1 DNA disruptors (antibacterial therapies)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what are the fluoroquinolones
- cipro (ciprofloxacin); IV, PO, otic, ophthalmic
- levaquin (levofloxacin); IV, PO, ophthalmic, inhalation
- avelox (moxifloxacin); IV, PO, ophthalmic
- baxdela (delafloxacin); IV, PO
- ofloxacin
when do we use fluoroquinolones
- urinary tract infections (EXCEPT moxi); not for just simple cystitis
- respiratory infections (levo & moxi)
- GI infections (moxi)
- moxi: mild intra-abdominal infections
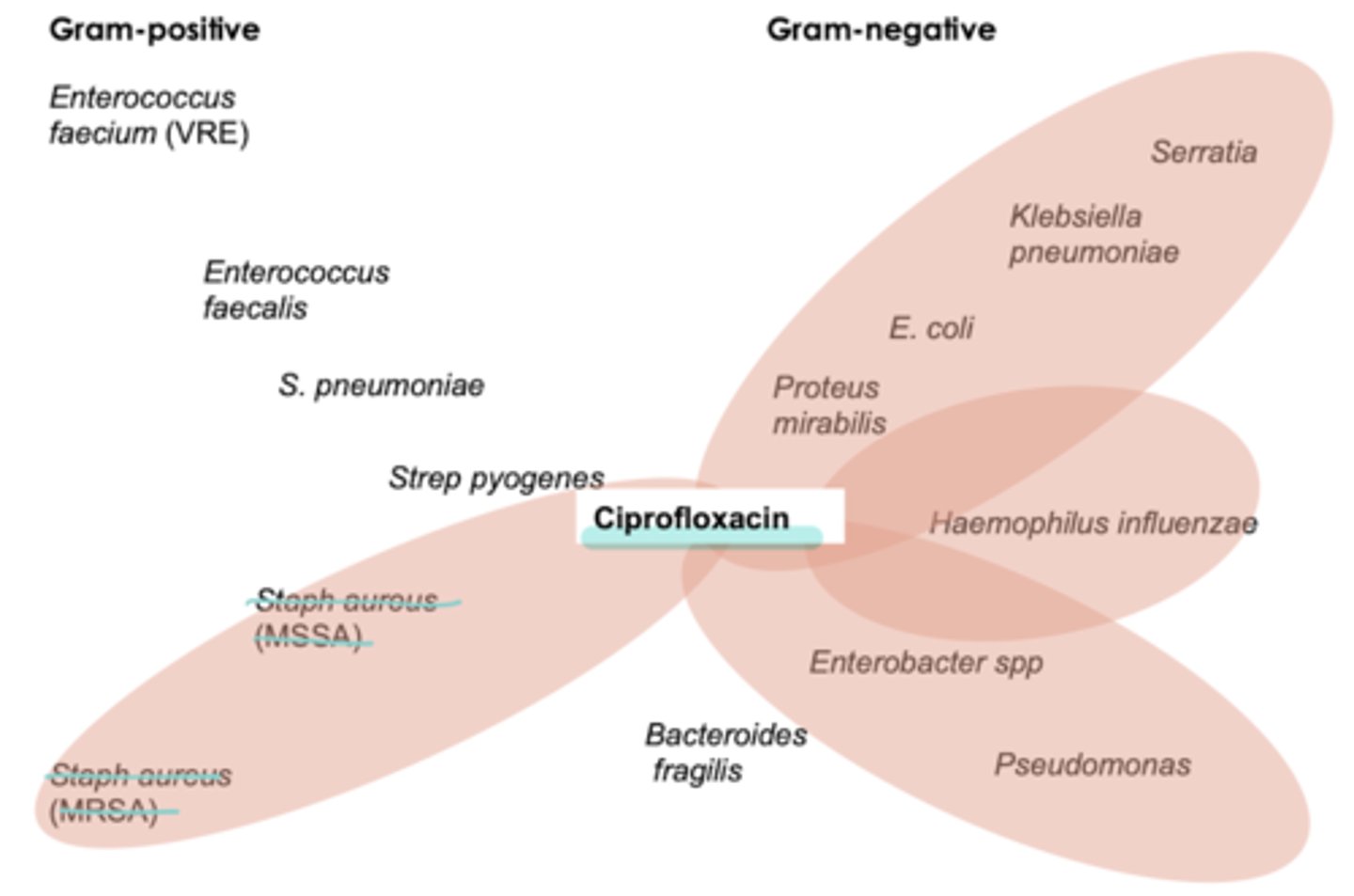
ciprofloxacin coverage
- pseudomonas aeruginosa **best
- atypicals
- weak Strep pneumoniae coverage
- not usu used for Staph coverage
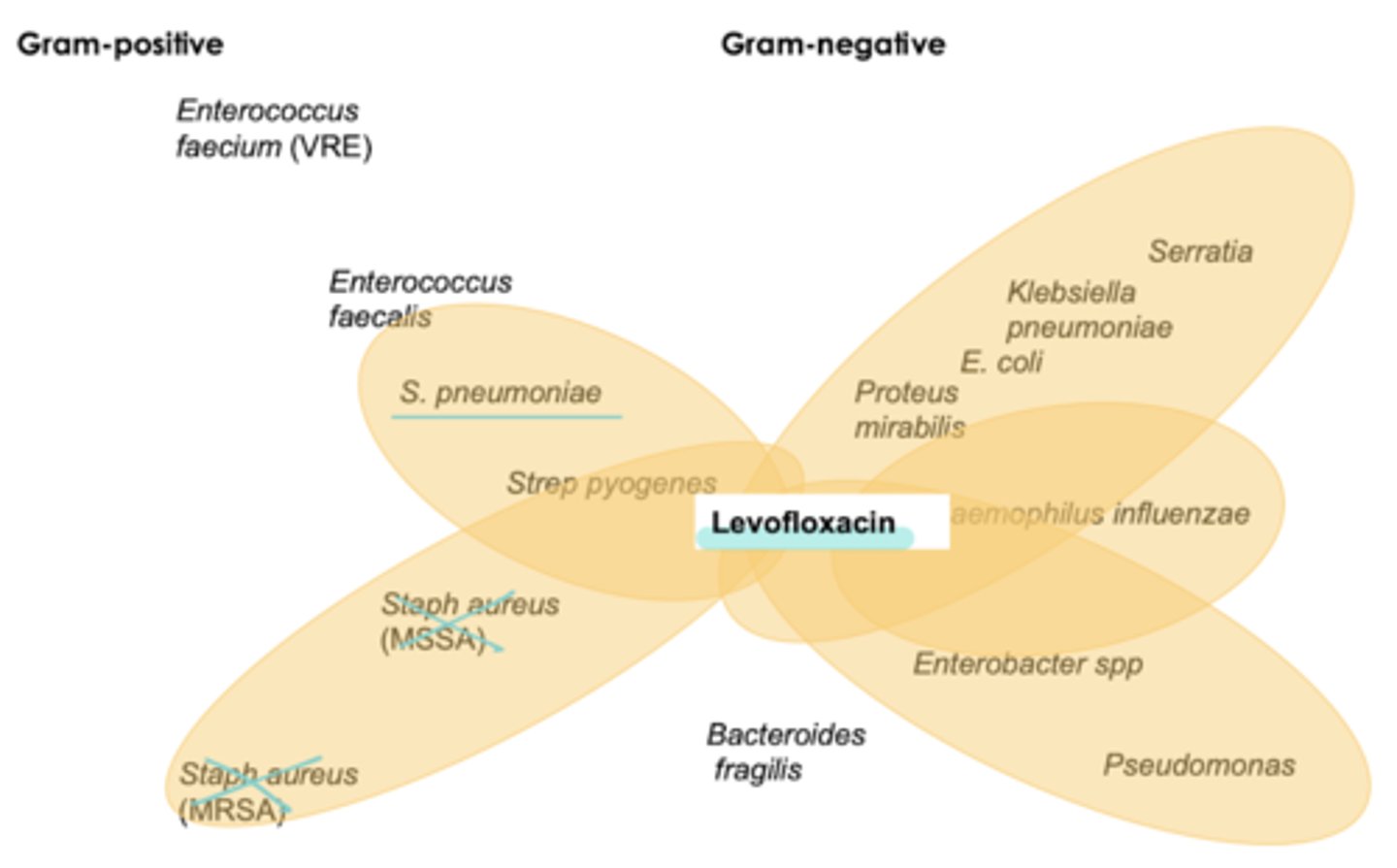
levofloxacin coverage
not usu used for Staph coverage
- pseudomonas aeruginosa
- strep pneumo (RF)
- atypicals
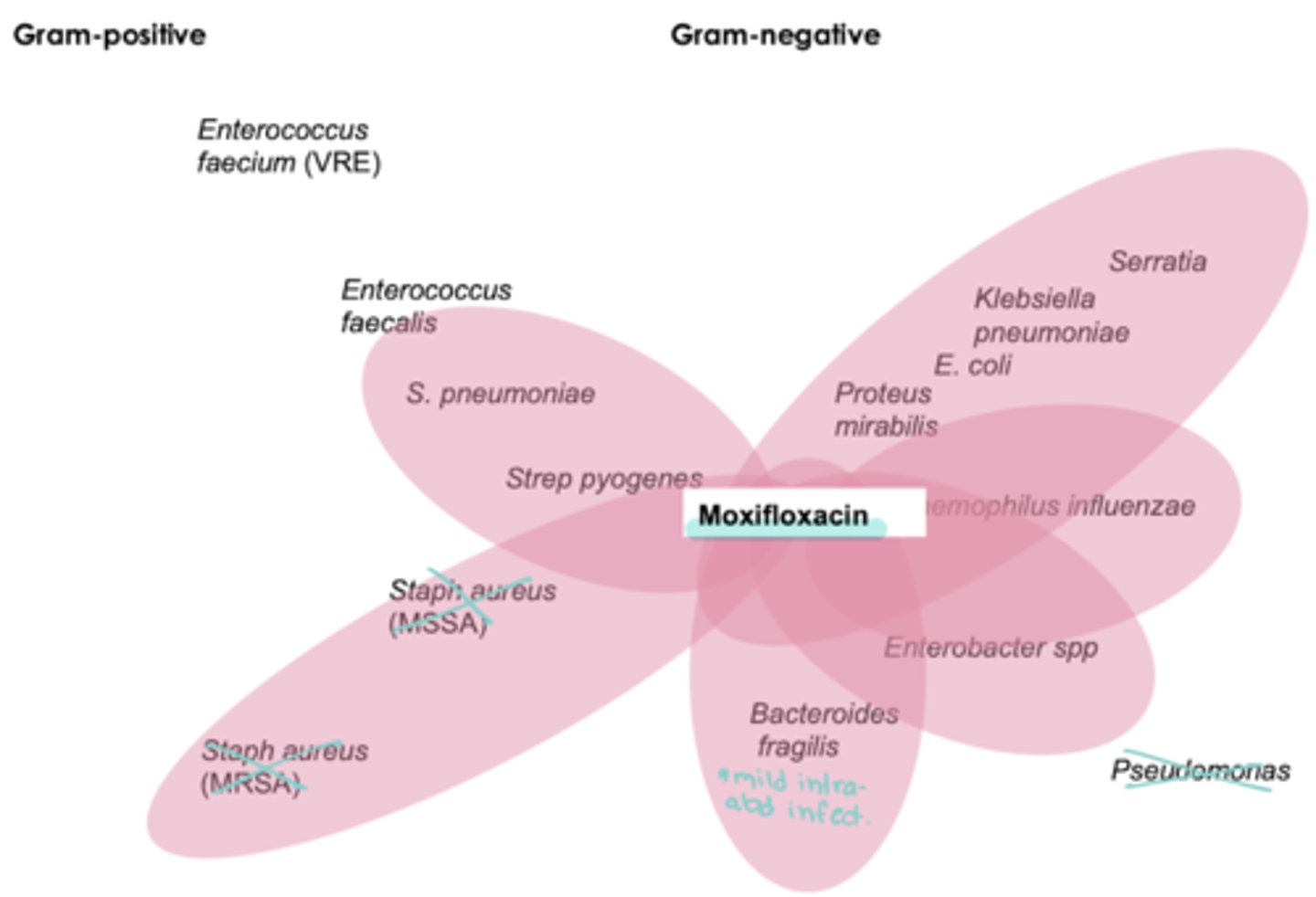
