UC Davis PSC 001 - Midterm 2
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Automatic Processing
tasks that are so well learned that they require little attention
Controlled Processing
difficult or unfamiliar tasks that require much attention
Selective Attention
some stimuli demand attention (important information) and virtually shut off the ability to attend to anything else (irrelevant information)
Keeping Busy
there are activities in which we can "lose ourselves" and enter an altered state: religion, exercise, escapist behaviors
Flow (keeping busy)
total engagement in an act for its own sake, not focusing on a reward
Psychoactive Drugs
mind-altering substances that change the brain's neurochemistry
Stimulants
drugs that increase behavioral and mental activity and activate the sympathetic nervous system
Depressants
reduce behavioral and mental activity by depressing the central nervous system
Opioids
sometimes called narcotics, reduces pain
Hallucinogens
sometimes called psychedelics, produce alterations in cognition, mood, and perception
Paradoxical Sleep
REM sleep is called this because it is the most active stage of sleep with regard to brain activity (dreaming), but our bodies are actually paralyzed: beta waves are present
Classical Conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
Phobia
learned fear that is disproportionate to the real threat posed by an object or situation
Addiction and Classical Conditioning
stimuli associated with drugs (syringe, dispensary) become conditioned stimulus (CS): stimuli can therefore induce cravings
Operant Conditioning
a learning process in which the consequences of an action determine the likelihood that it will be performed in the future
Schedules of Reinforcement
continuous reinforcement: behavior is reinforced every time it occurs;
partial reinforcement: behavior is reinforced intermittently
Classical vs. Operant Conditioning
through classical conditioning, we learn associations between two stimuli or events;
through operant conditioning, we learn to associate our behavior with good or bad consequences
Latent Learning
learning that takes place in the absence of reinforcement or punishment
Modeling (observational learning)
imitating the behavior of others
Bandura's "Bobo doll" study
children who observed the aggressive model with the Bobo doll made far more aggressive responses than those who were in the non-aggressive or control groups
Attention
the process of focusing awareness on a particular stimulus while ignoring other stimuli
Phases of Memory
encoding: processing information so that it can be stored
storage: retention of encoded representations over time
retrieval: act of recalling or remembering stored information when needed
all together, these phases make up...
Sensory Memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
Short-term/ Working Memory
the part of your memory system that contains information you are consciously aware of before it is stored more permanently or forgotten
Long-term Memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system
Serial Position Effect
our tendency to recall best the last (a recency effect) and first items (a primacy effect) in a list
Explicit Memory
the system underlying conscious memories
episodic memory: memory for one's personal past experiences
semantic memory: memory for knowledge about the world
Implicit Memory
the system underlying unconscious memories
procedural/ motor memory: involves motor skills and behavioral habits
Prospective Memory
remembering to do something at some future time
Shallow Encoding
based on surface features (e.g., what something looks or sounds like)
Deep Encoding
based on semantic meaning (e.g., what something means)
Schemas
cognitive structures that help us perceive, organize, process, and use information; generalizations about concepts and categories
Association Networks
metaphor for how neurons are connected to make up mental representations
Encoding Specificity Principle
any stimulus encoded with an experience can trigger a memory of that experience
context-dependent memory: memory enhancement due to similarity between encoding and recall situations
state-dependent memory: memory enhancement due to similar internal states during encoding and recall
Proactive Interference
prior information inhibits the ability to remember new information
Retroactive Interference
new information inhibits the ability to remember prior information
Flashbulb Memories
vivid episodic memories for the circumstances in which people first learned of a surprising, consequential, or emotionally arousing event
Memory Storage
memory is distributed throughout the brain rather than in a specific location; they're stored in multiple regions and linked through memory circuits; but specific regions of the brain are important for memory
Hippocampus
a neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage
Consolidation
the process by which encoded information becomes stored in memory
Reconsolidation
neural processes involved when memories are recalled and then stored again for retrieval
Analogical Representations
correspond to and have some physical characteristics of actual objects or things around us
Symbolic Representations
abstract representations that do not correspond to physical features of objects or ideas
Scripts
schemas about sequences of events
direct behavior in specific situations
learned through experience and observation & shaped by culture
Deductive Reasoning
using general rules to draw conclusions about specific instances
Inductive Reasoning
taking a specific instance and generalizing it to other instances to draw a conclusion
Heuristics
mental shortcuts used to reduce the amount of thinking that is needed to make decisions
Crystallized Intelligence
factual knowledge about the world, word meanings, arithmetic, etc.
