Unit 1: Biochemistry - #6 Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Nucleic Acids
Assembly instructions for all proteins in living organisms
Includes DNA and RNA
DNA and RNA are polymers that are made up of monomer units, these are called nucleotides
Nucleotides have three parts:
Nitrogenous base
5-C sugar
Phosphate group (s)
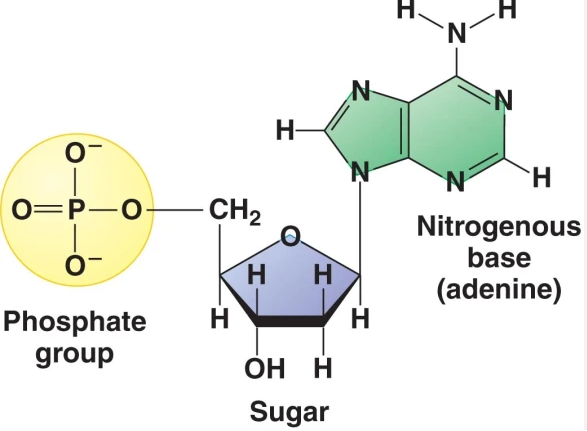
DNA
Source of genetic information for every living organism
Directs all cellular activities and is able to replicate itself so that new cells and organisms can be created
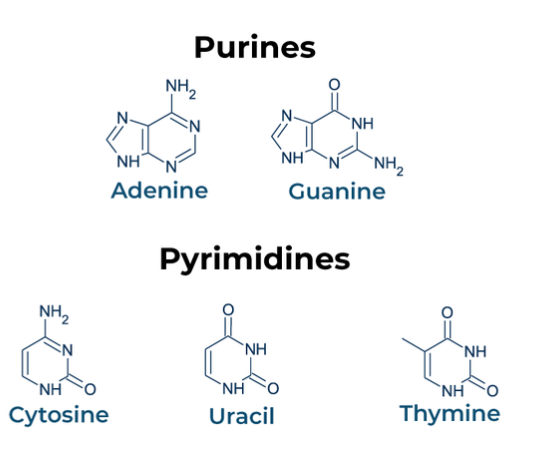
Nitrogenous Base
Divided into two groups based upon the number of rings in the structure
Purines: Two rings, adenine and guanine
Pyrimidines: One ring, thymine and cytosine
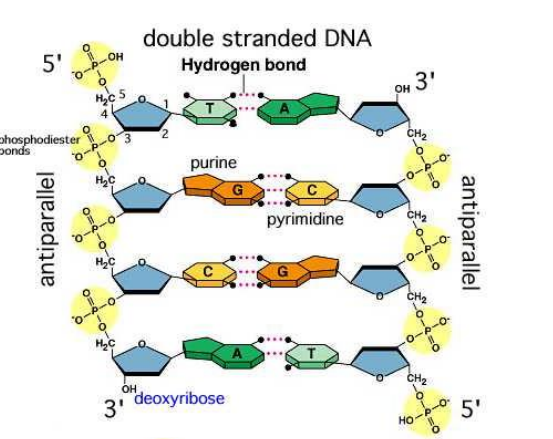
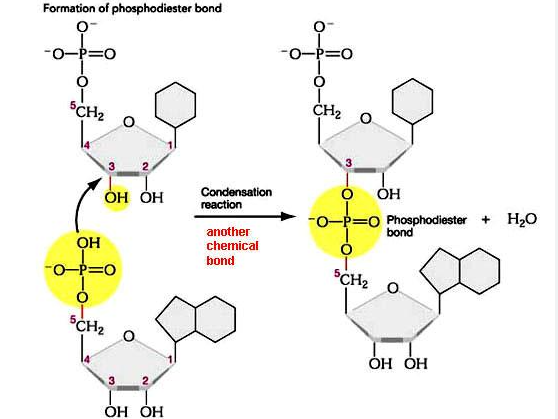
Linkage and Phosphodiester Bonds
DNA nucleotides are joined together at the phosphate group through phosphodiester bonds between carbon 5 of one molecule to the hydroxyl group at carbon 3 from another molecule
Additional nucleotides are always added in the 3 end of the previous nucleotide

Hydrogen Bonds
DNA is a double stranded molecule where the 2 strands run anti-parallel to each other
Hydrogen bonds unite strands of DNA together
Adenine will always bind to thymine by 3 hydrogen bonds
Guanine and cytosine will always bond together by 3 hydrogen bonds
A purine will only pair up with its complementary pyrimidine
RNA
Single stranded polymer
Involved in protein synthesis
Composed of:
Ribose sugar
Phosphate group
4 nitrogen containing bases (C, G, A and U)
All of the bases are the same as those found in DNA except Uracil (uracil replaces thymine in RNA)
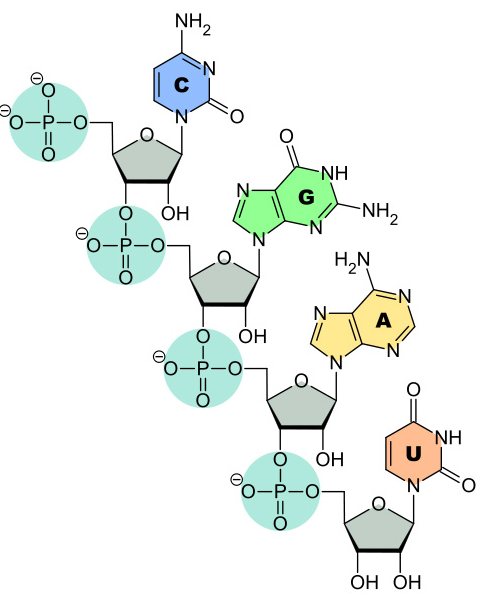
RNA Linkages: Phosphodiester Bonds
Also synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction in a condensation reaction
A phosphodiester bond forms between phosphate group from one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group from the second nucleotide
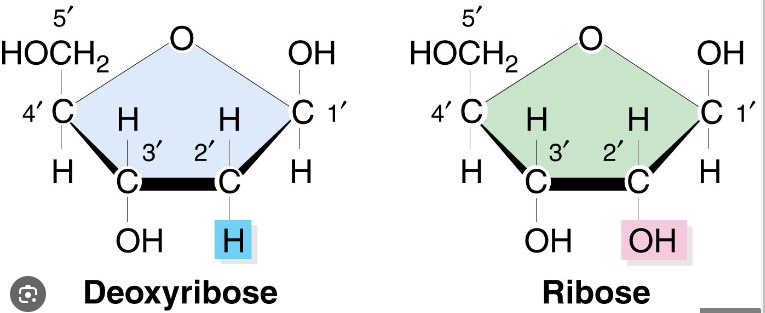
Deoxyribose vs. Ribose
. Ribose sugar has a hydroxyl (OH) group at position 2, whereas deoxyribose sugar has a hydrogen (H) atom at position 2.
DNA vs. RNA
DNA is double-stranded, forming a double helix, while RNA is usually single-stranded. The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, whereas RNA contains ribose.