Chem States of Matter
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Physical Change
A change that alters a substance without changing properties.
Chemical Change
A change in which one or more substances turns into a new substance.
Physical Property
A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the samples composition(color, temperature, density).
Properties of matter(2)
Intensive and Extrusive
Extrusive
Dependent on how much of a substance is present. Ex: mass, volume, length
Intensive
Dependent on what the substance is and not how much of it you have. Ex: Density
Chemical Property
The ability of a substance to combined with or change into one or more substances. Ex: iron from rust, copper from air.
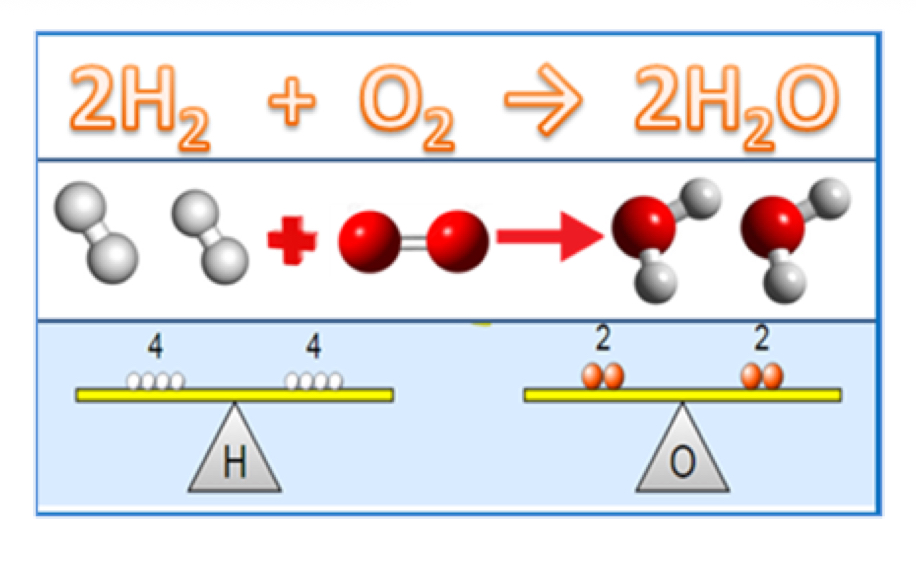
Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, it is conserved. Mass of Reactants = Mass or Products
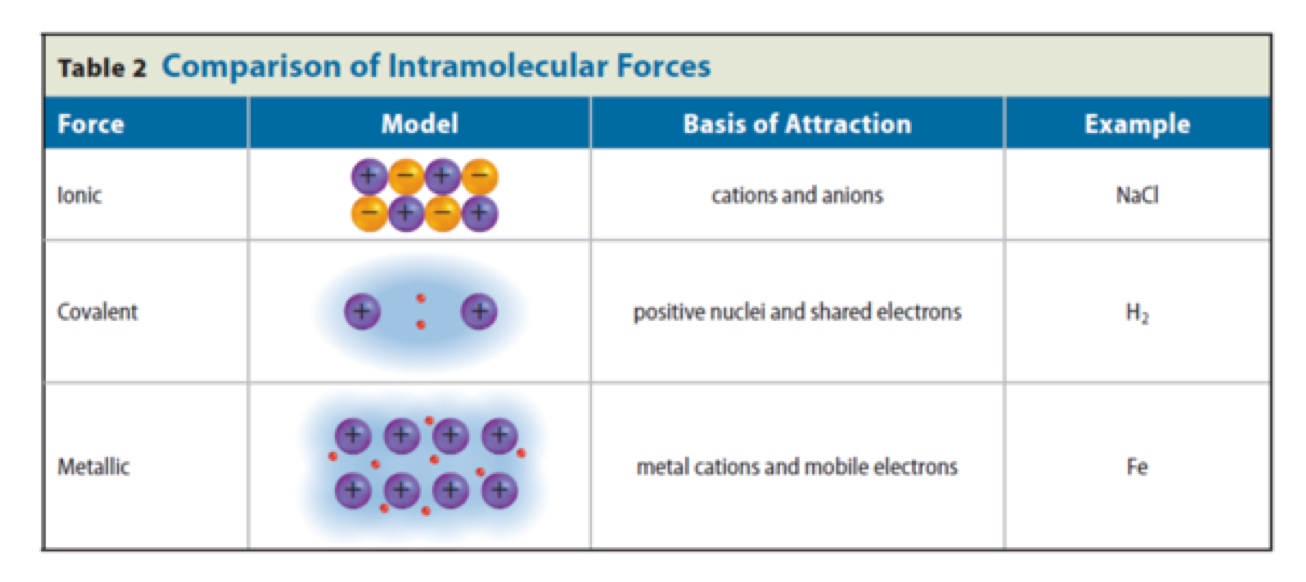
Intermolecular Forces(3)
London Dispersion Forces, Dipole-Dipole Forces, Hydrogen bonds
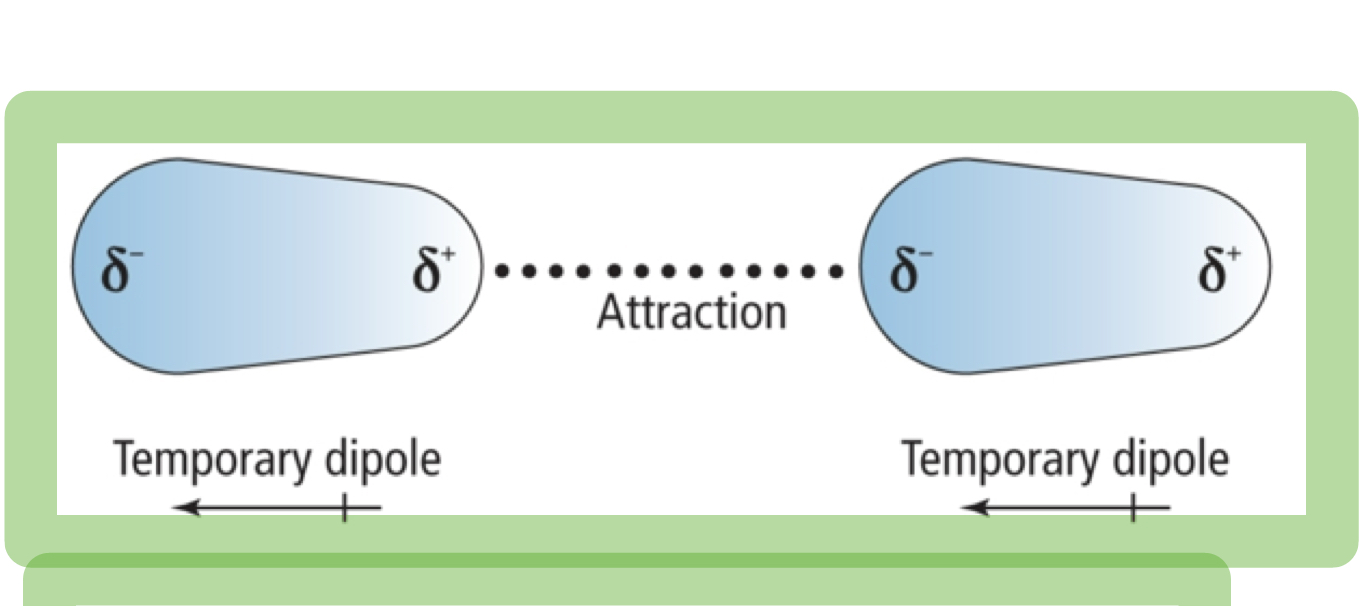
London Dispersion Forces
Weak forces that result from temporary shifts in density of electron clouds(weakest).