Fluid Intelligence
the ability to think on the spot by drawing inferences and understanding relations between concepts not previously encountered
IQ (intelligence quotient)
the overall quantitative measures of a child's intelligence relative to that of other children of same age
mental age/ chronological age * 100
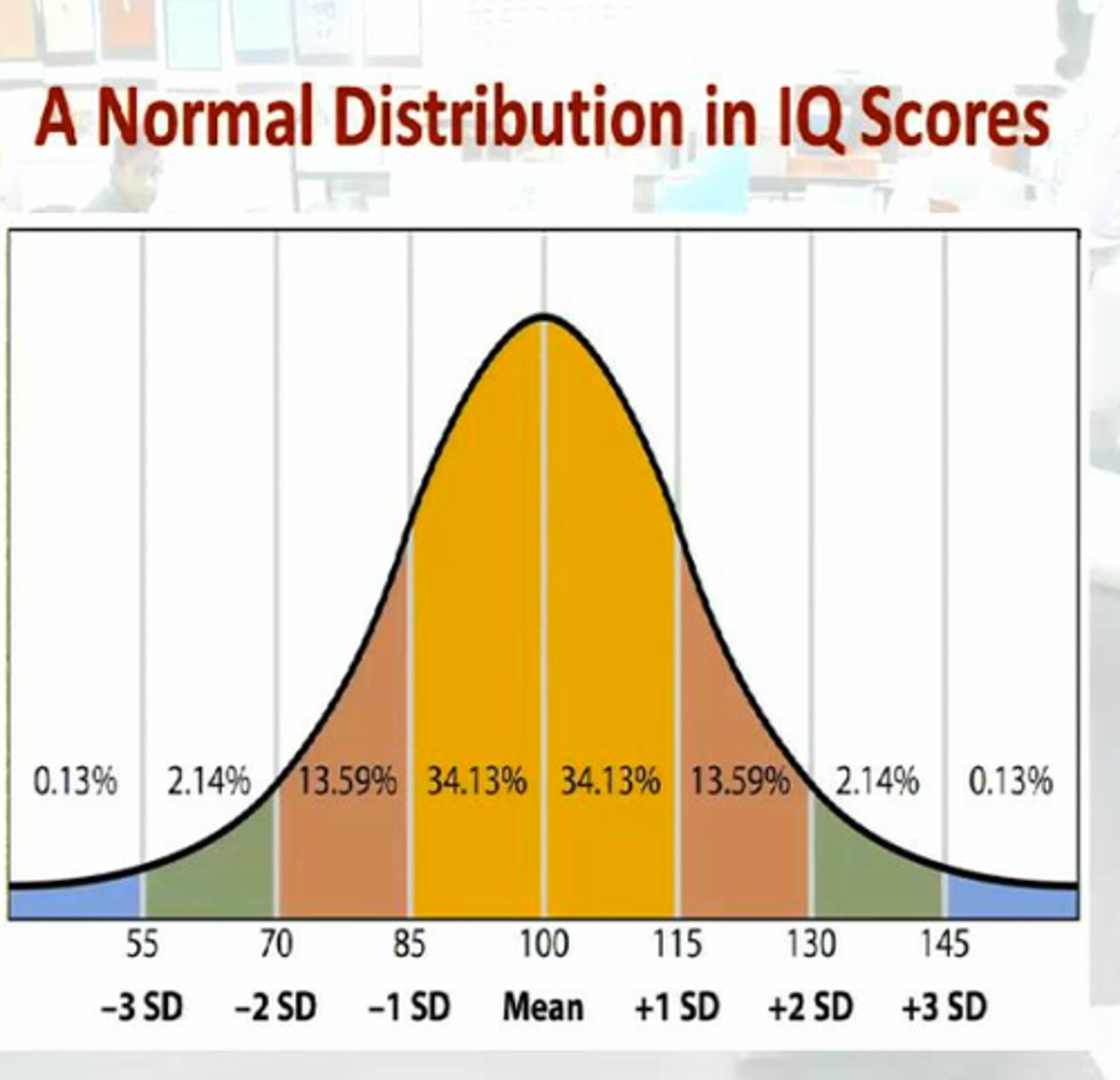
Distribution of IQ Scores
IQ tests have a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of about 15 or 16, depending on the test
Complexity of Intelligence
the development of intelligence is embedded within context and genetics (polygenetic/ epigenetic studies)
Stereotype Threat
apprehension about confirming negative stereotypes related to one's group
Primary Emotions
innate, evolved, and universal
anger, fear, sadness, disgust, happiness
Secondary Emotions
blends of basic emotions
remorse, guilt/ shame, jealousy, embarrassment, anticipation
Valence
how unpleasant or pleasant
Activation
how arousing
Amygdala
processes emotional significance of stimuli & generates immediate reactions; critical for emotional learning
Prefrontal Cortex
important for experiencing, expressing and regulating emotions
James-Lange Theory
interpretation of physical changes leads to emotion experience
stimulus→arousal→emotion
Cannon-Bard Theory
mind & body experience emotions independently
stimulus→arousal
↳emotion
Two-Factor Theory
we label emotions based on how we interpret the situation
stimulus→arousal→appraisal→emotion
Excitation Transfer
residual arousal caused by one event is transferred to a new stimulus
Non-verbal Expression of Emotion
our faces communicate our emotions to others; specific facial muscles in expressions can identify emotions
tone of voice; body position, gestures
Display Rules
rules learned through socialization that dictate which emotions are suitable to given situations
Emotion Regulation Strategies
rumination: "Keep thinking about it!"
suppression: "Don't feel it!"
distraction: "Keep your mind busy!"
humor: "Laugh about it!"
Motivations
needs: a state of biological or social deficiency
homeostasis: tendency for bodily functions to maintain equilibrium
drive: psychological state that motivates an organism to satisfy need via arousal
Freud's Pleasure Principle
people seek pleasure and avoid pain
Self-regulation
process by which people change their behavior to attain personal goals
Delayed Gratification
postponing immediate gratification for long-term goals
Hot Cognition
thoughts that focus on the rewarding aspect of the object (associated with amygdala)
Cold Cognition
thoughts that focus on the conceptual or symbolic meanings of the object (associated with prefrontal cortex)