Exam 1
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
Medical Definition of a Drug
Any substance that may prevent or cure disease or enhance physical or mental welfare
Pharmacological Definition of a Drug
Any chemical agent that alters biochemical processes of tissues or organisms
Common use definition of a Drug
Psychoactive drugs, used non-medically as well as medically
Drug classifications
By origin (plants, etc.)
By therapeutic use (stimulant, painkiller, etc.)
By site of drug action (e.g., CNS)
By chemical structure
By mechanism of action (how it produces its drug effects)
By street name (e.g., “speed,” “uppers,” “downers”)
Drug classification by origin
Plants, etc (Ex: opiates)
Drug classification by theraputic use
Stimulant, painkillers (Ex: Antidepressants)
Drug classification by site of drug action
CNS, etc
Drug classification by Chemical sturcture
barbituates
Drug classification by mechanism of action
how it produces its drug effects
Drug classification by street name
speed, uppers, downers
Drug classification by legality (illicit)
Illegal drugs (heroin, cocaine, marij)
Drug classification by legality (licit)
Legal drugs (alcohol, caffeine, nicotine)
Schedule 1 drug
the drug or substance has a high potential for harmful use. it has NO currently accepted medical use in treatment in the US. lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision.
Schedule 2 Drug
the drug or other substance has a High potential for misuse. It HAS a currently ACCEPTED medical use or use with SEVERE restrictions. Misuse of the drug may lead to severe psychological or physical Dependence.
Schedule 3 Drug
the drug or other substance has a potential for misuse less than the drugs or other substances in Schedule 1 or 2. HAS an accepted medical use. Misuse may lead to Moderate or Low physical dependence or High psychological dependence.
Schedule 4 Drug
the drug or other substance has a Low potential for misuse relative to schedule 3 drugs. HASan accepted medical use. Misuse of the drug may lead to Limited physical dependence or psychological dependence relative to Schedule 3 drugs
Schedule 5 Drug
the drug or other substance has a LOw potential for misuse compared to schedule 4 drugs. HAS an accepted medical use. misuse may lead to Limited physical dependence or psycological dependence compared to Schedule 4 drugs
Pharmacology
How drugs act on biological systems, how the body responds
Psychopharmacology
The effects of drugs on behavior
National Survey on Drug Use and Health
1)Conducted annually by Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA):
•ongoing since 1971 for those 12 and older
•Data on overall prevalence of use in last year and last month and lifetime use
•Includes alcohol and tobacco as well as marijuana, cocaine, heroin, opioid
Monitoring the Future
Conducted annually by the University of Michigan, funded by NIDA)
§ongoing for 12th graders since 1975
§added 8th, 10th graders in 1991
Past year illicit drug use (18-25)
38.0
Past year Marijuana Use (18-25)
35.4
•Estimated cost of alcohol abuse
$249 billion
•Estimated cost of tobacco and illicit drugs
$493 billion
International Comparisons of Drug Use
•17 countries, 54,069 respondents
•Americas, Europe, Japan, New Zealand reported more alcohol and cannabis use than Middle Eastern countries, Africa, China
•U.S. had highest lifetime use of cocaine of all countries responding
•Several similarities with NSDUH survey:
•More males used all drugs than females in all countries
•Younger adults are more likely to use all drugs than older adults
Any mental illnesses (18-25)
33.7
Serious mental illnesses (18-25)
11.4
Three sets of factors in the drug experience
Pharmacological (pharmacokinetics & pharmacodynamics)
Characteristics of the drug user (set)
Setting in which the drug is used (setting)
Pharmacokinetics
“What the body does to the drug”
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME)
•Absorption and distribution = how much drug reaches sites of action
•Metabolism and excretion = two routes of drug elimination
•Required to learn a drug’s effect after it enters the body
Pharmacodynamics
Study of “biochemical and physiological effects of drugs and their mechanisms of action” (What the drug does to the body)
•Language used by pharmacologists to describe drug effects and ways to depict them
•Biological bases of observed drug effects
Standards followed in describing and representing drug effects
Absorption and distribution
how much drug reaches sites of action
Metabolism and excretion
two routes of drug elimination
•Administration
How does the drug enter the body?
