methotrexate, sulfasalazine) +/- short course prednisolone
CRP and DAS28 to assess response
Flare – oral/IM corticosteroids
TNF-inhibitor (infliximab) if inadequate response to at least 2 DMARDs including MTX
Next line - Rituximab
What is Felty’s syndrome?
Triad of RA, splenomegaly, neutropenia
Methotrexate - adverse affects? Co-prescribed with? Monitoring? What meds would you avoid?
· Adverse effects – myelosuppression, pneumonitis, liver fibrosis
· Taken weekly – co-prescribe with folic acid – not taken on same day
· FBC, U&E, LFT monitoring before starting, weekly until stabilised and then every 2-3 months
· Avoid with trimethoprim, co-trimoxazole – risk of marrow aplasia
Osteoarthritis - XR changes? Management?
· XR – loss of joint space, subchondral sclerosis, subchondral cysts, osteophytes forming at joint margins
· Management – topical NSAIDs → oral NSAIDs
Ankylosing spondylitis - gene? Feature? XR changes? Management?
HLA-B27
Reduced lateral flexion of lumbar spine
XR – sacroiliitis, squaring of lumbar vertebrae, bamboo spine (late, uncommon), syndesmophytes, CXR – apical fibrosis
NSAIDs are 1st line management. DMARDs only useful if peripheral joint involvement
SLE - type of hypersensitivity reaction? ESR and CRP? Associated antibodies and complements? Management?
· Type 3 hypersensitivity reaction
· High ESR, normal CRP
· ANA, anti-dsDNA, anti-Ro, anti-Sm, anti-a
· Low C3, low C4
· Hydroxychloroquine – retinopathy risk – baseline ophtho exam and annual screening
· Corticosteroids, immunosuppressants if severe
Psoriatic arthritis - which joints? XR changes?
· DIPS (spared in RA)
· XR – periostitis, ankylosis, osteolysis, dactylitis, pencil-in-cup deformity
Reactive arthritis - triad? Causative organisms? When do sx present and how long do they last?
· Arthritis, urethritis, conjunctivitis
· Post-STI (chlamydia), post-dysenteric (shigella, salmonella)
· Sx within 4 weeks of initial infection, last 4-6 months
Anti-phospholipid syndrome - features? Associated antibodies? APTT?
· Venous and arterial thromboses, recurrent fetal loss, thrombocytopenia
· Antibodies – lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin, anti-beta-2 glycoprotein I – at least 1 on 2 occasions 12 weeks apart
· Paradoxical rise in APTT – prolonged
Antiphospholipid syndrome - primary thromboprophylaxis? Secondary thromboprophylaxis? Pregnancy/planning pregnancy management?
· Primary thromboprophylaxis – low-dose aspirin, LMWH in high-risk scenarios
· Secondary thromboprophylaxis – initial VTE = lifelong warfarin INR target 2-3. Recurrent VTE while on warfarin = lifelong warfarin, target INR 3-4, consider adding aspirin
· Arterial thrombosis = lifelong warfarin INR target 2-3
· Pregnancy/planning = low dose aspirin plus LMWH
Sjogren’s - associated antibodies? Investigations? Management?
· Anti-Ro, anti-La
· RF 50%, ANA 70%
· Schirmer’s test, histology – focal lymphocytic infiltration
· Artificial saliva and tears, pilocarpine can stimulate saliva production
Systemic sclerosis - 3 types? What is affected in each? Associated antibodies with each?
Limited cutaneous
- Raynaud’s, scleroderma affects face and distal limbs mostly
- Subtype is CREST – Calcinosis, Raynaud’s, Esophageal dysmotility, Sclerodactyly, Telangiectasia
- ANA, anti-centromere
Diffuse cutaneous
- Scleroderma affects trunk and proximal limbs mostly
- ANA, anti-scl-70
- Common cause of death resp involvement, renal disease (captopril usually used – rapid onset and short half-life)
Scleroderma (without internal organ involvement)
- Tightening and fibrosis of skin
Polymyalgia rheumatica - age? Onset? Symptoms? Management?
>60, onset <1 month
Morning stiffness proximal limb muscles
15mg prednisolone daily 1-2 years – usually respond dramatically
F/u after 1 week
Giant cell arteritis - features? Fundoscopy findings? Biopsy findings? Management?
Headache, jaw claudication
RAPD, can get amaurosis fugax
50% have PMR features
Fundoscopy – swollen pale disc and blurred margins
Temporal artery biopsy – granulomatous inflammation with multinucleated giant cells. If negative biopsy, cannot be fully ruled out due to skip lesions.
Start steroids before biopsy, same day ophtho review
40-60mg prednisolone (high dose steroids) daily if no visual/jaw symptoms
500mg-1000mg methylprednisolone daily otherwise
Treat for 1-2 years
Polymyositis/dermatomyositis - features? What is raised? Antibodies? Management?
Dermatomyositis - proximal muscle weakness (PMR doesn’t cause weakness), gottron’s papules on back of hands, heliotrope rash affecting eyelids
Poly is same but without skin involvement
CK raised
ANA positive
Anti-Jo-1 antibodies, anti-Mi-2 antibodies – myositis specific antibodies
Manage with high-dose steroids
Behcet’s disease - what is it? Triad? Gene variant? Investigations?
