PDTI Mod 1: Introduction to Drug Therapy Individualization
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
B
Which of the following correctly defines pharmacokinetics?
A. What the drug does to the body
B. What the body does to the drug
C. How a drug binds to receptors
D. How effects are produced after a drug binds to receptors
A
Which of the following correctly defines pharmacodynamics?
A. What the drug does to the body
B. What the body does to the drug
C. How a drug is absorbed and distributed throughout the body
D. How a drug is metabolized and eliminated by the body
C
The concentration vs time graph shown is representative of which of the following?
A. Pharmacodynamics/Pharmacokinetics
B. Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
C. Pharmacokinetics
D. Pharmacodynamics
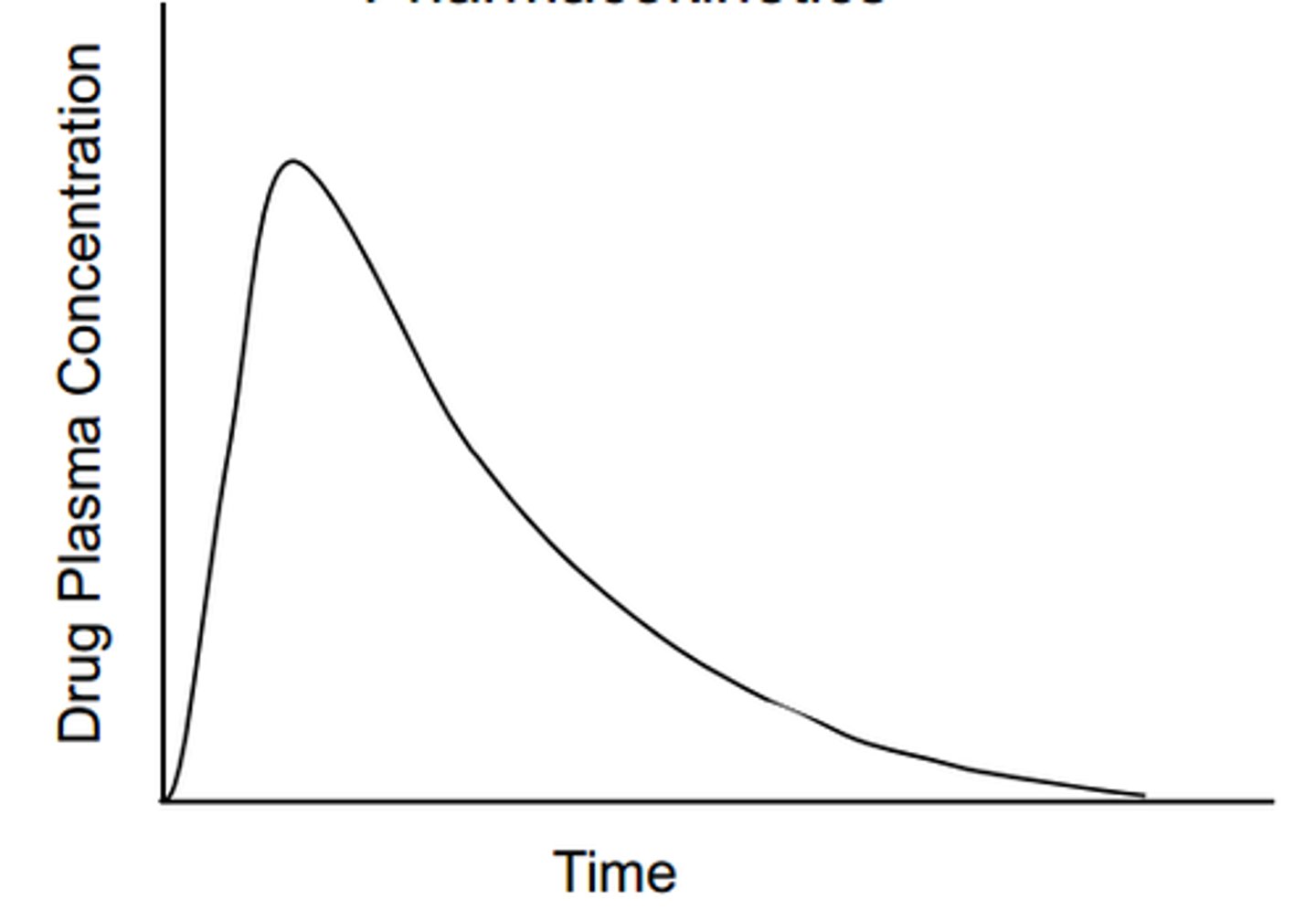
D
The concentration vs time graph shown is representative of which of the following?