Absorption
How does the drug move from site of administration into the body’s circulatory system
•Distribution
How does the drug move to various areas of body?
Activation
How and where does the drug produce its effects?
•Biotransformation/elimination
How is the drug inactivated and excreted from body
Drug Dose
Pharmacologists compute drug dose according to a person’s body weight
•Volume of body fluid correlates positively with body weight
•The greater the drug concentration at a site, the greater the drug effect
Determine the desired dose, expressed in milligrams of drug per kilogram (mg/kg) of body weight
routes of admininstration
may be either the site where a drug is taken or how a drug is taken; route of administration can strongly influence drug effects
Main routes of administration
Oral
•Injection
•Subcutaneous
•Intramuscular
•Intravenous
•Inhalation
•Intranasal (sniffing)
•Sublingual (under the tongue)
Transdermal (through the skin
oral administration
usually the safest, most ecnonomical way to take a drug, causes slower absorption than other routes, and Outcome: diminished drug effect
Injection administration
bypasses the difestive process entirely and delivers the drug more directly into the bloodstream
Intravenous (IV) injection
drugs are administered directy into the bloodstream, FASTEST but MOST dangerous
Avoids most absorption problems, effects can be immediate
Most highly associated with complications: Large quantities of drug too quickly
Intramuscular (IM) Injection
Drugs are injected into muscle tissue, can be painful/irritating
absorption rates may differ by rat of blood flow to muscle and solution used
Subcutaneous (Sub-Q) injection
injecting drug just below the layers of skin, easiest injection route, only small volumes, slowest absorption rate of injections but constant absorption
Relatively slow but faster than oral administration
Inhatation administration
some drugs may be inhaled then absorbed through the LUNGS’ membrane
Fast and effective absorption
Tobacco smoke or freebase
Intranasal administration
snorting, sniffing (Cocaine, heroine, powdered tobacco snuff)
Rapid and effective way to absorb fat-soluble drugs
Sublingual administration
tablet dissolves in saliva under tongue, is absorbed through mouth’s mucous membranes (Nitroglycerin to treat heart pain)
Transdermal administration
through the skin- alternative to oral administration when a drug may cause unwanted gastrointestinal effects (Nicotine patches)
Absorption of a drug into the bloodstream
rate and extennt to which a drug leaves its site of administration; plays major role in the drug experience
factors that influence absoption
Drugs by all routes except IV must pass through at least 1 body membrane to reach the circulatory system
Drug distribution
body regions with the most bloor flow receive the most drug (heart, brain kidney and liver) areas recieving less bloodflow like muscles, viscera nad fat may take longer to recieve the drug
Diffusibility
the more diffusible tissues revieve the drug more rapidly
fat solubility
drugs more soluble in lipids penetrate body membranes, reach action site and brain more easily (Valium)
chemical binding of a drug to certain plasma proteins
the more “tightly” bound a drug, the slower its distrubution to action sites
bioavailability of a dryg
Route, absorption and diffusion all influence the ………
Liver enzymes
play a major role in drug metabolism; enxymes also in kidneys and GI tract
Kidney
Most important organ for ec=xcretion of drugs and their matabolites
First order Kinetics
amount of drug metabolized depends on amount in blood
Zero order kinetics
Rate of drug metabolism ia independent of its concentration in blood (Alcohol)
Half-life
time needed for amount of drug in the bodyto be cut in half
Set (characteristics of the user that effect drug effects)
Age (young vs old)
weght
gender (% body fat)
hormones
inherited differences in initial sensitivity and reactions to drugs and drug tolerance
Psycological state, personality abd expectations of an individual while using drugs
Setting
the physical and social environment in which drugs are used
Laws pertaining drug use
taking drugs alone vs with others influences the effects pf alcohol, marijuana, hallucinogenic drugs
immediate physical environment
Dose-effect curve
standard way to graphically represent the relationship between drug dose and the size of an effect.
