BSC 111L Practical #1 G
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
evolution
Genetic change over multiple generations
What leads to speciation?
natural selection
Facts of Natural Selection
- many traits are heritable
-More offspring are produced than can survive
inferences of natural selection
- Some organisms will have traits which make them better able to survive and/or reproduce (a measure of fitness)
- The "better" more competitive trait will be transmitted in greater numbers to offspring
positive selection
genotypes which improve survival/reproduction
negative selection
genotypes which decrease survival/reproduction and are nonadaptive.
taxonomy order
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
how do you write binomial nomenclature?
- capitalize the genus but not the species
- italics if typed
- underline if written
what are the three domains?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
4 kingdoms of eukarya
Protista (not a kingdom), Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
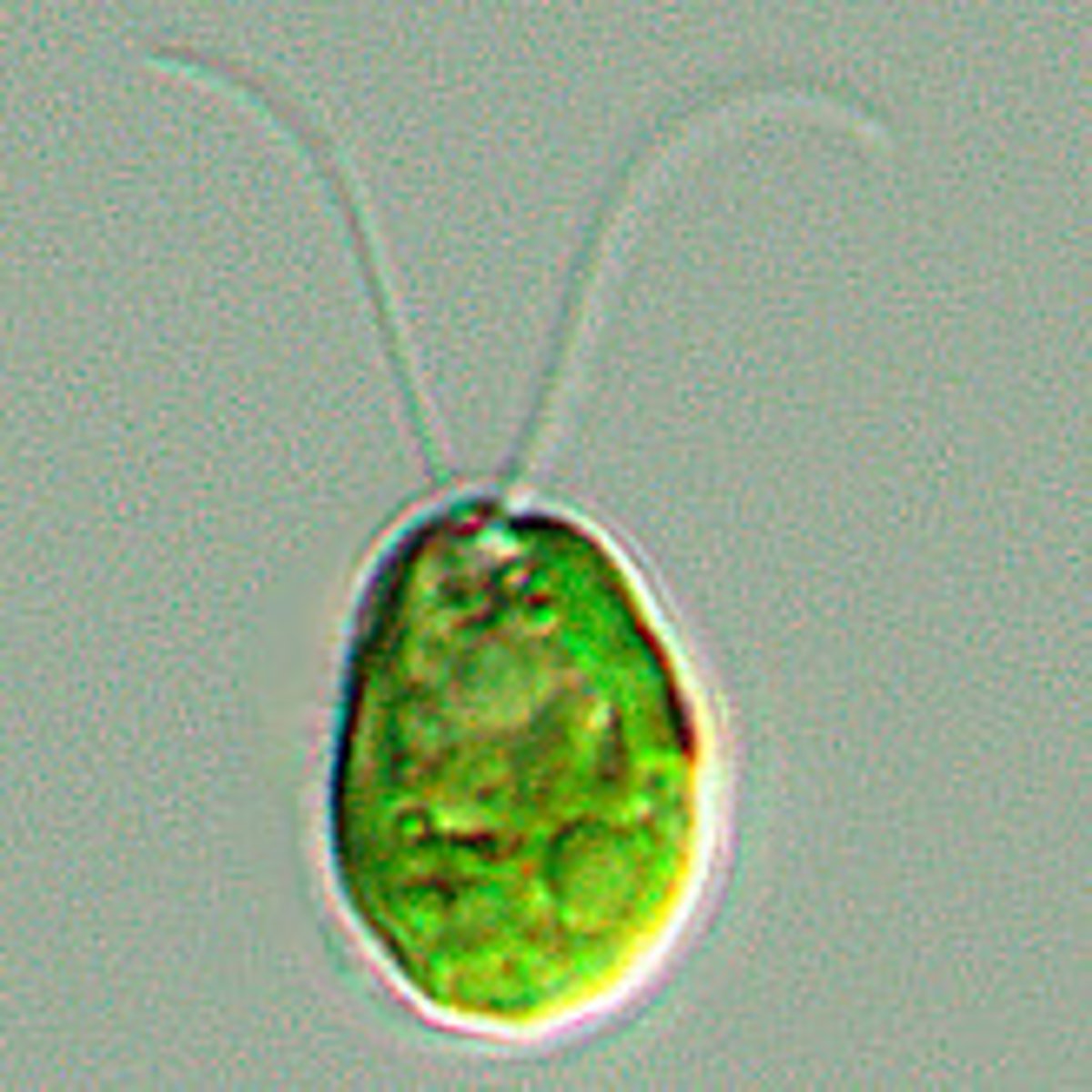
Chlamydomonas
unicellular photosynthetic green algae; two flagella
Gonium
-unicellular
-colony size of 4,8,16,32
-gel holds cell together
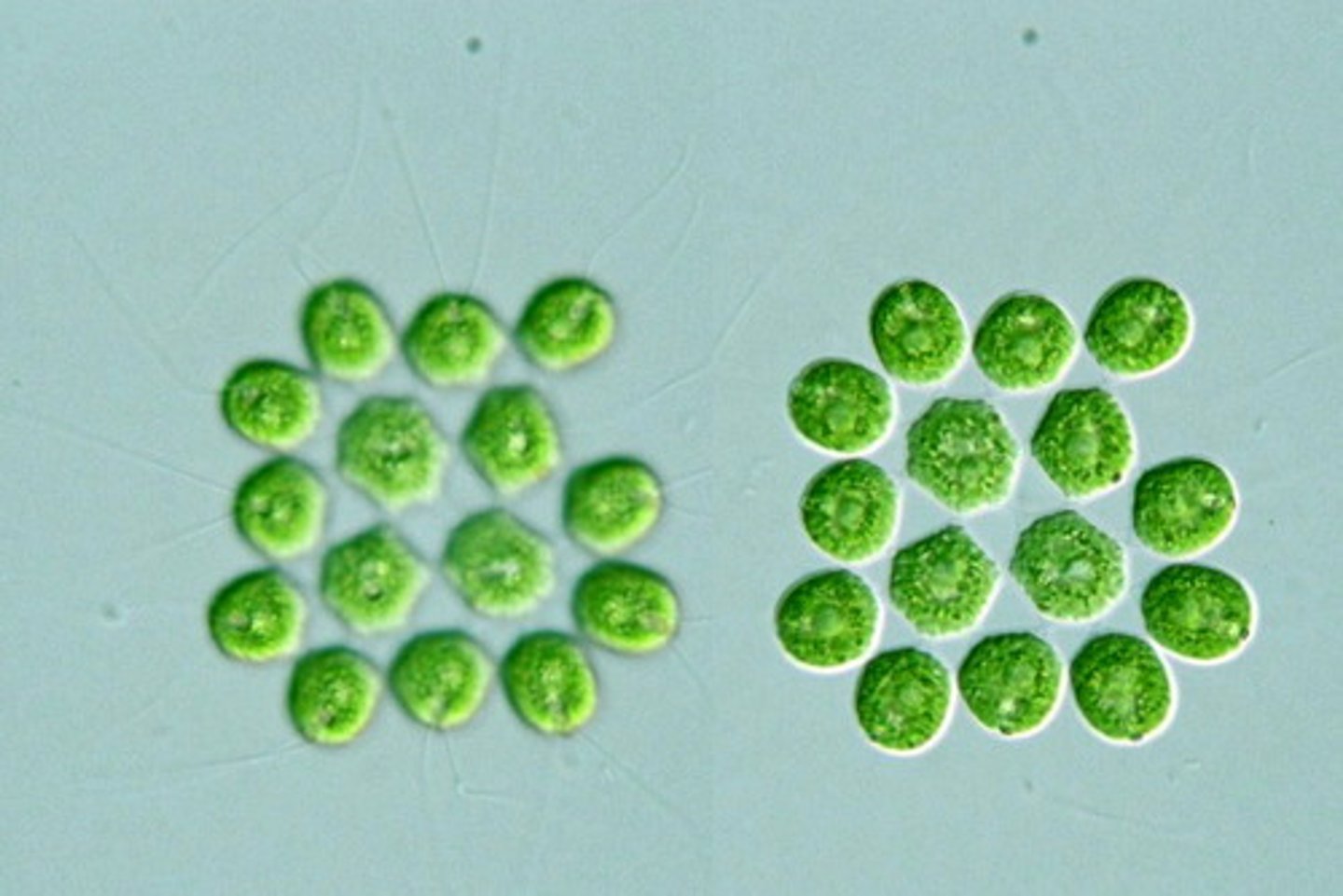
Pandorina
-unicellular
-colony size of 16 or 32
-gel holds cells together
-directional movement
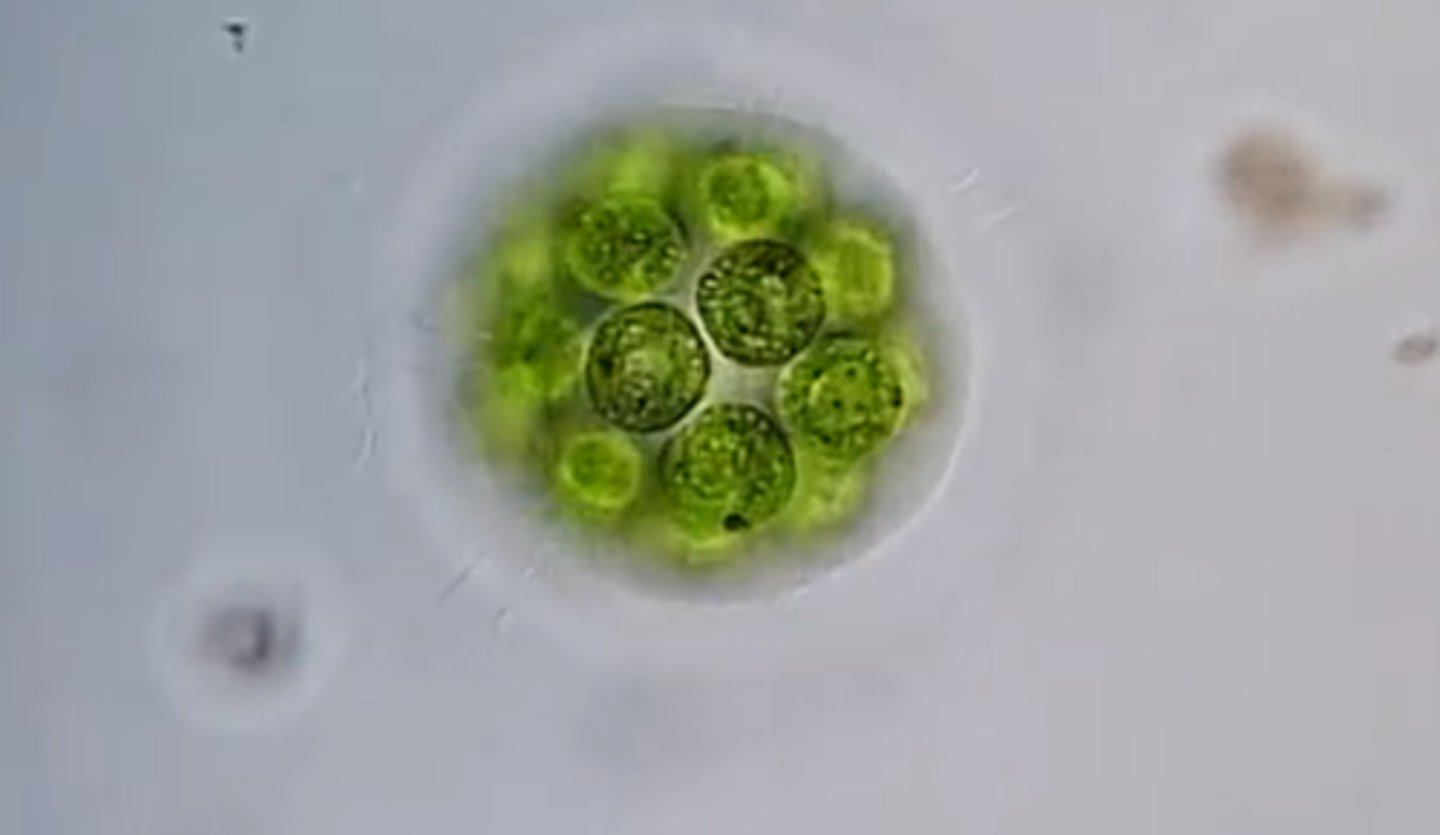
Eudorina
-unicellular
-colony size of 32,64, or 128
-directional movement
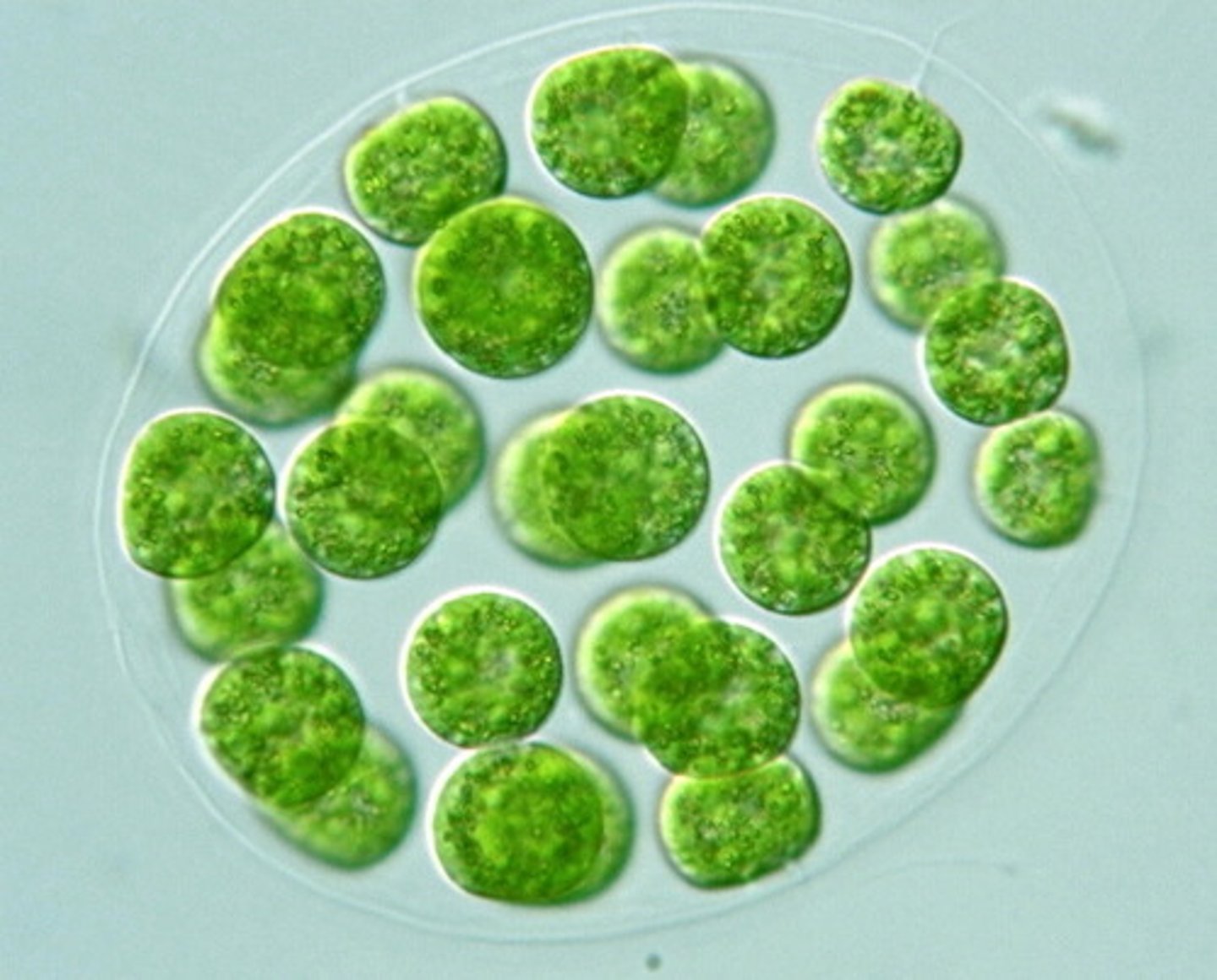
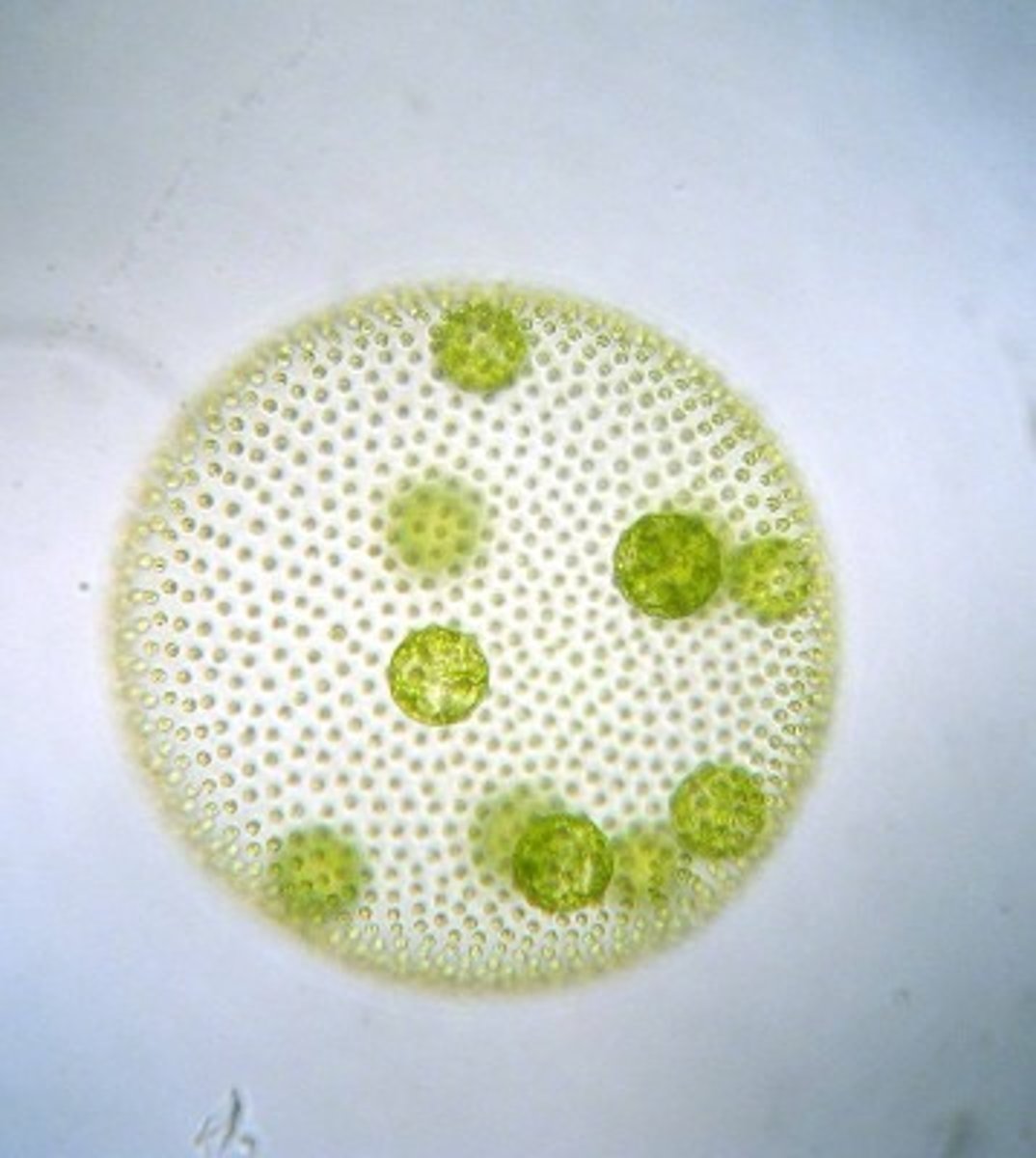
volvox
-unicelluar, photosyntheic algae
-colony of 100s
-communication
prokaryote
Cells have no membrane bound organelles or nucleus
eukaryote
Cells contain organelles and a nucleus. single or multiple cells
archaea
oldest life form. All single celled. Unique prokaryotes, many are extremophiles and anaerobes.