moxifloxacin coverage
not usu used for Staph coverage
- Strep pneumo (RF)
- anaerobes
- atypicals
NO pseudomonas
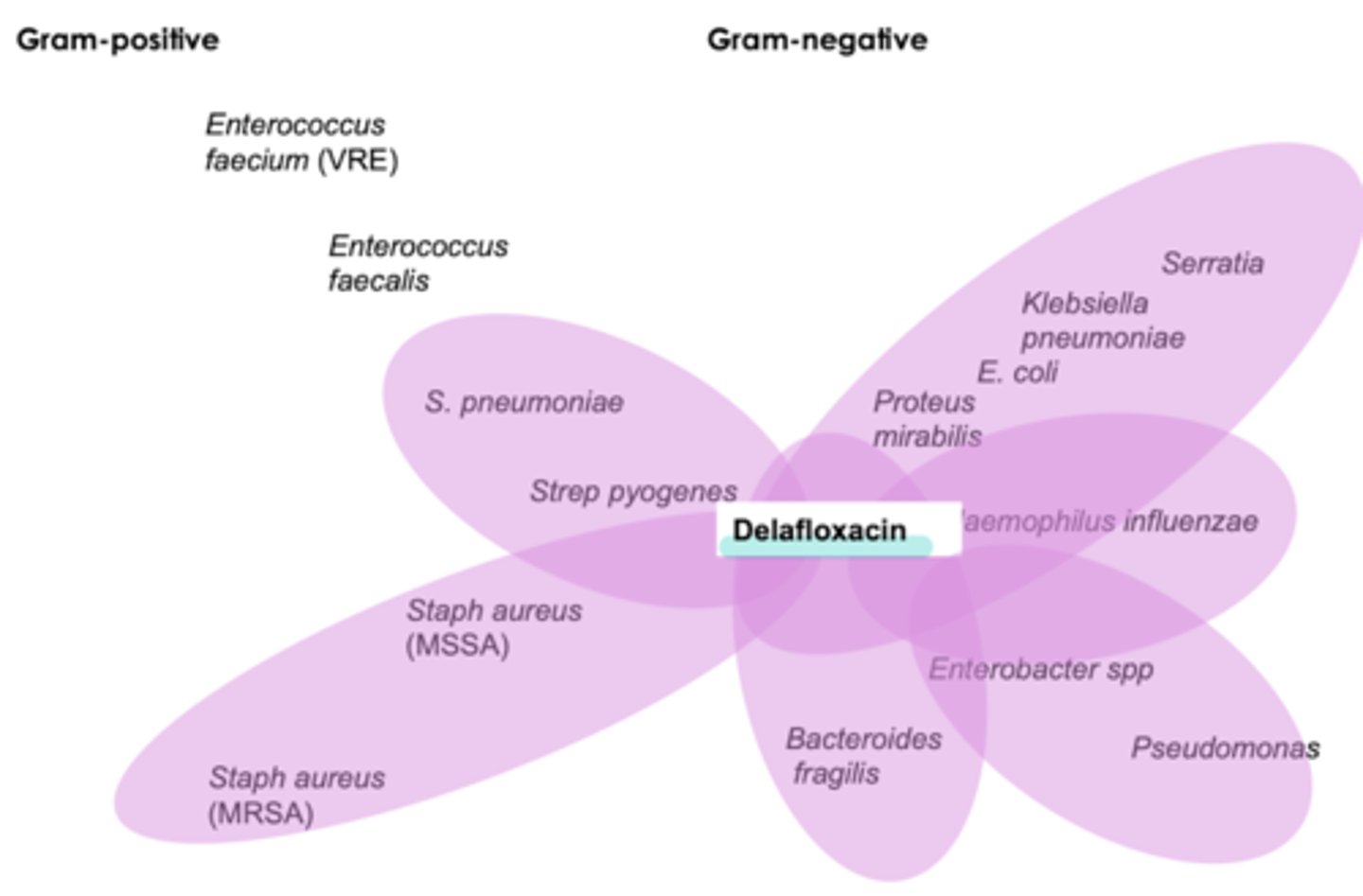
baxdela (delafloxacin) coverage
used for diabetic foot ulcers
broadest spectrum
- pseudomonas
- anearobes
- strep pneumo
- MRSA
MOA of fluoroquinolones
- inhibits DNA gyrase: better for gram - / PSA
- topoisomerase IV: better or gram +/ strep pneumo
which MOA of fluoroquinolones is more helpful for gram negatives
- inhibition of DNA gyrase
- ciprofloxacin has a higher affinity for DNA gyrase (does NOT treat strep pneumo)
which MOA of fluoroquinolones is more helpful for gram positives
- inhibition of topoisomerase IV
- moxifloxacin has a higher affinity for topoisomerase IV (does NOT treat pseudomonas)
fluoroquinolones have ___ bioavailability
high
which fluoroquinolones will NOT treat a UTI? why?