A. Pharmacodynamics/Pharmacokinetics
B. Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
C. Pharmacokinetics
D. Pharmacodynamics
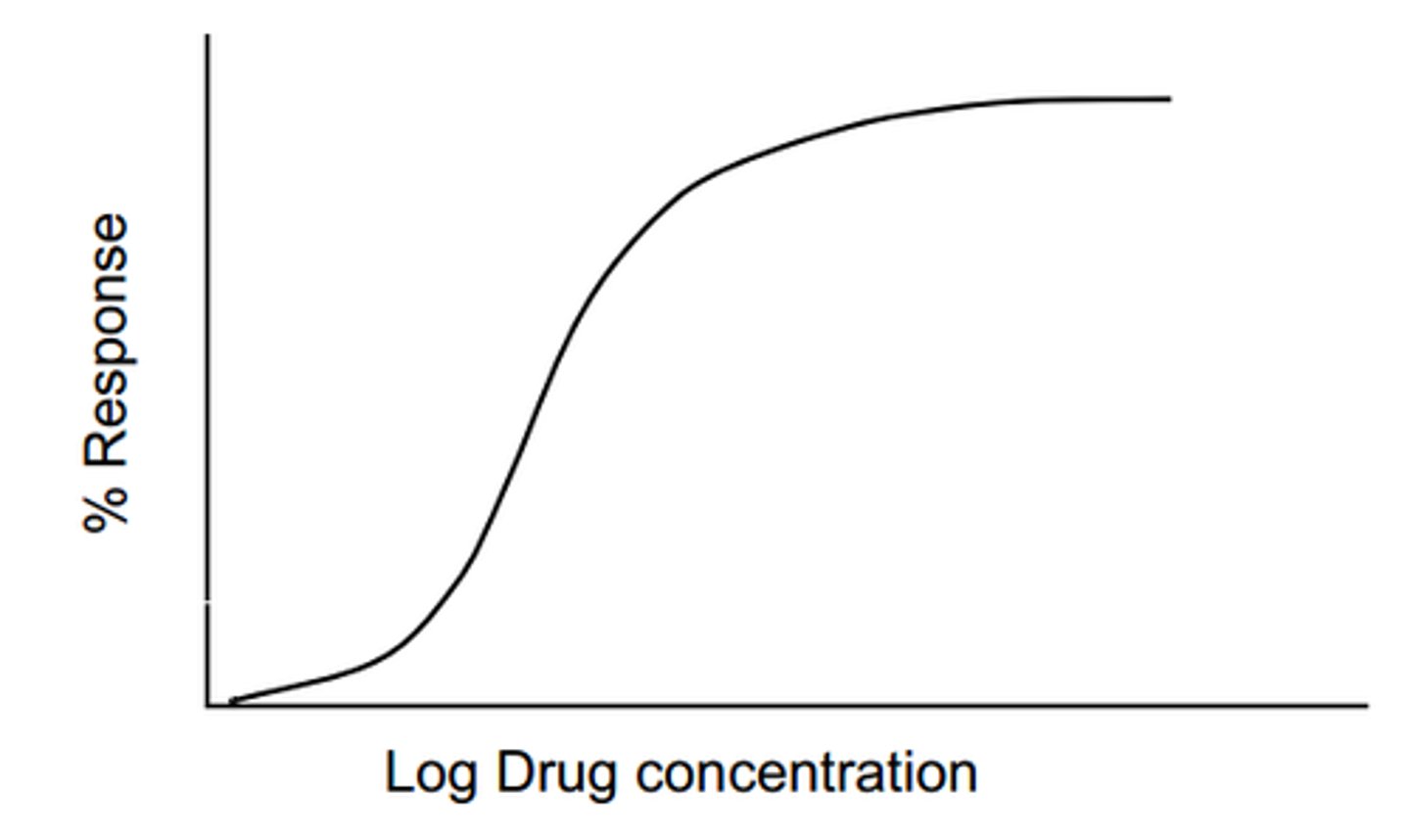
E
Which of the following is not an action of the body on a drug?
A. Absorption
B. Distribution
C. Metabolism
D. Elimination
E. Side Effects
B
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring is:
A. Not useful in optimizing drug dosage for patients on an individual basis
B. Especially useful for drugs with a narrow therapeutic window
C. Especially useful for drugs with a wide therapeutic window
D. Used often when risk of toxicity is low
E. Outdated and not performed clinically
B
Which of the following statements is true?
A. Drug targets are typically located in blood/plasma.
B. Drug targets are typically located in tissues and organs.
C. Drug targets are typically located in red blood cells.
D. Plasma concentrations of drug always correlate well with the target concentrations of the drug.
E. Target concentrations of drug are always easy to measure as compared to plasma concentrations
E
Which of the following does not affect the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic properties of a drug?
A. Genetic Polymorphisms
B. Dosage Forms
C. Demographics of Study Population
D. Routes of Administration
E. Switching to a generic version of a drug
B
Which of the following statements is/are true for a narrow therapeutic index drug?
A. Takes longer to elicit its therapeutic effects
B. Small changes in dose or interaction with other drugs could cause adverse effects.
C. Therapeutic drug monitoring is typically not required.
D. Pharmacokinetic variability is usually very low.
E. Pharmacodynamic variability is usually very low.
A
If warfarin was given to a large sumo wrestler, they could potentially bleed to death while the small sumo wrestler given the same dose would be just fine. This is due to variation in metabolism abilities.
A. True
B. False