BE 450 PPT 5 Composites
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
composite
engineered or natural materials made from 2 or more constituent materials
composite
have significantly different physical or chemical properties which remain separate and distinct on a macroscopic level w/in the finished structure
attractive
composites provide the "best of both worlds" since they draw on the ____________ properties from each component
fiberglass
composite examples: strength of the small diameter glass fibers (ceramic) combined with ductility of the polymer matrix
bone
composite examples: hydroxyapatite (ceramic) and collagen (polymer)
high, low
composite major advantage: can obtain a more desirable combination of properties - _______ strength, ______ density
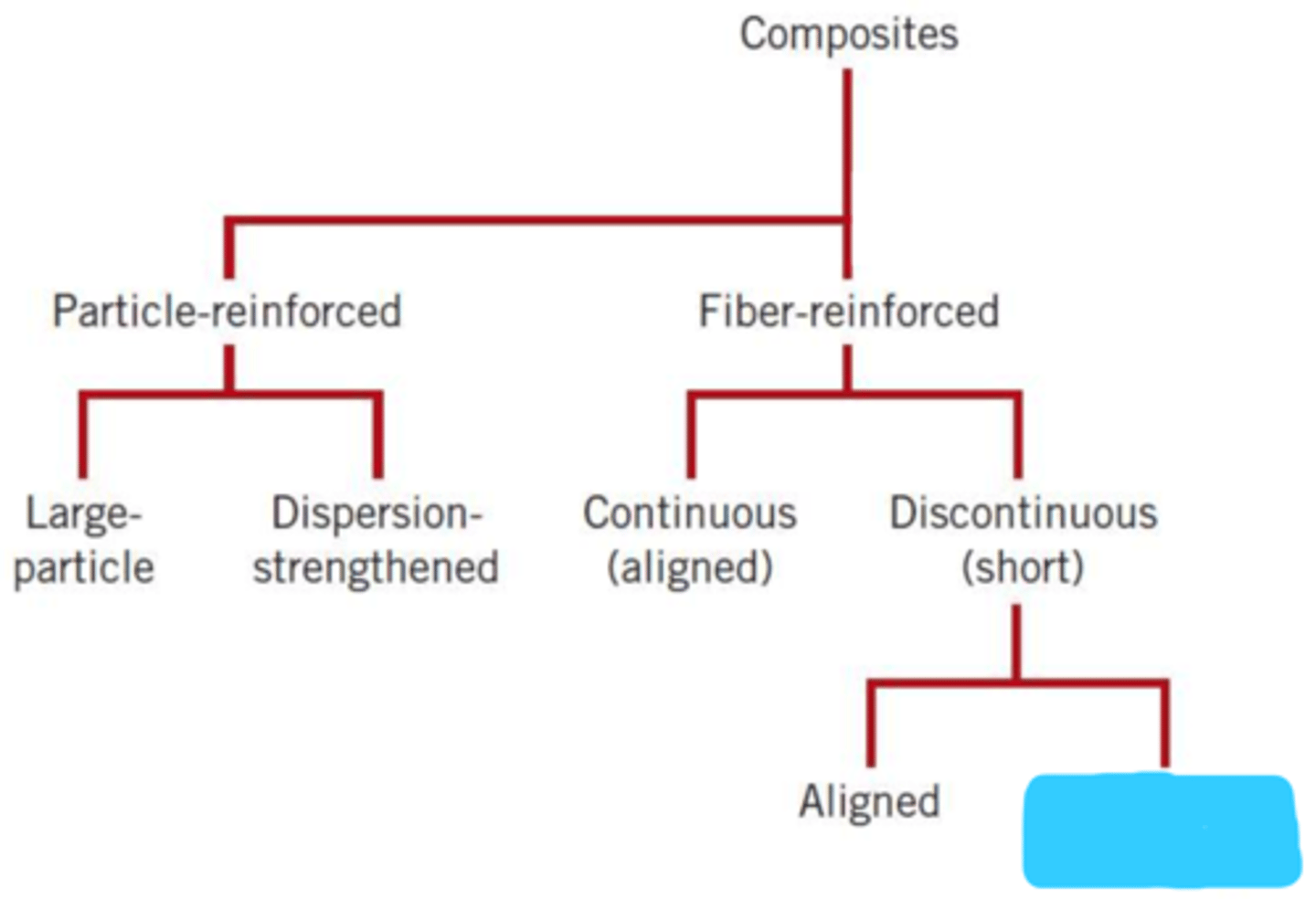
discontinuous
composites consist of 1 or more ________________ phases embedded w/in a continuous phase
continuous phase
matrix, provides environmental protection and transfers stress to the other phase
discontinuous/dispersed phase
