Chapter 14-15 | The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
Mendel's first law, stating that the two alleles in a pair segregate (separate from each other) into different gametes during gamete formation
Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment
Mendel's second law, stating that each pair of alleles segregates, or assorts, independently of each other pair during gamete formation; applies when genes for two characters are located on different pairs of homologous chromosomes or when they are far enough apart on the same chromosome to behave as though they are on different chromosomes
Wild type (W+)
The phenotype most commonly observed in natural populations; also refers to the individual with that phenotype
Sex-linked trait
A gene located on either sex chromosome. Most sex linked genes are on the X chromosome and show distinctive patterns of inheritance; there are very few genes on the Y chromosome
Parental type
An offspring whose phenotype that matches one of the true-breeding parental (P generation) phenotypes; also refers to the phenotype itself
Recombinant
An offspring whose phenotype differs from that of the true-breeding P generation parents; also refers to the phenotype itself
Linkage map
A genetic map based on the frequencies of recombination between markers during crossing over of homologous chromosomes
One map unit
A unit of measurement of the distance between genes. Is equivalent to a 1% recombination frequency
Nondisjunction
An error in meiosis or mitosis in which members of a pair of homologous chromosomes or a pair of sister chromatids fail to separate properly from each other. Can lead to trisomy or monosomy
Aneuploidy
A chromosomal aberration in which one or more chromosomes are present in extra copies or are deficient in number
Polyploidy
A chromosomal alteration in which the organism possesses more than two complete chromosome sets. It is the result of an accident of cell division
Genomic imprinting
A process that regulates gene expression by silencing one copy of a gene from either the mother or father. Expression of the allele in offspring depends on whether the allele is inherited from the male or female parent
Hemizygous
Having only one copy of a gene or chromosome segment, instead of the usual two
Thomas Morgan’s fruit fly experiment
Demonstrated that traits like eye color are inherited through chromosomes. In his study, red eye color (dominant, W+) was crossed with white eye color (recessive). The F1 generation showed all red eyes, and the F2 generation showed a 3:1 ratio, with white eyes appearing only in male offspring. This established that genes on the X chromosome follow a sex-linked inheritance pattern, confirming that chromosomes are the basic unit of inheritance
SRY (sex-determining region on the Y)
A gene that is responsible for development of the testes in an embryo
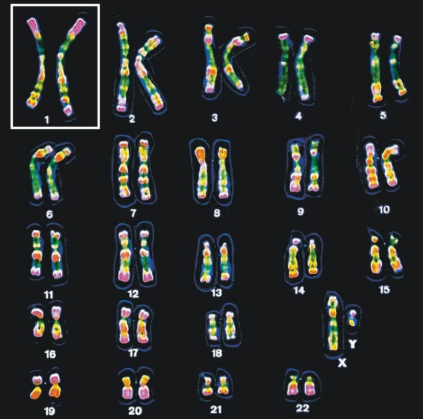
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape
X-inactivation
A process that occurs in female mammals during embryonic development. It inactivates one of the two X chromosomes in each cell, ensuring that the correct number of genes are expressed. This process balances the number of X-linked genes between females and males
Autosome
A chromosome that is not directly involved in determining sex; not a sex chromosome
Dependent assortment
Where different traits are inherited together, meaning the alleles for different genes would not separate independently during gamete formation, essentially staying linked and passing on specific combinations of alleles as a unit
Crossing over
The reciprocal exchange of genetic material between nonsister chromatids during prophase I of meiosis
Recombination frequency
( # of recombinants / total # of offspring ) x 100%
Maximum Recombination Frequency
Multiple crossover events during meiosis can result in a 50/50 split of recombinants and parentals for genes that are very far apart. This makes genes appear to assort independently, even though they are physically linked on the same chromosome
Autosomal Aneuploids
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome), Trisomy 13
Aneuploids on sex chromosomes
XO - Monosomy X - female is sterile
XXX - Trisomy X - female is completely normal
XXY - Klinefelter - males that develop female characteristics
XYY - Jacobs syndrome - causes increased height and learning or behavioral issues
Deletion
A piece of the chromosome is removed/missing
Duplication
A piece of DNA is repeated
Inversion
Reversing the order of a piece of the chromosome
Translocation
Removing a segment of DNA from a chromosome and adding it to another piece
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which the phenotypic expression of one gene alters that of another independently inherited gene
Codominance
The situation in which the phenotypes of both alleles are exhibited in the heterozygote because both alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways
Pleiotropy
When a single gene or DNA variant affects multiple traits in an organism
Polygenic inheritance
Occurs when one characteristic is controlled by two or more genes
Quantitative trait
A heritable feature that varies continuously over a range rather than in an either-or fashion
Multifactorial traits
Referring to a phenotypic character that is influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors
Trisomy
Referring to a diploid cell that has three copies of a particular chromosome instead of the normal two
Monosomy
Referring to a diploid cell that has only one copy of a particular chromosome instead of the normal two
Endosymbiont theory
The theory that mitochondria and plastids originated as prokaryotic cells engulfed by a host cell. The engulfed cell and its host cell then evolved into a single organism
Mitochondrial Inheritance
The genetic pattern where individuals inherit their mitochondrial DNA solely from their mother, meaning that only females pass on their mitochondrial DNA to their offspring. This is considered "maternal inheritance" because the mitochondria are exclusively inherited from the mother's egg cell
Chromosomal Aberrations
Gene duplication, inversion, deletion, and translocation