bacteria
found in most environments, widely distributed. All single celled.
extremophile
Archaea that live in extreme environments.
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food; self feeders
Heterotroph
get energy from other organisms, usually dead things (decomposers)
binary fission
copy dna→ divide in two
anaerobic
without oxygen
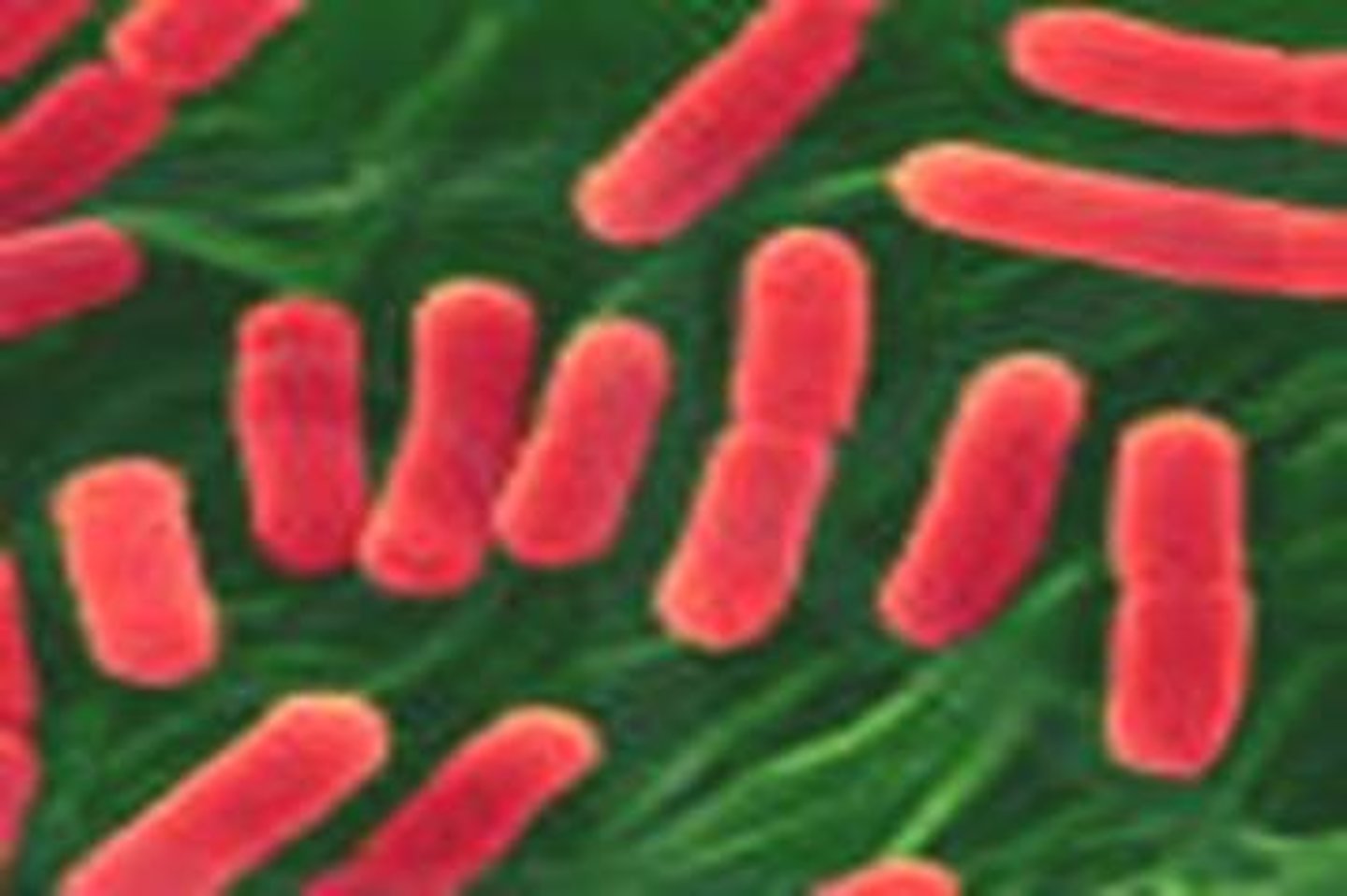
bacilli
Rod shaped bacteria
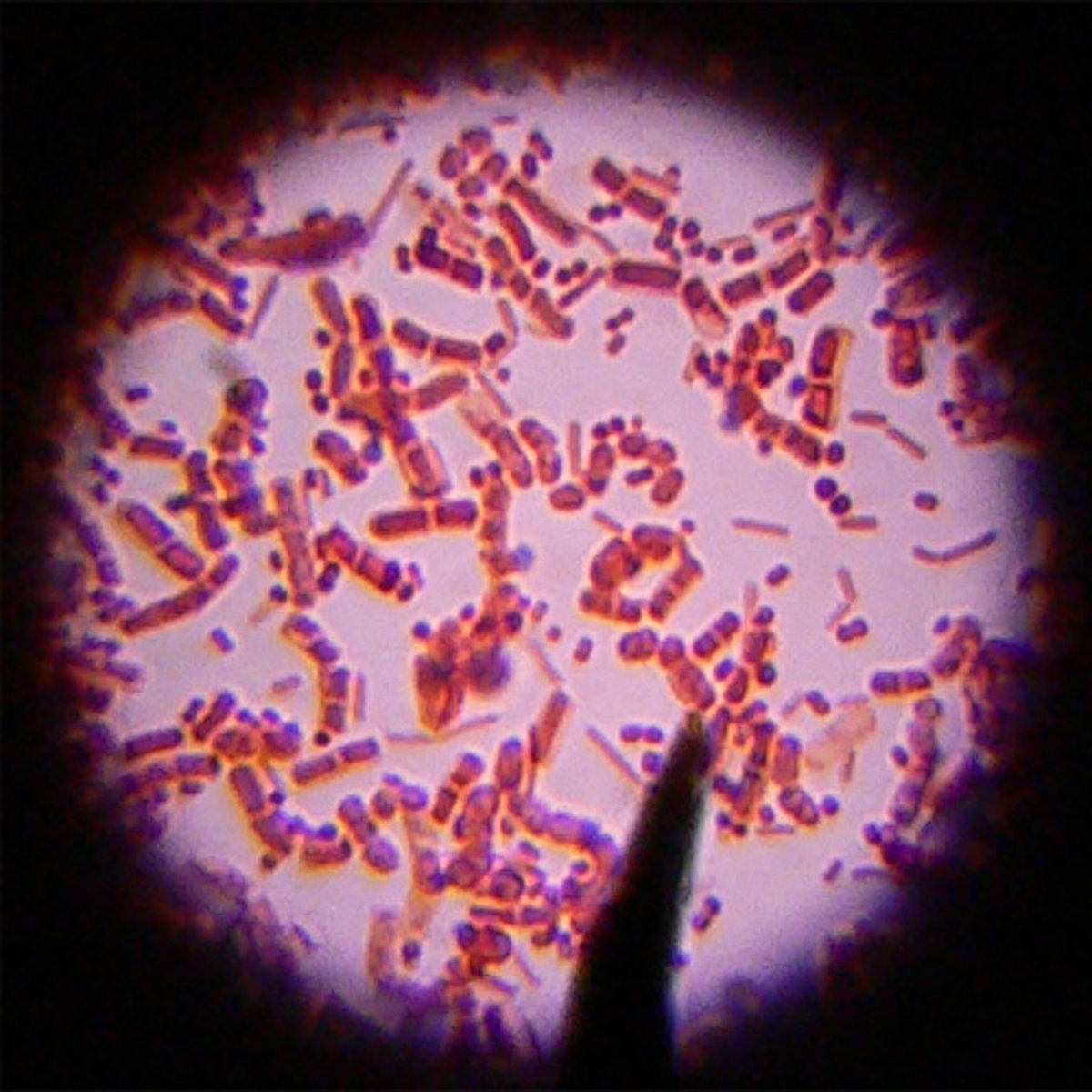
Cocci
spherical bacteria
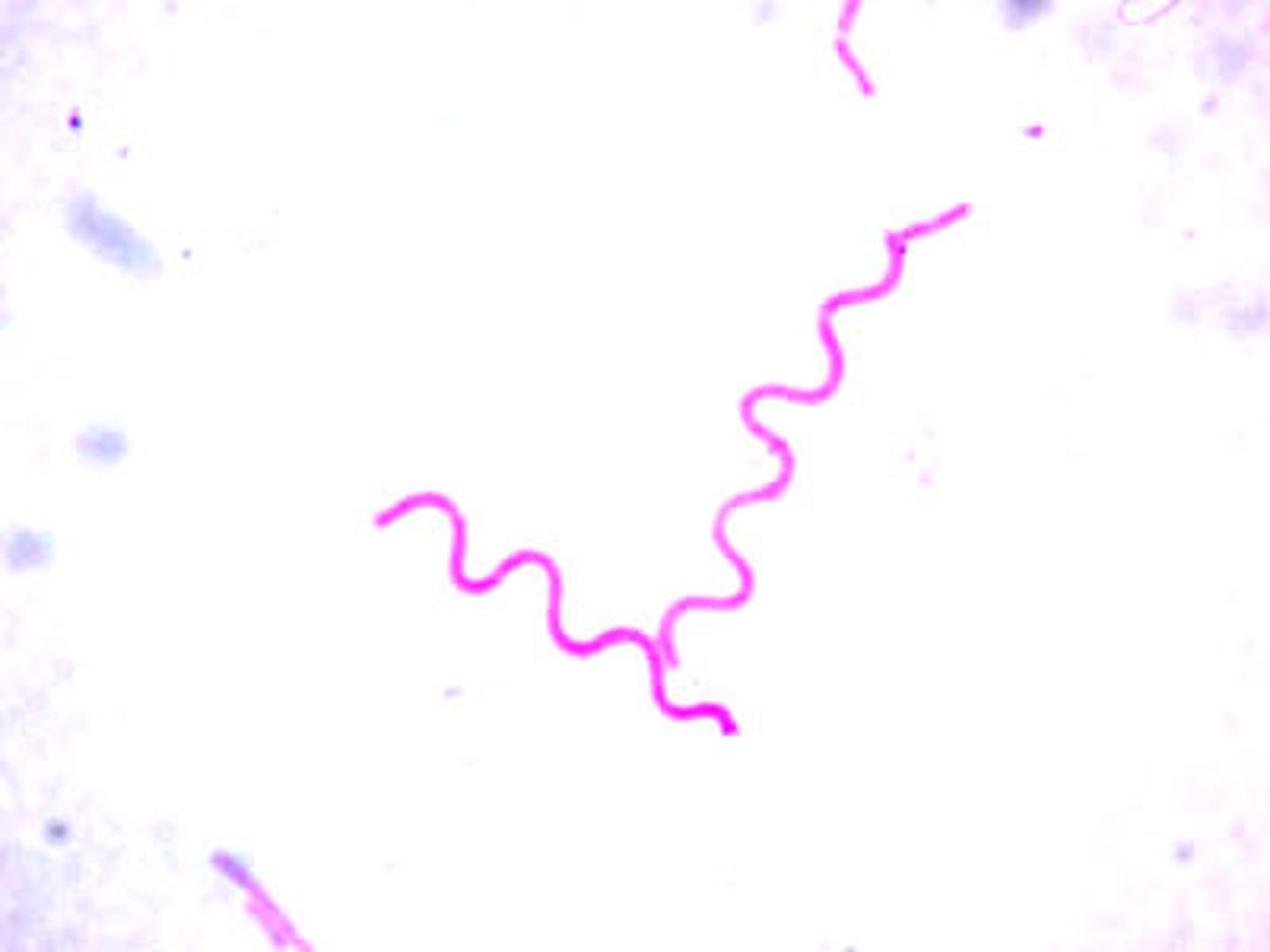
Sprillia
spiral shaped bacteria
what is the oil immersion technique
-using immersion oil to view specimen
-ONLY used with 100X lens
-NEVER used with 40X lens
-you do not use the coarse adjustment knob
wet mount
a glass slide holding a specimen suspended in a drop of liquid (as water) for microscopic examination
prepared slide
a permanent slide where the specimen is mounted permanently with a mounting medium and a coverslip
what is gram staining?
