CHAPTER 1 - MANAGEMENT ASPECT (ENTREP REVIEWER)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
BUSINESS PROFILE
a document that includes a description about the business. It also includes the vision and goals of the business.
(ito ay isang dokumentong naglalaman ng deskripsyon tungkol sa itatayo o naitayong negosyo. Ito rin ay naglalaman ng vision at goals ng iyong negosyo.)
VISION
describes the future of the business or what the owner wishes to achieve for his/her business in the future. It doesn’t necessarily provides the way on how to achieve the goal stated.
paglalarawan sa negosyo para sa kinabukasan o ang nais marating na katayuan ng isang negosyo sa hinaharap. Tandaan na ito ay hindi nagbibigay ng partikular na pamamaraan o gawain para marating ang ninanais para sa negosyo.
MISSION
General Statement of how you will achieve the vision.
MISSION STATEMENT
is an action statement that usually begins with the word “to”.
Example:
“To provide unique and high quality dairy products to local consumers.”
GOALS (LAYON)
The set tasks or conditions that need to be achieved to ensure the fulfillment of the vision for your business.
These define the indicators that show whether you have achieved or are on the path to achieving the vision for your business.
It may be short-term or long-term.
SHORT-TERM GOAL
Identify the type of goal stated in the situation:
“Magsimula sa pagbebenta ng sampung (10) masarap at abot-kaynag BananaQ sa loob ng isang araw, 900 na BananaQ sa loob ng tatlong buwan”
LONG-TERM GOAL
Identify the type of goal stated in the situation:
“Mapalago at magdagdag ng iba pang masarap, malinis at murang meryenda katulad ng KamoteQ at palamig sa loob ng tatlong taon.”
UNDERSTANDABLE, SUITABLE, ACCEPTABLE, FLEXIBLE
Criteria for goals
OBJECTIVES
provide specific milestones with a specific timelines for achieving a goal.
Examples:
Increase market share by 10 percent over the next three years.
Lower operating costs by 15 percent over the next two years through improvement in the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
Reduce the call-back time of customer inquiries and questions to no more than four hours.
SUITABLE, MEASURABLE, FEASIBLE, COMMITMENT, OWNERSHIP
CRITERIA FOR OBJECTIVES
BUSINESS DESCRIPTION
This includes the structure of the business or the type of operation, statement whether the business is new or already established, legal form; principals and their roles, target market, mode of distribution, support systems, product description, and unique selling proposition (USP).
STRUCTURE OF THE BUSINESS
Wholesale, Retail, Food Service, Manufacturing, Service-Oriented
LEGAL FORM
Sole/Single Proprietorship, Partnership, Corporation, Cooperative
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
clear idea of your intention, unique features and variations that can typically be found in the industry
UNIQUE SELLING PROPOSITION (USP)
any proprietary information that will set your concept apart from the crowd.
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
organizational hierarchy that promotes communication, defines the chain of command and shows employees how to advance their careers up the ladder.
FUNCTIONAL, DIVISIONAL, MATRIX, FLAT
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
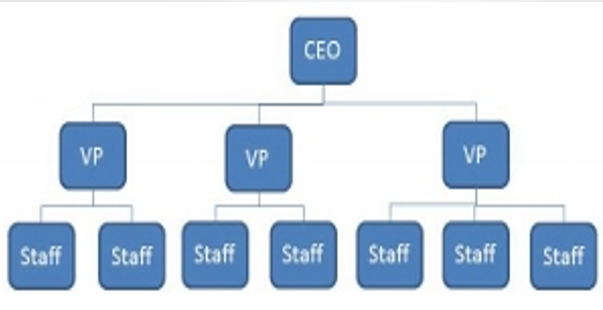
FUNCTIONAL
Organizational structure where people who do similar tasks are grouped together based on specialty.
Advantages:
a. quick decision making, because the group member can easily communicate
b. Members can also learn from each other, since they already posses similar skill sets and interests.
DIVISIONAL (MARKET-BASED STRUCTURE)
workers are grouped into teams based on the products or projects that meet the needs of a certain type of customer.
Advantage:
- The division of labor in this kind of structure ensures workers making similar products can achieve greater efficiency and higher output.
MATRIX
combines elements of the functional and divisional models
groups people into functional departments of specialization, then further separates them into divisional projects and products.
Advantages:
- Increases the productivity of the team.
- fosters greater innovation and creativity,
- allows managers to cooperatively solve decision-making problems through group interaction
FLAT
attempts to disrupt the traditional top-down management system of most companies.
management is decentralized so there is no everyday “boss”
Advantages:
a. Each employee is the boss of themselves, eliminating bureaucracy and red tape and improving direct communication.
b. The employee simply communicates directly with the target on a peer-based level.
FUNCTIONAL
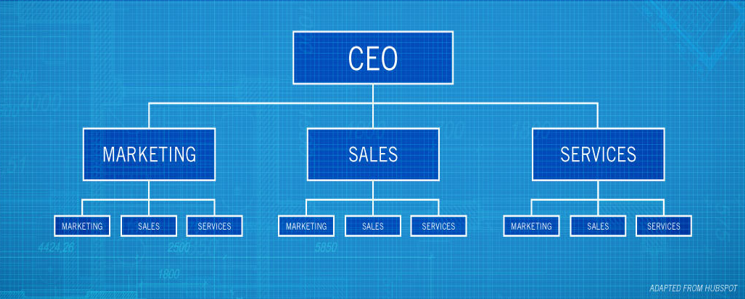
DIVISIONAL
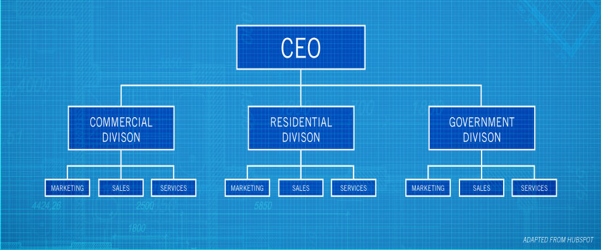
MATRIX
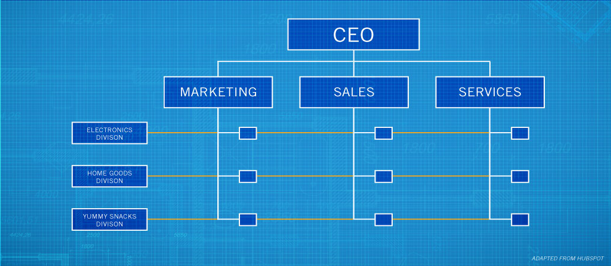
FLAT