Dose-effect curve Slope
steepness of a dose-effect curve reflects how much the drug dose changes before the effect gets larger
Dose-effect curve Efficacy
the peak of the dose-effect curve for a given effect
Dose-effect curve drug potency
minimum dose of a drug that yields its efficacy
Effective Dose (ED)
the dose at which a given percentage of individuals show a particular effect of a drug
Lethal Dose (LD)
the dose of a drug at which a given percentage of nonhuman subjects die withing a specified time
More
……… danger of accidental death whem difference between a drugs ED and LD is small
Theraputic index
a easure of a drugs saftey in medical care
Ratio= LD 50/ED 50 for a given drug
drug interactions
the effect of one drug alters the effect of the other
enhancing cobinations (Synergism)
the effects of taking teo drugs together are greater than the effects of taking either drug alone
diminishing combinations (Antagonism)
reduced effect of a drug in another drugs presence
neurons
basic building blocks of the nervous system; cells that can communicate with one another
Dendrites and axon
structures unique to the neruon- the provide for neural communication, WHICH IS BOTH ELECTRICAL AND CHEMICAL
electrical message
a nerve impulse or action potential is the ………… that is transmitted down
results form the mobement of ions in and out of the cell
the speed of nerve impulses ranges from approximately 1 m/s to 100 m/s
restng membrane potential
refers to the state of the neuron prior to the sending of a nerve impulse
the inside of the membrane is slightly negative with resct to the outside
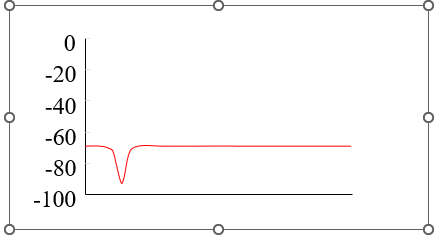
hyperpolarization
apply small negative current tp increase negative membrane potential
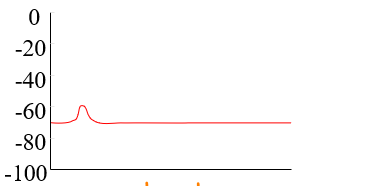
depolarization
apply depolarizing current to decrease membrane potential towards neutrality
action potential
disproportionately large depolarization occurs when membrane reaches or exceeds the threshold of excitation- at this point the sodium channels open up
local anesthetic drugs
block sodium channels and therefore prevent action potentials from occuring
chemical communication
the synapse of the jucture between neurons
presynaptic neuron
the neuron that delivers ‘the message’ whoch is a chemical or neurotransmitter
postsynaptic neuron
the neuron that recieves ‘the message’- the chemical
synaptic cleft
the space in between across which the chemical travels
Neurotransmitters
are chemical substanes that a neuron uses to communicate information at the synapse
the “big 7” neuroteansmitters
Acetylcholine
Norepinephrine
Dopamine
Serotonin
GABA
Glutamate
endorphins
norepinephrine
discovered early- found outside as well as inside the brain
norepinephrine outside the brain
mediates the physical changes of emotional arousal
norepinephrine inside the brain
important in regular hunger, alertness and arousal
serotonin
important in regulating sleep
dopamine
regulates coordinated motor movements
monoamine dysregulation
is implicated in psychiatric disorders like depression and schizophrenia
endorphins
large molecules in the peptide family: functionally like morphine, heroine and other opitates, modulate pain relief
GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid)
among most abundant on known neurotransmitters on brain tissue and more significant inhibitory one: impedes neural firing
Glutamate
among most abundant of excitatory neurotransmitters; important in learning and memory processes
Anandamide
active chemicla in marijuana seems to mimic anandamide, a lipid