Used to identify the 2 types of bacteria- those with and those without an outer layer of lipid
Gram +
thick peptidoglycan layer, purple
gram -
red; pink-ish, thick peptidoglycan layer
nitrogen fixation
Process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia
cyanobacteria
Bacteria that can carry out photosynthesis
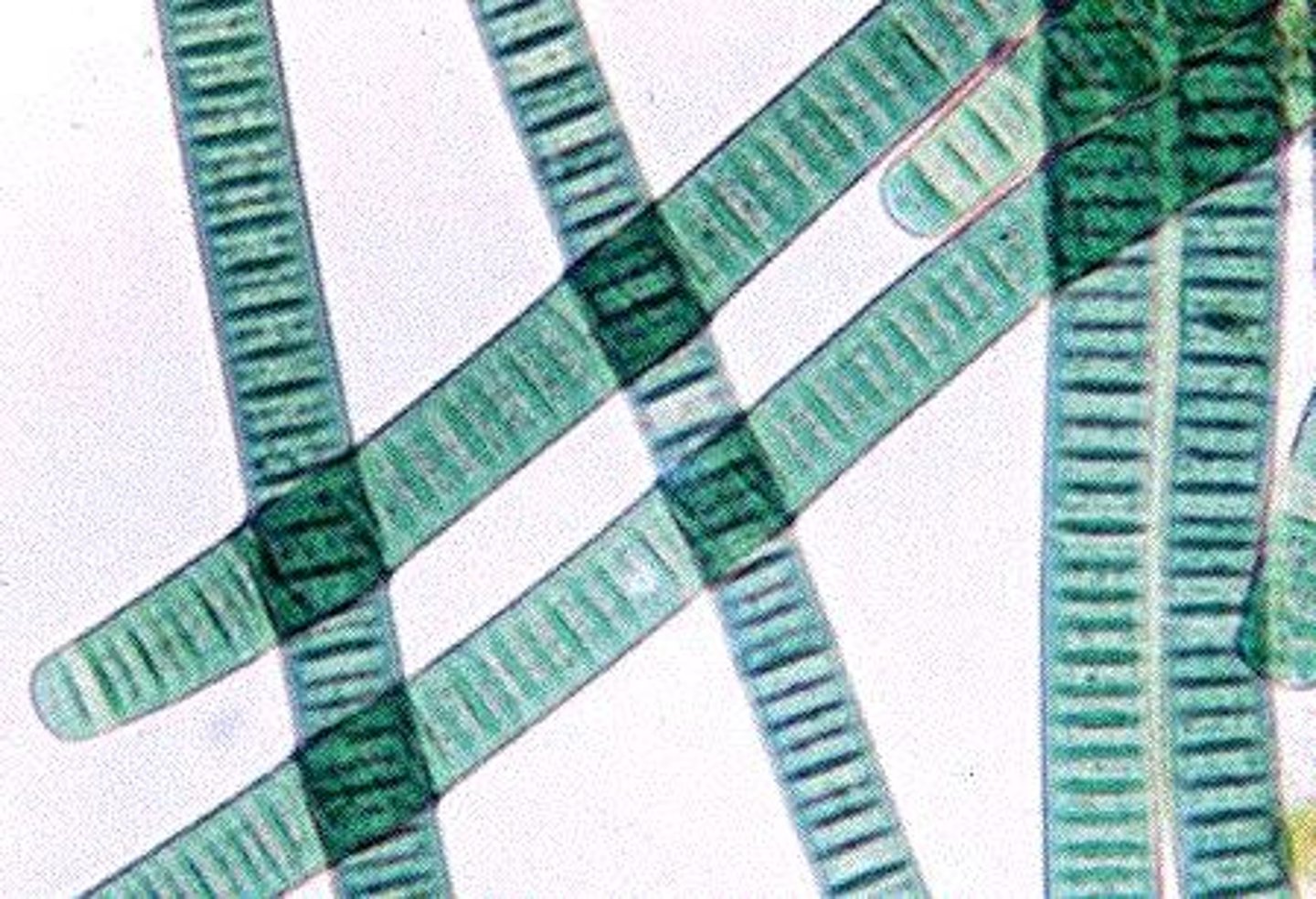
oscillatoria
long filament of cells; photoautotrophs; cyanobacteria
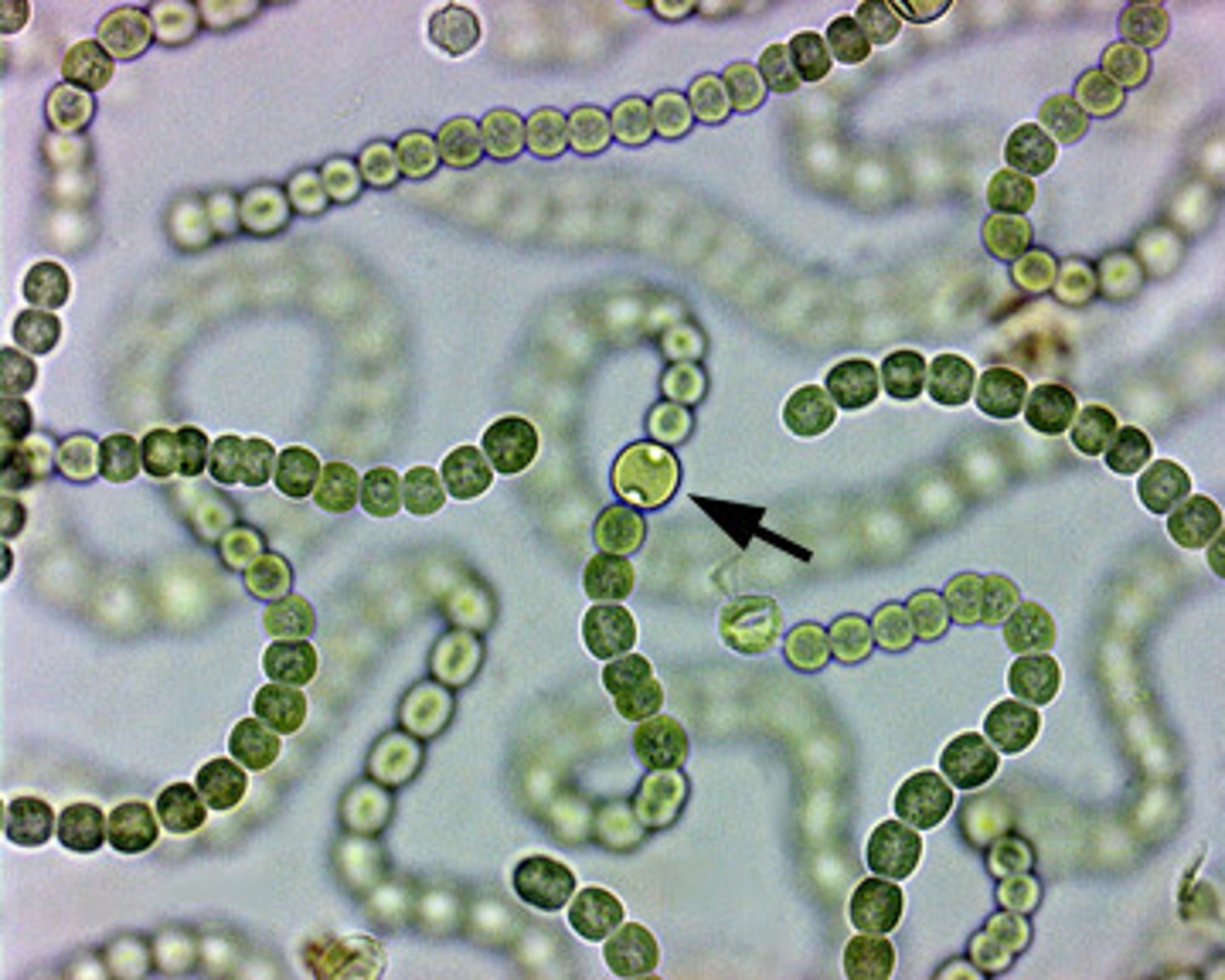
nostoc
this cyanobacteria forms grape-like macroscopic colonies that contain two types of cells
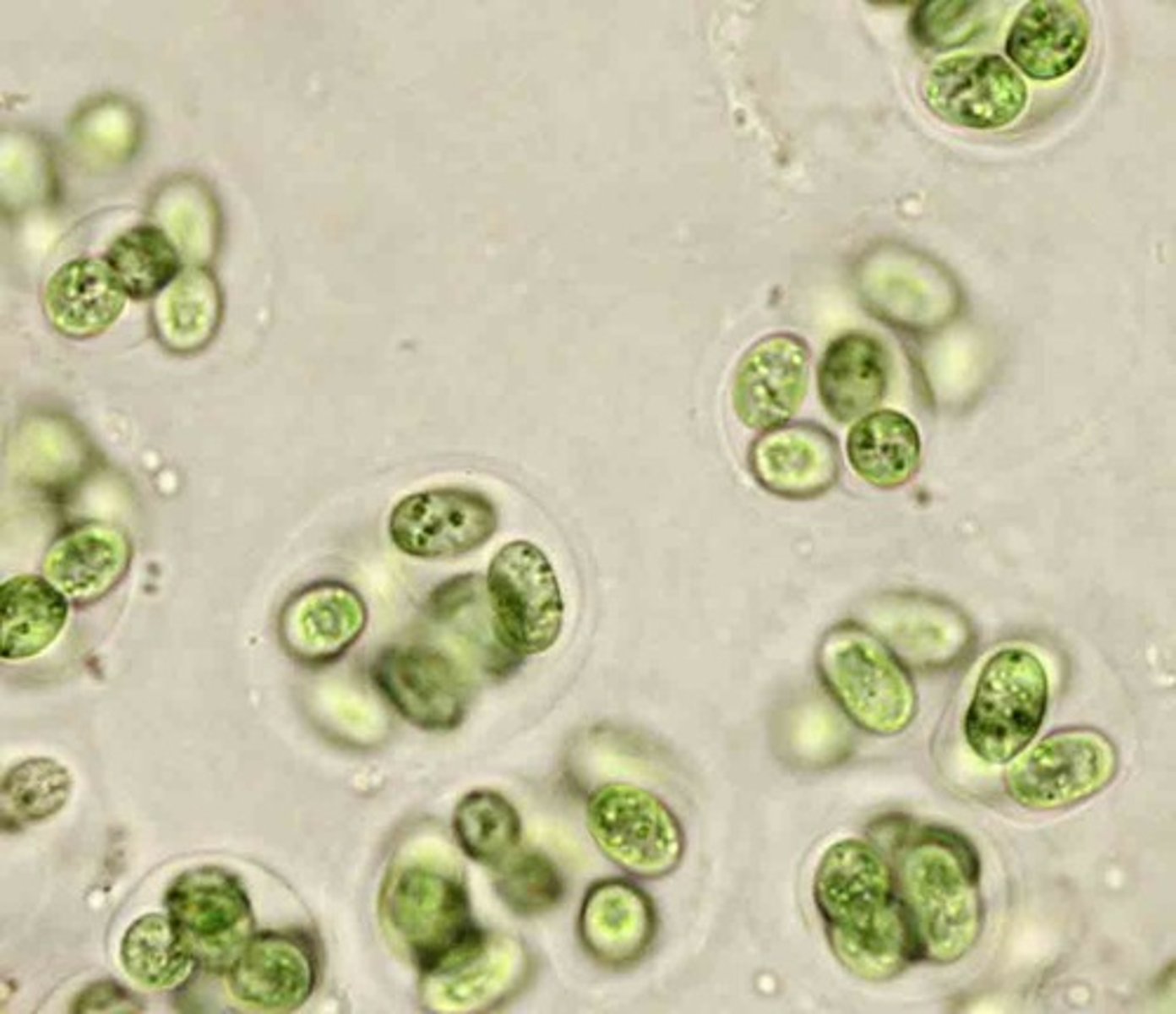
Gloeocapsa
Cyanobacteria; unicellular with gelatinous sheath surrounding cell; looks like clusters of colonies
what is the zone of inhibition
The area around the antibiotic disk in which bacteria cannot grow
why are protists not considered a kingdom?
there a diverse group, making the original a polyphyletic group
protists are eukaryotes, but....
they have huge diversity
two categories of protists