Complex multisystem disorder, presumed autoimmune-mediated inflammation of arteries and veins
Triad – oral ulcers, genital ulcers, anterior uveitis
Thrombophlebitis, DVT, arthritis, GI stuff
Relapsing-remitting
HLA-B51
Oral and genital ulcers – red halo
Pathergy test suggestive of diagnosis, no definite test
Gout - drug causes? Diagnosing with uric acid? XR changes? Management of flare and long-term?
Drug causes – diuretics, ciclosporin, alcohol, pyrazinamide, aspirin
Uric acid >360 = diagnostic. <360 – if strongly suspected repeat 2 weeks after flare settled
XR – joint effusion, well-defined ‘punched-out’ erosions with sclerotic margins, preservation of joint space until late disease, no periarticular osteopenia (vs RA)
Flare – NSAID, colchicine
Allopurinol, febuxostat
Pseudogout - risk factors? XR changes?
Risk factors – dehydration, hyperparathyroidism, surgery, trauma, low magnesium
XR – chondrocalcinosis
Osteoporosis - if someone has had a fragility fracture when would you start bisphosphonates without DEXA?
>75
Paget’s disease - what is it? Blood results? XR findings? Complications? Management?
· Excessive bone turnover
· High ALP, normal calcium and phosphate
· XR – osteolysis in early disease, mixed lytic/sclerotic lesions later
· Skull XR – thickened vault, osteoporosis circumscripta
· Can cause hearing loss, osteosarcoma, heart failure, spinal stenosis
· Bisphosphonates
Osteomalacia - what is it? Blood results? XR findings? Management?
Softening of bones due to low vit D which causes decreased bone mineral content. (rickets in kids)
Low vit D, low phosphate, low calcium
High PTH, high ALP
XR – translucent bands (Looser’s zones or pseudofractures)
Osteogenesis imperfecta - inheritance pattern? Features? Blood results?
Autosomal dominant
Childhood onset, fractures following minor trauma
Blue sclera, deafness.
Normal calcium, phosphate, PTH, ALP
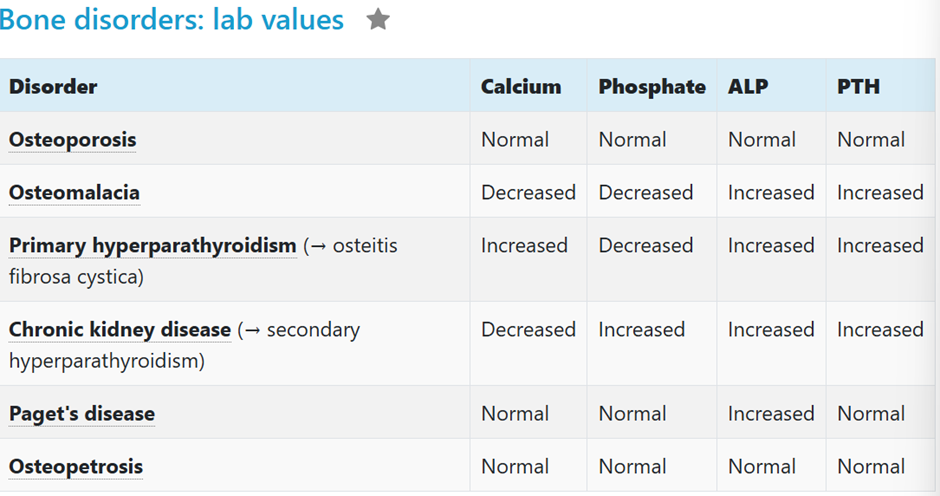
Calcium, phosphate, ALP, PTH in 1) Osteoporosis? 2) Osteomalacia? 3) Primary hyperparathyroidism? 4) CKD? 5) Paget’s disease?
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome - inheritance pattern? What does it affect? Features? Scoring system? Ix? Management?
· Autosomal dominant – mostly affects type III collagen
· Hypermobility and POTS, fragile skin, easy bruising, AR, mitral valve prolapse
· Beighton score
· ECHO recommended, can do genetic testing
· Management – supportive, CVS monitoring
Marfan’s syndrome - inheritance pattern - features?
Autosomal dominant
Tall, high arched palate, arachnodactyly, pectus excavates, scoliosis, heart disease – dilatation of aortic sinuses, mitral valve prolapse, lungs – pneumothoraces, eye issues
Benign bone tumours? (3)
Osteoma – overgrowth of bone, typically on skull
Osteochondroma – bony projection on external surface of bone
Giant cell tumour – epiphyses of long bones, XR shows double bubble appearance
Malignant bone tumours? (3)
Osteosarcoma metaphyseal region of long bones prior to epiphyseal closure, XR shows Codman triangle and sunburst pattern
Ewing’s sarcoma – pelvis and long bones, XR shows ‘onion skin’ appearance
Chondrosarcoma – axial skeleton
Vasculitis - Small? Medium? Large?
Small
- HSP – no thrombocytopenia!!
- Microscopic polyangiitis – P-ANCA
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis – C-ANCA
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis – P-ANCA, high ESR, late-onset asthma
Medium
- Polyarteritis nodosa – renal impairment, HTN, CVD, tender skin nodules
- Kawasaki disease
Large
- Giant cell arteritis – high ESR
- Takayasu’s arteritis – aortic arch affected, pulseless disease
Before starting biologics what test would you do?
IGRA as can reactivate TB
What test would you do before starting azathioprine?
TPMT test to look for individuals prone to toxicity (TPMT metabolises it)
CFS - duration of sx for a diagnosis?
3 months
Raynaud’s management?
CCB 1st line e.g. nifedipine