Production, costs and revenue
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is production?
Converts inputs into outputs of goods/services
What is short run production?
When a firm adds variable factors of production to fixed factors of production
E.g. Employing more labour
What is long run production?
When the firm changes the scale of all factors of production
Define productivity
Output per unit input
We can measure labour and capital productivity
What is a productivity gap?
Difference between labour productivity in the UK and other developed economies
What fundamental economic principle did Adam Smith establish?
Output could be increased if workers specialise at different tasks in the manufacturing process
He used a pin factory example
Define specialisation
When a worker becomes skilled at one task as a result of repetitively preforming it
Define division of labour
Different workers are assigned to perform different tasks
3 reasons why specialisation increases output
Workers will not switch between tasks- saving time
Workers become more efficient or productive at the task they specialise in. Due to the extensive amount of time spent on the task
Better capital can be employed as specialisation increases efficiency and sales so firms can afford to purchase more machinery,
What are the negative implication of speacialisation?
Workers get bored of the repetition
Division of labour can create alienation
De-skilling in other skills that could be necessary in the future
Why is trade and exchange important?
Larger markets can be accessed
A country can use trade to get products they don’t specialise in
Money is what helps make these exchanges
What are fixed costs?
Costs of production
That do not vary with output
What are variable costs?
Production costs
They do vary with output
Formula for total costs
FC+VC
Formula for average costs
Total costs/Output
Explain average cost curve
Firms average costs of production initially fall as the six of output increases
Costs are spread over output
Point x/c is where the firm produces at the lowest possible cost per unit
This is the most productively efficient level of output
Beyond this point AC begin to rise
This is because as a firm expands production, it becomes harder to mange causing a lack of coordination
Or more expensive inputs are required to maintain production
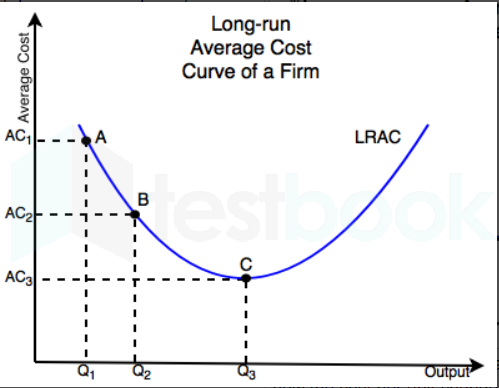
Define productively efficient level of output
The level of output at which average costs are minimised
Another formula for average costs
AC= AFC+AVC
Explain the average fixed cost curve
If fixed costs are £1000 and a firm only produces one unit the average fixed costs are £1000
But if a firm increases output average fixed costs decrease
AFC will never be 0 as there will always be a fixed cost when producing something
Even if output is heavily increases the fixed cost will remain £1000
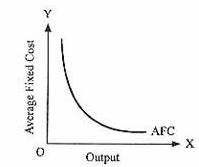
Explain the average variable cost curve
Initially production increases- with the employment of variable factors of production like labour and raw material to fixed inputs
Average variable costs more spread out over output
But after a certain point diminishing marginal returns sets in-After a while each additional unit of variable input contributes less to output. Causing marginal returns (extra output) to fall
As addition of variable inputs becomes unmanageable and less efficient
Explain the difference between LRAC curve and SRAC curve
Both are U- shaped but the reasoning behind it is different
SRAC curve assumes labour becomes more productive as it is added to fixed capital before eventually becoming less productive
LRAC curve is explained by economies and diseconomies of scale.2 concepts that dont operate in the short run
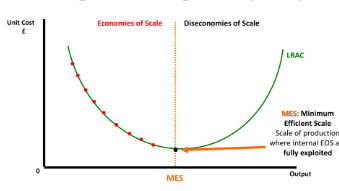
Define economies of scale
Falling long run average costs of production that result from an increase in the size of the firm
Define diseconomies of scale
An increase in long run average costs of production that result from the increase in the size of the firm
Define technical economies of scale
A reduction in average costs generated through changes in the productive process such as
Indivisibilities-Larger firms can afford high tech machinery that smaller firms cannot, leading to greater efficiency
Volume economies-Increasing the size of storage, means firms can store more goods at a lower cost per unit as volume increases faster than surface area
Why are indivisibilities disadvantageous for smaller firms?
Some machinery is only efficient at a minimum size
Below that size it wont operate efficiently
Smaller firms cant afford to operate or purchase the machinery at the minimum size
Define managerial economies of scale
A larger scale firm can benefit from the specialisation of managers
Can afford to hire specialist managers that can help improve efficiency and morale
Define marketing economies of scale
Large firms can negotiate lower rates for supplies due their ability to bulk buy
Can also advertise their products at a lower costs as they have stronger bargaining power compared to smaller firms.
Define financial/capital raising economies of scale
Larger firms can often borrow from banks at a lower rates of interest and on better terms
Because they are viewed as low risk by financial institutions due to their strong stream of revenue
Define risk bearing economies of scale
Large firms are less exposed to risks as they can spread risks by diversifying their output, markets and sources of supply.
Such economies of diversification can make firms less vulnerable to sudden changes in demand or supply
Define economies of scope
Firms reduce their average cost per unit by producing multiple products using the same resources
This also applies to marketing- a strong brand image allows firms to advertise multiple products under 1 name. Reducing costs
E.g. Apples ecosystem
Reason for diseconomies of scale
Firms may suffer as they grow in size for various different reasons
Managerial diseconomies of scale
As a firm grows administration (management) of the firm becomes more difficult
Delegation of managerial functions to people lower in the organisation may lead to bad decisions
More rules and regulation(bureaucracy) in a large firm may cause a delay of approval for new products or capital
Lack of coordination between departments
How does communication failure contribute to managerial diseconomies of scale
Too many layers of management causing a barrier between workers and managers
This may lead to staff feeling underappreciated and more like a replaceable asset
Staff may then become unproductive and costs begin to rise
Motivational diseconomies of scale
Harder to satisfy and motivate workers in large firms
Over specialisation may lead to de-skilling as workers perform repetitive mundane tasks
They have little incentive to use personal initiative which could boost innovation
How does performing tasks repetitively lead to de-skilling ?
Traditional problem solving and craftsmanship skills become less exercised due to a reliance on capital
Stunting creativity
Define internal economies of scale?
Cost saving resulting from the growth of the firm itself
Define external economies of scale
Cost saving resulting from the growth of the market/industry the firm is apart of
What is the cluster effect?
Can cause external economies of scale
When firms in the same industry are located close together providing sources of supply and a pool of labour for each other
What are external diseconomies of scale caused by?
The cluster effect operating in a negative way
Large number of similar firms located close together could mean there is competition for labour
This can cause an increase in wages which increase costs
May also increase traffic congestion locally, lengthening delivery times and raises delivery costs for consumers and firms
How can market fragmentation lower the significance of economies of scale?
Market segmentation is when the market is broken down into smaller sectors based on certain characteristics and caters to different consumer wants and needs
Economies of scale relies on mass production of the same good which is not effective when producing goods that complement different types of people
increases costs because divergent machinery may be needed, advertising costs if the products have to be marketed differently and different raw materials.
Define total revenue
All the money received by a firm from selling its total output
Average revenue formula
Total revenue/output
Average revenue=
Price