protozoa and algae
how does algae gain nutrition?
photosynthesis
how does protozoa gain nutrition?
phagocytosis
how do protists defend themselves?
-fast movement
-release of toxins
-cellulose or silica walls
How are algae distinguished?
cellular organization
unicellular algae
Algae with bodies consisting of a single cell. Examples are diatoms and dinoflagellates.
filamentous algae
single celled organisms, existing as a chain of cells
colonial
exist as clump of cells
three common methods of movement among protists
cilia
flagella
pseudopodia
Cilia
The hairlike projections on the outside of cells that move in a wavelike manner
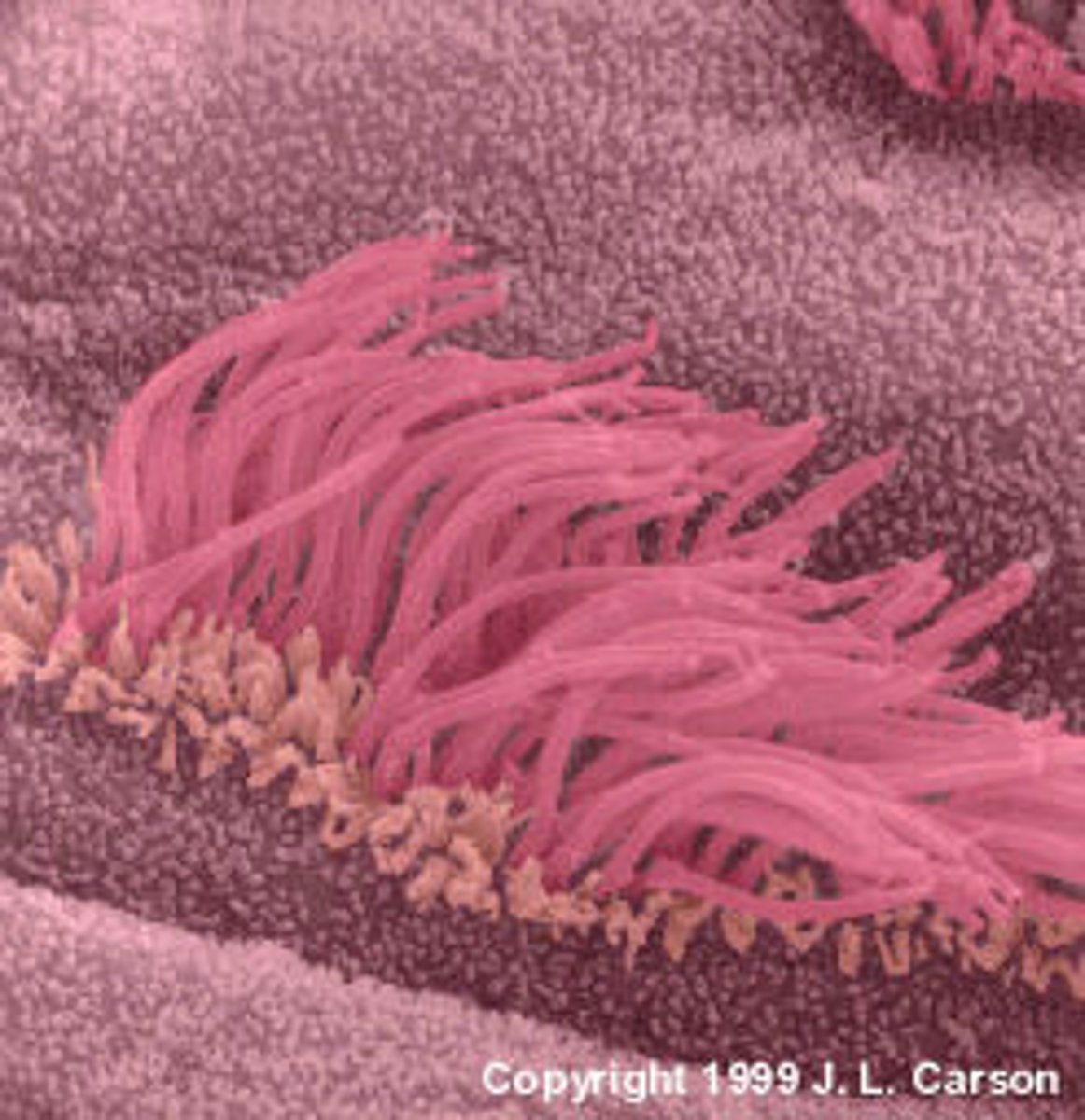
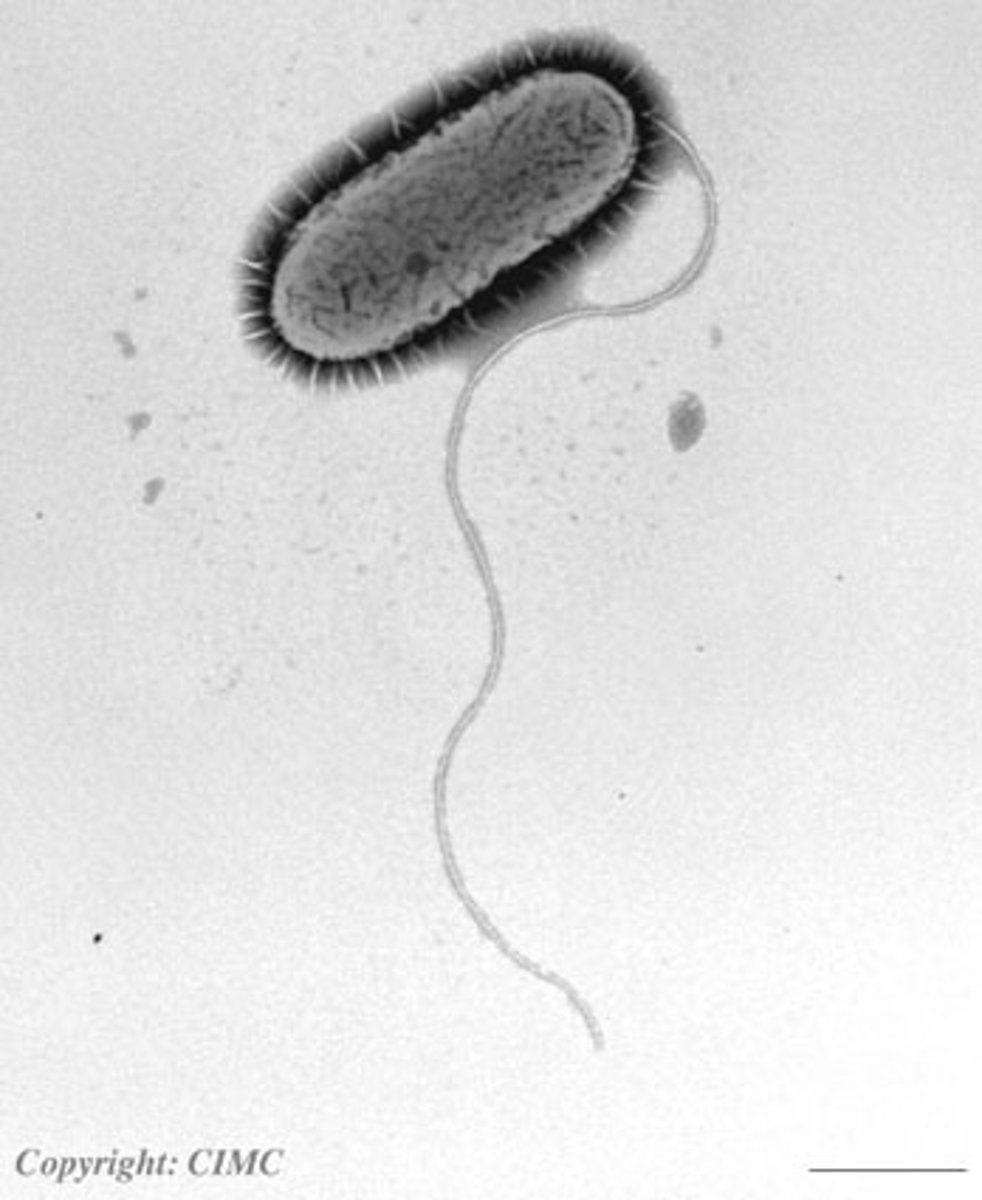
flagella
whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
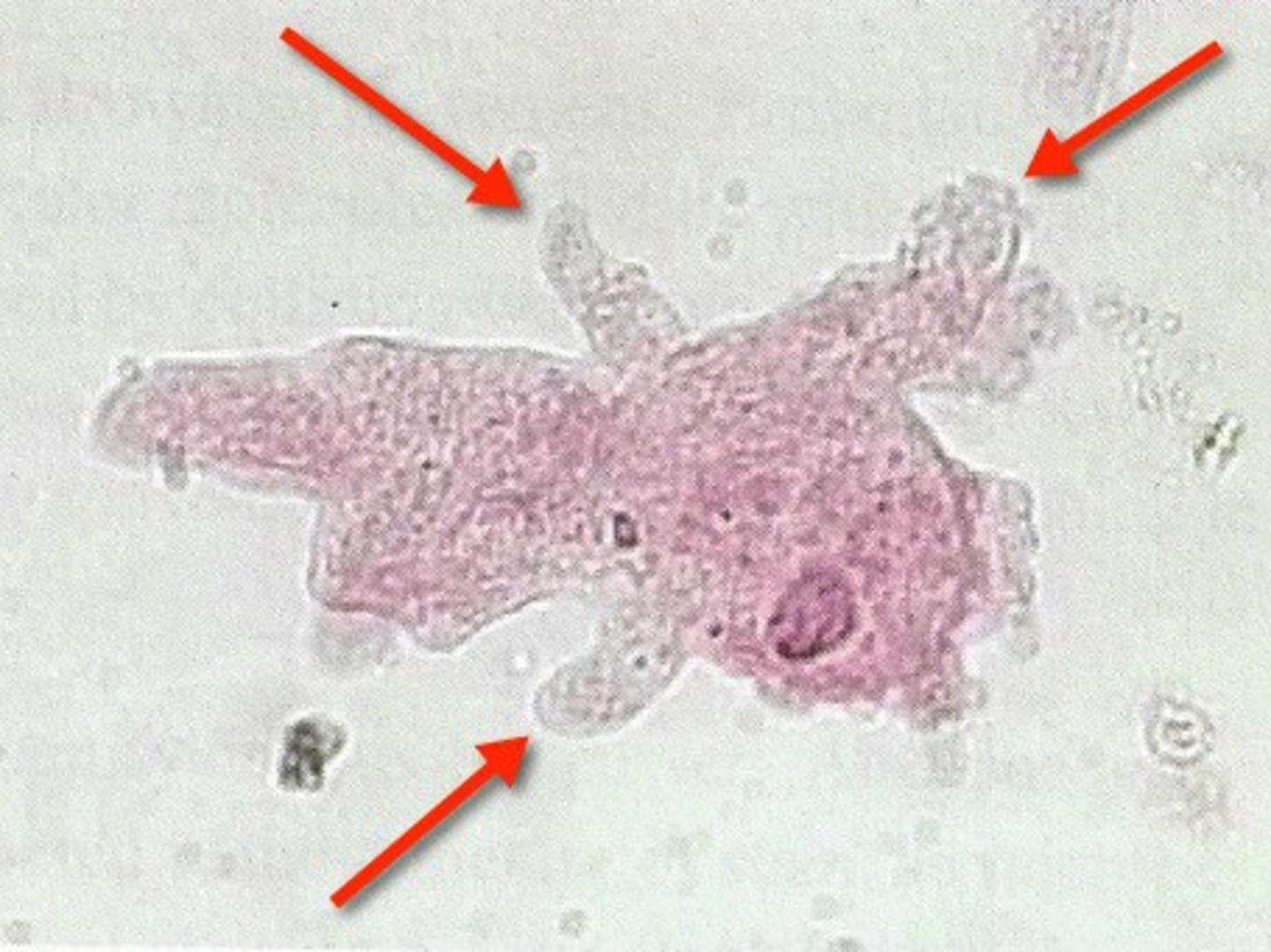
pseudopod
A temporary, foot-like extension of a cell, used for locomotion or engulfing food
photosyntheic algaes:
chlamdyomomas, spirogyra, volvox, diatoms, dinoflagellates, euglenoids