- moxifloxacin
- bc it does NOT concentrate in the urine
absorption of fluoroquinolones is decreased when taken with ____
aluminum
zinc
Mg
Fe
Ca++
D -- D interactions with fluoroquinolones
- other QT prolonging drugs
- CYP P450 system (warfarin, theophylline**Esp cipro)
adverse effects of fluoroquinolones
MANY!! rlly not first line
- N/V/D/HA/dizzy
- hypo & hyperglycemic
- photoxicity (sun protection)
- hepatotoxicity (monitor LFTs)
- C. diff
- QT prolong
- hemolytic anemias in G6PD pt
BBW with fluoroquinolones
- tendinitis/ tendon rupture (BBW)
- peripheral neuropathy
- CNS effects
- exacerbates mm. weakness in MG pt
do NOT use fluoroquinolones in ____
- preg
- breast feeding
- pediatric patients
what are the sulfa / sulfa combo drugs
- bactrim (sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim)
- dapsone
spectrum of activity for sulfa / sulfa combo drugs
- broad spectrum
- gram + (including MRSA)
- gram - (including strenotrophomonas & legionella & pneumocystis jirovecii)
**NO strep coverage
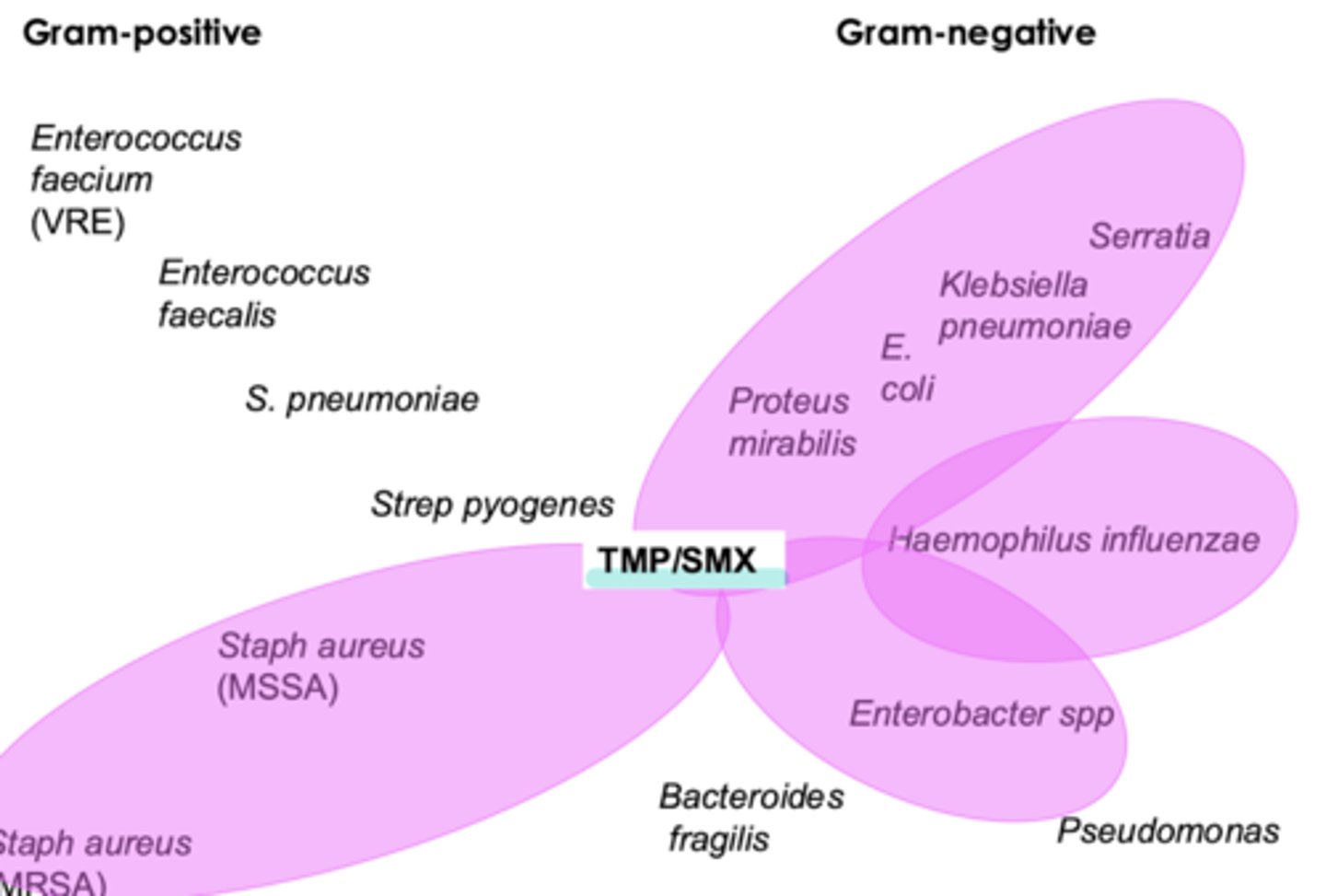
when do we use sulfa / sulfa combo drugs
- bactrim: PCP PNA, strenotrophomonas
- dapsone: leprosy
MOA of sulfamethoxazole
mimics PABA --> inhibition of dihydropteroate synthase
MOA of trimethoprim
its a structural analog of dihydrofolate --> inhibits dihydrofolate reductase
CI of sulfa / sulfa combo drugs
severe hepatic failure
D--D with sulfa / sulfa combo drugs
