lab med lecture 20
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
- HPV vaccination
- screening
what is the reason we have a low rate of cervical cancer here in the US
HPV
what is cervical cancer due to
sexual activity
how is HPV transmitted
none, they are asymptomatic
what are symptoms that someone would present with when diagnosed with HPV
- 16
- 18
- 31
- 33
which HPV strands lead to cervical cancer
- 6
- 11
which HPV strands cause genital warts
true
true or false:
your body often clears HPV naturally within 1-2 years
- HPV infects epithelilal cells in lining
- infection presents
- HPV inactivates tumor supression genes
- cells experience uncontrolled growth
- precancerous cells develop
- cervical cancer develops
how does cervical cancer develop
21
what age do you start screening for cervical cancer
every 3 years
how often should you pap smear screen people from age 21-29
every 5 years and 3 years for pap smear
how often should you screen for cervical cancer from age 30-65
Pap smear
what is the screening method for cervical cancer
vaginal swab
what is the screening method for HPV
- females <25
- men who have sex with men
- patients with HIV
- individuals entering correctional facilities
who is considered high risk for getting an STI
usually present as asymptomatic and it can lead to serious complications
what is so scary about STIs
- women older than 25 and sexually active
- women less than 25 and sexually active
- men who have sex with women only
- men who have sex with men
who should you screen for STIs
if they are at risk
when is the time you would screen women older than 25 and sexually active
only if they are high risk
when should you screen men who have sex with women only
HIV
what screening should you do anually if its a man having sex with a man
- painful urination
- genital sores
- unusual discharge
- pain during sex
- fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes
what kind of symptoms should cue you to screen for STI
- urine test
- blood test
- swab test
how can you screen for STI
The patient needs additional
testing to rule out latent TB
A 37-year-old male presents to the clinic after returning home from travels in Bangladesh. He had
been working in the homeless shelter and is now concerned after having learned about a rampant
tuberculosis outbreak there. He is asymptomatic but is still concerned he might have contracted TB.
You obtain a chest x-ray and a CBC. The bloodwork is normal. The chest x-ray is as below. Which of
the following is true?
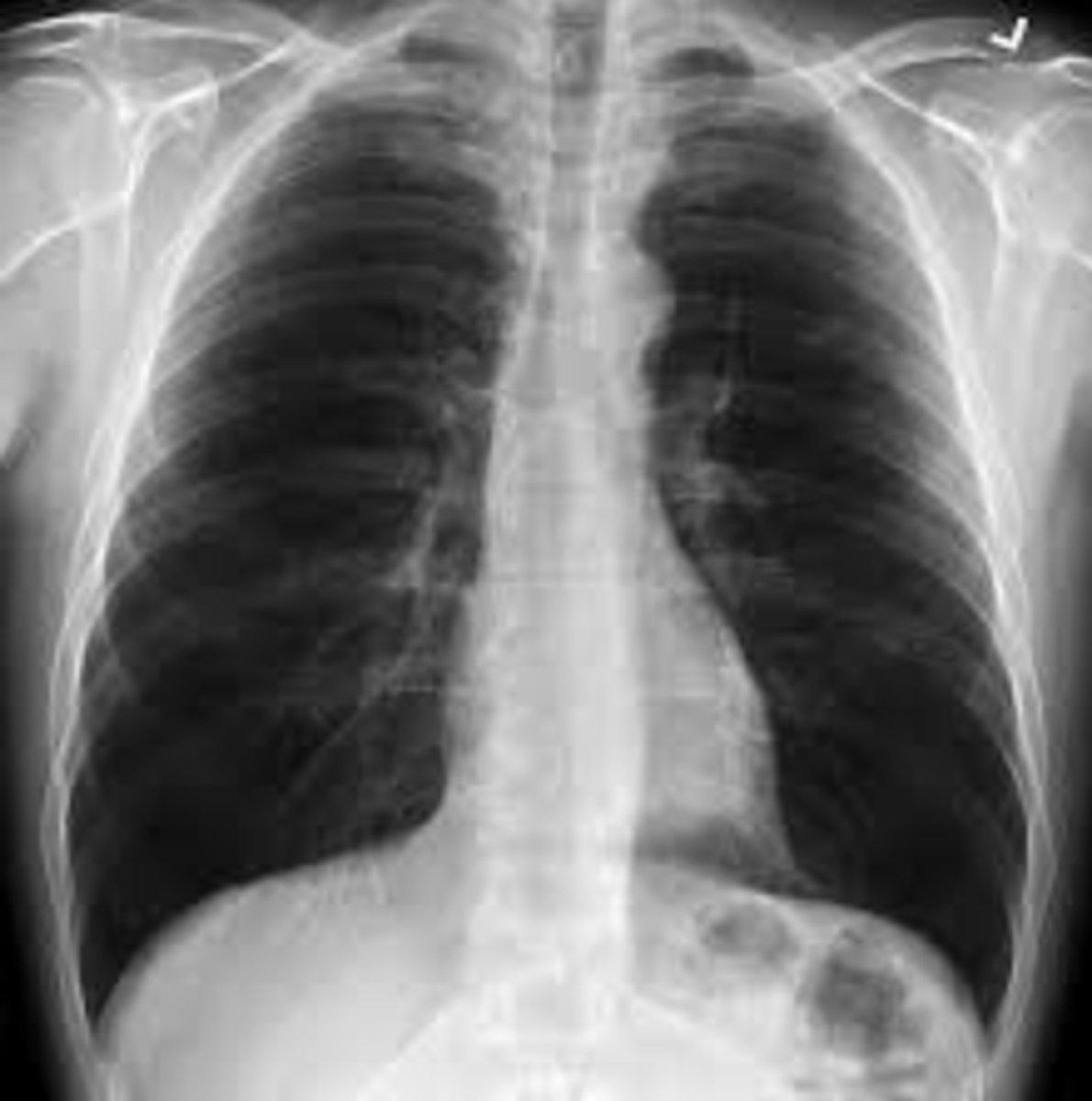
TB
infection of the respiratory system or other organs with myobacterium tuberculosis, acid fast bacilli
TB
leading cause of death from an infectious agent worldwide
- close contact to someone with it
- crowded conditions
- immunosupression
what are risk factors for getting TB
- Immediate clearance
- Primary disease
- Latent Infection
- Reactivation
what are the four outcomes that could present with inhalation of myobacterium tuberculosis
- prolonged fever
- cough, chest pain, hemoptosis
- fevers, chills
- weight loss
what are clinical presentations for TB
true
true or false
Patient is asymptomatic
and NOT contagious with
latent TB
NO
will latent TB have imaging findings
false
true or false
someone with latent TB can spread it
Both A and B (TST
and Quantiferon Gold (IGRA)
Which of the following lab tests can help
establish the diagnosis of latent TB?
- Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)
- Interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) AKA
Quantiferon Gold
what are tests you can do to screen for TB
