Neuromuscular System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
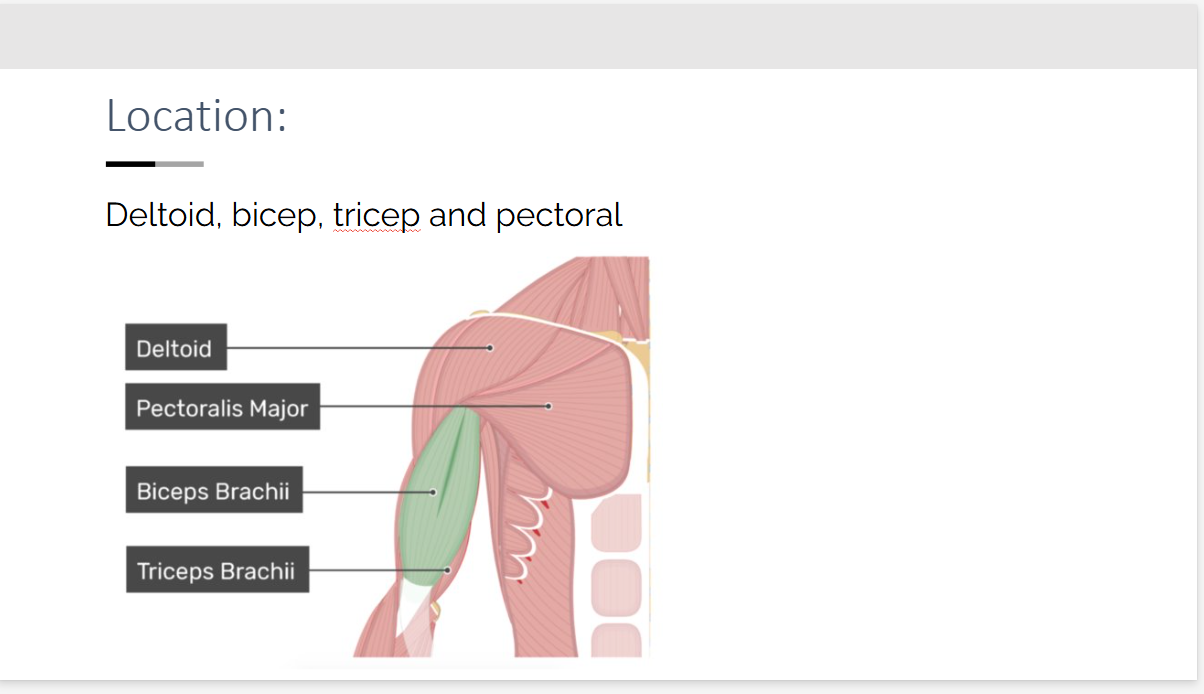
Deltoid, bicep, tricep and pectoral Location?
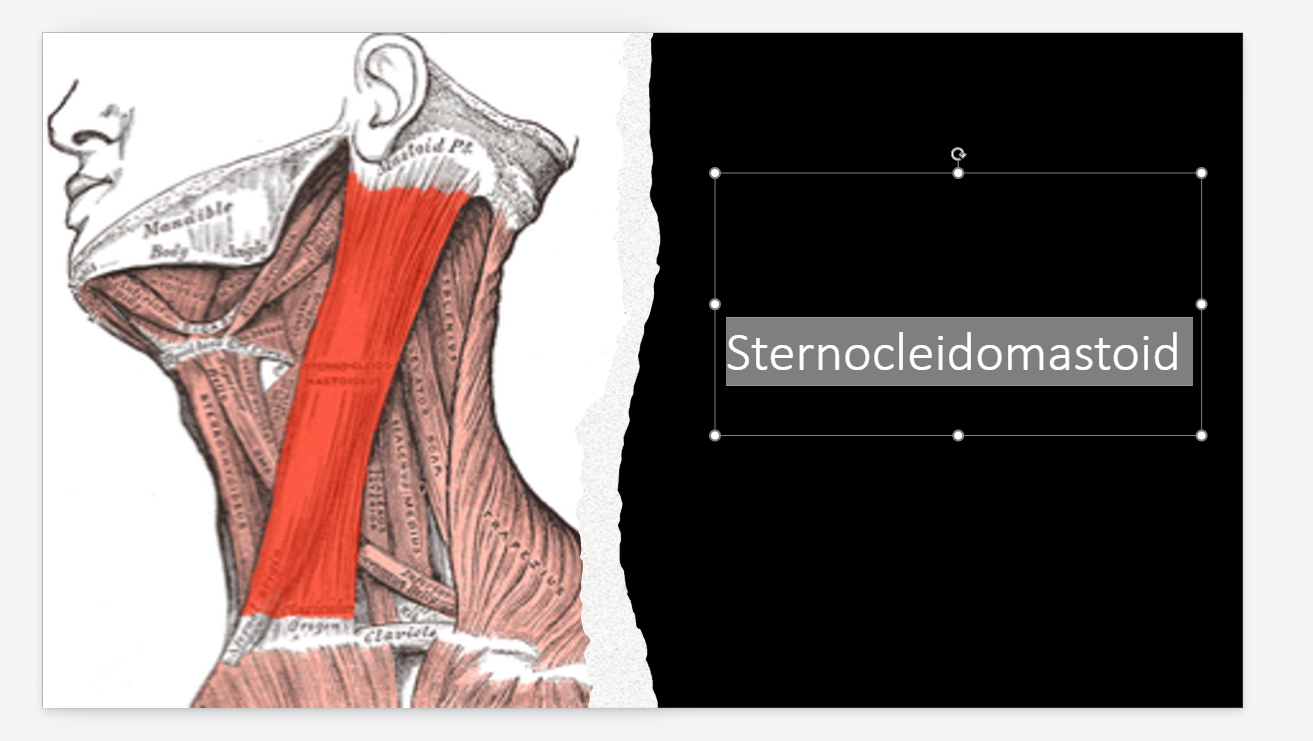
