chapter 4 energetics
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
why is the amount of energy involved important to know
measure the energy values of fuels
calculate the energy requirements for industrial processes
working out the theoretical amount of energy rquiredto break bonds and make bonds
to predict weather a reaction occurs or not
thermochemistry
the study of heat changes during chemical reactions
define exothermic
when energy is given out after bonds are broken and formed
define endothermic
when energy is taken in after bonds are broken and formed
features of an exothermic reaction
give out heat as they proceed
adding water to anhydrous copper sulfate
e.g neutralising an acid with an alkali
e.g combustion
temperature increases
features of an endothermic reaction
take in energy from their surrounding as they proceed
e.g breakdown of calcium carbonate
heating hydrated copper sulfate
temperature decreases
e.g thermal decomposition
what unit is used to measure energy
kilojoules/mol KJ/mol
uses of exothermic reactions
to produce large heat outputs / release lots of energy
by burning carbon or natural gas
uses of endothermic reactions
to treat sports injuries
using cold packs
symbol equation of reactions in cold packs
NH4NO3(s) +(aq) → NH4NO3(aq)
why is thermochemistry used
to compare the efficiency of different fuels and for finding alternatives
hydrogen as a fuel
hard to use because its a gas
highly flammable/ explosive
hard to store
stores lots of energy per gram because of its high density
enthalpy change
heat change measure at a constant pressure
what are the standard conditions for measuring enthalpy changes
100KPa
298 Kelvins
when does a reaction end
once the products cool back to the starting temperature of 298k
enthalpy change in exothermic reactions
less heat because energy is lost
so delta H is negative
enthalpy change in endothermic reactions
product has more energy than the starting materials
delta H is positive
why does pressure affect the amount of energy given out
energy is required to push away the atmosphere when releasing a gas
so greater atmospheric pressure = greater energy used for a reaction to occur
how do the physical states of reactants and products affect enthalpy change
state symbols must always be included
because the physical states affect the enthalpy change of reaction
examples of why the physical states matter
the enthalpy change caries based on the physical states

uses of enthalpy level diagrams
represent enthalpy changes
to convey the relative enthalpy levels of reactants
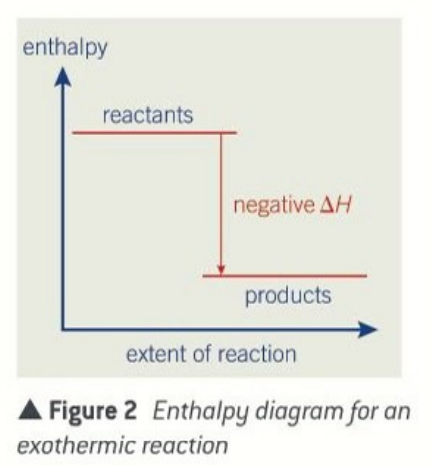
enthalpy level diagrams for exothermic reactions
products have less enthalpy than than the reactants
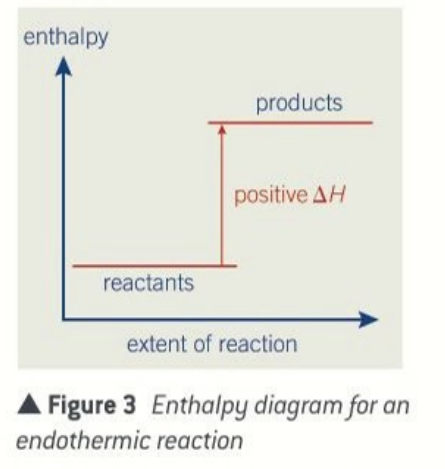
enthalpy level diagrams for endothermic reactions
products have more enthalpy than the reactants
general name for enthalpy change for any reaction
standard molar enthalpy change of reaction
define enthalpy of formation
is the enthalpy change when one mol of a substance is formed from its constituent elements under standard conditions in their standard state
define enthalpy of combustion
enthalpy change when 1 mol of a substance is completely burnt in oxygen under standard conditions in its standard state
define temperature
average kinetic energy of particles in a system
define heat
measure of total energy of all particles present in a given amount of a substance
how does temperature relate to kinetic energy
as particles move faster the kinetic energy increases
this increases the temperature
temperature is independent of the number of particles present
what depends on how much of a substance is present
heat
because the energy of each particle is included
why does a bath have more heat than a red hot nail
because there are mor particles in it
factors affecting the enthalpy change of a reaction
mass of a substance
temperature change
specific heat capacity
define specific heat capacity
the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a 1 g of a substance by 1 kelvin
equation for enthalpy change
mass X specific heat capacity X temperature change
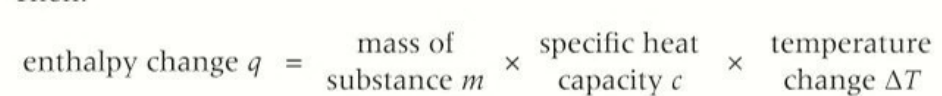
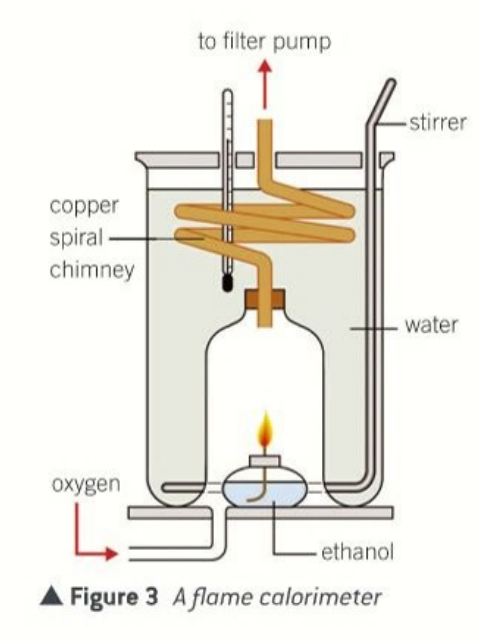
uses of a calorometer
find the approximate enthalpy change when a fuel burns
to compare the enthalpy of combustion with a series of similar compounds
how does a calorimeter work
burn the fuel to heat a known mass of water
measure the temperature rise
assume all the heat goes into the water
how to do calorimetry questions
step 1: find the enthalpy change
step 2 : convert joues into kilojoules
step3: calculate the moles using cXv=m
step 4:use -q/n to find the enthalpy change per mol
feature of a flame calorimeter that reduce heat loss further
spiral chimney made of copper
enclosed flame
fuel burns in pure oxygen
why is it easy to measure heat changes for reactions that occur in solutions
the heat is generate in the solutions themselves
expanded polystyrene is used
neutralisation reactions
acid + alkali → salt + water
displacement reactions
when a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive one from a compound
example of displacement reactions
copper sulfate + zinc
symbol equation for a displacement reaction
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
allowing for heat loss practical
apparatus are left in the lab so all reach the same temperature as the starting temperature

hess’s law
The total enthalpy change in a chemical reaction is independent of the route taken
thermochemical cycle
ΔHf(CO2)=ΔH1+ΔH2
direct pathway + indirect pathway = enthalpy change
define enthalpy of formation
The enthalpy change when one mole of substance is formed from its constituent elements, under standard conditions with all reactants and products in their standard states
The symbol is ΔHfꝊ