Cell Chemistry (Ch 2)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
Basic Chemical Reactions
Must be balance
* Ex: 2H2 + O2 → 2H20
* Reactant → Product
* Ex: 2H2 + O2 → 2H20
* Reactant → Product
2
New cards
Biological Molecules important to cells
1. Protein
2. Carbohydrate
3. Nucleic Acid
4. Lipid (have different structures so are not polymers)
3
New cards
Macromolecules (Polymers)
Very large and composed of monomers
* Protein
* Carbohydrate
* Nucleic Acid
* Protein
* Carbohydrate
* Nucleic Acid
4
New cards
Monomer
* Amino Acid
* Monosaccharide
* Nucleotide
* Monosaccharide
* Nucleotide
5
New cards
Polymer
* Polypeptide
* Polysaccharide
* Polynucleotide
* Polysaccharide
* Polynucleotide
6
New cards
Polymer Formation
Long molecules made of repeating building blocks called monomers
7
New cards
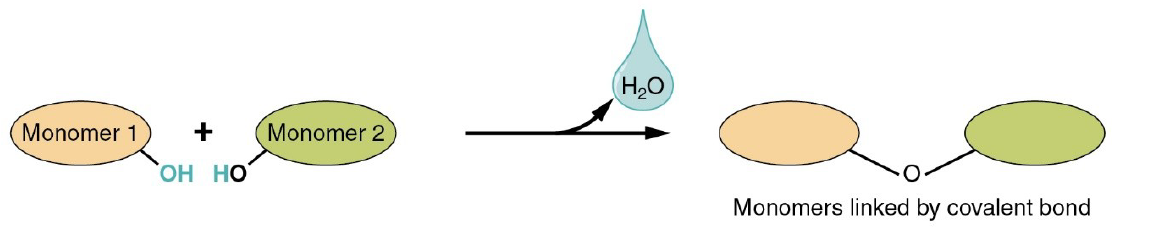
Dehydration Synthesis
Reaction creates a water molecule.
* Polymer is formed
* Monomer is joined by removal of OH from one monomer and removal of H from other at site of bond formation
* Polymer is formed
* Monomer is joined by removal of OH from one monomer and removal of H from other at site of bond formation
8
New cards
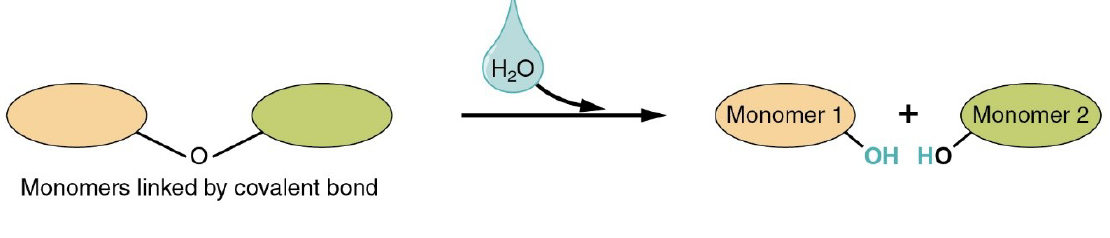
Hydrolysis Reaction
Takes in a water molecule
* Polymers are broken apart
* Monomer is released by addition of water adding OH to one monomer and H to the other.
* Polymers are broken apart
* Monomer is released by addition of water adding OH to one monomer and H to the other.
9
New cards
Protein
* Monomer: Amino acid (20 of these)
* Polymer: Polypeptide (peptide bond)
* Enzyme
* Polymer: Polypeptide (peptide bond)
* Enzyme
10
New cards
Amino acid
20 different kinds. The sequence of these is what determine the shape and function of a protein.
11
New cards
Peptide bond
amino acids bonded together by covalent bond.
12
New cards
Denature
proteins that are exposed to harsh conditions (ex: high heat) become nonfunctional. Cannot be undone.