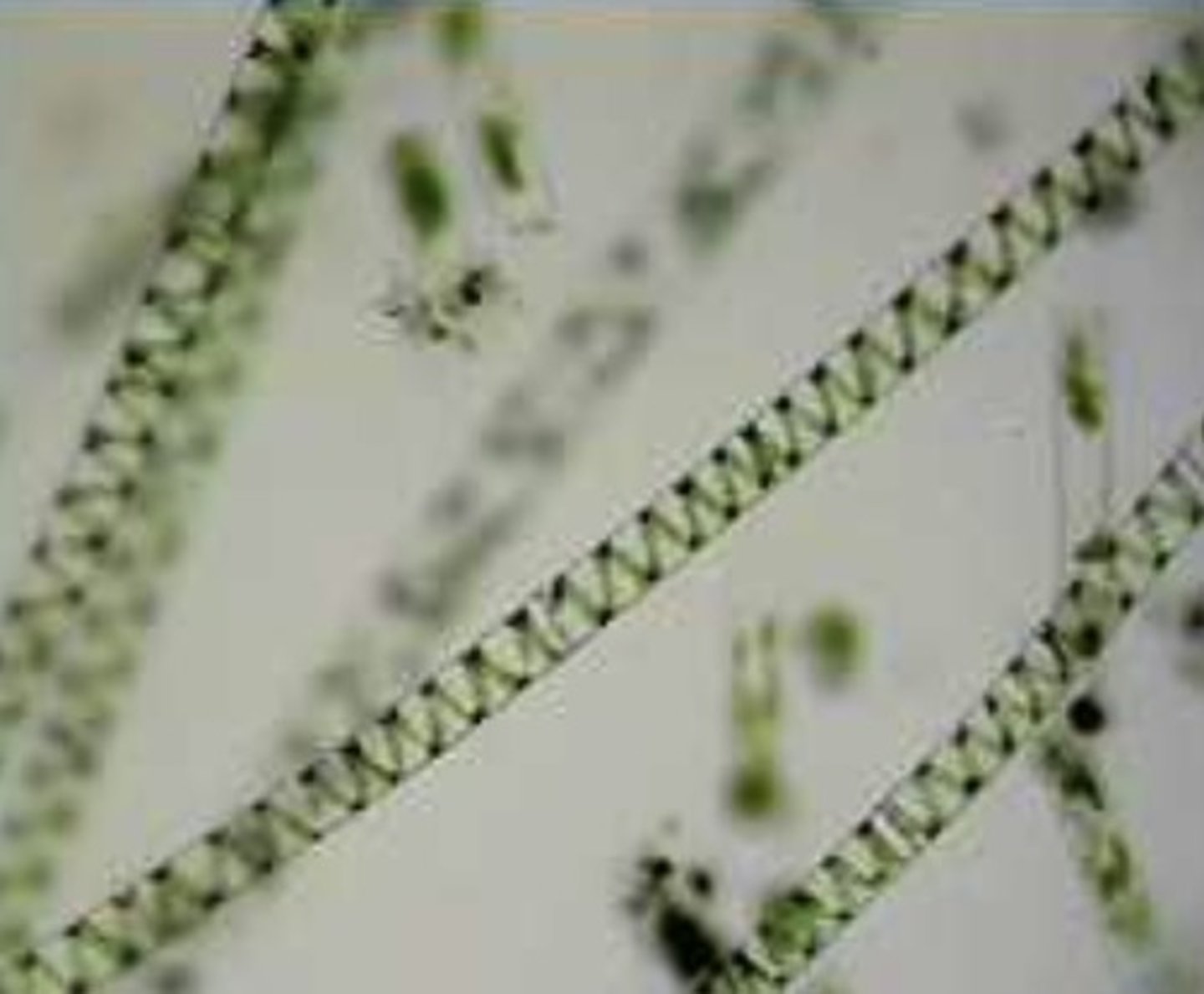
Sprirogyra
green photosynthetic algae

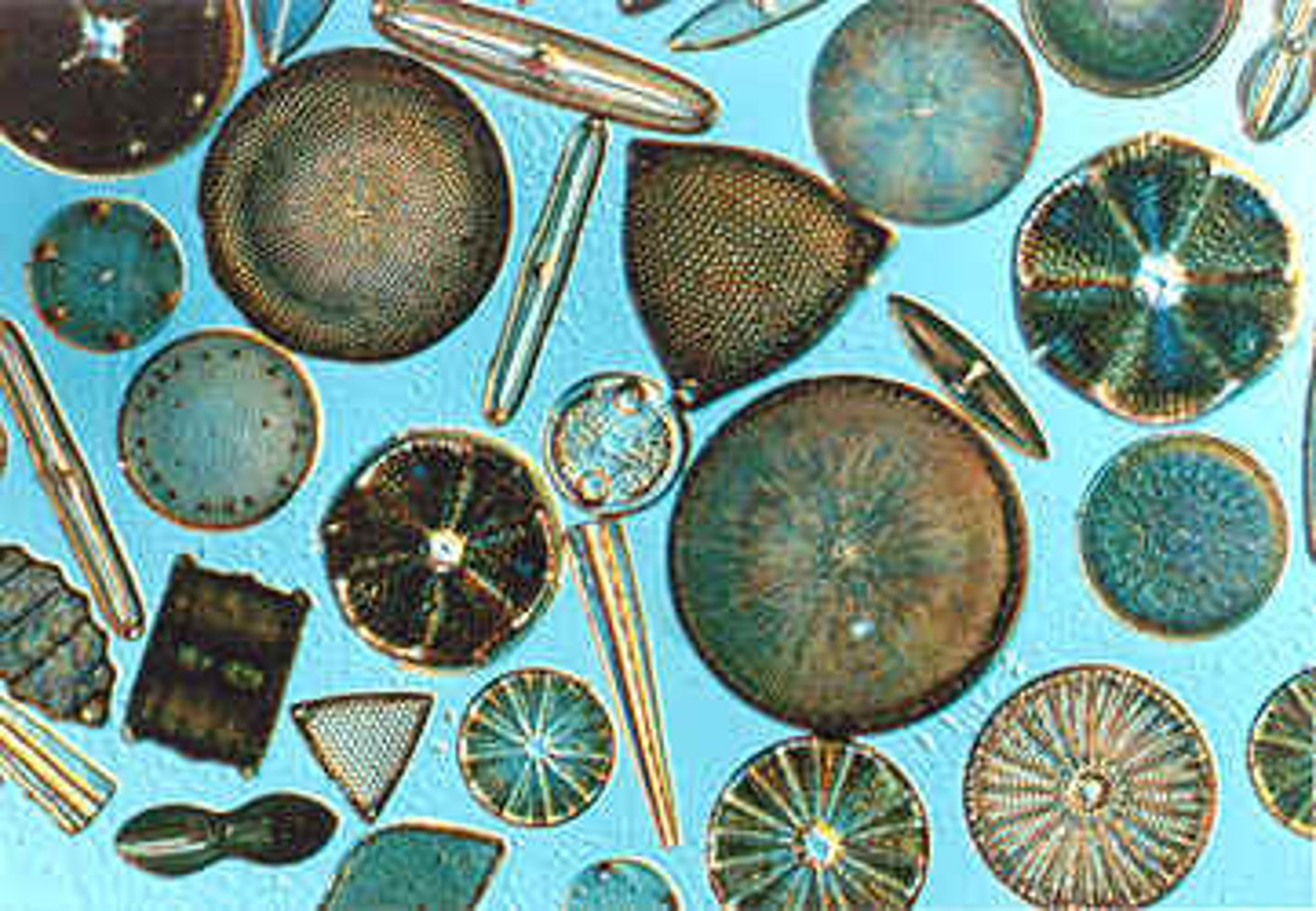
diatoms
cell wall of silica which forms shoebox aorund cell

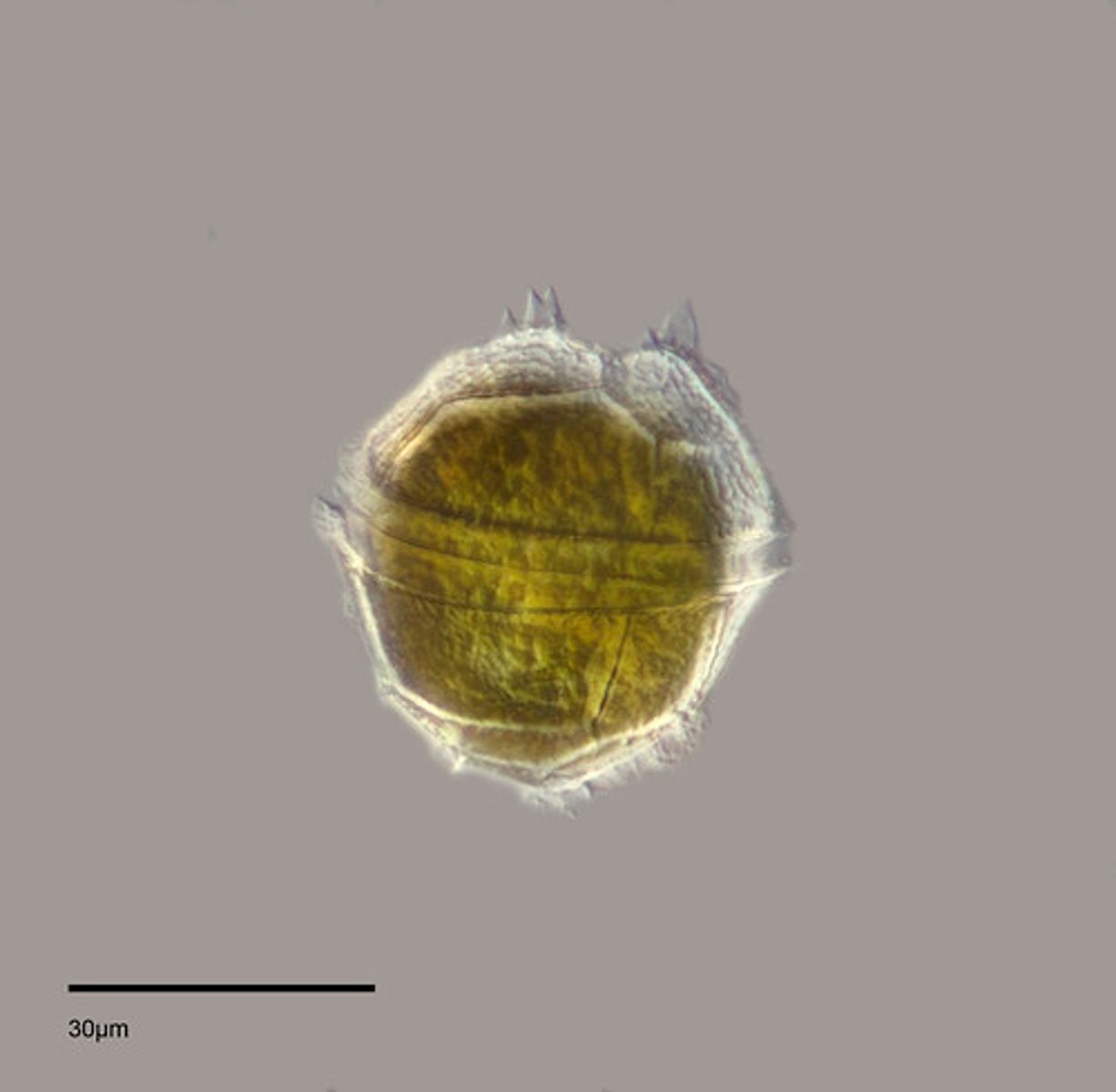
dinoflagellates; PERIDINIUM
plant-like protist that causes red tide
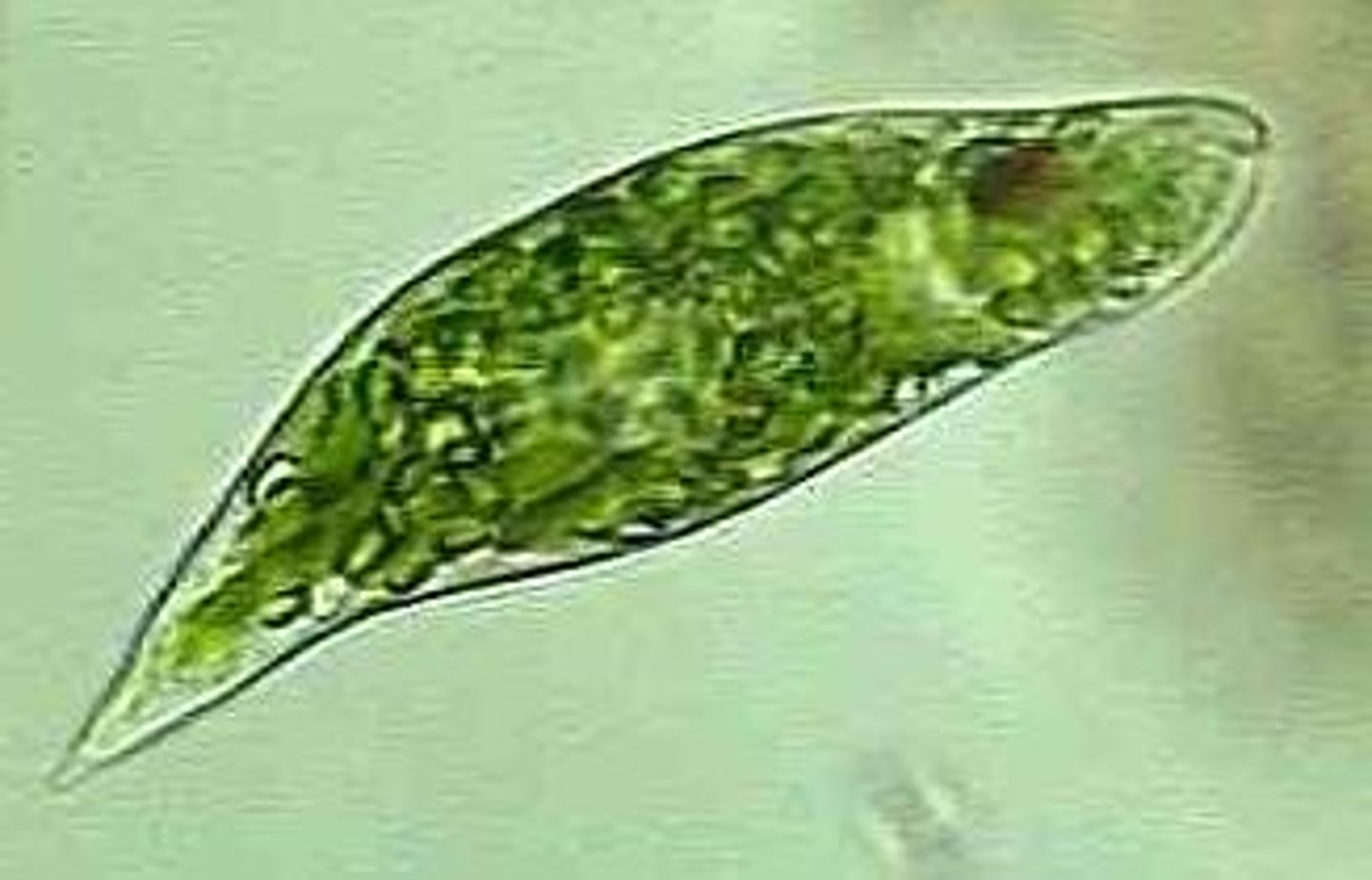
euglenoids; euglena
freshwater, capable of both autotrophy and heterotrophy (mixotroph) flagellated for movement
Ameoba
protist that moves and feeds with the help of pseudopods
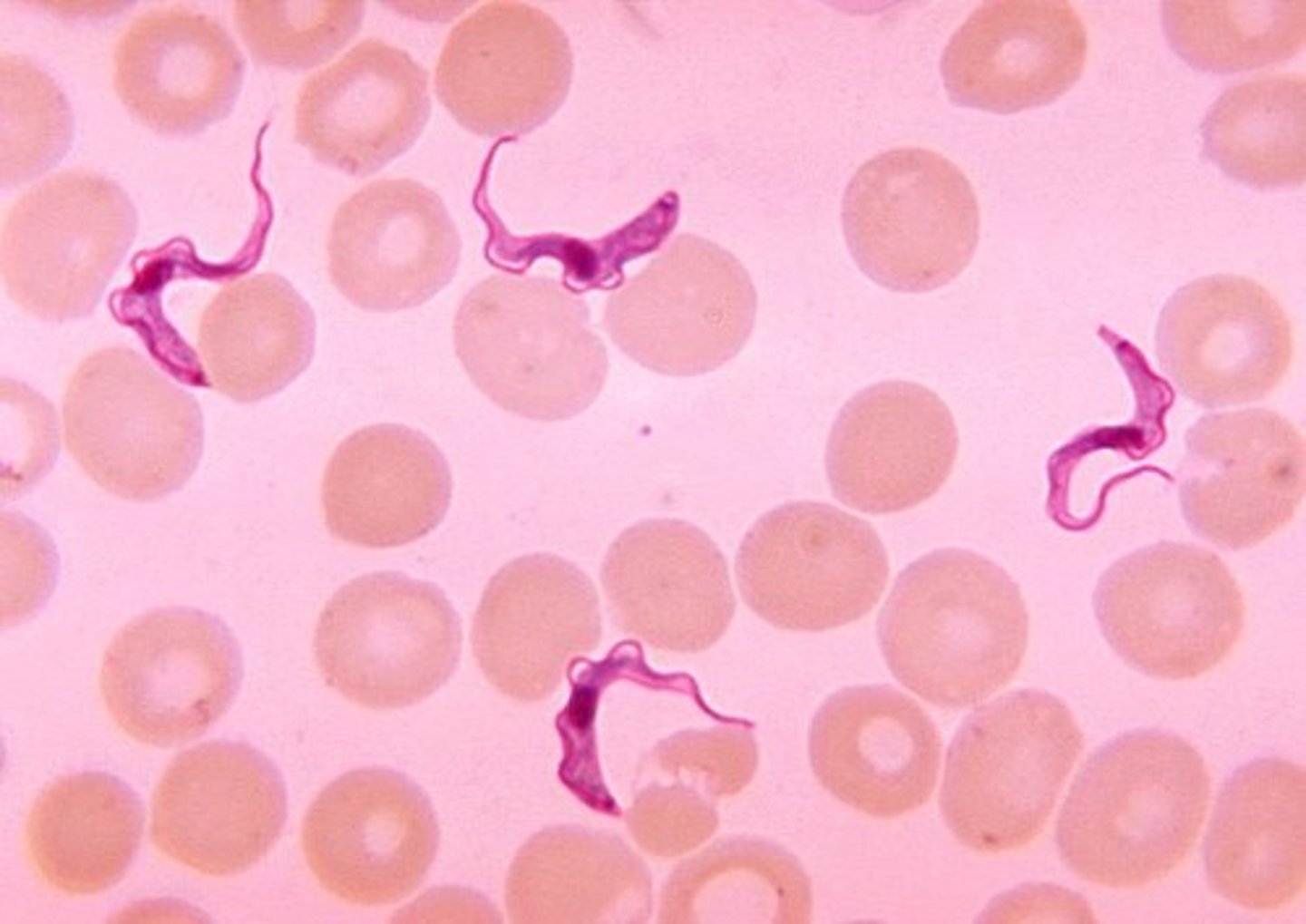
Flagellates (Trypanosoma)
parasitic and free-living
at least one flagellum
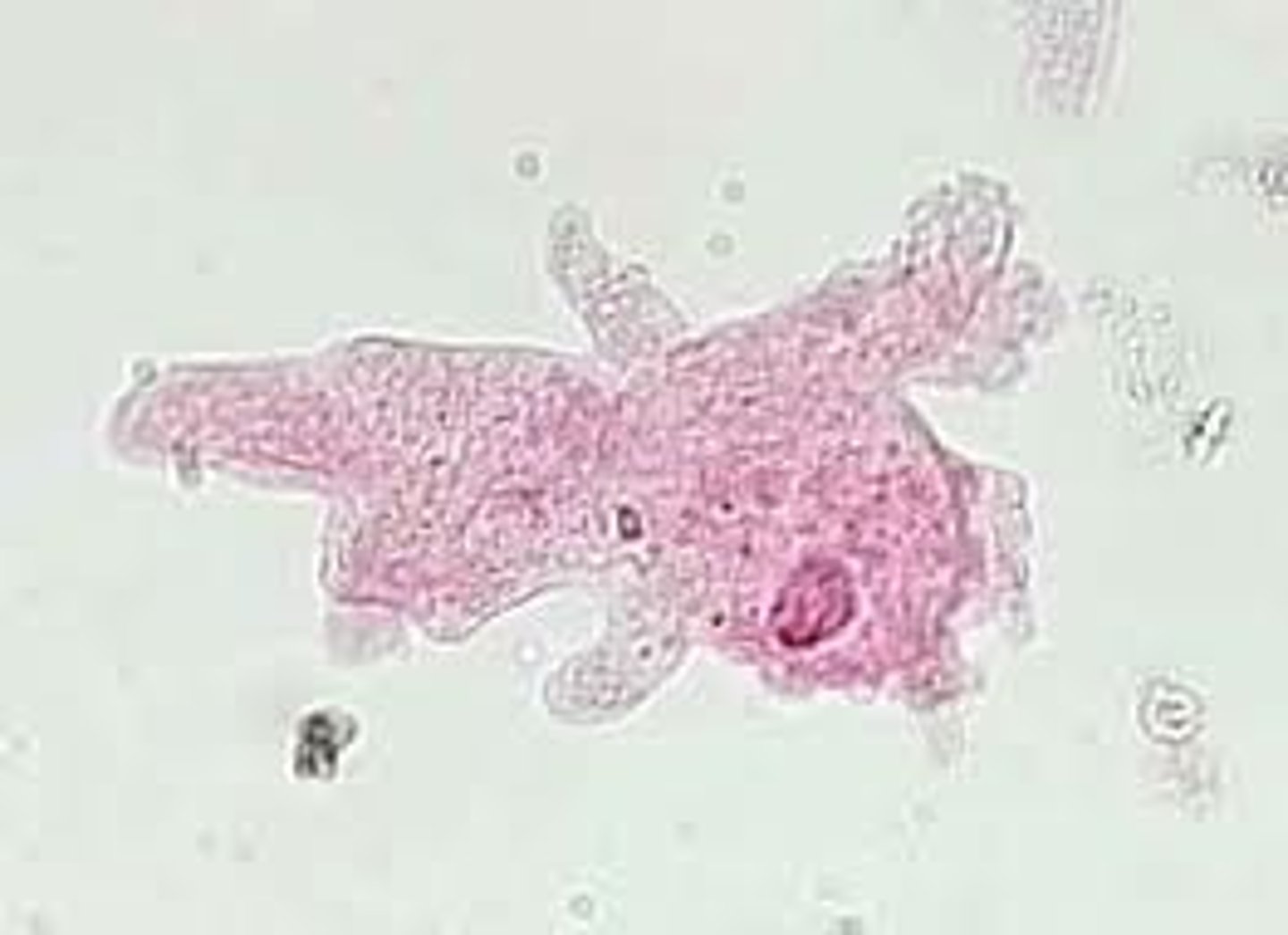
ciliates (paramecium)
single celled ciliated organisms; have cilia
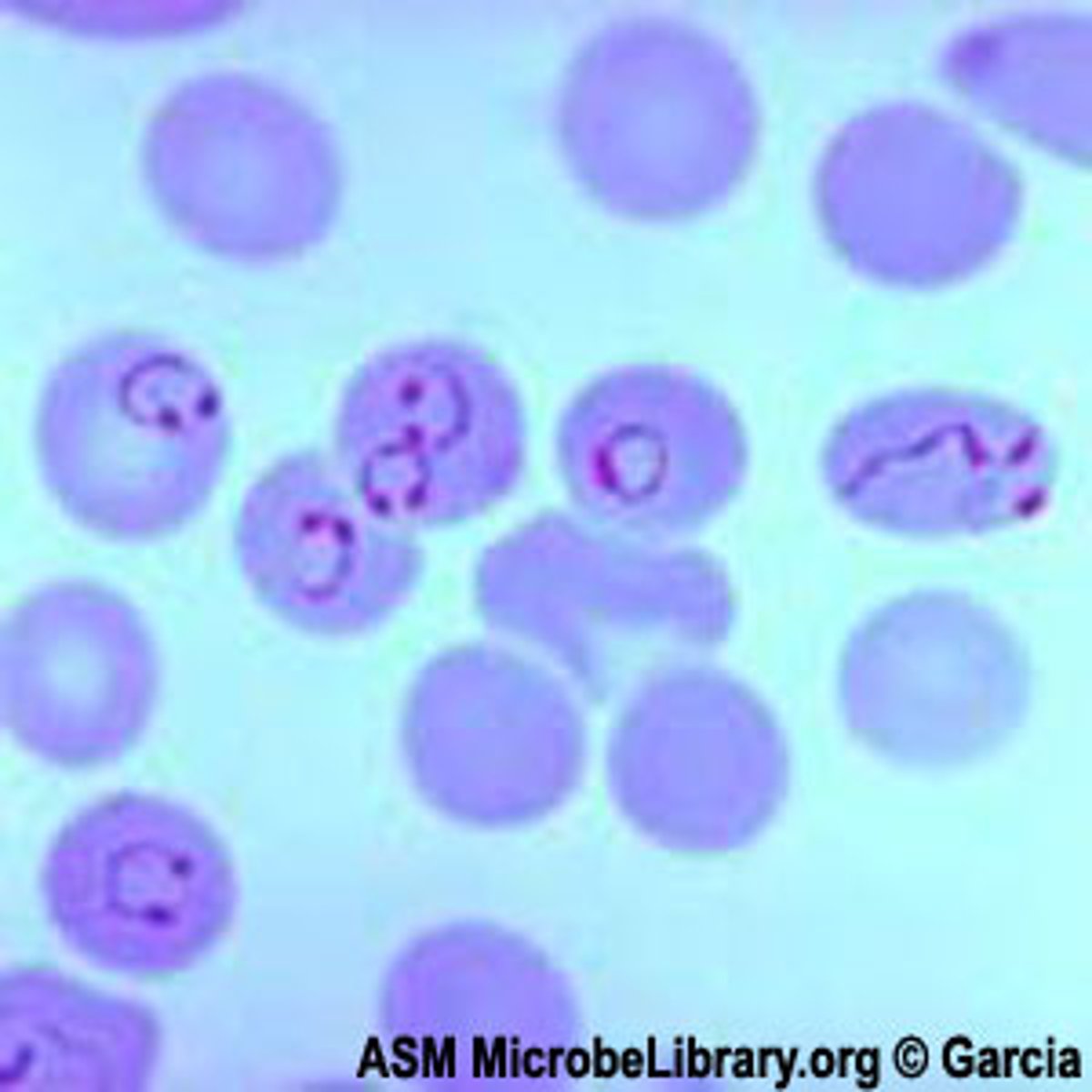
plasmodium
causes malaria;
parasite that causes malaria
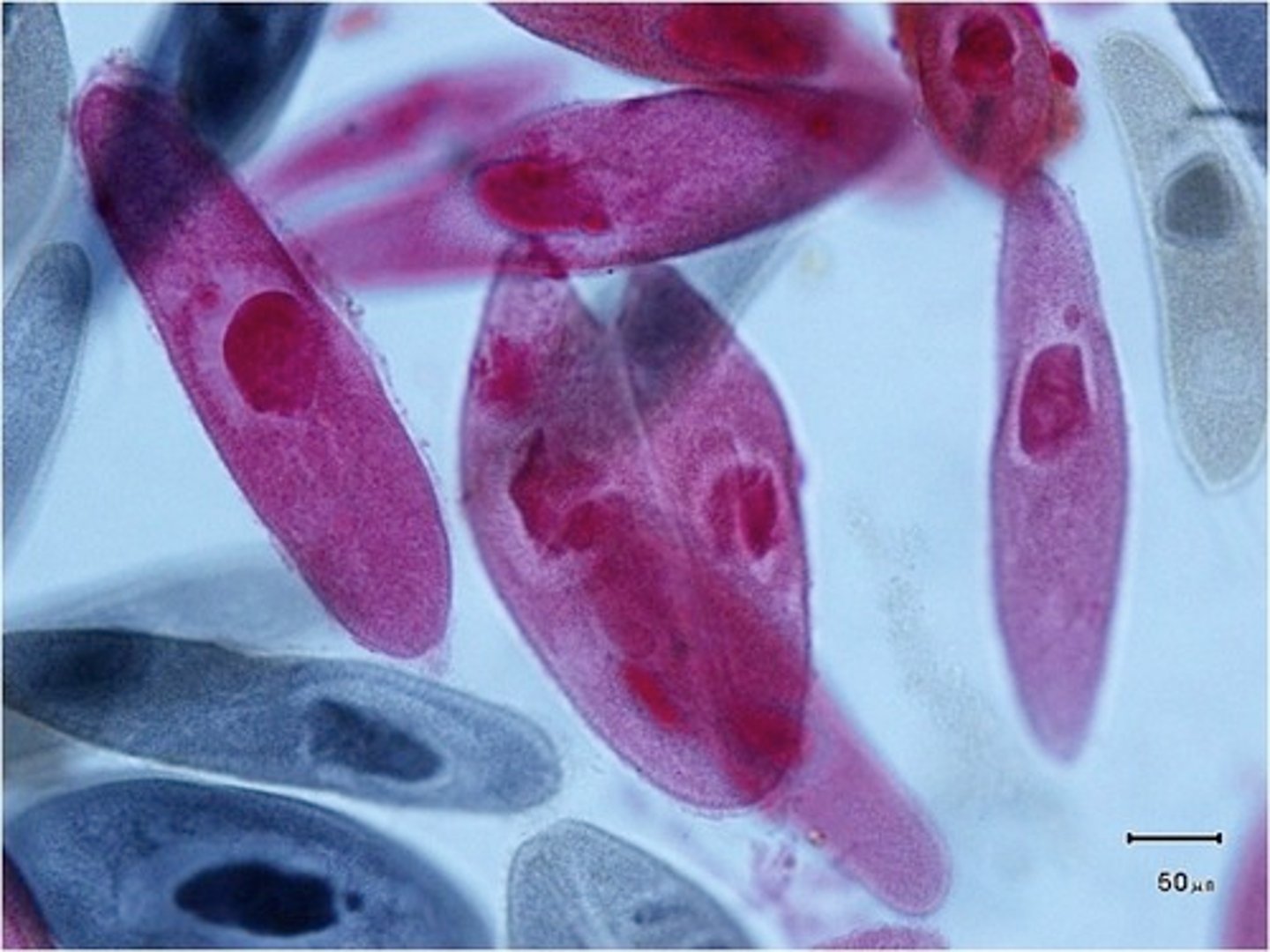
fungi
Kingdom composed of heterotrophs; many obtain energy and nutrients from dead organic matter
what is fungi's ecological and economic importance?