usually harder and stronger than the other phase, surrounded by matrix, termed reinforcement or reinforcing material
phases
__________ of a composite can be metals, ceramics, or polymers
composites
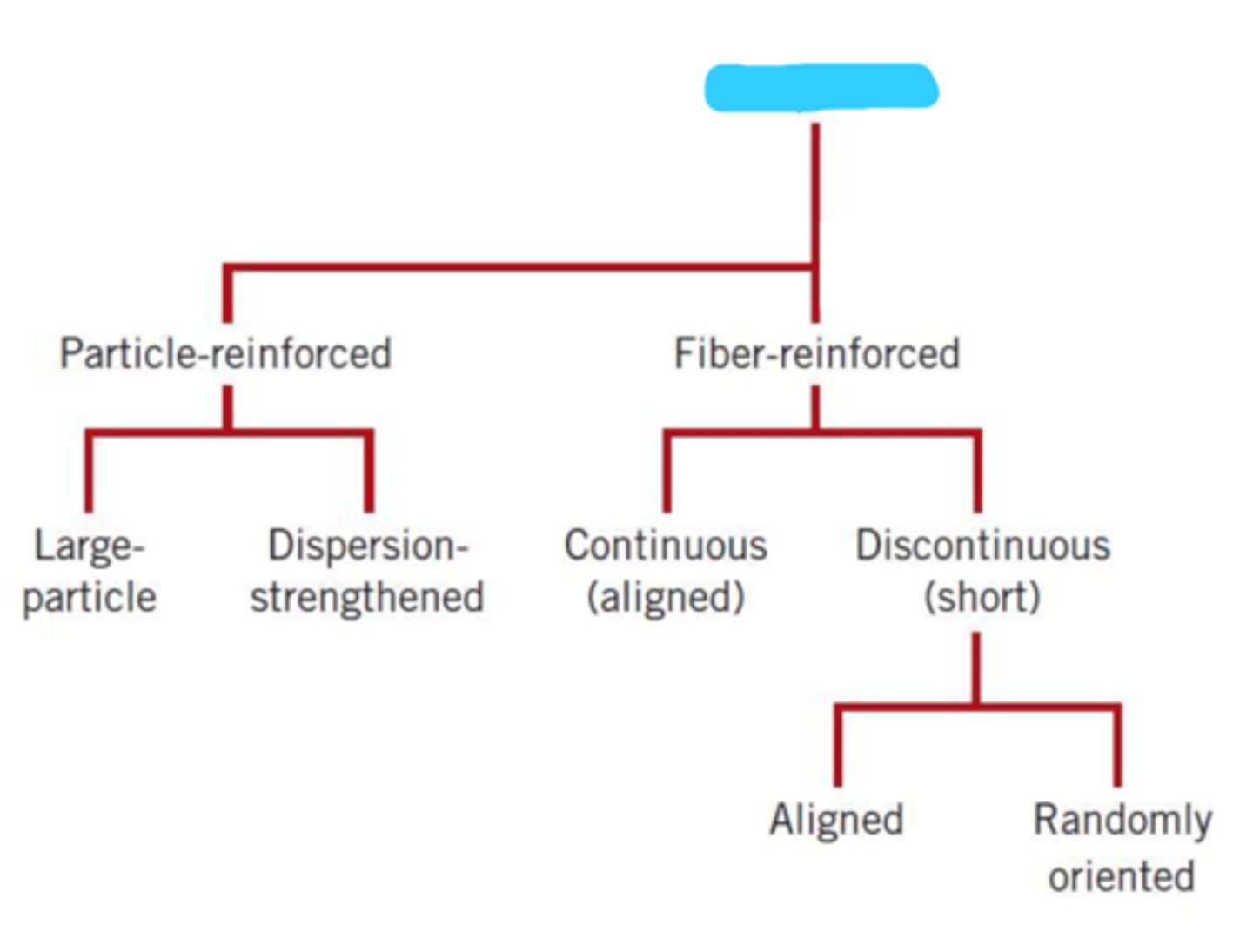
particle-reinforced
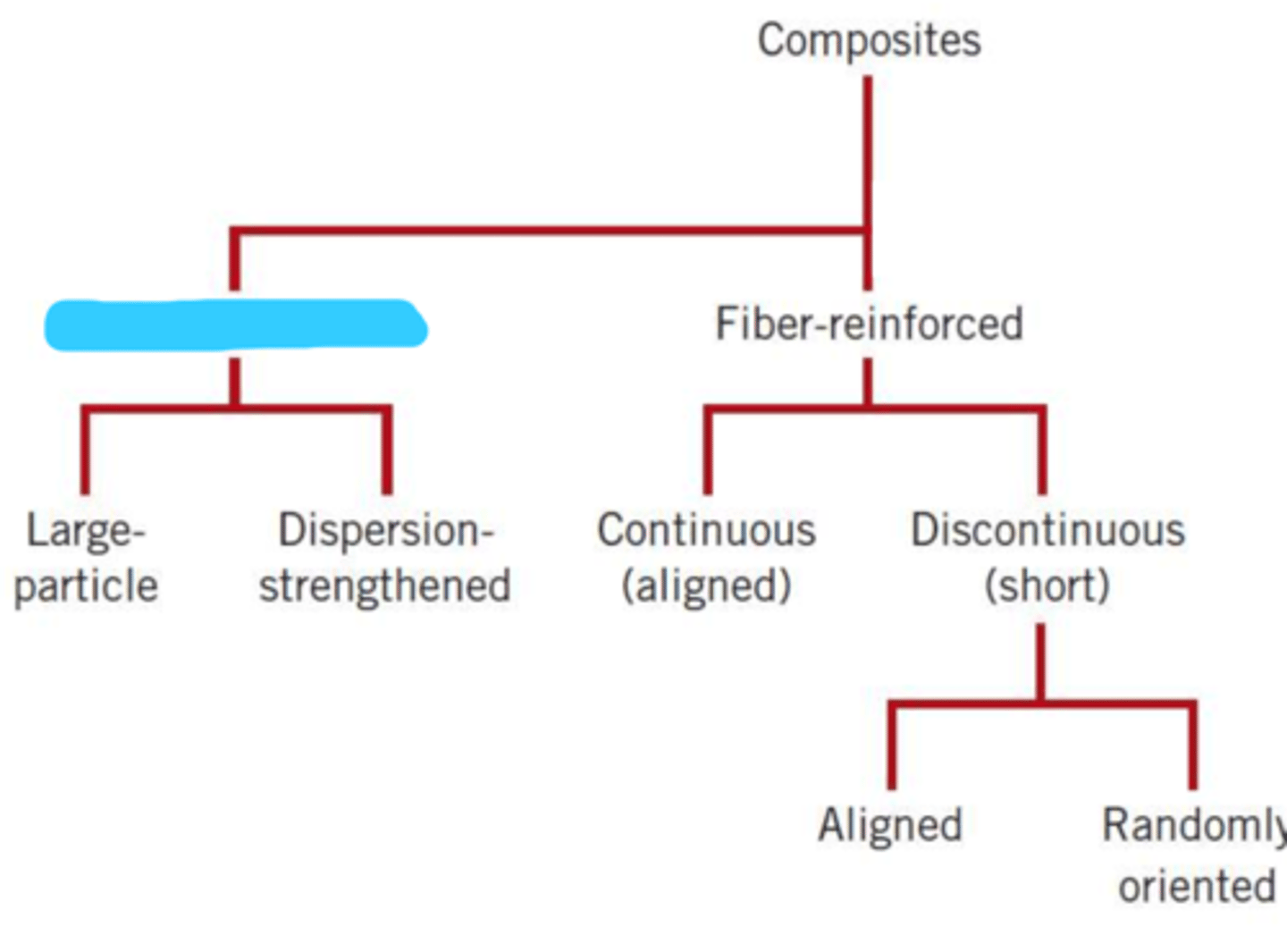
fiber-reinforced
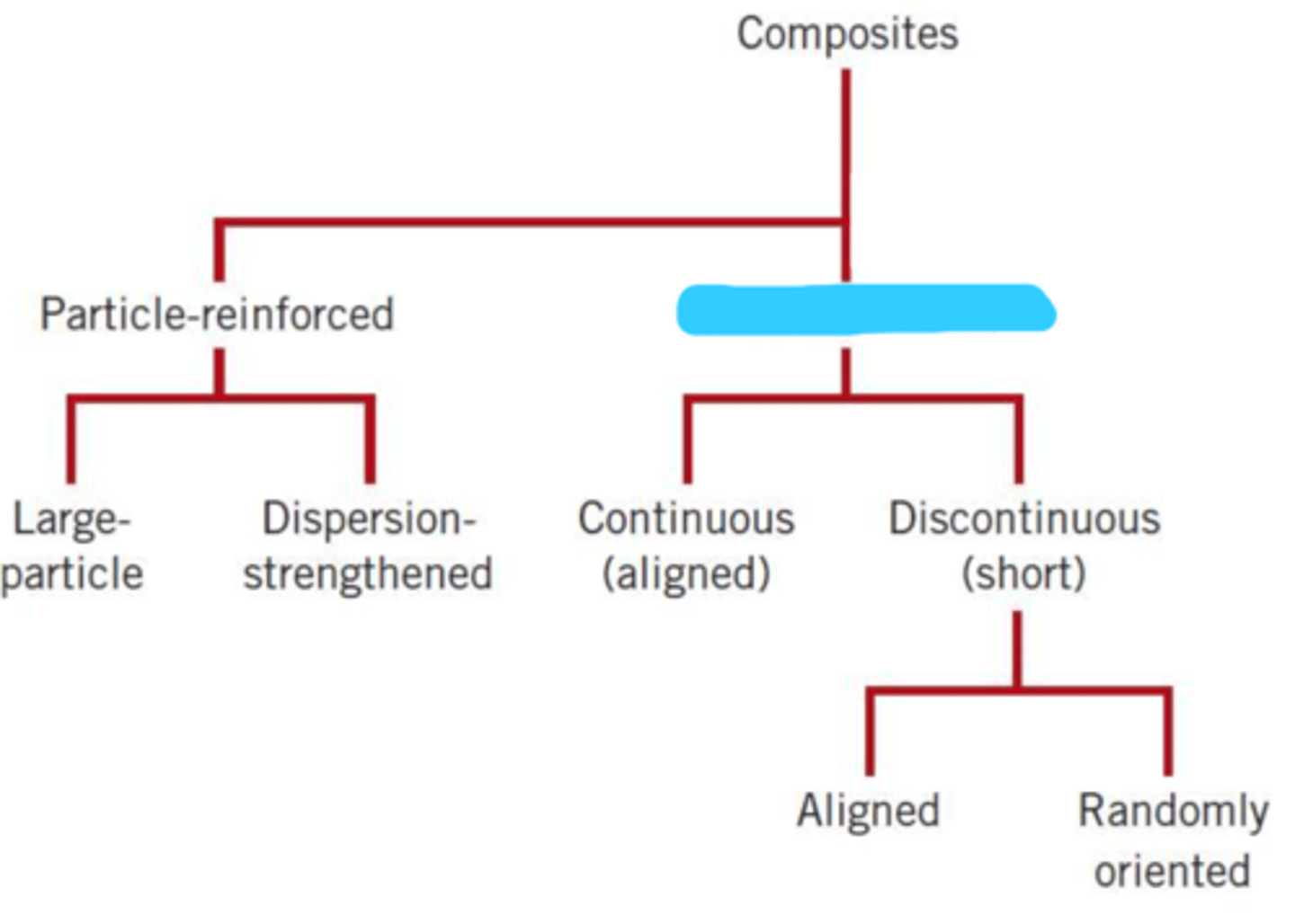
large particle
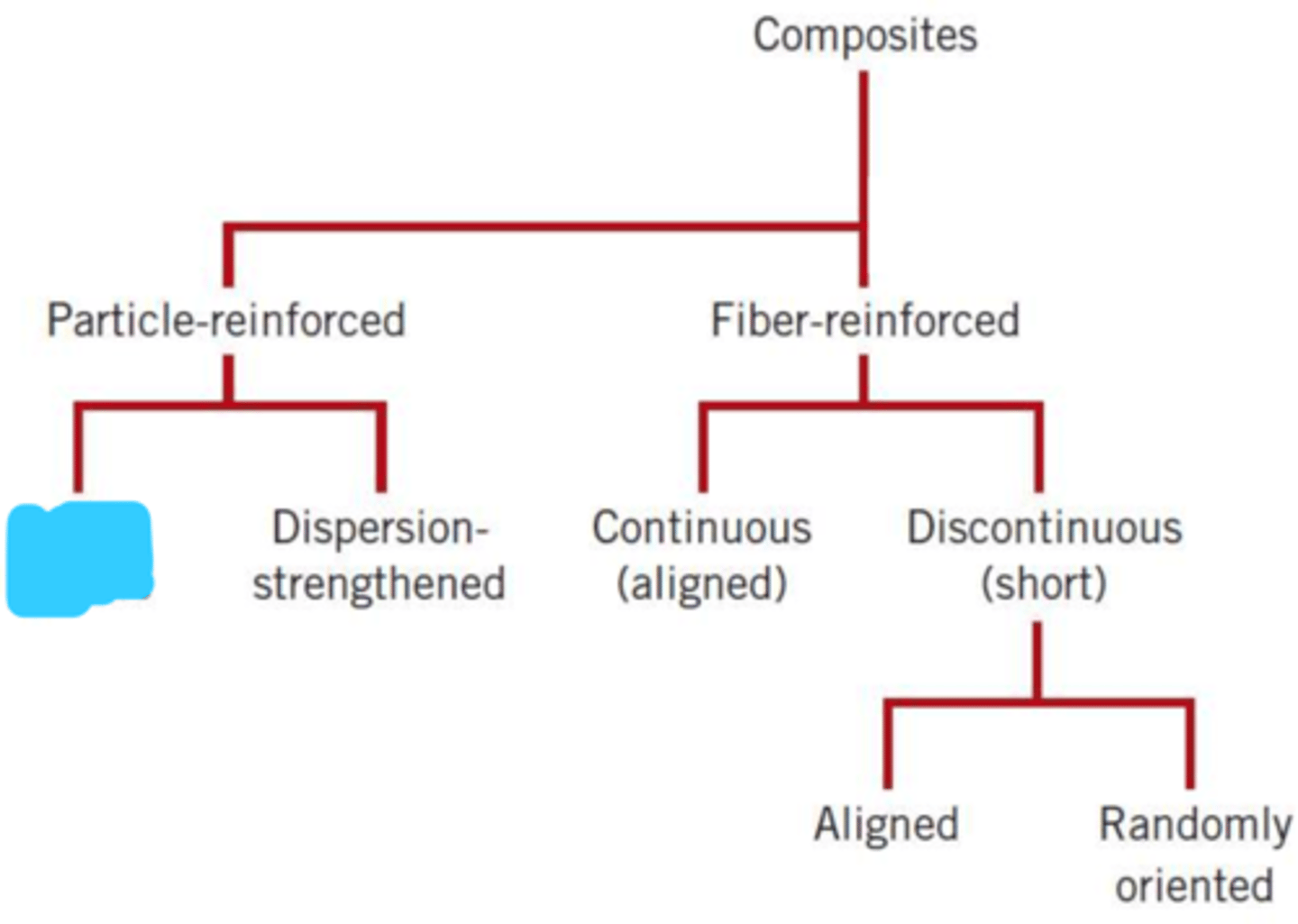