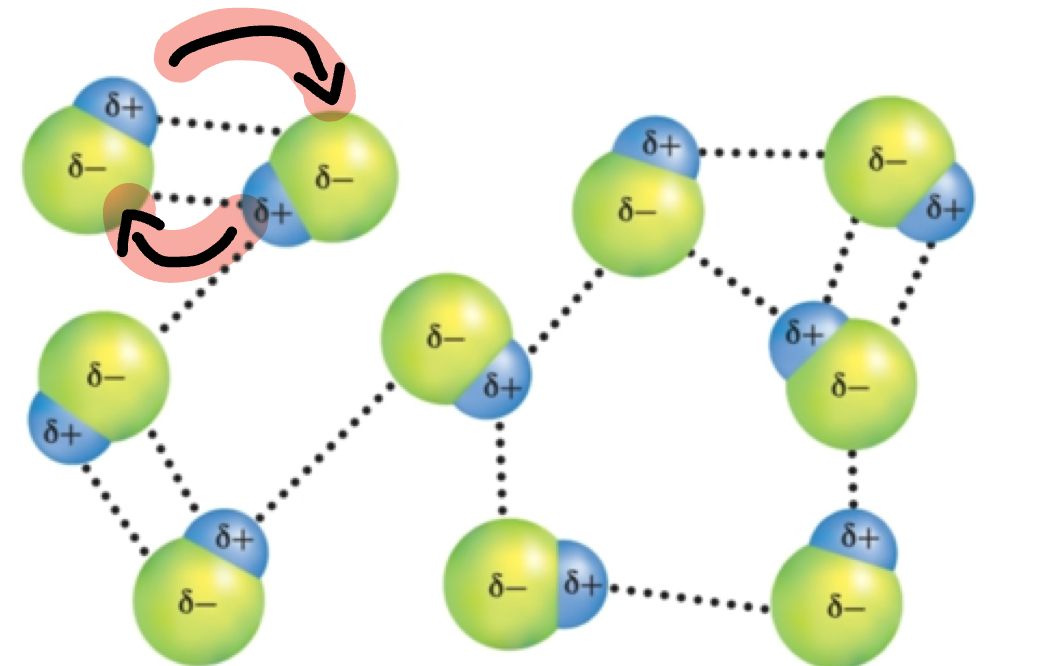
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Attractions between opposite charges regions of polar molecules(middle).
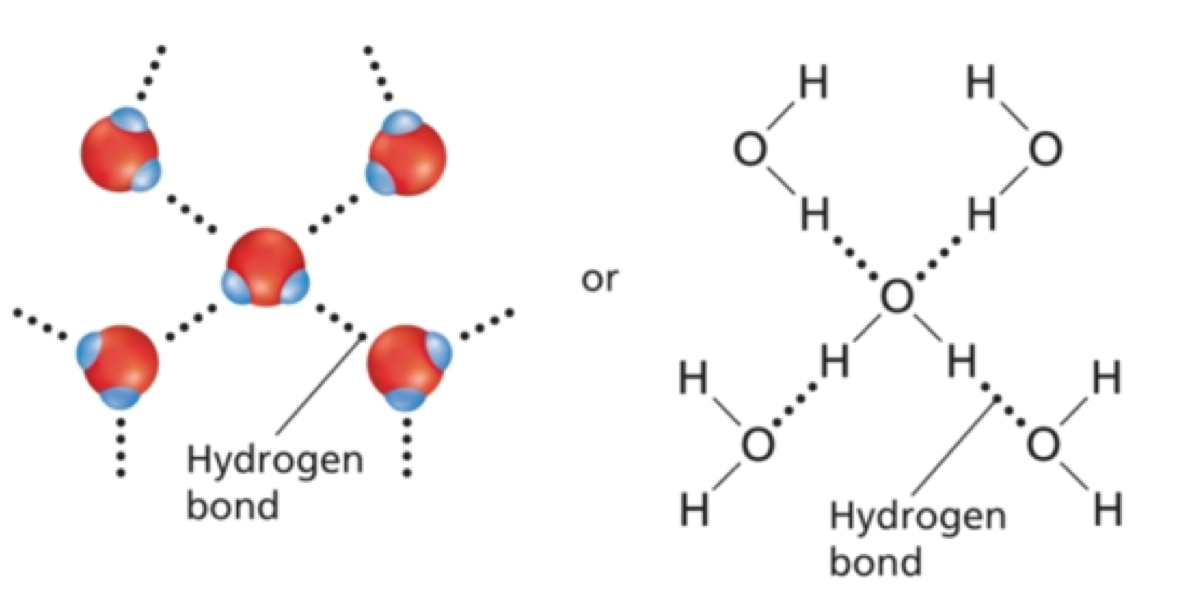
Hydrogen Bonds
A special type of dipole-dipole attraction that occurred between molecules that contain hydrogen atom bonded to a small, highly electronegative atom, with at least one lone pair of electrons. Usually oxygen(O), Florine(F), or Nitrogen(N). Always polar and the (strongest).
Matter
anything that has mass and takes up space(solid, liquid, gas).