- warfarin
- phenytoin
- methotrexate
adverse effects of sulfa / sulfa combo drugs
- common: N/V
- hyperK+
- hematologic disturbances (megaloblastic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia)
- crystalluria
- rashes (SJS, TENs)
- kernicterus
pearls with sulfa / sulfa combo drugs
- patients need to be hydrated (oral form must be administered w at least 8oz H2O
- do not use w patients w G6PD deficiency --> hemolytic anemia
- do not use in kids < 2 & preg women
what are the nitroimidazoles
flagyl, metrogel (metronidazole)
spectrum of activity of metronidazole
- anaerobic gram -
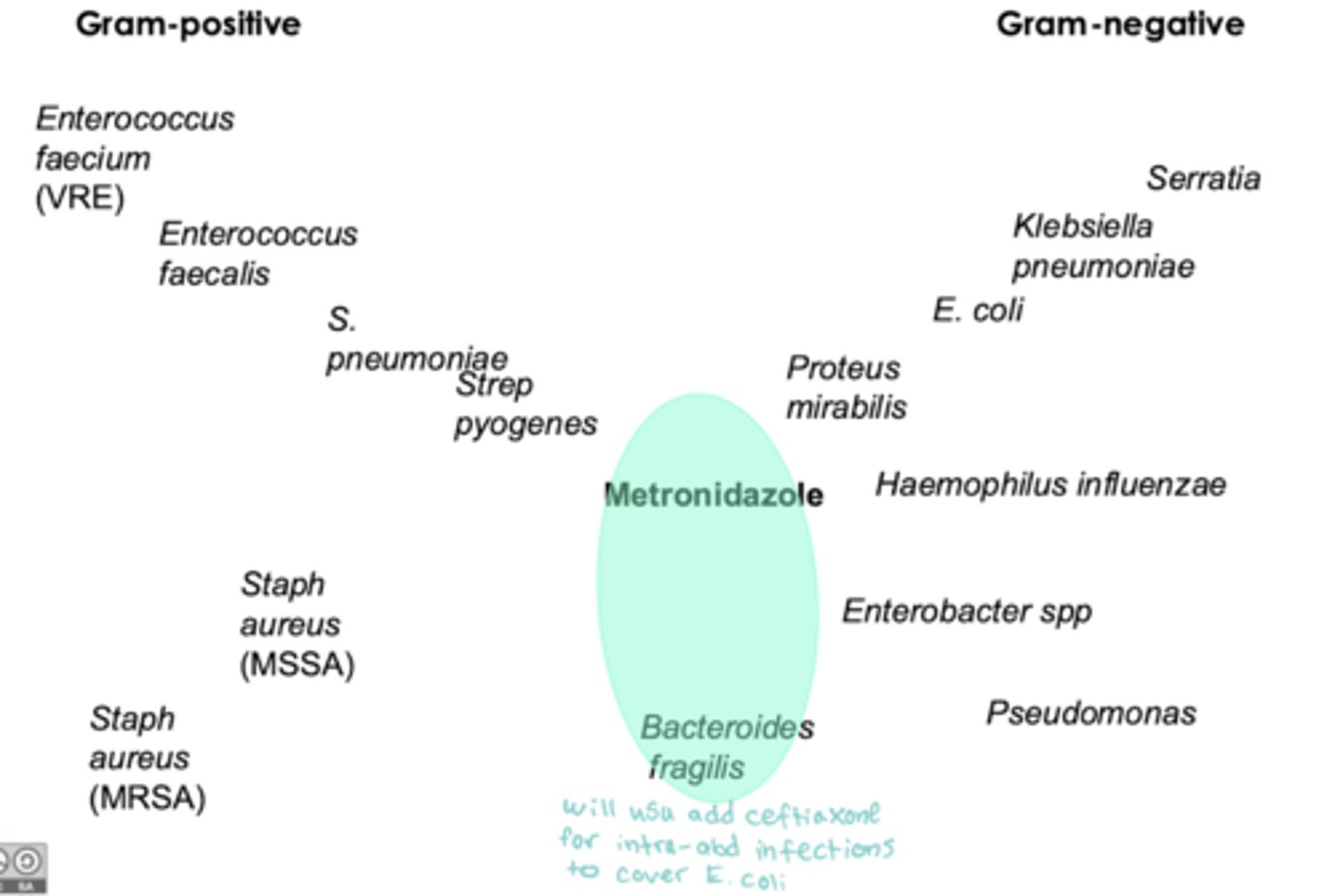
when to use metronidazole
- PO/IV: intra abdominal infections, BV, trichomoniasis
- topical: bacterial vaginosis, rosacea, trichomoniasis
MOA of metronidazole
- nitro group has to be "reduced" to be activated... once it is --> forms free radicals --> breaks up DNA of bacteria --> cell death
D--D with metronidazole
- disulfiram-like rxn when taken with alcohol
** medical myth but could be on exams
adverse effects of metronidazole
- common: N/V, epigastric discomfort
- unpleasant metallic taste
- furring of tongue
- peripheral neuropathy
- carcinogenic (BBW)
what are the nitrofurans
- macrobid, macrodantin (nitrofurantoin)
spectrum of activity of nitrofurans
- aerobic gram +: enterococcus & staph saprophyticus
- aerobic gram -
when do we use nitrofurans