dispersion-strengthened
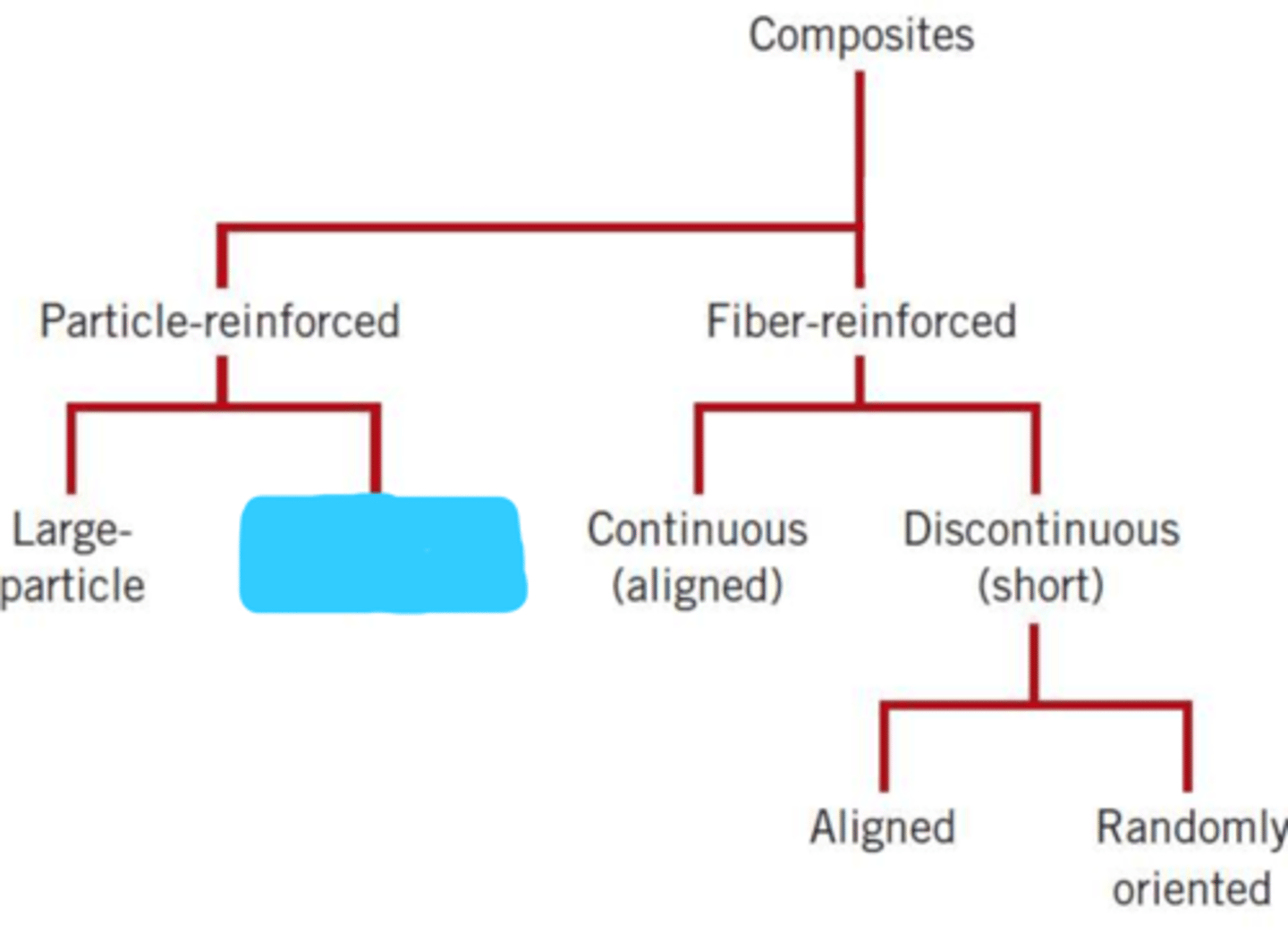
continuous (aligned)
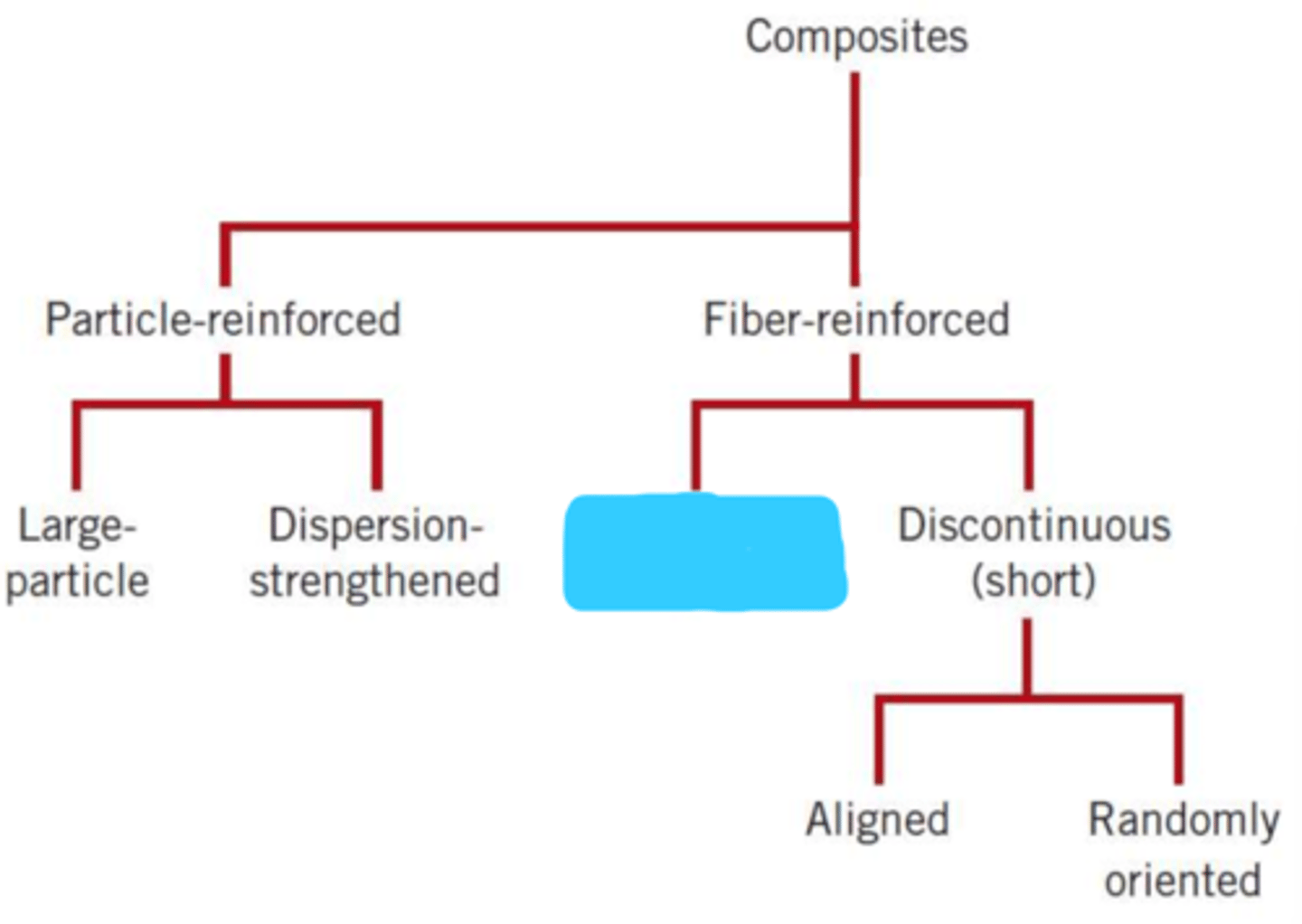
discontinuous (short)
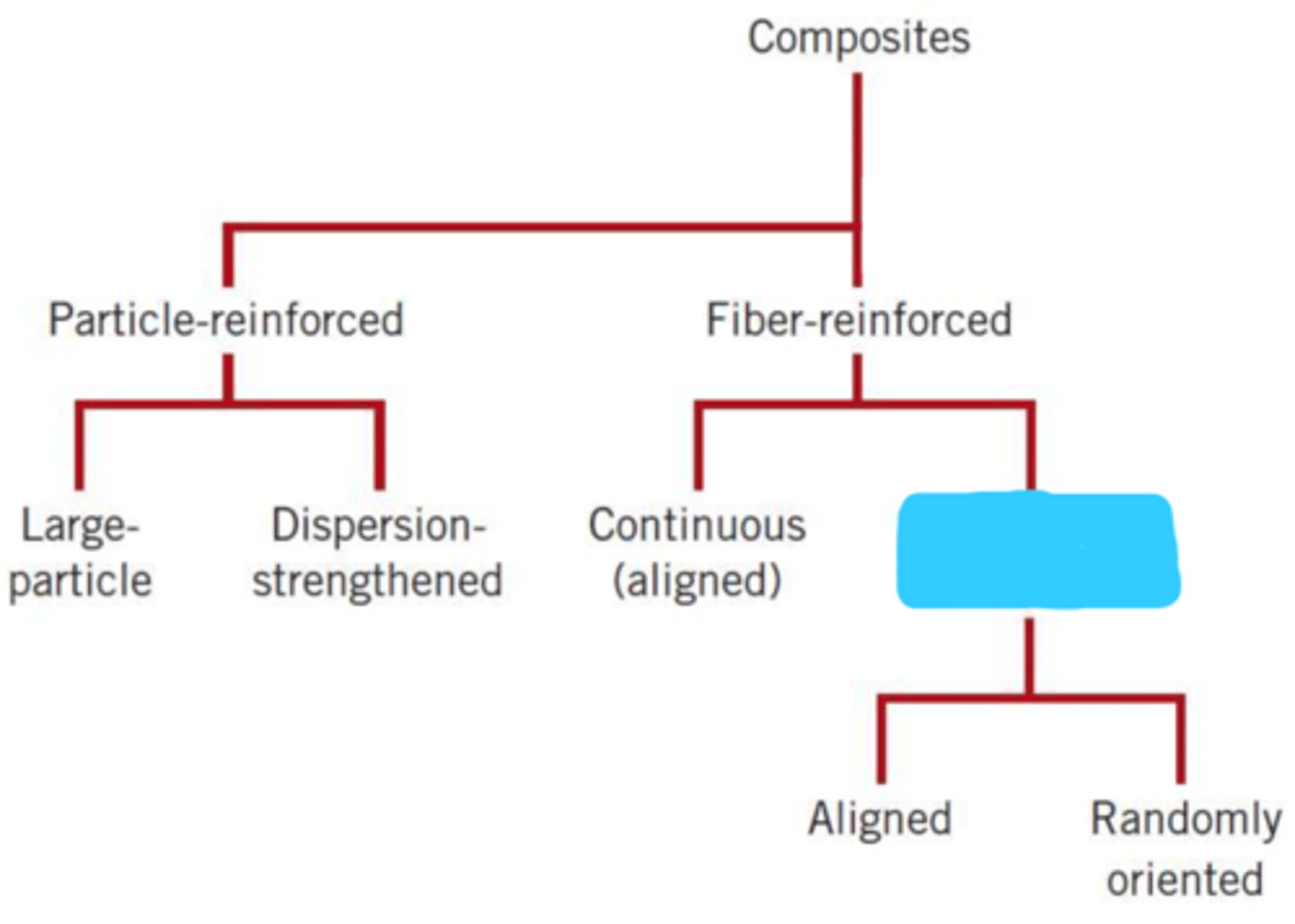
aligned
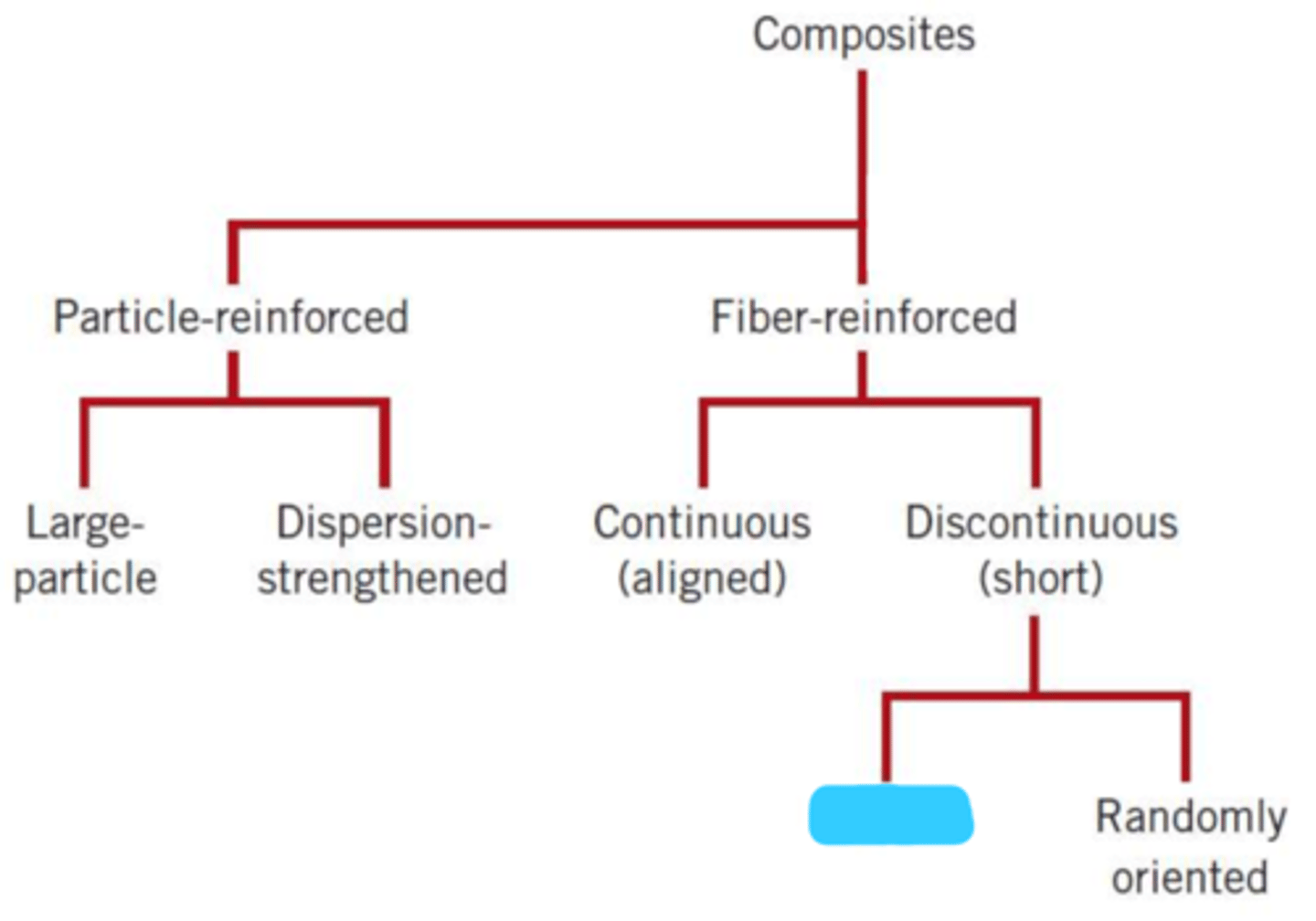
randomly oriented
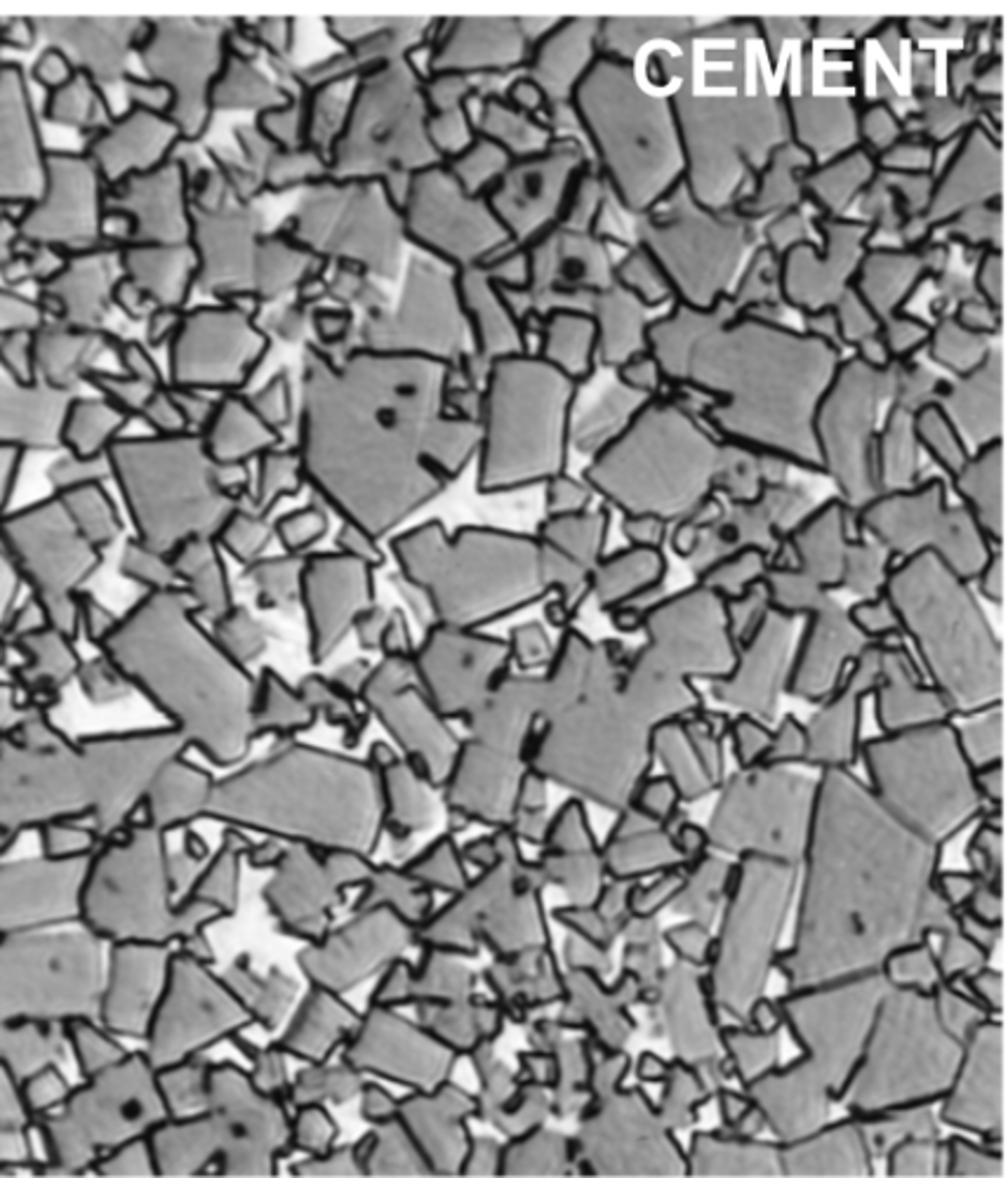
large particles
type of common particle configuration for composites?