Sternocleidomastoid Location?
Neck
Abdominals and obliques Location?
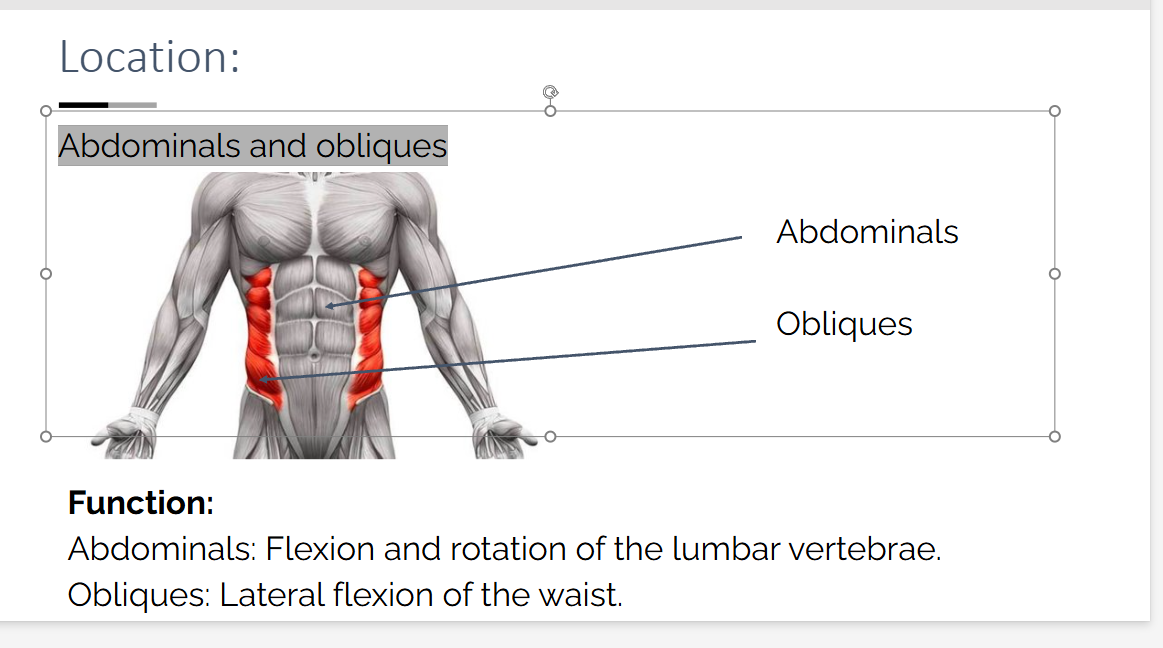
Function of Abdominals
Flexion and rotation of the lumbar vertebrae.
Function of Obliques
Lateral flexion of the waist.
