Cardiac Cycle
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Superior/inferior vena cava
Where oxygen-poor blood from upper and lower body moving to right atrium
Right atrium, tricuspid
Oxygen-poor blood from vena cava moves to __ __, permitting opening of the __ valve
right ventricle, tricuspid
Oxygen-poor blood from right atrium moves to __ __, permitting closing of the __ valve
pulmonary artery, pulmonary
Oxygen-poor blood from right ventricle moves to __ __, permitting closing of the __ valve
Vein
Oxygen-rich blood returns from lungs thru pulmonary __
Left atrium, mitral
Oxygen-rich blood from pulmonary vein moves to __ __, permitting opening of the __ valve
Left ventricle, mitral
Oxygen-rich blood from left atrium moves to __ __, permitting closing of the __ valve
Aortic valve, aorta
Oxygen-rich blood from left ventricle moves to __ valve, opening of this valve allows entry to __ and spread blood thru body
Systole
Heart contraction, pumping/ejecting of blood (systole vs diastole)
Diastole
Heart relaxation, filling of blood (systole vs diastole)
Late diastole
Atria and ventricles are relaxed and AV valves are open
Fluid flows passively from atria into ventricles
Ventricular filling
(cardiac cycle)
Atrial systole
Atrial contraction pushes small amount of additional blood into ventricles
(cardiac cycle)
Isovolumic Ventricular Contraction
Ventricles start to contract and generate enough pressure to close AV valves (“lub”)
Semilunar valves remain closed
Pressure builds in ventricles without changing volume
(cardiac cycle)
Ventricular Ejection (ventricular systole)
When pressure in ventricles exceeds pressure in arteries, semilunar valves open and blood is ejected
(cardiac cycle)
Isovolumic Ventricular Relaxation
Ventricular pressure falls below artery pressure
Snaps semilunar valves closed (“dub”)
Without change in volume since both sets of valves are closed
(cardiac cycle)
Systemic arteries, pulmonary vein, umbilical vein
(3) vessels carrying oxygenated blood
Systemic veins, pulmonary artery, umbilical artery
(3) vessels carrying deoxygenated blood
Pressure, higher, lower, pressure, resistance
Fluid (i.e. liquids, gases) flows down __ gradients
Blood flows from a __ to a __ pressure (lower vs higher)
Flow is proportional to __ and inversely proportional to __
Contraction, relaxation
Pressure gradients are generated by cardiac __ and __ (actions)
Cardiac Output
Volume of blood pumped to the entire body, per unit of time
Units: L/min
stroke volume x heart rate
Cardiac output = ?
Stroke volume (SV)
How much blood ejected per beat
EDV - ESV
Stroke volume = ?
EDV, ESV
__ is the amount of blood in ventricle when it is full
__ is the amount of blood left in ventricle after it ejects blood
Ejection Fraction (EF)
Percent of blood in ventricle ejected each beat
SV / EDV x 100
Ejection fraction = ?
EF, low contractility, increased afterload
A low __ can mean decreased ability to squeeze (__ __) OR
Heart pushing against increased resistance (__ __load)
EF and systolic heart failure
Atrioventricular (AV) Valves
Tricuspid and mitral/bicuspid (valve type)
Semilunar Valves
Pulmonary and aortic (valve type)
Lub
AV valves (mitral and tricuspid) close (lub vs dub)
Dub
Semilunar valves close (lub vs dub)
Stenosis
Blood being forced through stiff/narrowed valve (turbulent flow)
Regurgitation
Backward flow through valve that hasn’t closed completely (turbulent flow)
Openings between chambers
Septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus leads to backflow (turbulent flow)
Normal EKG
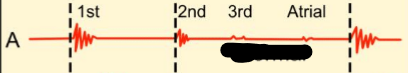
Aortic stenosis
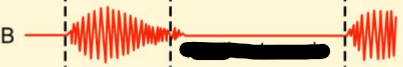
Mitral regurgitation

Aortic regurgitation

Mitral stenosis

Patent ductus arteriosus (heart defect)