-decomposers
-symbiotic relationships with plants, protists, and bacteria
- source of foods (mushrooms, beer, whine, cheese)
- source of meds (penicillin, cyclosporine)
-parasitic infections of plants an animals (jock itch, athletes foot, etc.)
absorptive heterotrophs
secrete enzymes, digest externally, absorb nutrients
Saprotrophs
feed of dead or dying
parasites
feed off of living
hyphae
threadlike filaments
mycelium
mass of hyphae forming the body of a fungus
chitin
Polysaccharide found in fungal cell walls.
sporangia
multicellular organs that produce spores
spores
single-celled reproductive bodies highly resistant to cold and heat damage; capable of new organisms
life cycle of fungi- sexual
plasmogamy (fusion of cytoplasm), karyogamy (fusion of nuclei), and meiosis (reduction of chromosome number)
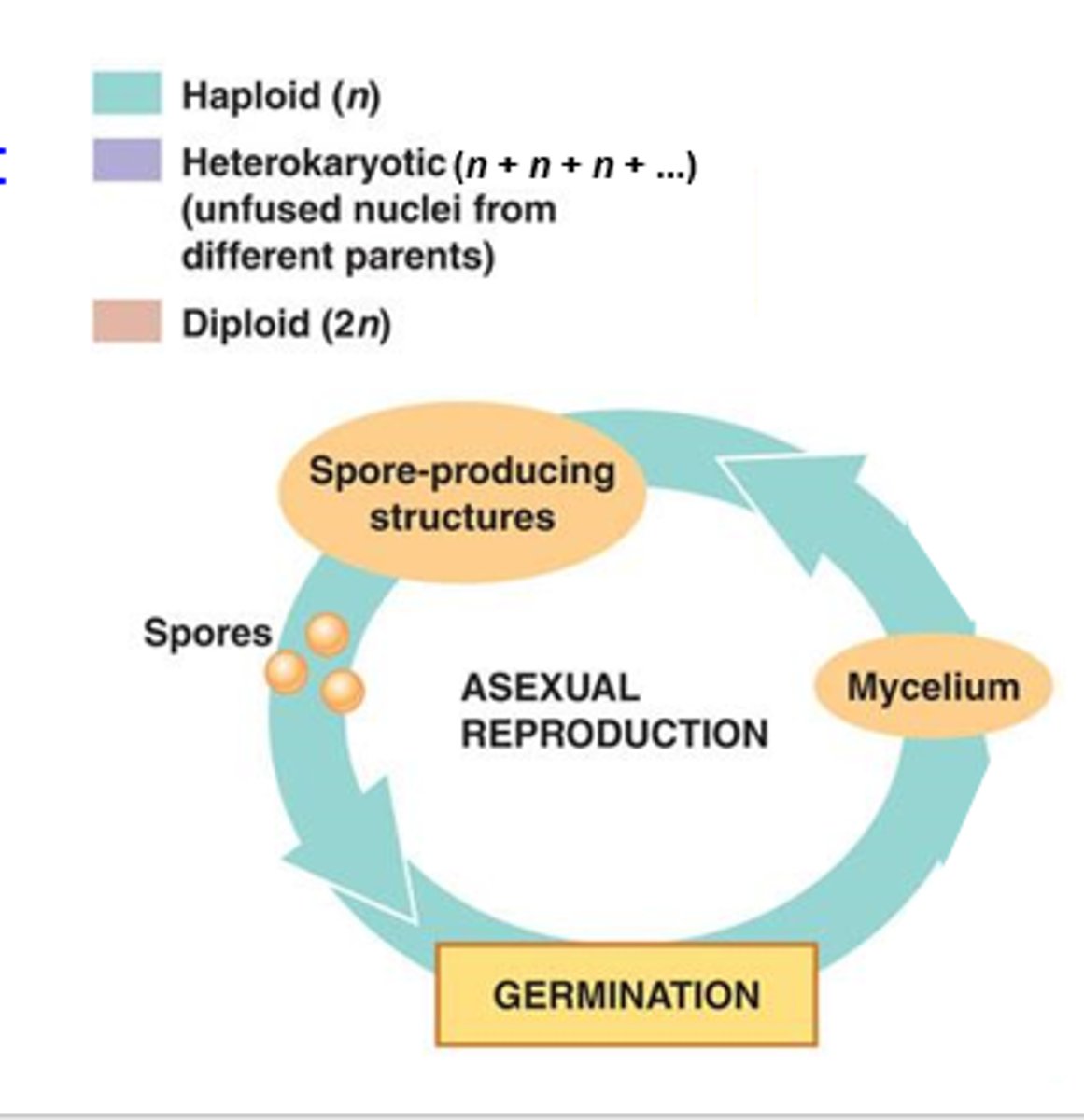
life cycle of fungi- asexual
a single parent organism produces genetically identical offspring through methods like spore formation, budding, or fragmentation, allowing for rapid reproduction and dispersal
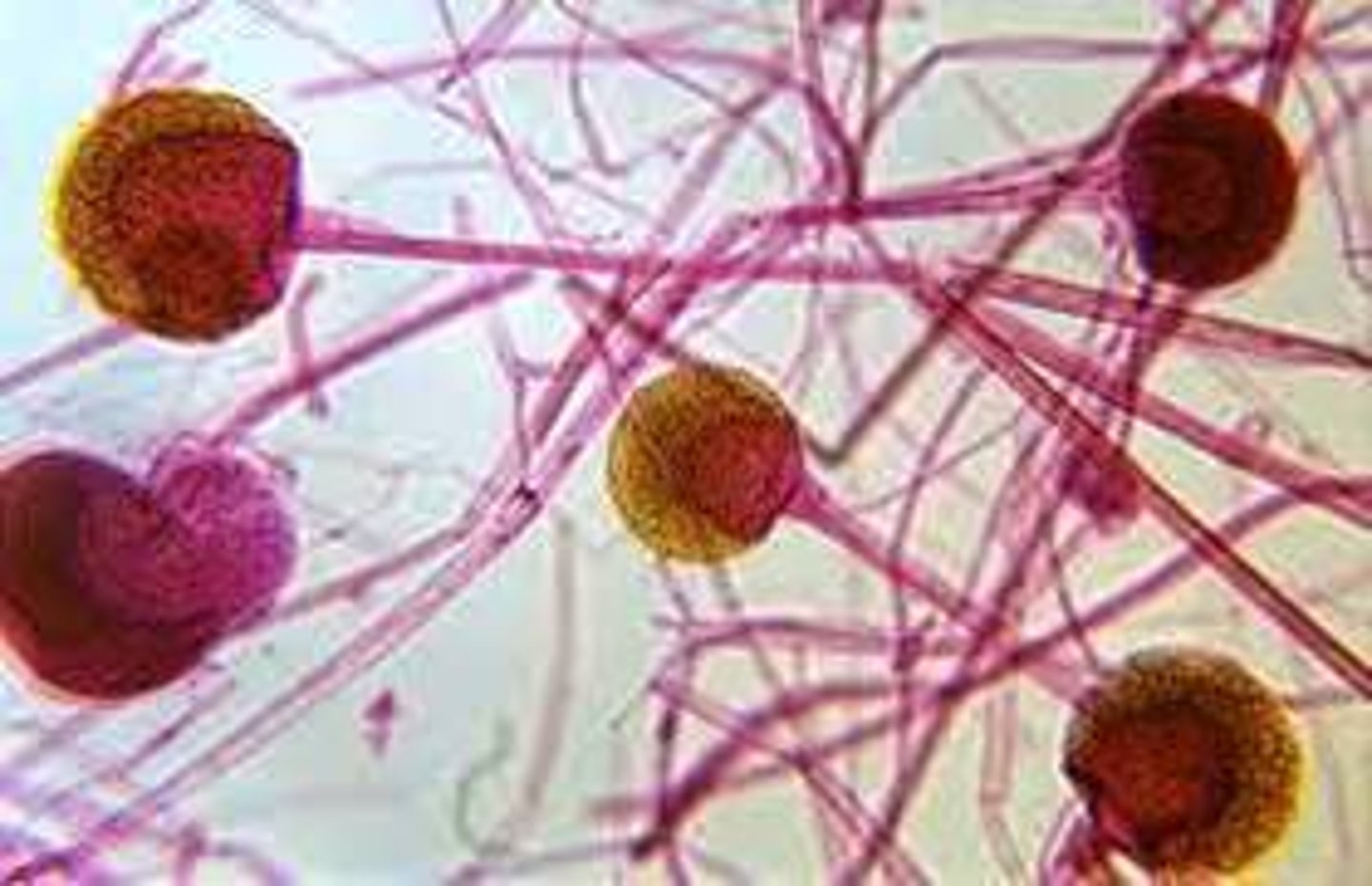
what is phylum Zygomycota
bread molds
can be sexaul or asexual
Asexual Rhizopus
sporangium produces idenctical spores
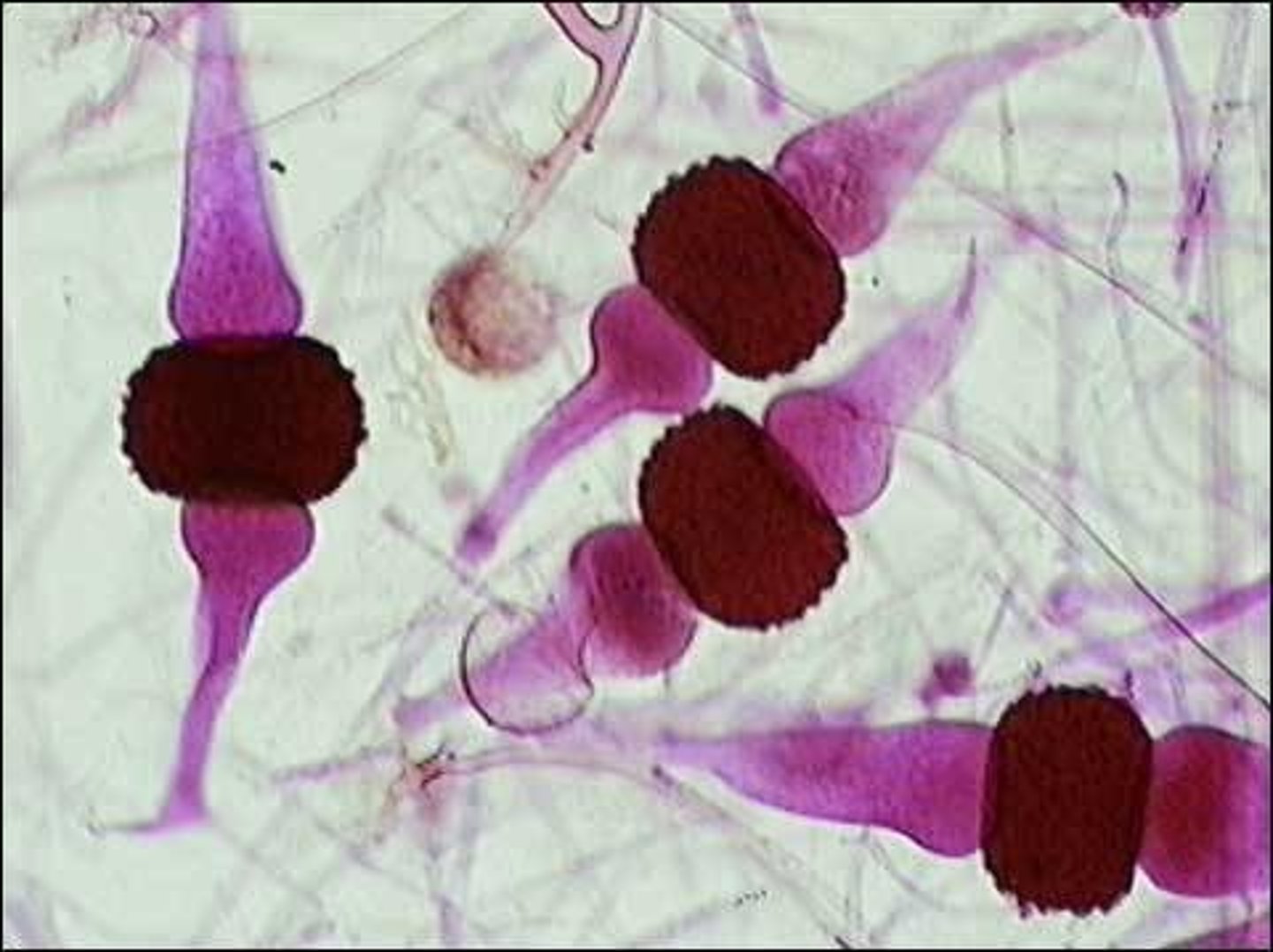
sexual Rhizopus zygosporangium
following karyogamy, a zygosporangium produces unique zygospores
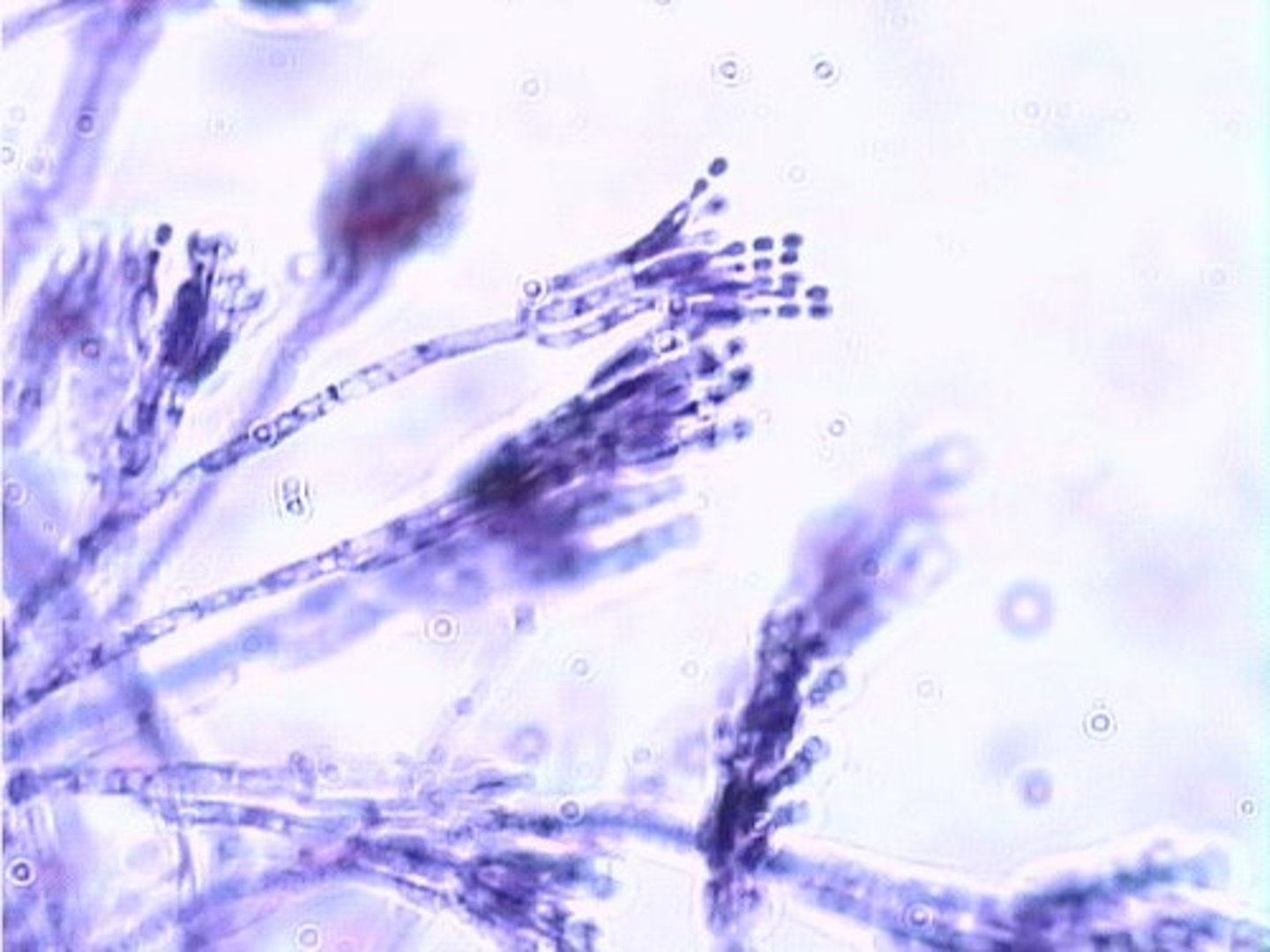
what is Phylum Ascomycota
sac fungi
includes yeasts, molds, and truffles
Penicillium
conidiophore produces identical conidia
Saccharomyces
budding cells
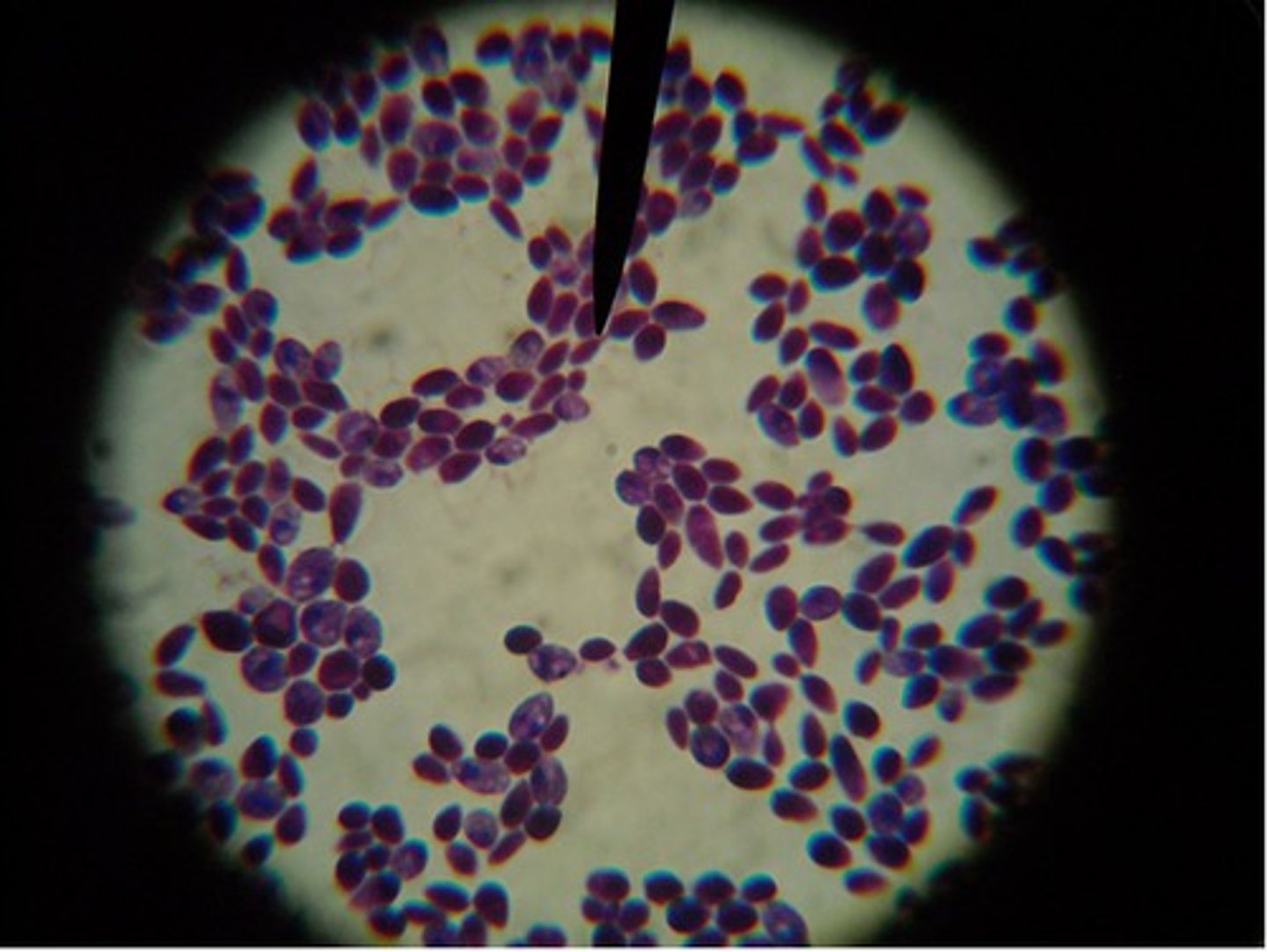
Peziza
During sexual reproduction in a sac fungus ,an ascocarp is formed. The ascocarp interior is lined with "sac"-shaped asci. Each ascus produces eight ascospores.
