Using protein structures to understand disease
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what can +ve & -ve charged patches on proteins signify
+ve = electrostatically associated with the plasma membrane
-ve = electrostatically associated with phospholipid heads of membrane
what can we learn by mapping conserved residues
is this residue important for folding
in hydrophobic core
at oligomer interface
is this residue important for function
interactions with small molecules
is it important for both
slide 6
how can nonsense & missense mutation affect proteins
nonsense - portions of the protein chain are synthesized, lacks structure that forms the oligomer interface
missense - amino-acid substitution may cause loss of favorable interactions
what is a steric clash
occurs when two atoms in a molecule that aren’t covalently bonded are positioned close to each other, causing their electron clouds to overlap and creating high, repulsive energy.
how can mutations disrupt functionally important oligomeric state
polar residue in a cluster of non-polar residues
a charge-altering mutation
how can mutations reduce enzymatic activity
mutations that change the chemical nature residues that form direct interactions with substrate
mutations that don’t alter the chemical nature residues that directly interact with the substrate, but change the way the protein chain folds in active site
what are prions
proteinaceous infectious particles, they are misfolded proteins that cause other proteins to misfold leading to death
caused by fluid-filled holes where neurons have died.
what are some similarities between viruses & prions
prions & viruses are infectious agents that are not cells
rely on host cells to provide machinery for replication
describe the mechanism of prions
fibrils are composed of misfolded prions
β-helix is likely a core structure of protease-resistant fibrils
the fibrils are thought to cause disease
what is PrPc
a normal glycosylated cell-surface protein, abundant on surface of nerve cells in the brain
misfolded form = PrPSc
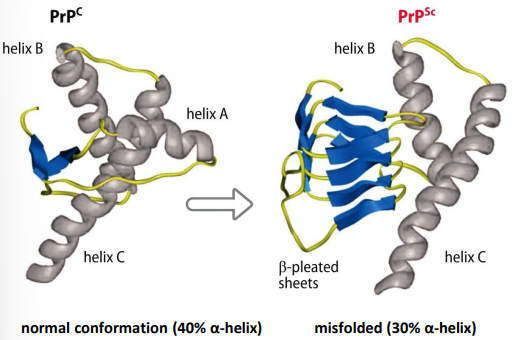
why is it difficult to detect prions
no intrinsic defense mechanism, as they are hosts own proteins
It is thought that negative selection eliminates B & T cells that recognize PrPSc prions because they autoreact against PrPC
what is the difference between cofactor & coenzyme
cofactor - a small molecule ligand that is tightly bound & remains bound after reaction is complete
coenzyme - a small molecule require for an enzymatic reaction, loosely bound & can dissociate from the enzyme
how can protein-ligand interactions be blocked
blocked through feedback inhibition, enzymes early in the pathway are regulated by the end-products
competitive inhibitor
allosteric inhibitor
what is the function of the positive modulator
a molecule that binds to optimize the shape of the conformation of the binding site for the catalytic subunit
what is the equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd)
for P + L ⇌ PL
Kd = [P][L] / [PL]
low Kd = tight binding or high affinity
high Kd = loose binding or low affinity
what is a binding curve
a measure of the fraction of protein bound against free ligand concentration
Fraction P bound = [L] / Kd + [L]
Kd = concentration of free ligand when 50% of protein is bound
![<p>a measure of the fraction of protein bound against free ligand concentration</p><ul><li><p>Fraction P bound = [L] / K<sub>d</sub> + [L]</p></li><li><p>K<sub>d</sub> = concentration of free ligand when 50% of protein is bound</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d937cf14-adc4-46a6-94cb-b6fdb89d7f70.png)