AQA - Ecology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is an ecosystem?
The relationship between all living and non-living parts of a habitat
What is a population in an ecosystem?
Groups of individuals of the same species
What is a community in an ecosystem?
Made of many populations living together
What is competition in an ecosystem?
Organisms competing for resources
What do plants compete for?
Light, water, minerals from soil and space
What do animals compete for?
Food, mates and territory
What is interdependence?
When species rely on each other for food, shelter, pollination, seed dispersal etc
Why would removing one species from an ecosystem be bad for an ecosystem?
Because of interdependence, it can affect the whole community
What happens in a stable community?
All species and environmental factors are in balance so that population size stays fairly constant.
What is an example of a stable community?
A rain forest or ancient oak woodland
What is an abiotic factor?
A non-living factor that effects the community
What is a biotic factor?
A living factor that effects a community
What do abiotic factors include?
Light intensity, temperature, moisture levels, soil pH and mineral content, wind intensity and direction, carbon dioxide levels (Plants), oxygen levels (Aquatic animals)
What do biotic factors include?
Availability of food, new predators arriving, new pathogens, one species out-competing another
What are adaptations?
Features that allow an organism to survive in the conditions that they normally live in
What is a structural adaptation?
A physical adaptation. Features an organism has such as fur, beaks etc
What is a behavioural adaptation?
Something an organism does to allow it to survive
What are functional adaptations?
An internal working or body process that allows an organism to survive
What are extremophiles?
Organisms that can live in extreme conditions such as high pressure, high salt concentration, or high temperatures
What method can be used to study an ecosystem?
Transect line and a quadrat
What are decomposers?
Organisms that break down dead or waste material
What type of organisms are decomposers?
Fungi and bacteria
What do decomposers need?
Oxygen, moisture, a suitable temperature ans suitable pH
What can decomposers be used for?
Compost heaps
What is the carbon cycle?
It describes how carbon is recycled in nature
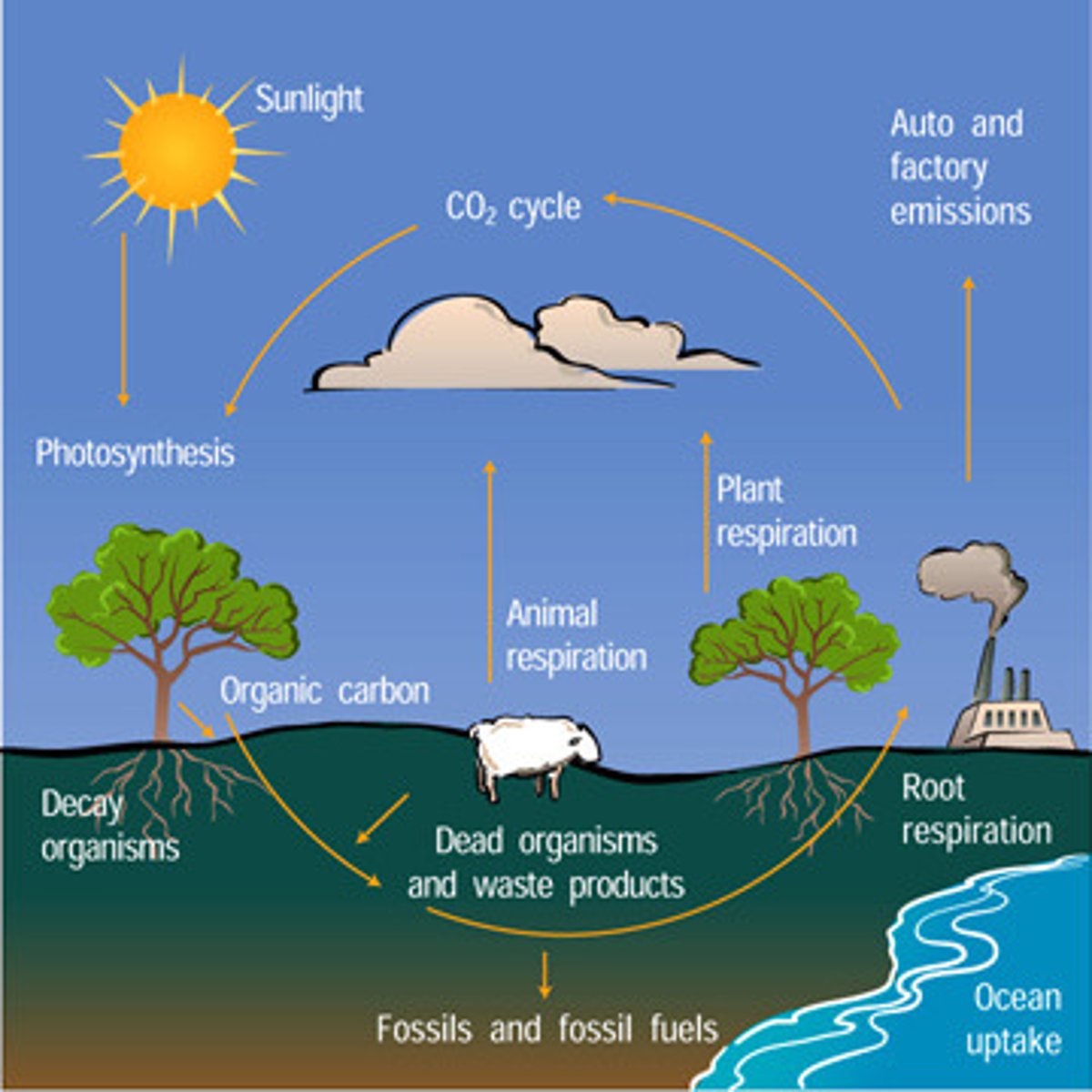
Why does the carbon cycle depend on decomposers?