inject a TB antigen inttradermally and watch for any reaction within 48072 hours
how does the PPD test work
a red bump over injection site
what is considered a positive TB test
4
which hypersensitive reaction is TB
positive for TB
what does it mean if the TB lump is >15 mm
positive test but could be someone who's at higher risk or was previously exposed
what does it mean if the TB lump is >10 mm
positive test but could be an immunosupressed person bc their immune system isnt as strong to make a higher response
what does it mean if the TB lump is >5 mm
IGRA
this test is a one time blood draw that is not affected by prior BCG vaccination compared to TST
- Patients who will not return for TST reading
(IVDU, homelessness)
- Those with previous BCG vaccination
- Those likely to have TB infection
who would you want to get a IGRA on
- high cost
- high rates of false results
what are some disadvantages to IGRA
Improper reading, cross reaction with an atypical
(Mycobacterium avium complex), test within 2-10
years of BCG vaccination
what would cause a false positive on a PPD test
Anergy (HIV, sarcoidosis, etc), faulty application,
acute TB (takes 2-10 weeks to convert), malignancy
what would cause a false negative on a PPD test
Obtain a chest x-ray
Your patient has a positive IGRA. What is your
next step?
Obtain a chest x-ray
Your patient has a positive PPD. What is your
next step?
get a chest xray
what do you do if your have a positive ppd OR igra
- positive tst or igra AND
- no symptoms of infections AND
- no imaging finding of active infection
how can you diagnose latent TB
colon polyps
Discrete mass lesions that protrude into
the intestinal lumen
asymptomatic
what is the clinical manifestation of clinical polyps
some of them are neoplastic so if you dont know or catch it over 10 years it can become cancer
why can it be bad that colon polyps are asymptomatic
screening early
how can you avoid malignant transformation of a colon polyp
45 years old
when should you start screening for colon cancer screening
colonoscopy
what is the gold standard for screening and diagnosing colon cancer
every 10 years
how often should you do a colonoscopy if its normal
- stool test
- colonoscopy
what are 2 ways we can screen for colon cancer
gFOBT
Screening test used to identify hidden (occult) blood in stool
gFOBT
Test identifies presence of hemoglobin in stool by turning
guaiac reagent purple-blue
- GI bleed
- colon cancer
what is gFOBT used to evaluate for
- Red meat
- Peroxidase-rich veggies/fruits: Turnips, banana, horseradish, etc
- Drugs (anticoagulants, aspirin, colchicine, iron, NSAIDS,
steroids)
what can cause a false positive for gFOBT
vitamin C
what can cause a false negative for gFOBT
FIT
Highly sensitive stool occult blood test that uses antibodies
that bind to human hemoglobin
FIT
Highly specific to human blood; less false positives than
gFOBT
FIT
this test Doesn't detect "non-blood" markers that can be present in early-stage or non-bleeding cancers (not all polyps bleed)
FIT and DNA testing
which test can detect blood and genetic mutations
FIT and DNA testing
this test is More sensitive than FIT alone; superior at detecting early- stage cancer and non-bleeding precancerous polyps
FIT
Sensitive stool tests that checks for presence of Hgb. Use for patients unable or unwilling to undergo colonoscopy. Must be done annually. If positive -> COLONOSCOPY
FIT-DNA
"Cologuard", highly sensitive stool test. Evaluates for Hgb + DNA mutation/methylation. Performed q 1-3 years. More sensitive but less specific than FIT. If positive -> COLONOSCOPY