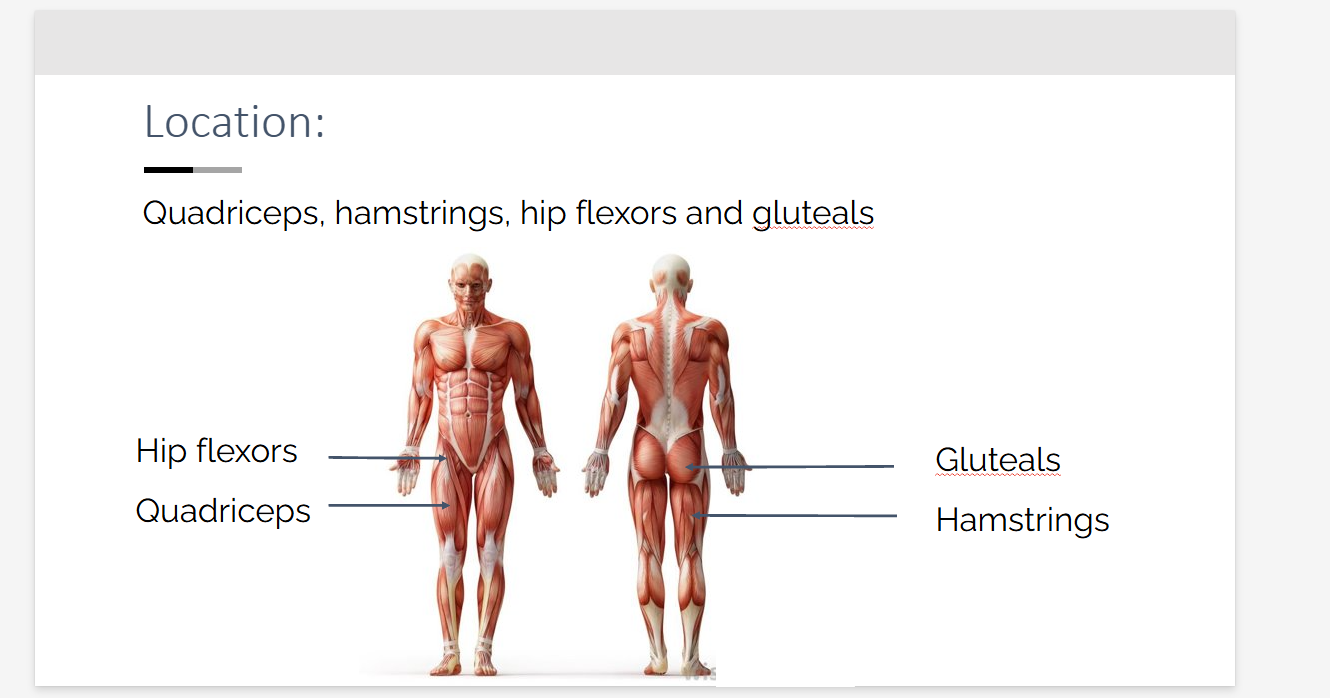
Quadriceps, hamstrings, hip flexors and gluteals Location
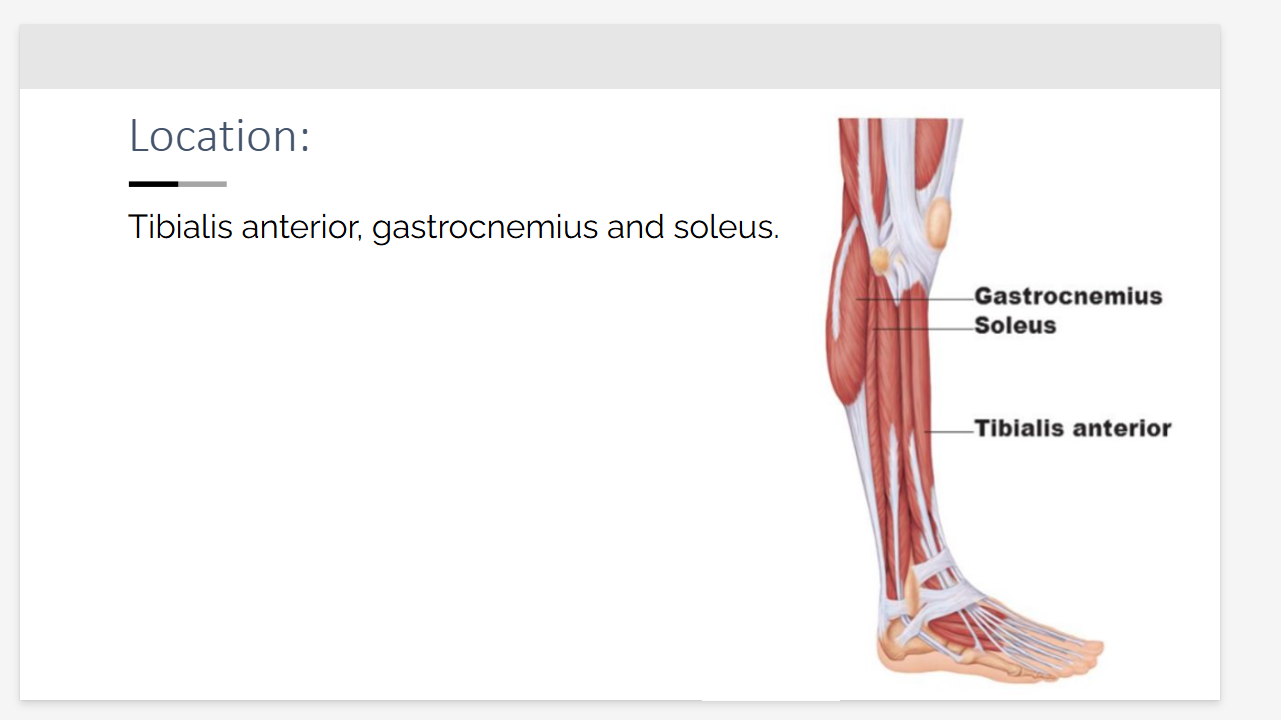