13
New cards
Enzyme
Protein that speeds up chemical reactions.
* Break apart or build molecules.
* Specific to substrate which is determined by shape.
* Name usually ends with -ase
* Break apart or build molecules.
* Specific to substrate which is determined by shape.
* Name usually ends with -ase
14
New cards
Carbohydrate
Source of chemical energy in living organisms (ATP)
* Important in the structure of some cells.
* Bacterial Cell walls
* Plant cell walls
* Monomer: Monosaccharides (simple sugar)
* Disaccharide: 2 sugars
* Polysaccharides: many sugars (polymer)
* Starch: used to make energy for cells.
* Important in the structure of some cells.
* Bacterial Cell walls
* Plant cell walls
* Monomer: Monosaccharides (simple sugar)
* Disaccharide: 2 sugars
* Polysaccharides: many sugars (polymer)
* Starch: used to make energy for cells.
15
New cards
Disaccharide
2 sugars
16
New cards
Polysaccharide
Polymer of many sugars
17
New cards
Starch
used to make energy for cells
18
New cards
Nucleic Acid
Store and transfer genetic information.
* Monomer: nucleotide
* DNA
* RNA
* Monomer: nucleotide
* DNA
* RNA
19
New cards
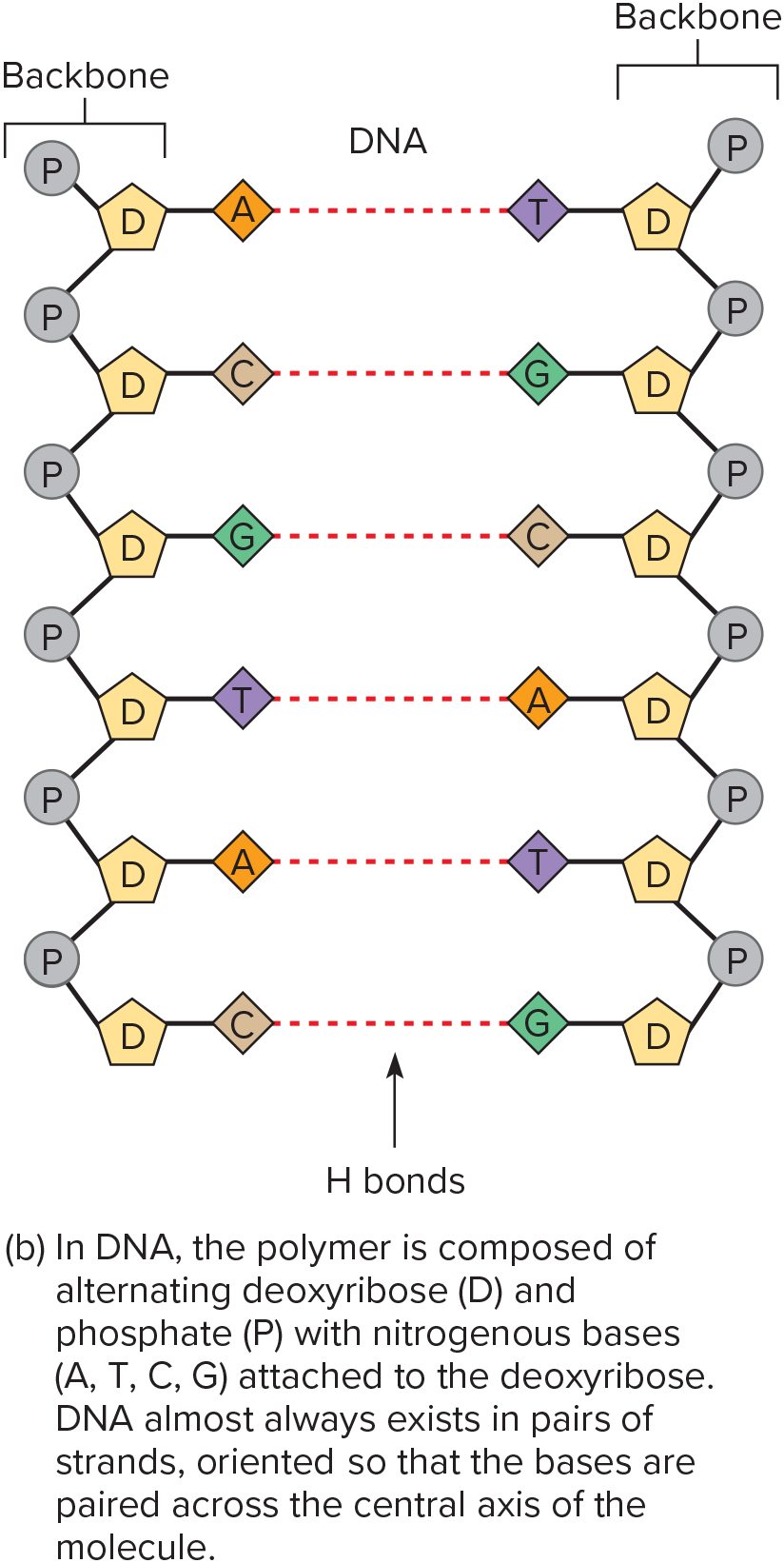