To return carbon to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide through respiration
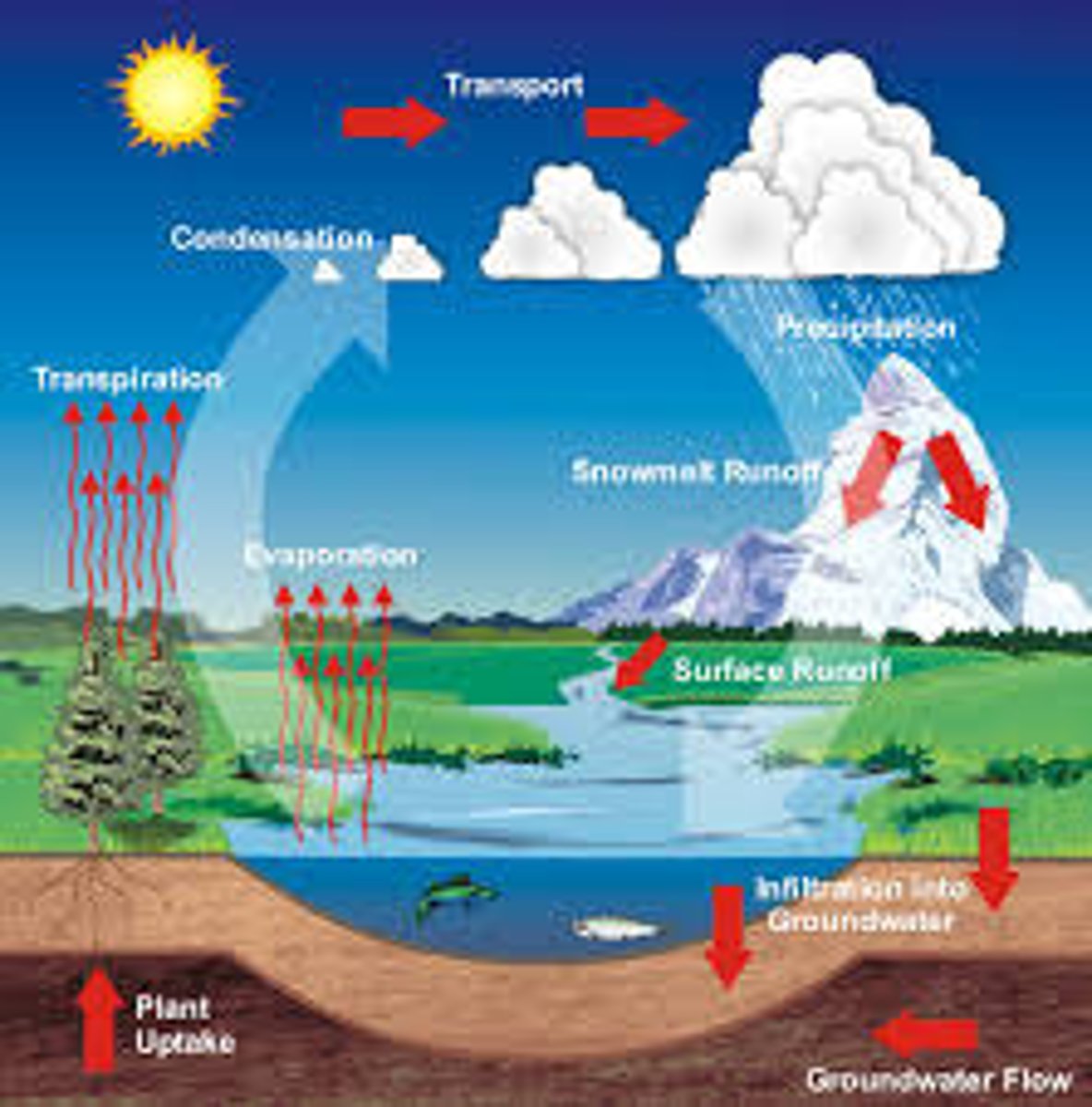
What is the water cycle?