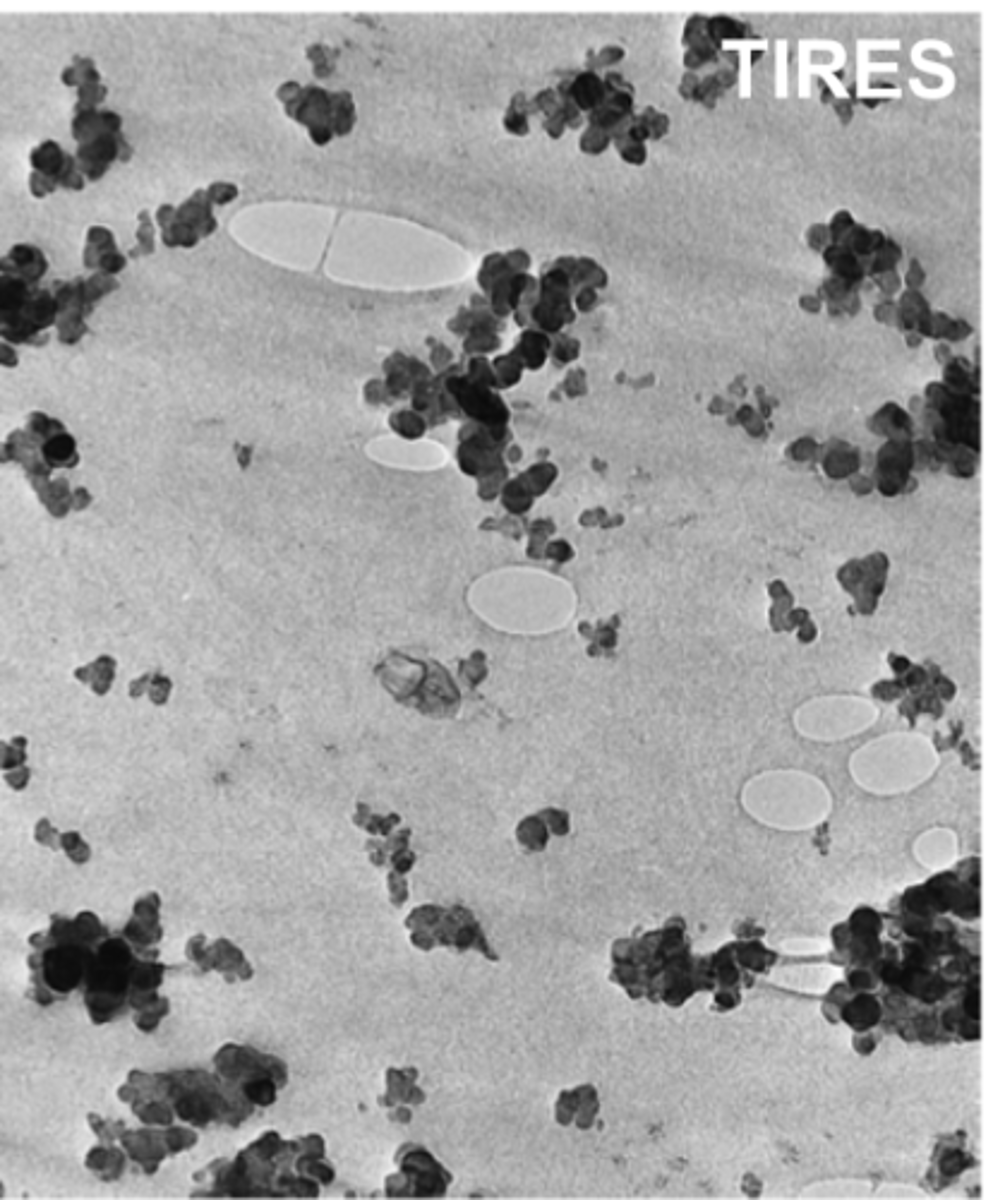
dispersion-strengthened
type of common particle configuration for composites?
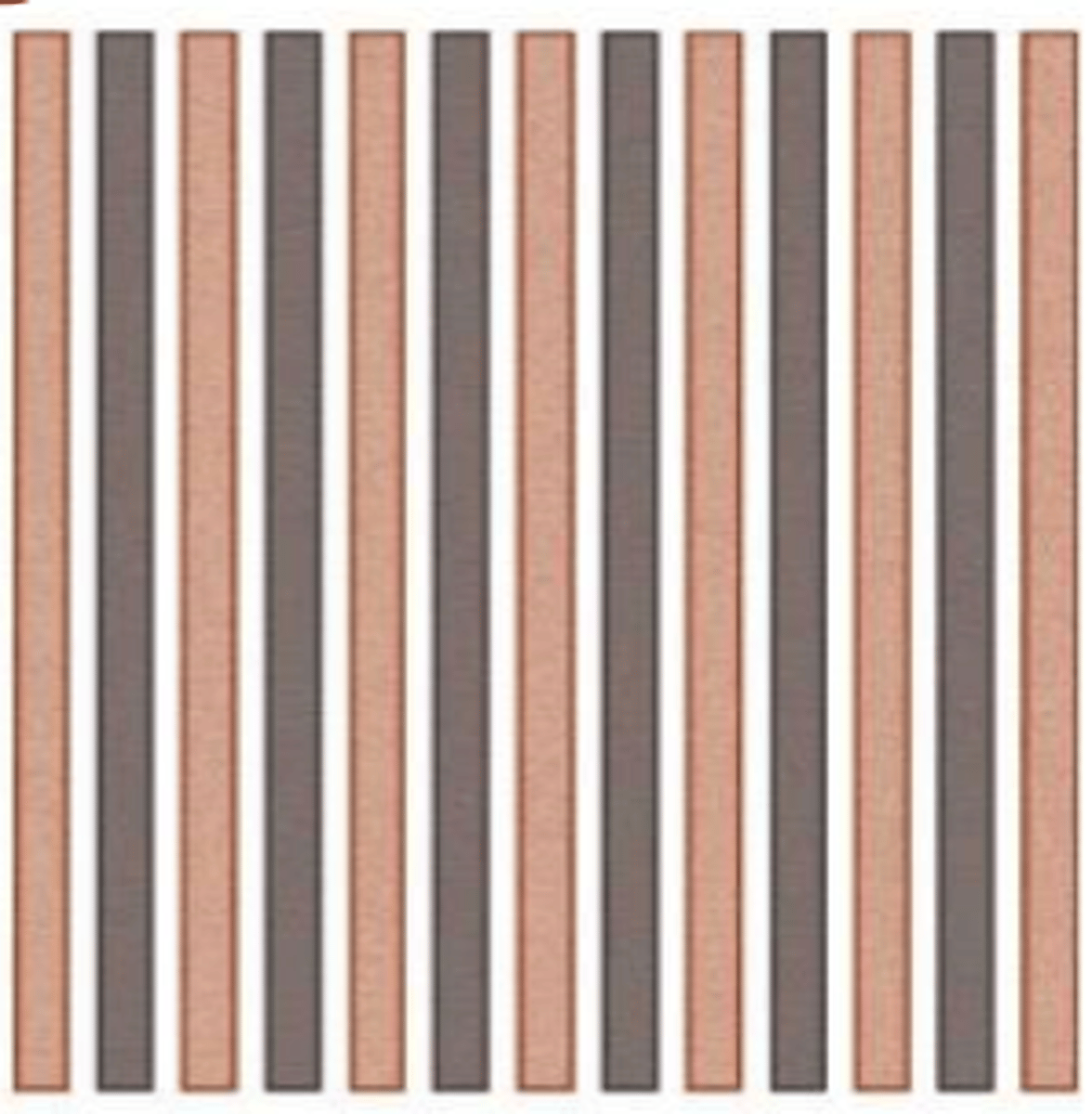
continuous and aligned
type of common fiber configurations for composites?