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Double helix structure bound by hydrogen bonds
20
New cards
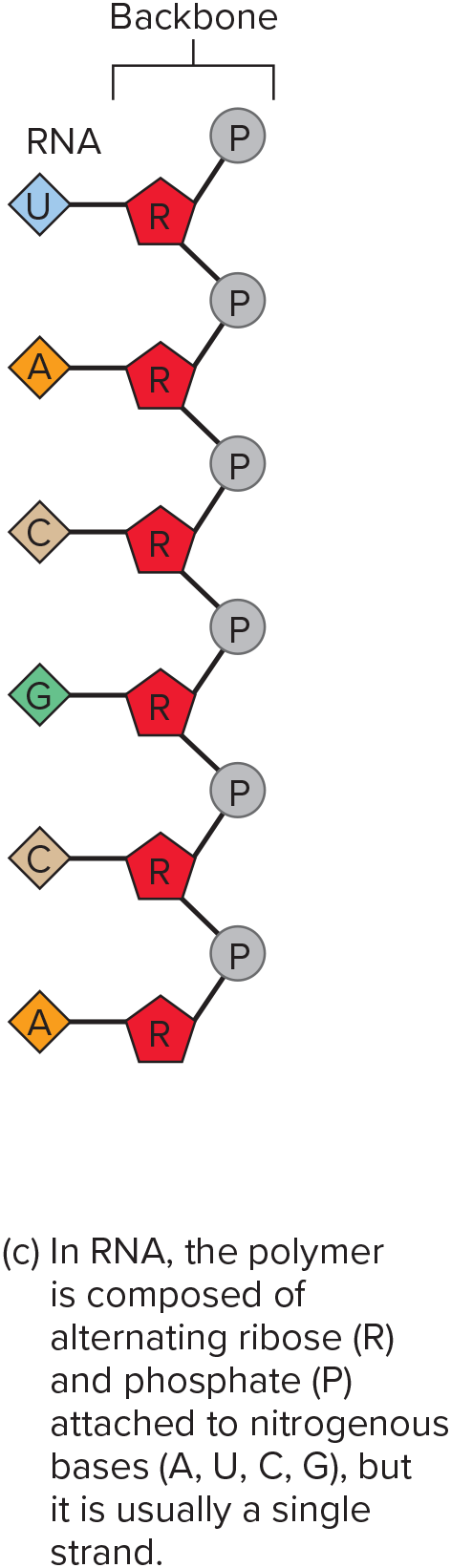
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Single stranded structure
21
New cards
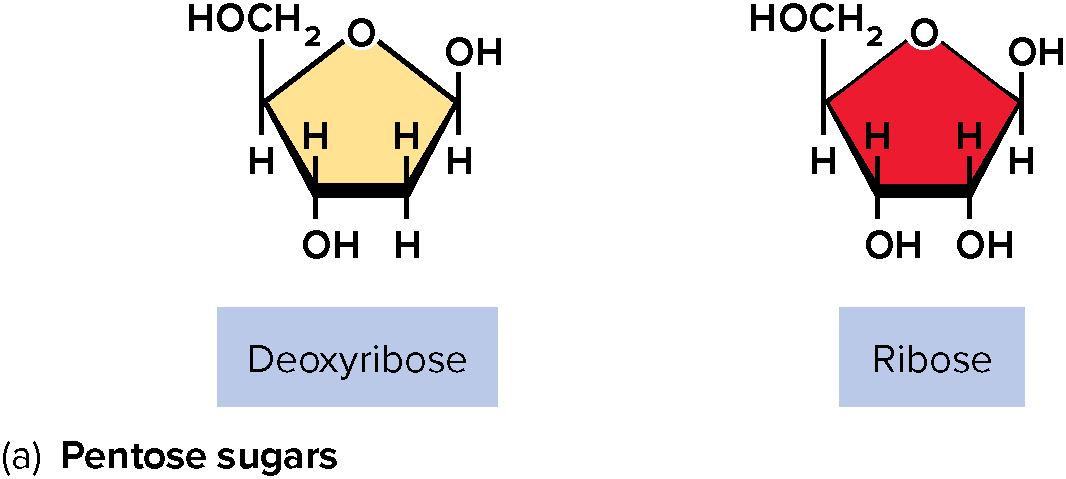
Pentose Sugar
Deoxyribose and Ribose
22
New cards
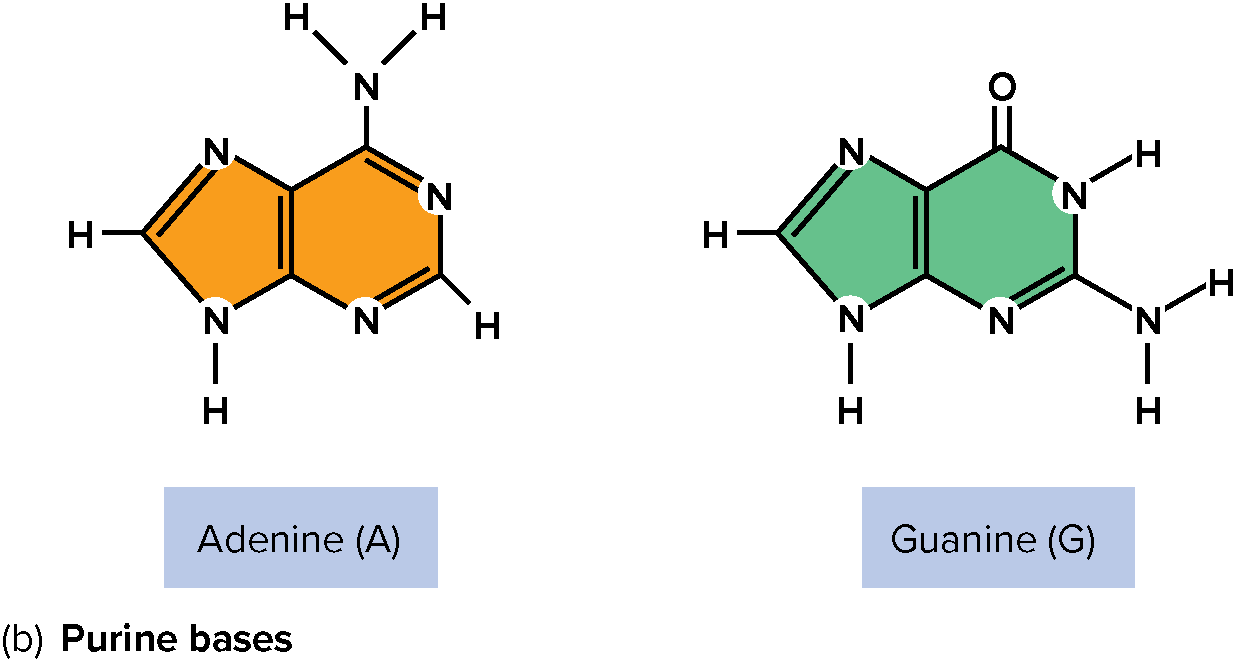
Purine Base
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
23
New cards
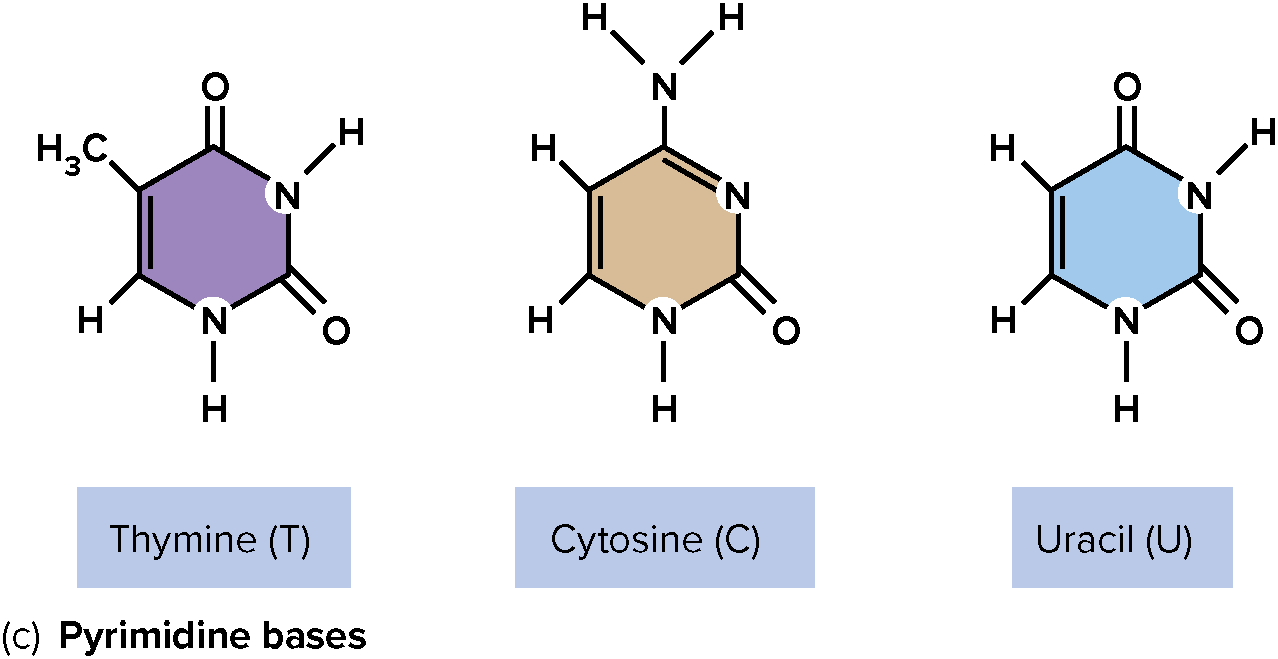
Pyrimidine Bases
Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Uracil (U)
24
New cards
Lipid
Macromolecule but not a polymer
1. Fat: 3 carbon backbone with fatty acid chains (long chains of carbon) attached.
2. Phospholipid: phosphate head, glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails.
3. Sterols: 4 carbon rings.
1. Fat: 3 carbon backbone with fatty acid chains (long chains of carbon) attached.
2. Phospholipid: phosphate head, glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails.
3. Sterols: 4 carbon rings.
25
New cards
Fat
3 carbon backbone with fatty acid chains (long chains of carbon) attached.