Describes how fresh water circulates between organisms, rivers and the sea.
What is a producer in a food chain?
It synthesises molecules
What is an example of a producer?
A green plant, which produces glucose molecules by photosynthesis
What are producers eaten by?
Primary consumers
What are consumers eaten by?
Secondary consumers
What are secondary consumers eaten by?
Tertiary consumers
What is each level of a food chain called?
A trophic level
What is a predator?
Consumers that eat other animals
What is prey?
The animals that are eaten by predators
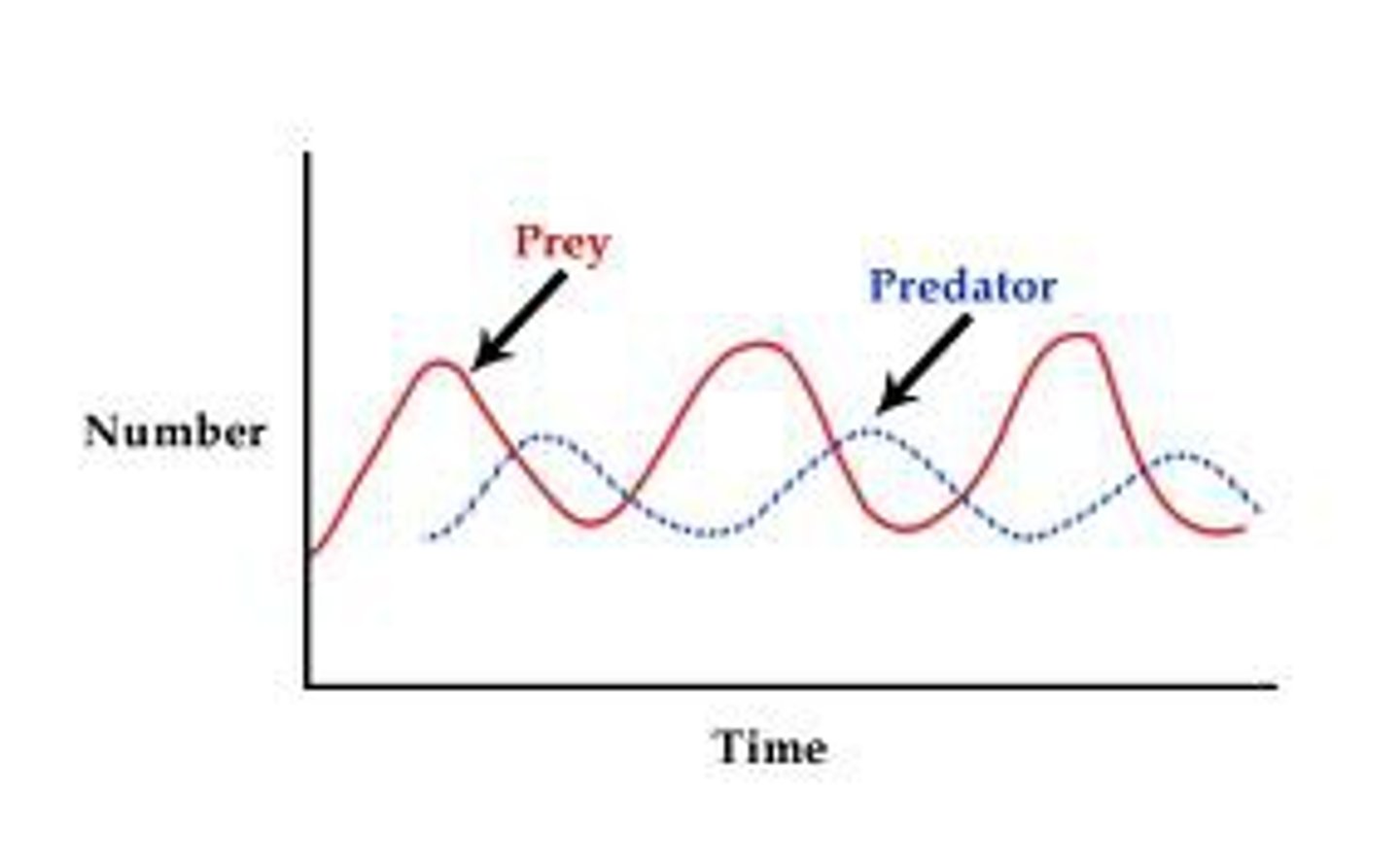
What happens to the number of prey and predators in a stable community over time?