discontinuous and randomly oriented
type of common fiber configurations for composites?
discontinuous and aligned
type of common fiber configurations for composites?
polymeric
most biomedical composites have ______________ matrices
thermoplastic, bioabsorbable
polymeric matrices: mostly _______________ for ease of manufacturing, some ________________
synthetic non-absorbable
2 types of polymeric matrices: polysulfone, PEEK, UHMWPE, PTFE, PMMA, hydrogels
synthetic absorbable
2 types of polymeric matrices: Polyesters, PLA, PGA, PLGA, polydioxanone, poly(glycolide-co-trimethylene carbonate), poly)ethylene carbonate), poly(iminocarbonates), polycaprolactone, polyhydroxybutyrate, poly(amino acids) etc...
carbon fiber
reinforcing fibers: lightweight, flexible, high strength, high tensile strength, poor shear strength, tendon repair, bone scaffolding
polyamide (kevlar)
types of non-absorbable polymer reinforcing fibers: low density, light, high tensile strength, resist impact and abrasion, poor compressive strength
UHMWPE fibers
types of non-absorbable polymer reinforcing fibers: high strength, high modulus, light weight, high energy dissipation ability, resist abrasion and water absorption
UHMWPE fibers
types of non-absorbable polymer reinforcing fibers: low MP makes it difficult for fabrication, used in joint prostheses, dentistry, intervertebral disk prostheses
PET fibers
types of absorbable polymer reinforcing fibers: high tensile and compressive strength, resist abrasion and water absorption, vascular grafts, tendons, ligaments, intervertebral disks
PLA/PGA and PLGA fibers
types of absorbable polymer reinforcing fibers: sutures, ligaments, tendons, orthopedic applications
glass fibers
type of reinforcing fiber: used to reinforce plastic matrices to form structural composites and molding compounds
glass fibers