Solid Properties
have a definite volume and shape.
Liquid Properties
Take the shape of the container, definite volume.
Gas Properties
Have no definite shape or volume, expand to fill the container.
Vapor
refers to gaseous state of a substance that is a solid or liquid at room temp. Ex: water
Kinetic Theory of Gases
1) Gas particles are small particles separated by empty space.
2) Gas particles are in constant, random, rapid motion with no attractions or repulsion’s between particles.
3) Collision are perfectly elastic and creates pressure(no kinetic energy lost, just transferred).
Heat
transfer of energy from an object of higher temperature to an object of lower temp.
Kinetic energy and temp are directly proportional (one goes up so does the other)
Temperature is measured in units (K) kelvins
At a temp of absolute zero (OK) particle moving ceases
Melting Point
temperature at which the forces that hold a solid together are broken and substances becomes a liquid
Boiling Point
Vapor pressure of liquid changes to a gas or vapor
Vaporization
Liquid changes to a gas or vapor
Evaporation
Vaporization only at the surface of a liquid
Sublimation
Solid changes to a gas without going through the liquid phase. Ex: dry ice
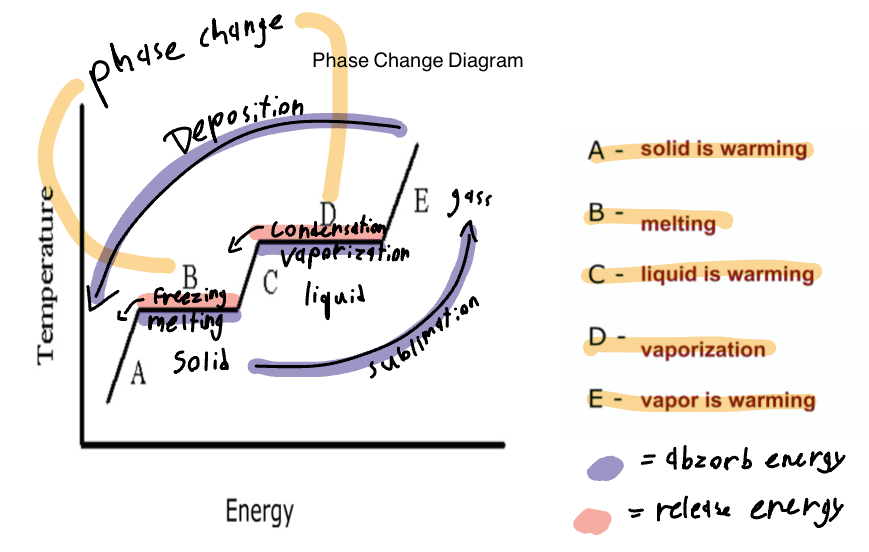
Phase Changes that release energy
Freezing point(liquid to solid), condensation(gas becomes a liquid), deposition(gas directly to a solid).
A, C, E, temp change. B and D have a constant temp and phase change.
A-solid is warming, B-melting, C-liquid is warming, D-vaporization, E-vapor is warming
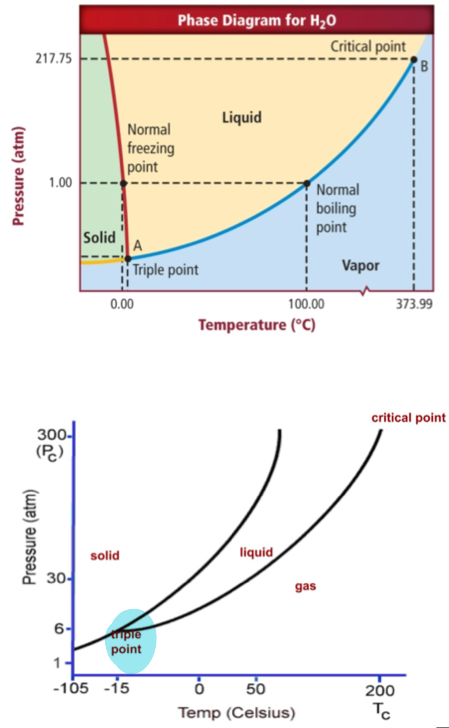
Phase diagram
Temp(Cº) + Pressure(atm). Triple Point: water can be all three. Left(solid)/Middle(liquid)/right(gas).