The numbers of each rise and fall in cycles
How can the balance of predators and prey be shown?
A predator-prey graph
What is biodiversity?
The variety of all different species on Earth or in an ecosystem
Why does a high biodiversity maintain a stable community?
Species depend on each other for food and shelter
What is pollution doing?
Killing plants and animals
When or where can pollution occur?
In water from sewage, fertilisers or toxic chemicals, in air from gases, on land from landfill and toxic chemicals
What is the effect of building, quarrying, farming and dumping waste?
It reduces the amount of land available for animals
What does the burning and decay of peat lead to?
The release of carbon dioxide
Why has deforestation occurred in tropical areas?
To provide land for cattle and rice fields , to grow crops which biofuel can be produced from
What is global warming?
The gradual increase in the temperature of the Earth
What do scientists think the causes of global warming are?
The changes in gases in the atmosphere
What are the changes of gases in the atmosphere caused by?
Pollution and deforestation
What are the gases that cause global warming?
Methane and carbon dioxide
What are the biological consequences of global warming?
Loss of habitat when low lying areas are flooded by rising sea levels, changes in the distribution of species when an areas temperature or rainfall has changed, changes in the migration patterns of animals
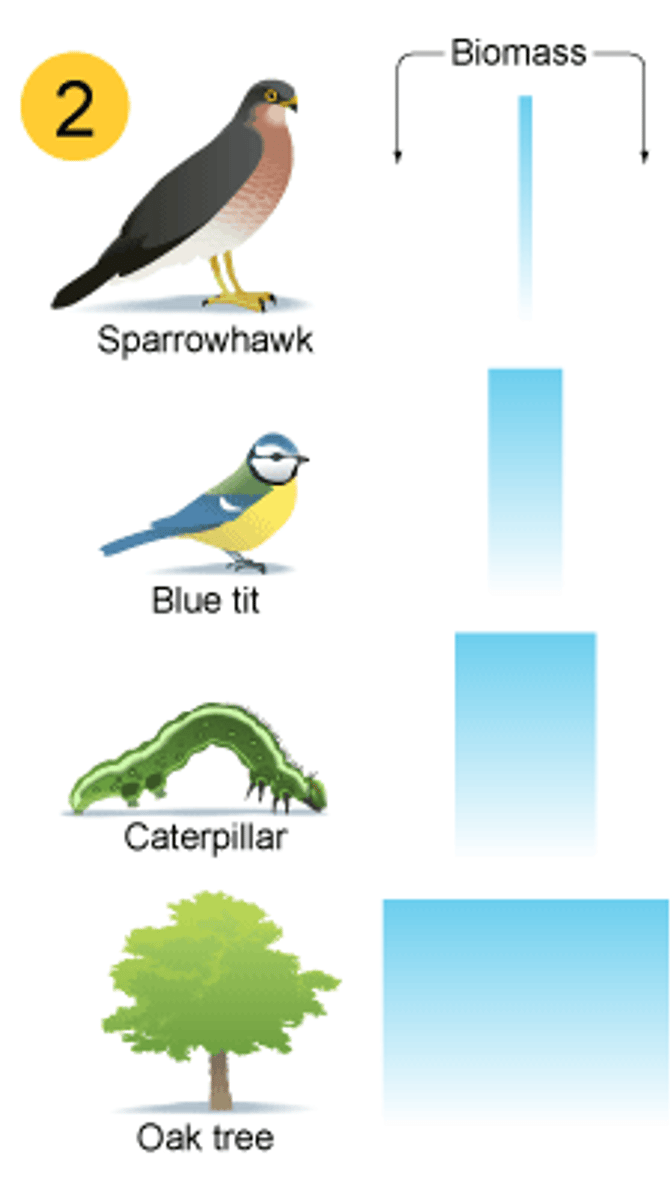
What is a pyramid of biomass used to show?
The amount of biomass in each trophic level of a food chain.