Tibialis anterior, gastrocnemius and soleus. Location?
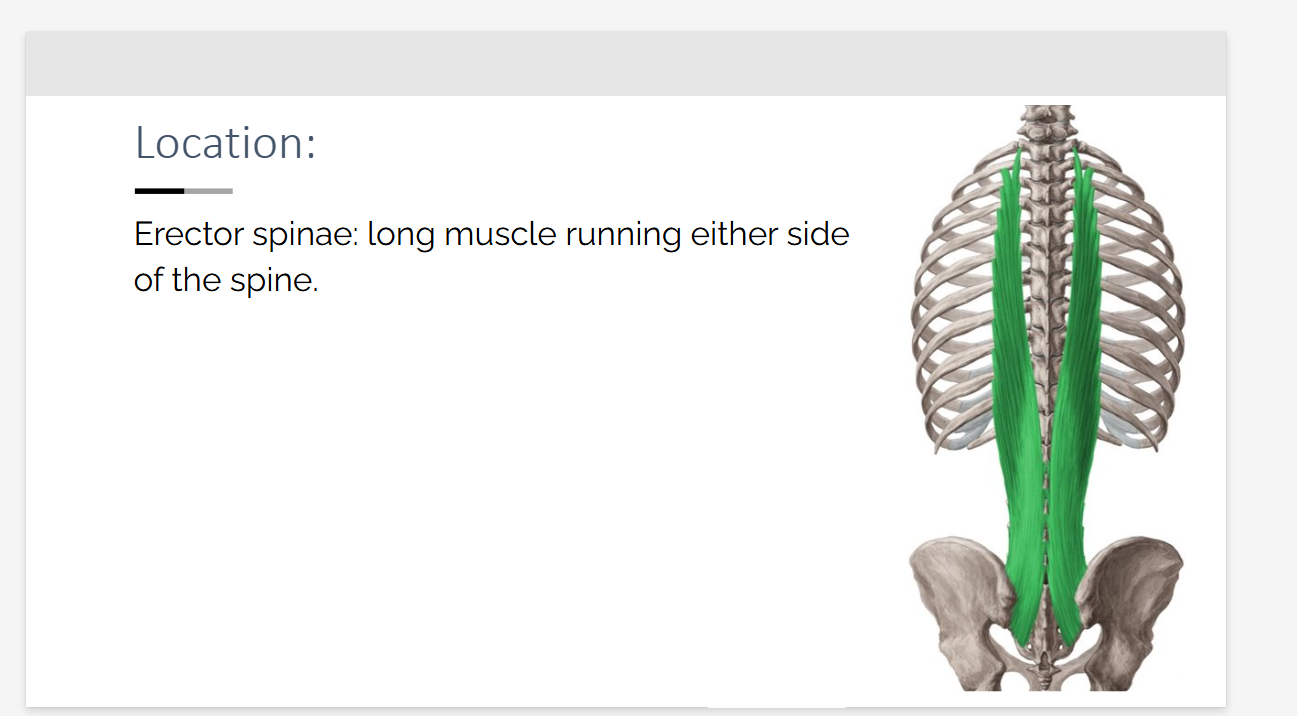
Erector Spinae location?
long muscle running either side of the spine.