* Unsaturated
* Saturated
* Unsaturated
* Saturated
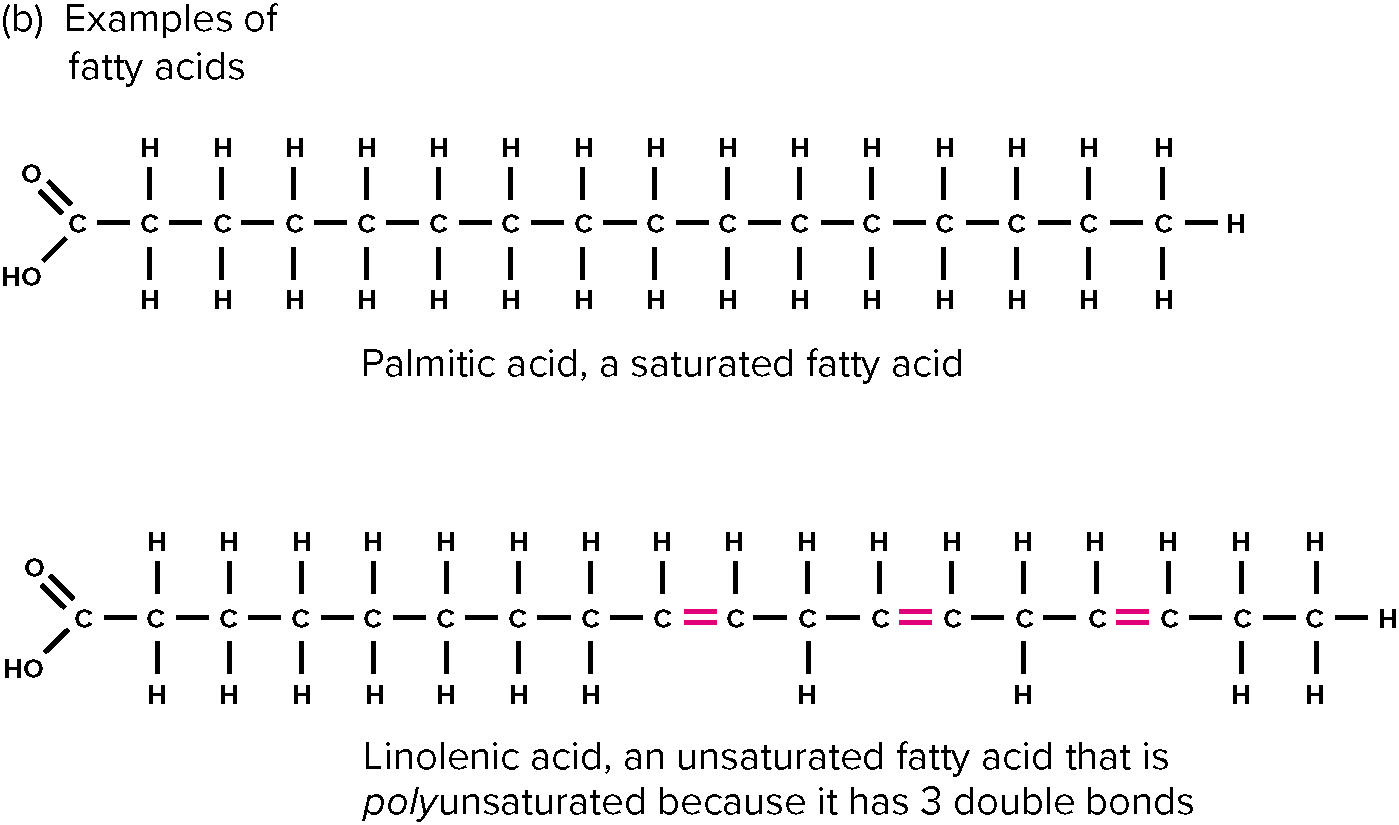
26
New cards