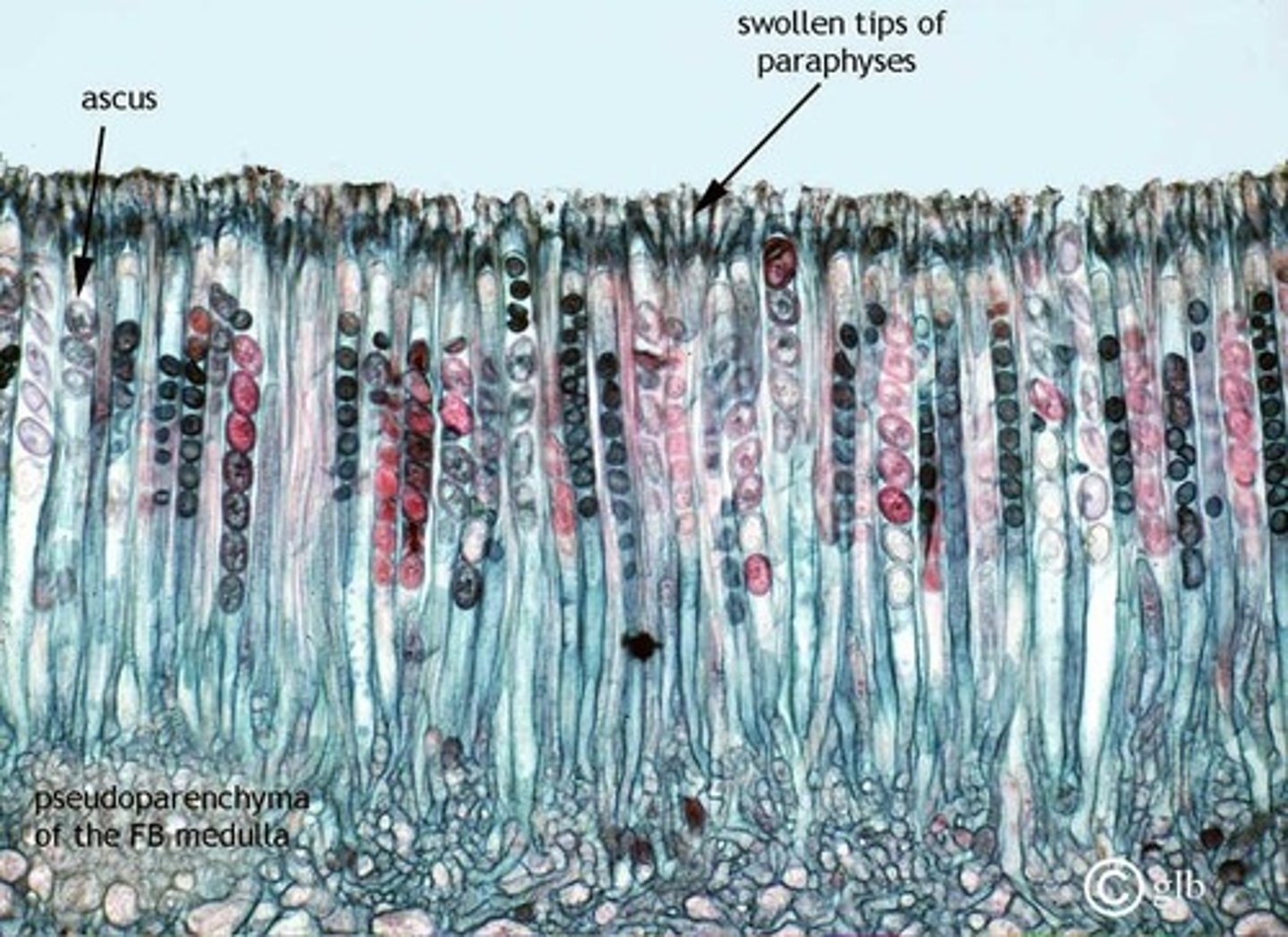
phylum Basidiomycota
club fungi (mushrooms, puffballs, shelf fungi, rusts, smuts)
Parts of a mushroom
annulus, gills, cap, stalk, basidiocarp
annulus
#4
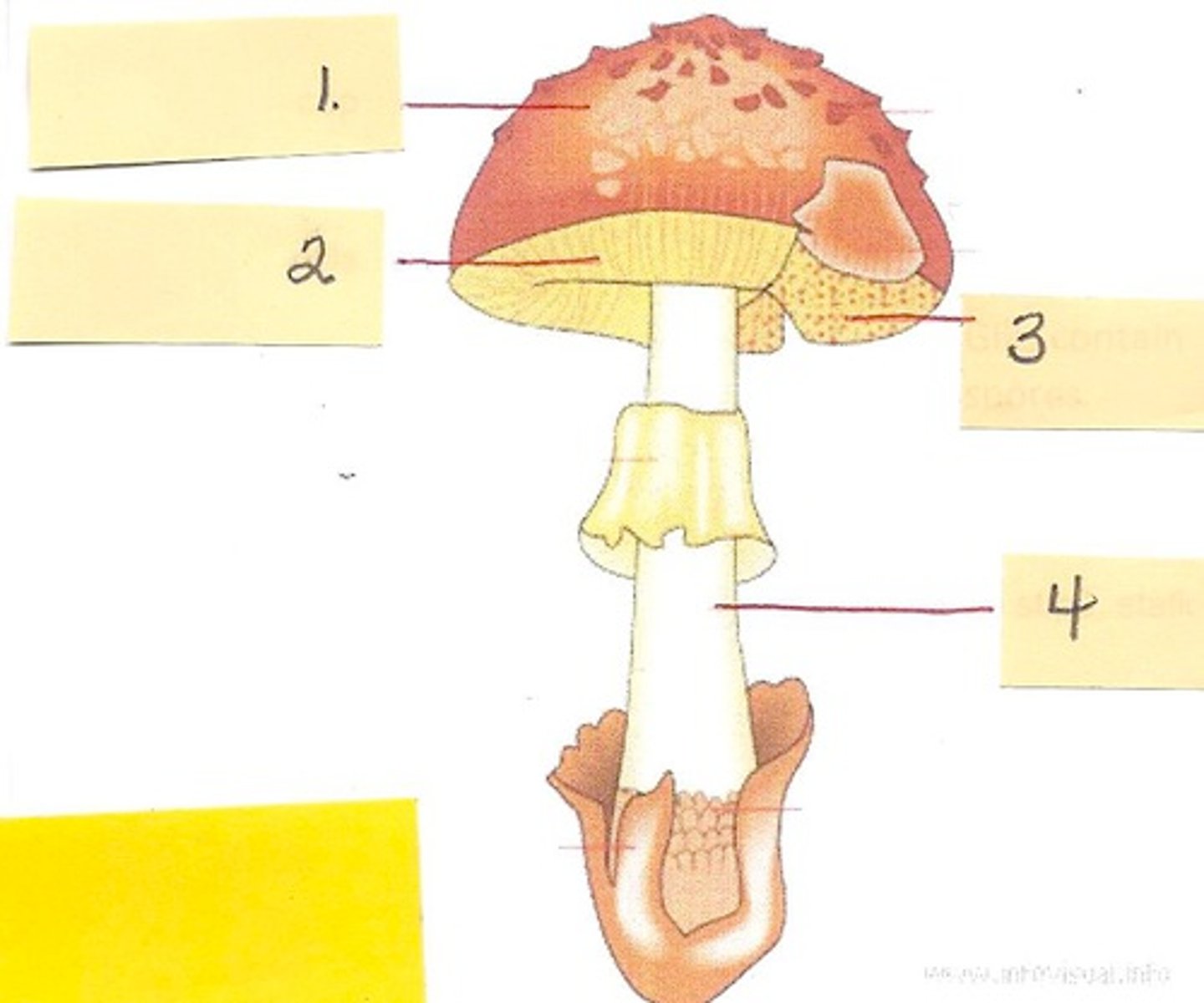
gills
underside of cap
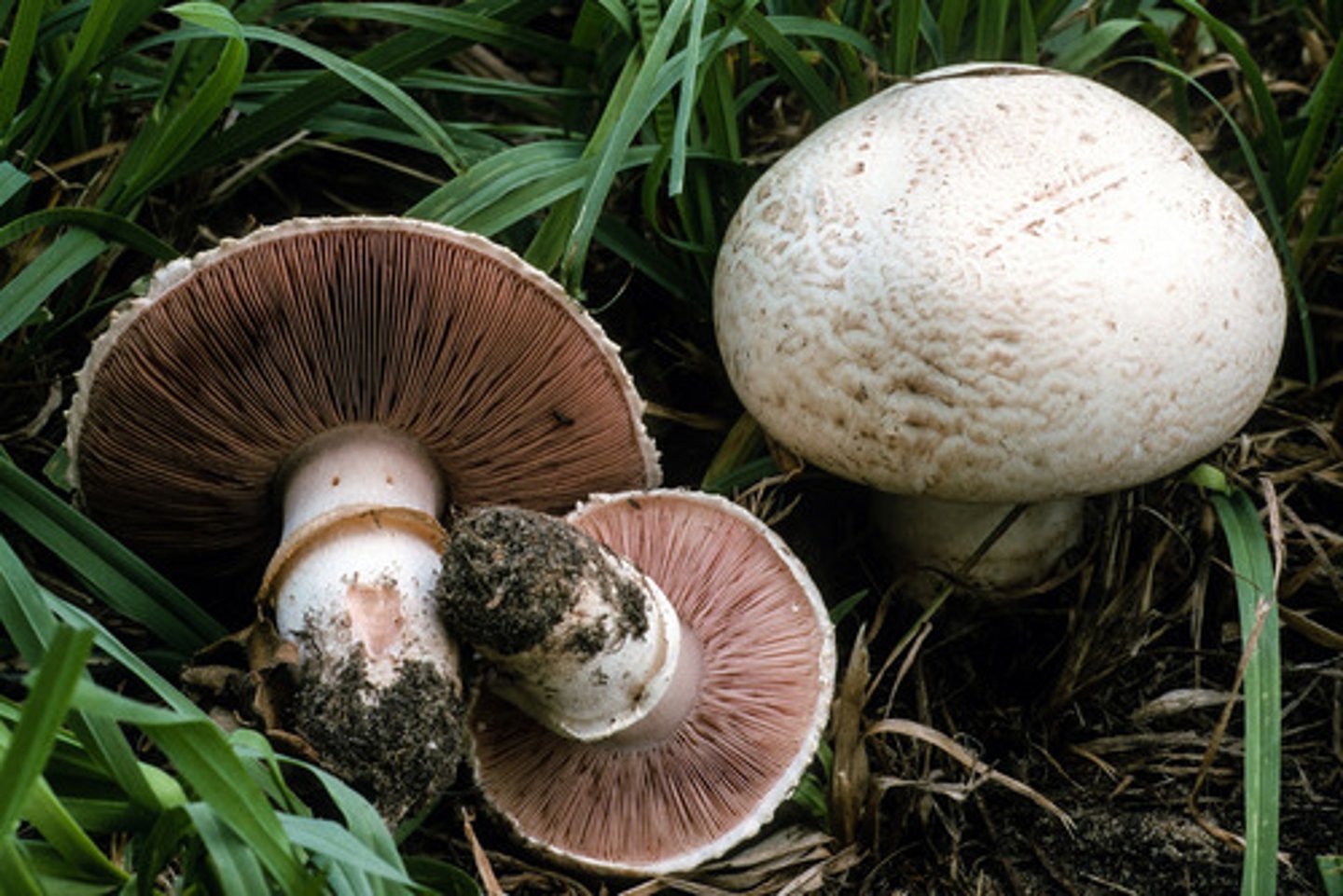

cap (mushroom)
top of mushroom #1
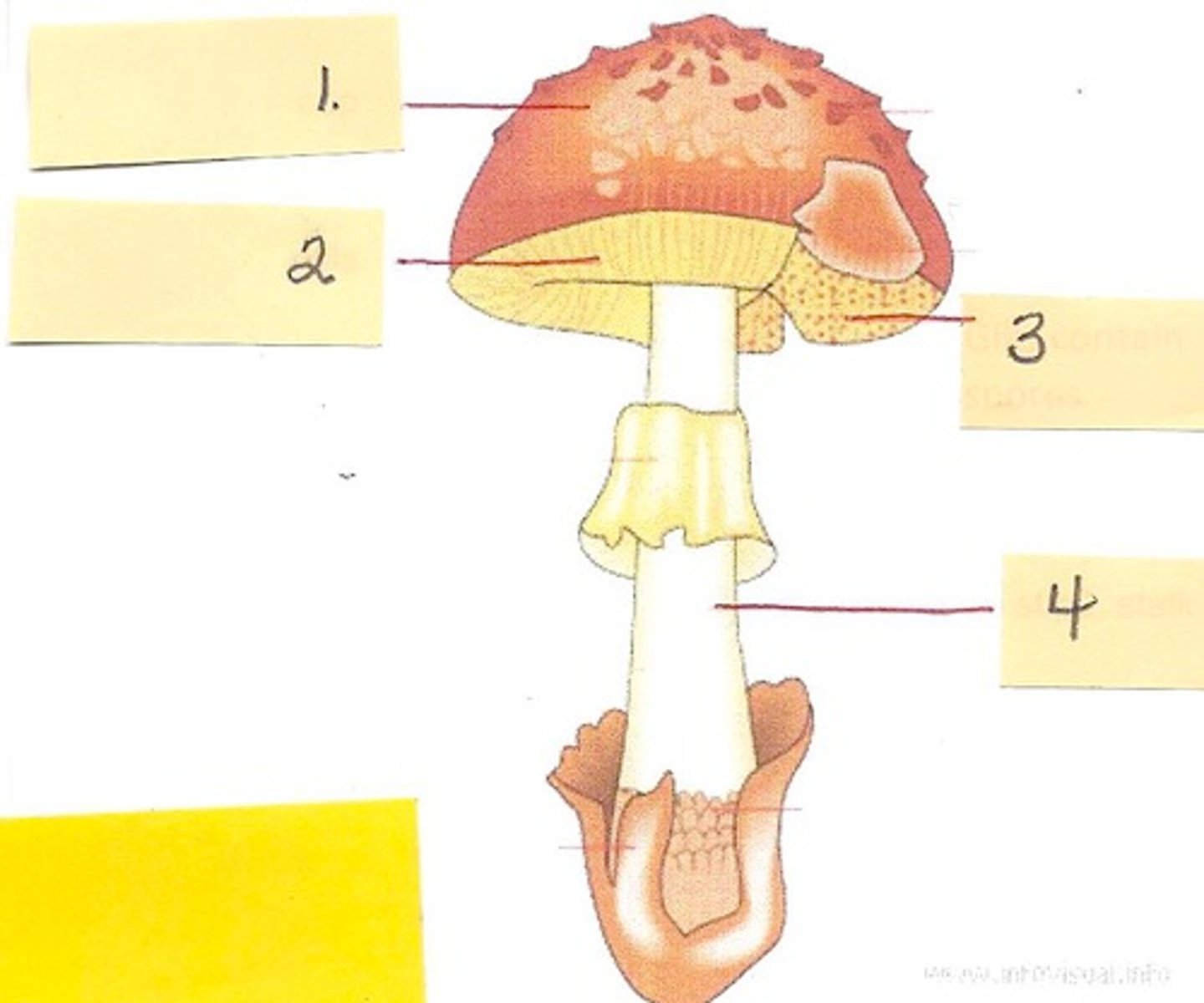
stalk (mushroom)
the upright portion that supports the cap
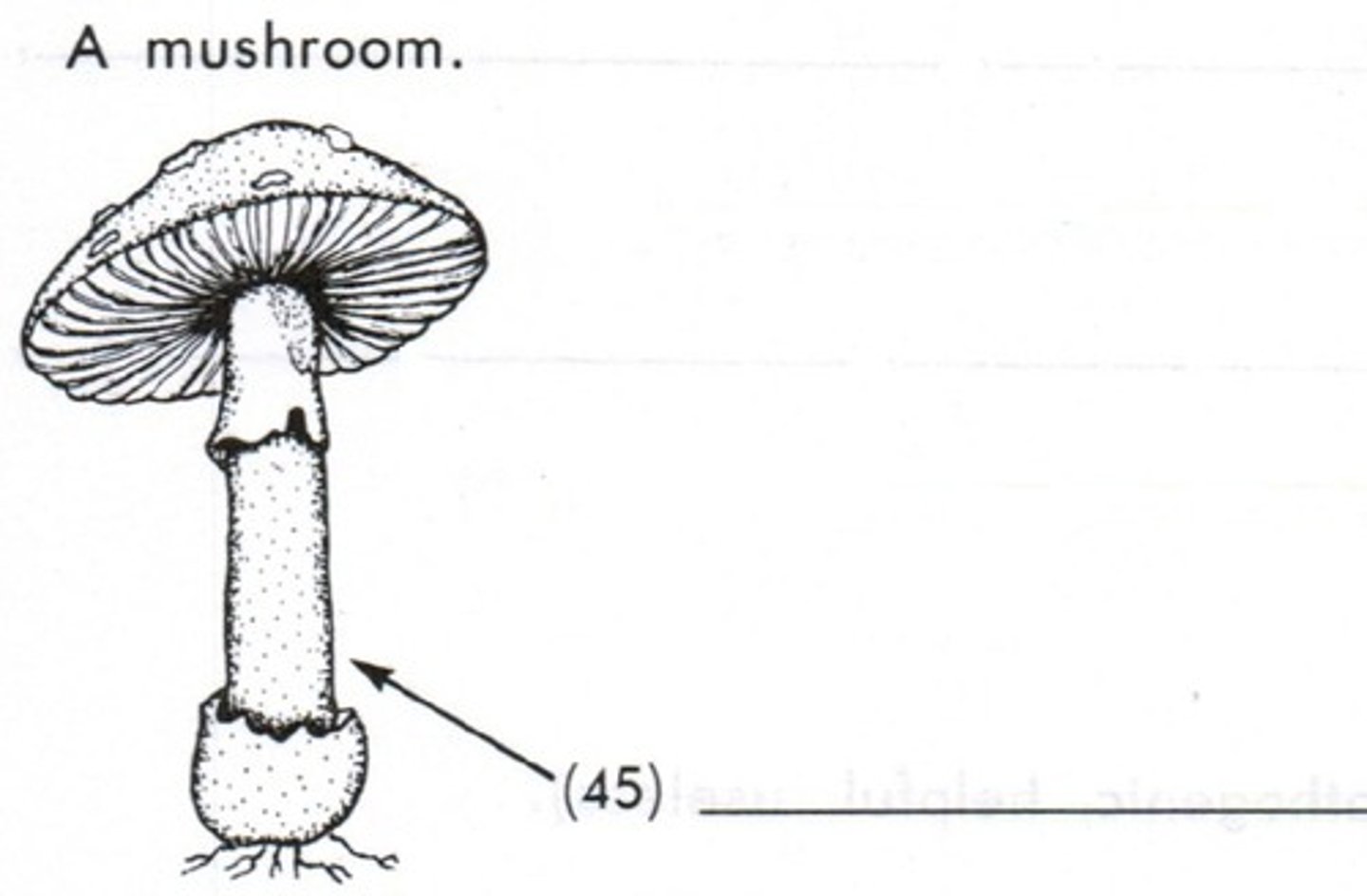
basidiocarp
fruiting body that protrudes from the ground and bears the basidia
Coprinus mushroom- what happens in the gills of the basidiocarp
Each basidium produces four basidiospores
Parasitism
One organism benefits and the other is harmed