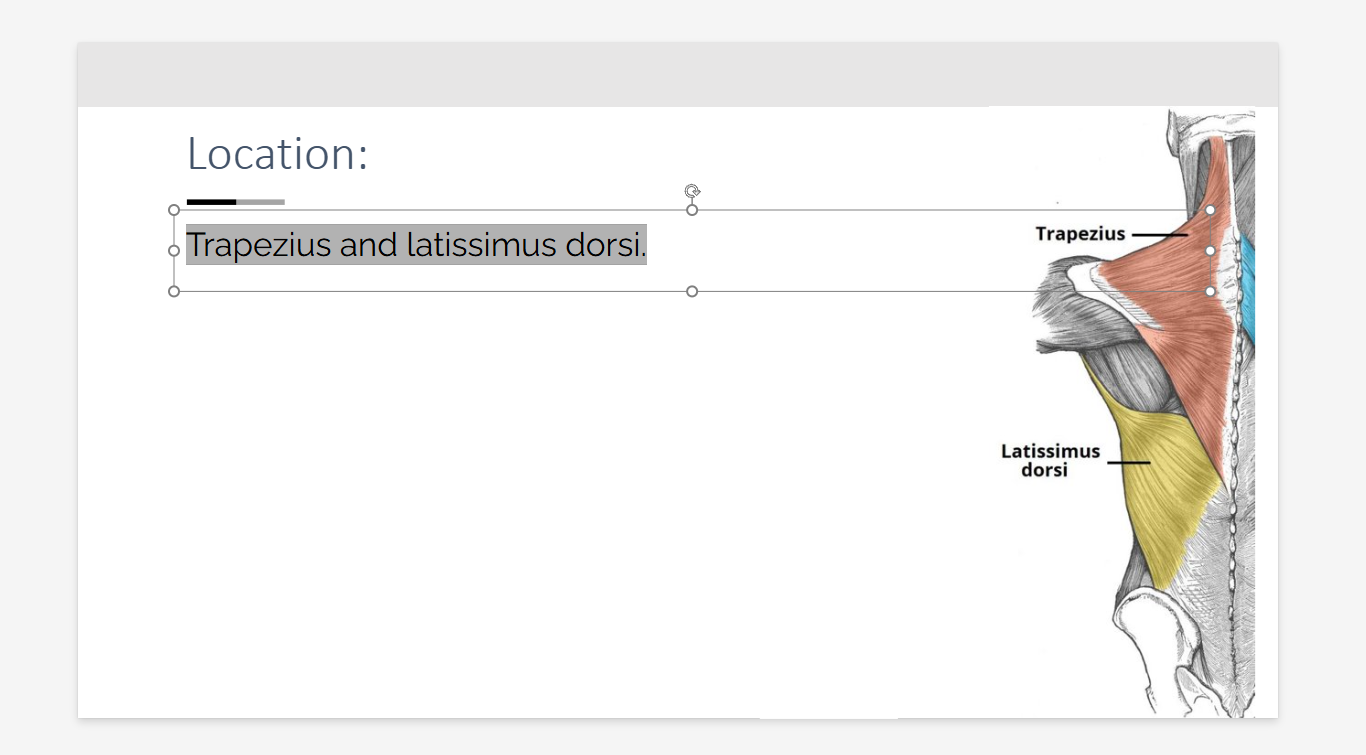
Trapezius and latissimus dorsi location?
What are the muscle fibre types
Slow twitch (type I)
Fast glycolytic (type IIx).
Fast oxidative glycolytic (type IIa)
Slow twitch (type I).
Type 1 are slow twitch
They contract slowly
They contract with less force
They are the most resistant to fatigue
They are suited to longer duration, aerobic activities
They have a rich blood supply
They contain many mitochondria (site for aerobic respiration)
They have a high capacity for aerobic respiration
‘Aerobic respiration; process of producing energy using oxygen’.