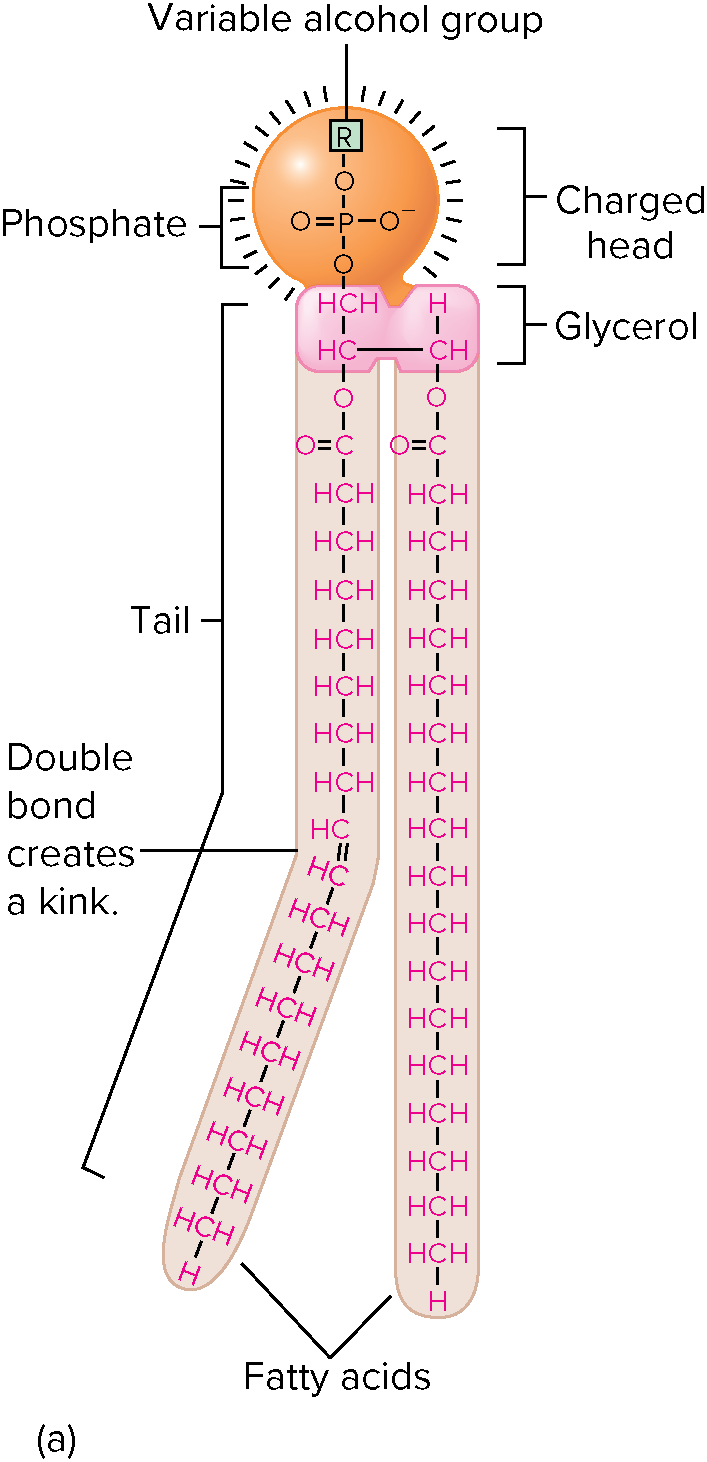
Phospholipid
phosphate head, glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails.