commensalism
one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
Mutualism
both organisms benefit
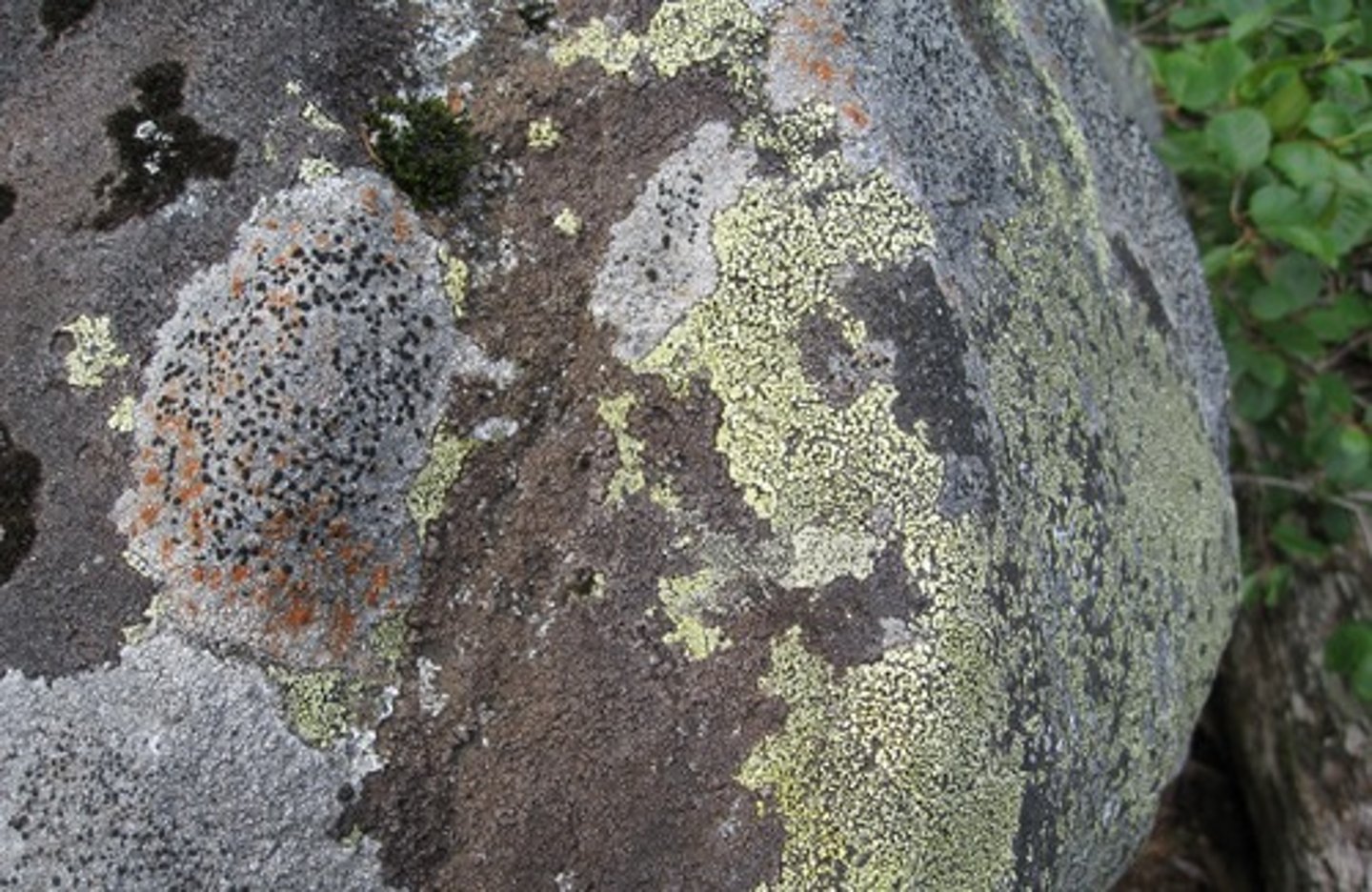
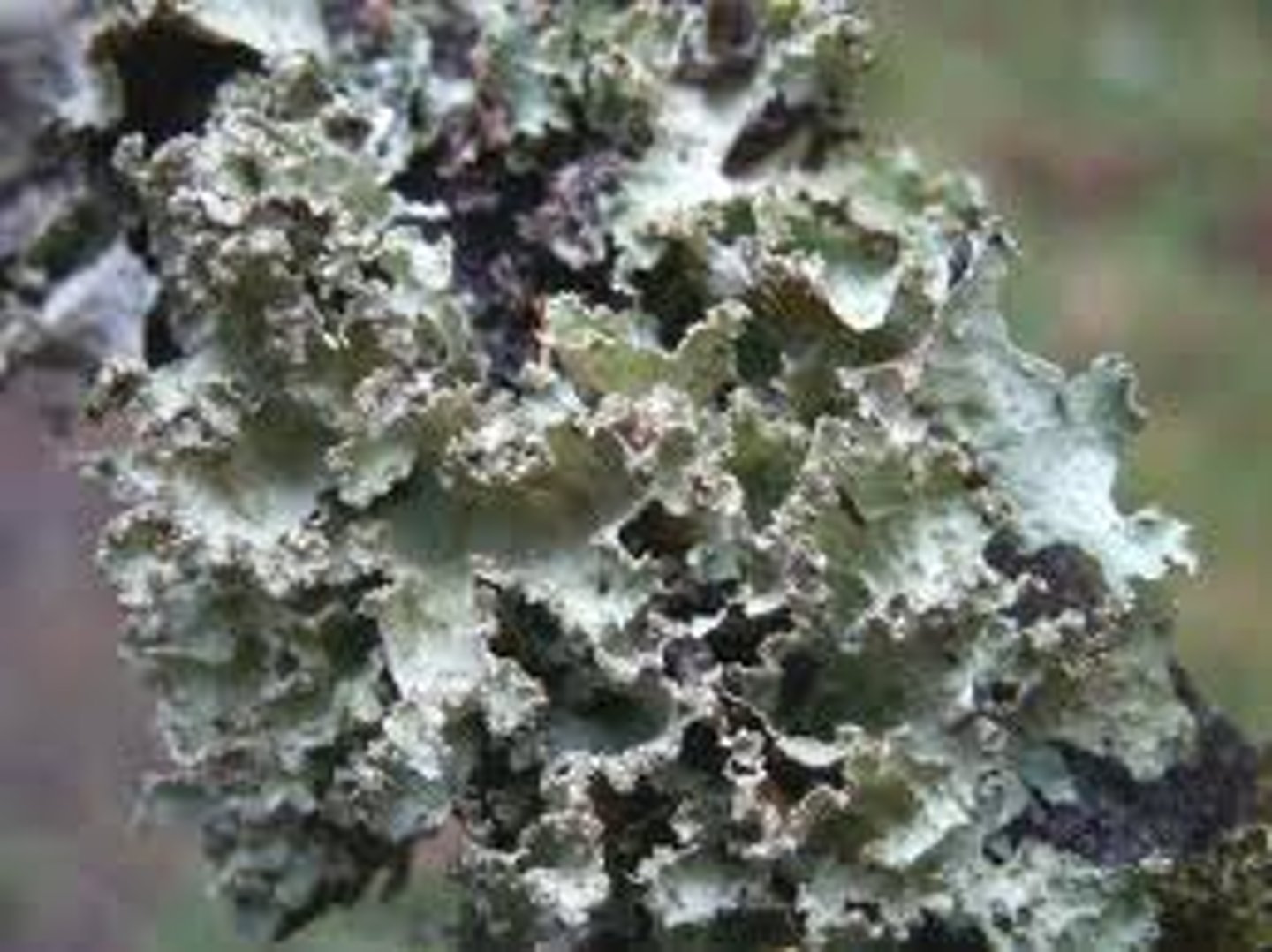
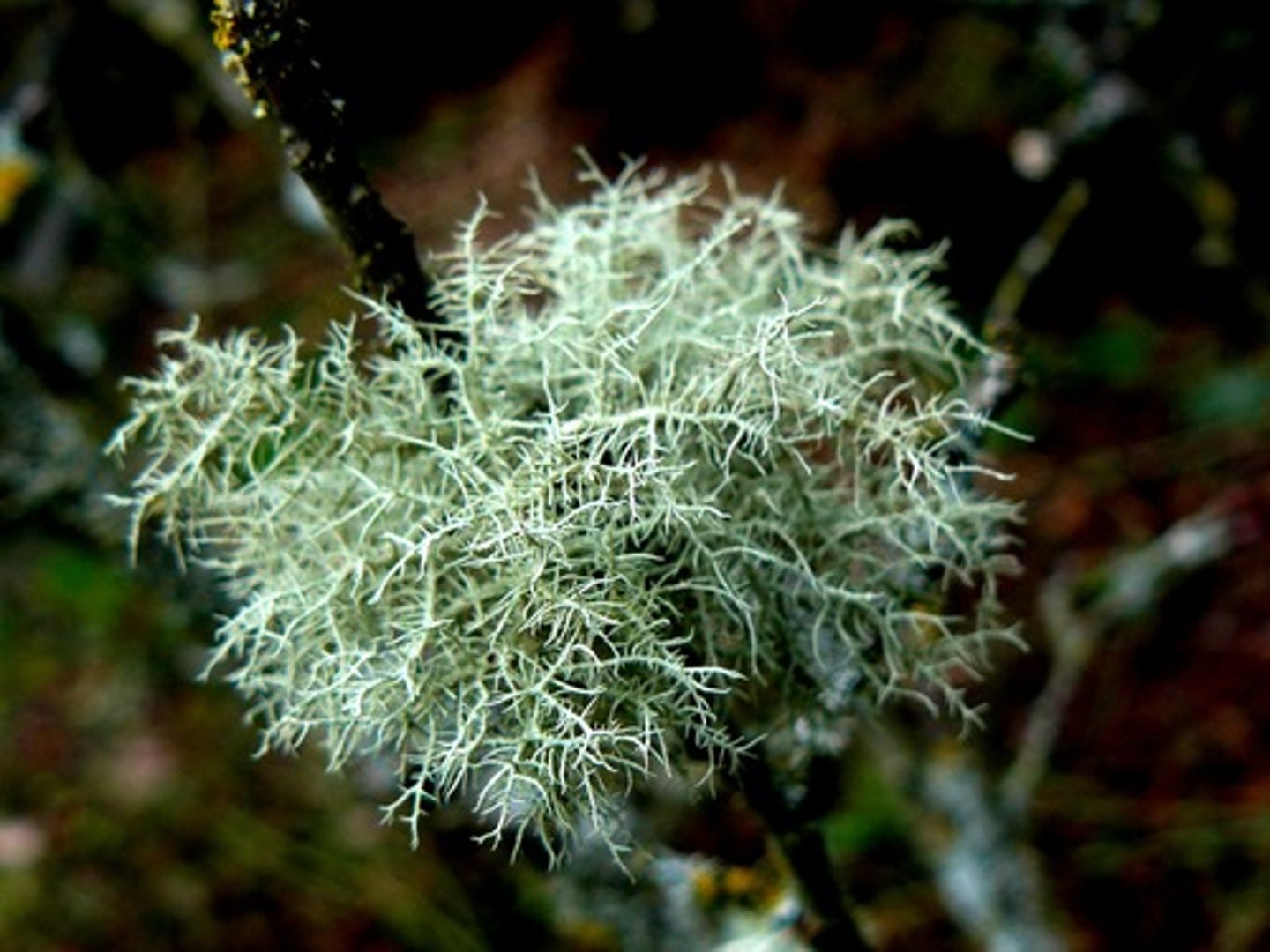
lichen
a mutualistic symbiosis of a fungus and either an algae or a cyanobacterium
crustose lichen

foliose lichen

fruticose lichen

Mycorrhizae
fungi which form a mutualistic symbiosis with plants through roots
How do fungi benefit from mycorrhizae
from the photosynthetic products of the plant
How do plants benefit from mycorrhizae
from the ability of the fungus to obtain water and inorganic nutrients
Lichen
a mutualistic symbiosis of a fungus and either an algae or a cyanobacterium