Fast glycolytic (type IIx).
They are known as fast twitch fibres/fast-glycolytic fibres
They produce the greatest force when contracting
They contract rapidly
They least resistant to fatigue (fatigue the quickest)
They are suited to anaerobic activities
They depend upon anaerobic respiration
Recruited for high intensity/short duration activities
‘Anaerobic respiration: The process of breaking down glucose without oxygen present.’
Fast oxidative glycolytic (type IIa)
They are known as fast twitch fibres/fast-oxidative fibres
They are able to produce a great force when contracting
They are resistant to fatigue
They fatigue faster than type 1 fibres
They use oxygen
They are suited to speed, power and strength activities
Muscle Fibres
The fibres that make up a muscle (which contract to cause movement)
Motor Neurones
The nerves which impulses travel down to stimulate the muscle fibres.
Motor Units:
A motor neurone and its muscle fibres.
How do muscle fibre types differ?
Type I: Low force, high endurance
Type IIa: Moderate force & endurance
Type IIx: High force, low endurance
What are Type I muscle fibres and when are they used?
Slow-twitch fibres used for endurance and aerobic activity.
Example: Marathon running, long-distance cycling.
What are Type IIa muscle fibres and when are they used?
Fast oxidative fibres used for moderate-intensity, sustained power.
Example: 800m running, repeated sprints in football or hockey.
What are Type IIx muscle fibres and when are they used?
Fast glycolytic fibres for explosive, anaerobic movements.
Example: 100m sprint, long jump, shot put.
Altitude Training specification

how does the nervous system work together?
The two systems work together to keep your body in balance
Sympathetic
Controlled by the Medulla Oblongata the sympathetic nervous system is the body's 'fight or flight' system which speeds up breathing rate. This occurs by dilating pupils, increasing HR and releasing adrenaline.
parasympathetic
Parasympathetic system is concerned with 'rest and digest', decreasing breathing rate.
Describe the “fight or flight” response and its physiological effects (2 marks)
The “fight or flight” response, controlled by the sympathetic nervous system (1), prepares the body to respond to stress or danger by increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and releasing adrenaline (1).
Motor Neurone:
Nerve cells which transmit the brains instructions as electrical impulses to muscles.
Neuromuscular Junction:
Where the motor neurone and the muscle fibres meet.
The ALL-OR-NONE Law
If the impulse sent to the muscle is above the threshold, all muscle fibres attached to that motor unit will contract.
If the impulse is below the threshold, none of the muscle fibres contract.
Spatial Summation
The addition of impulses at different places on the neuron at the same time.
Tetanic Contraction
A sustained, maximal muscle contraction caused by rapid, repeated nerve impulses with no time for relaxation.
Wave summation
Where there is repeated nerve impulses with no time to relax, so a smooth sustained contraction occurs
Describe spatial summation (1 mark).
The addition of impulses at different places on the neurone at the same time.
Explain how wave summation allows a gymnast to gain the required height in a floor routine (3 mark).
Wave summation allows the gymnast to produce more powerful contractions.
Because the muscle is stimulated again before it relaxes.
Therefore the gymnast can apply a greater force to adjust the height of her jump as she requires.
What does PNF Stand for
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation
Proprioceptors:
Found at muscles, tendons & joints and detect movement changes
Golgi Tendon Organs:
Found between the muscle fibre and the tendon and they detect increased levels of tension in a muscle.
When a muscle contracts isometrically, it overrides the stretch reflex mechanism causing the muscle to relax.
Muscle Spindles
Very sensitive proprioceptors found between muscle fibres which report to the central nervous system about how far and fast a muscle is being stretched.
If overstretch is detected the stretch reflex mechanism is triggered.
Stretch Reflex:
The bodies protective mechanism to bring an overstretched joint back to a save range of movement (ROM).
(This is achieved through the antagonist contracting to pull the joint back).
What does PNF do
PNF is an advanced stretching technique, which is very effective at increasing flexibility
Explain how the characteristics of fast twitch glycolytic muscle fibres are suited to producing ATP anaerobically during powerful contractions (2 marks).
High PC Stores - Increased energy source for ATP production via the ATP-PC system.
High glycogen stores - Increased energy source for ATP production via the lactate anaerobic system.
High myosin ATPase activity - Increased enzyme activity for ATP production via the ATP-PC system.