- only cystitis (lower UTIs)
** do NOT use for upper UTIs
MOA of nitrofurans
- bacteria enzymatically reduce NO2 group to active agent that inhibits bacterial enzymes & damages their DNA
adverse effects of nitrofurans
- common: GI upset
- pneumonitis or fibrosis
- peripheral neuropathy
- hepatic dysfunction
fidaxomicin
- dificid (fidaxomicin)
spectrum of activity of fidaxomicin
- NARROW: C. diff (gram + anaerobe)
** we usually use Vanc first, just fidaxomicin is $$$
MOA of fidaxomicin
- acts on RNA polymerase --> bacterial transcription disruption --> protein synthesis termination --> cell death
adverse effects of fidaxomicin
- cross reactivity w macrolides
- common: N/V/abd pain
- hematologic disturbances: anemia, neutropenia
what are the rifamycins
- rifadin (rifampin)
- mycobutin (rifabutin)
- priftin (rifapentine)
- xifaxan (rifaximin)
spectrum of activity of rifamycins
- staph (MRSA), mycobacteria
- rifaximin: meningitis prophylaxis for salmonella & campylobacter
when to use rifamycins
- rifampin/ rifabutin/ rifapentine: mycobacteirum (MAC)
- rifampin: staph infections, prophylaxis for pt exposed to H. influenzae or N. meningitidis meningitis
- rifaximin: travelers diarrhea
MOA of rifamycins
- work by inhibition of RNA polymerase
- resistance develops easily to these agents
adverse effects of rifamycins
- common: N/V/rash
- hepatic failure (caution w alcoholics!! no alc on med)