* Compose cell membrane
* From bilayer in water
* Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
* Compose cell membrane
* From bilayer in water
* Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
27
New cards
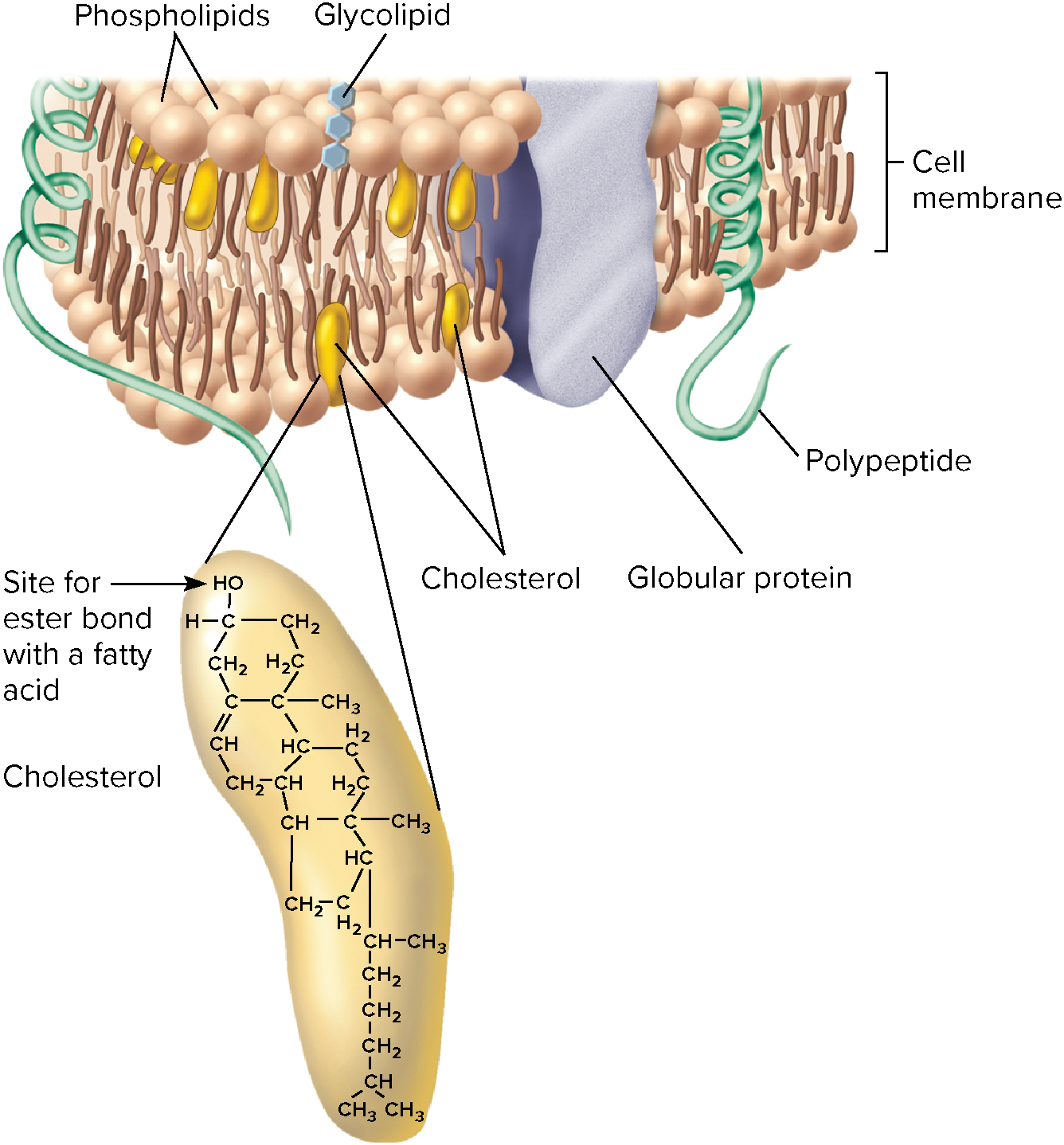
Sterol
4 carbon rings.
* Also known as steroids
* Cholesterol is a component of cell membranes
* Hormones
* Vitamins
* Also known as steroids
* Cholesterol is a component of cell membranes
* Hormones
* Vitamins