type of reinforcing fiber: high strength-to-weight ratio, good resistance to heat, cold, moisture and corrosion, good electrical insulation, used in dentistry
ceramics
material typically used as particulates in composites
tension, shear
ceramics in reinforcing particulates: most are weak and brittle in _________ and _________
compressive
ceramics in reinforcing particulates: enhances _______________ strength
reinforcing particulates
includes calcium phosphates, aluminum- and zinc-based phosphates, glass and glass-ceramics
constituent, distribution, interaction
general properties of a composite are strongly influenced by the properties of the _____________ materials, ______________, _______________
synergistic, volume
general properties of a composite may be: _______________, improve based on the _____________ fraction of constituent materials
average
due to the nature of composites, it is obvious that the properties must, in some way, represent an ____________ of the properties of the individual components
geometry
determining material properties of composites: the precise nature of the average is highly dependent on the microstructural _______________
parallel
3 idealized composite geometries: a direction ____________ to continuous fibers in a matrix
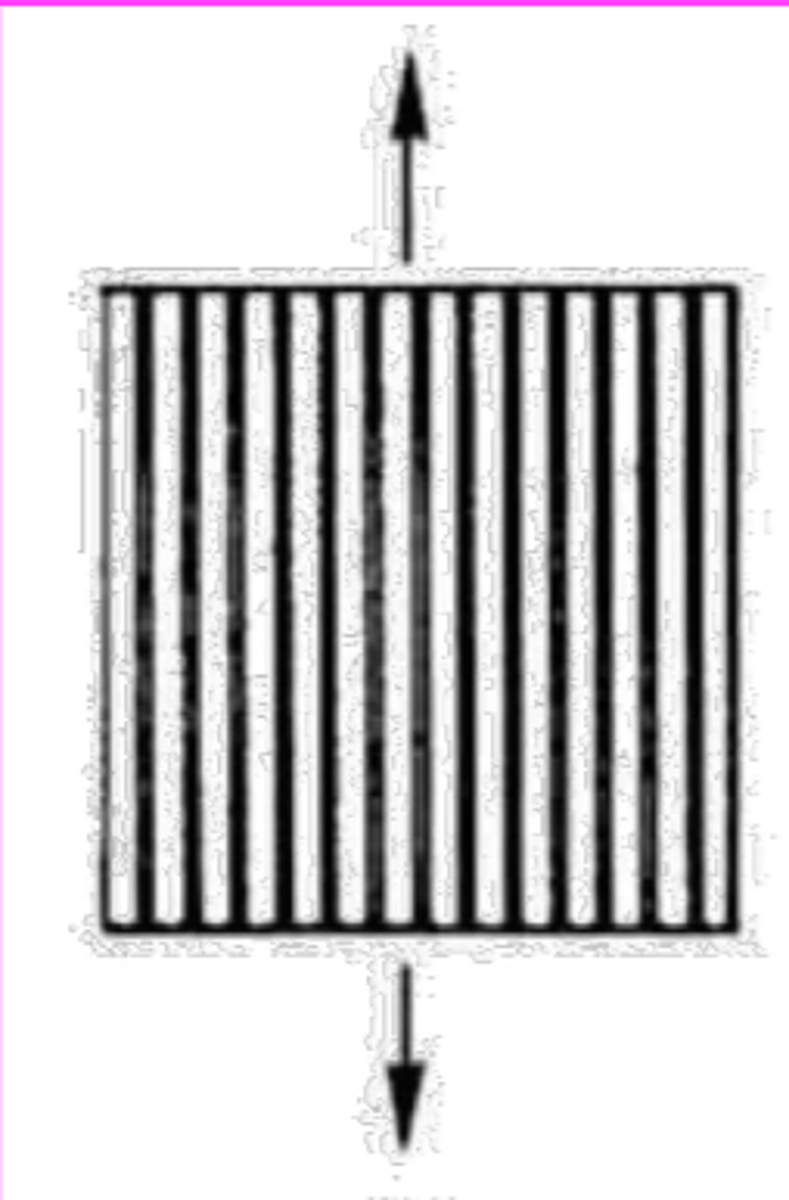
perpendicular
3 idealized composite geometries: a direction ____________ to continuous fibers in a matrix
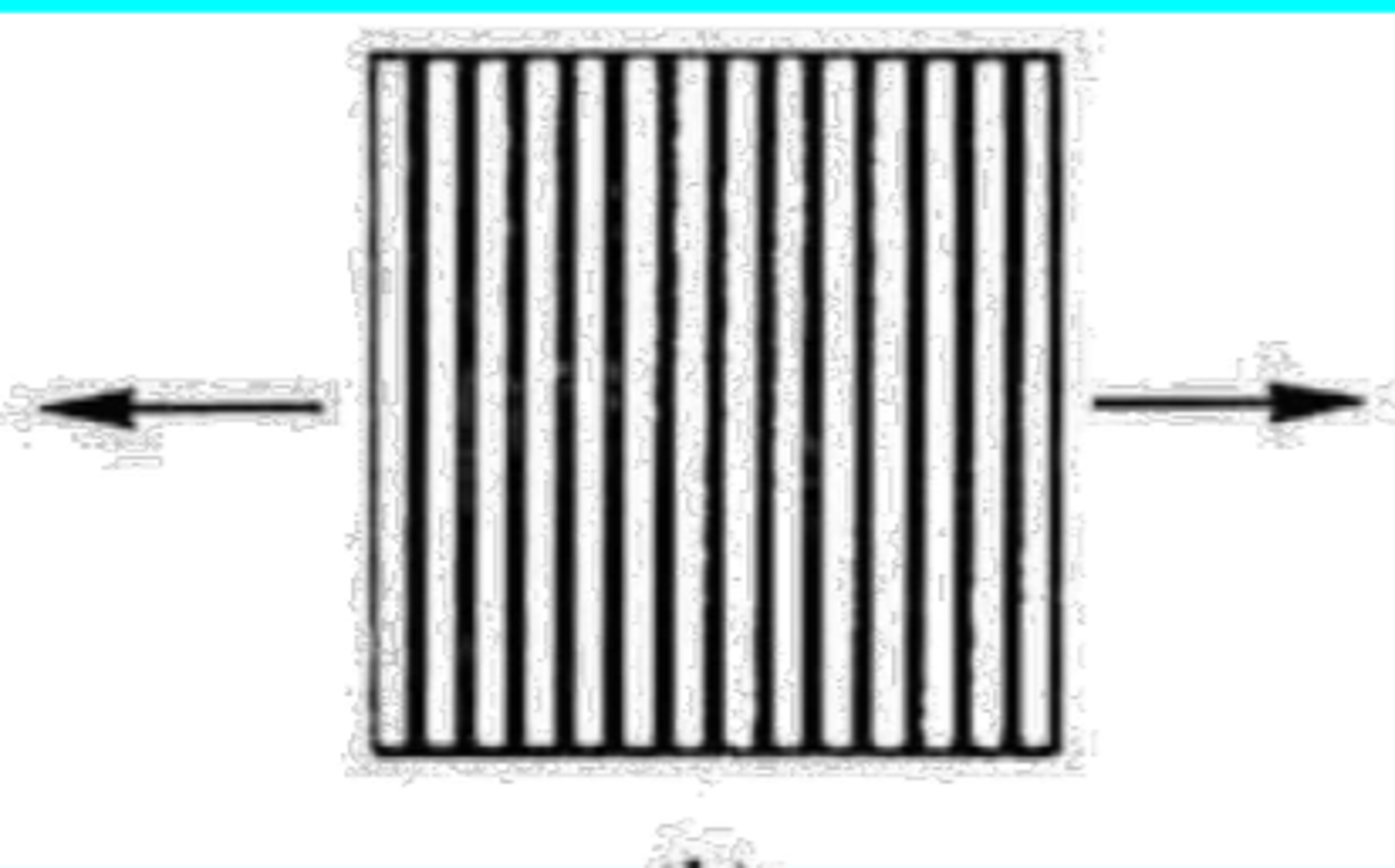
aggregate
3 idealized composite geometries: a direction relative to a uniformly dispersed _____________ composite
isostrain
unidirectional strain, loading parallel to reinforcing fibers
bonded
isostrain: assume the matrix is intimately ____________ w/ the reinforcing fibers
same
isostrain: the strain of both the matrix and the fibers must be the ________
different
isostrain: true even though the E's of each component will tend to be ____________
fibers
red
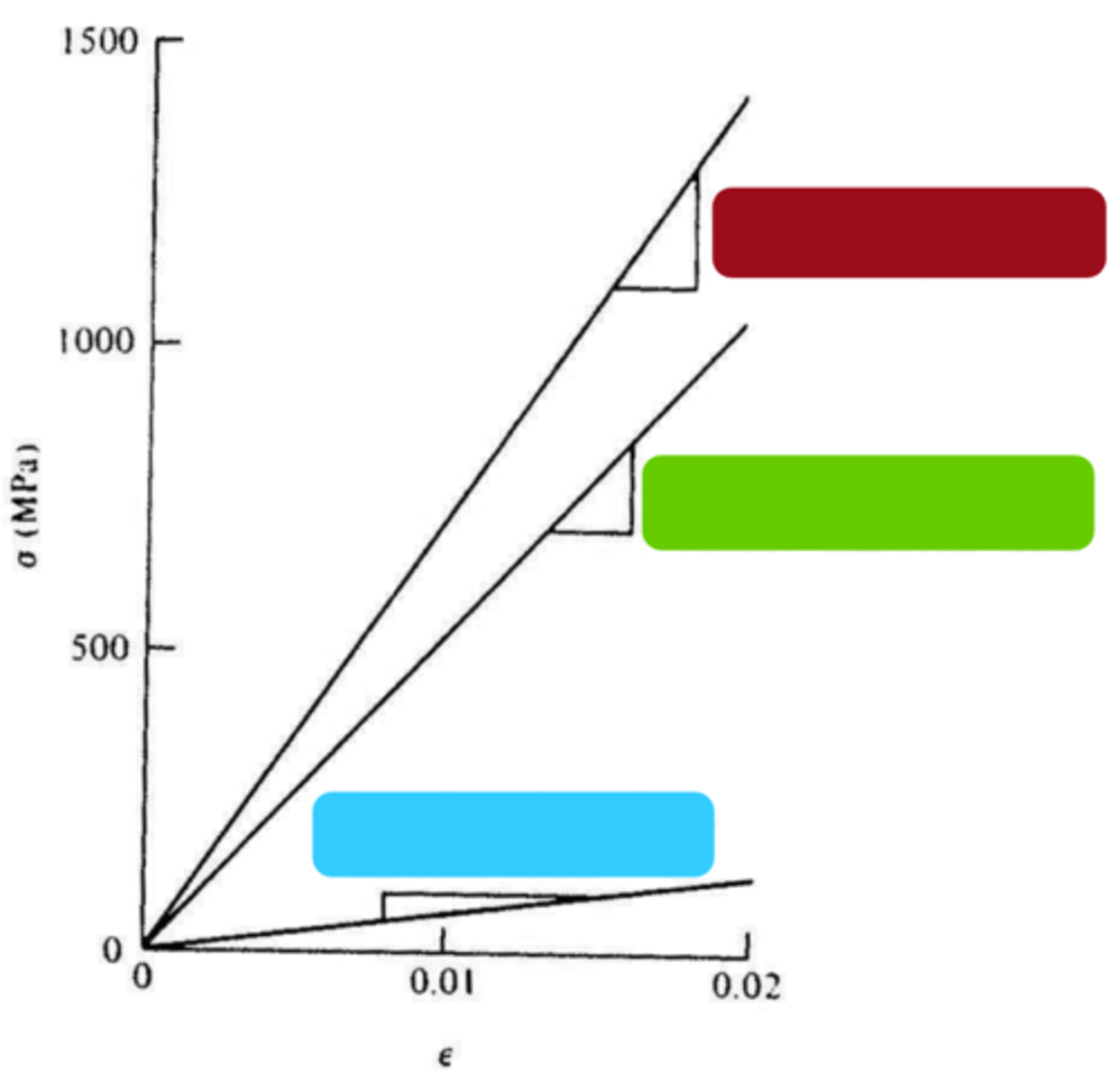
composite
green
matrix
blue
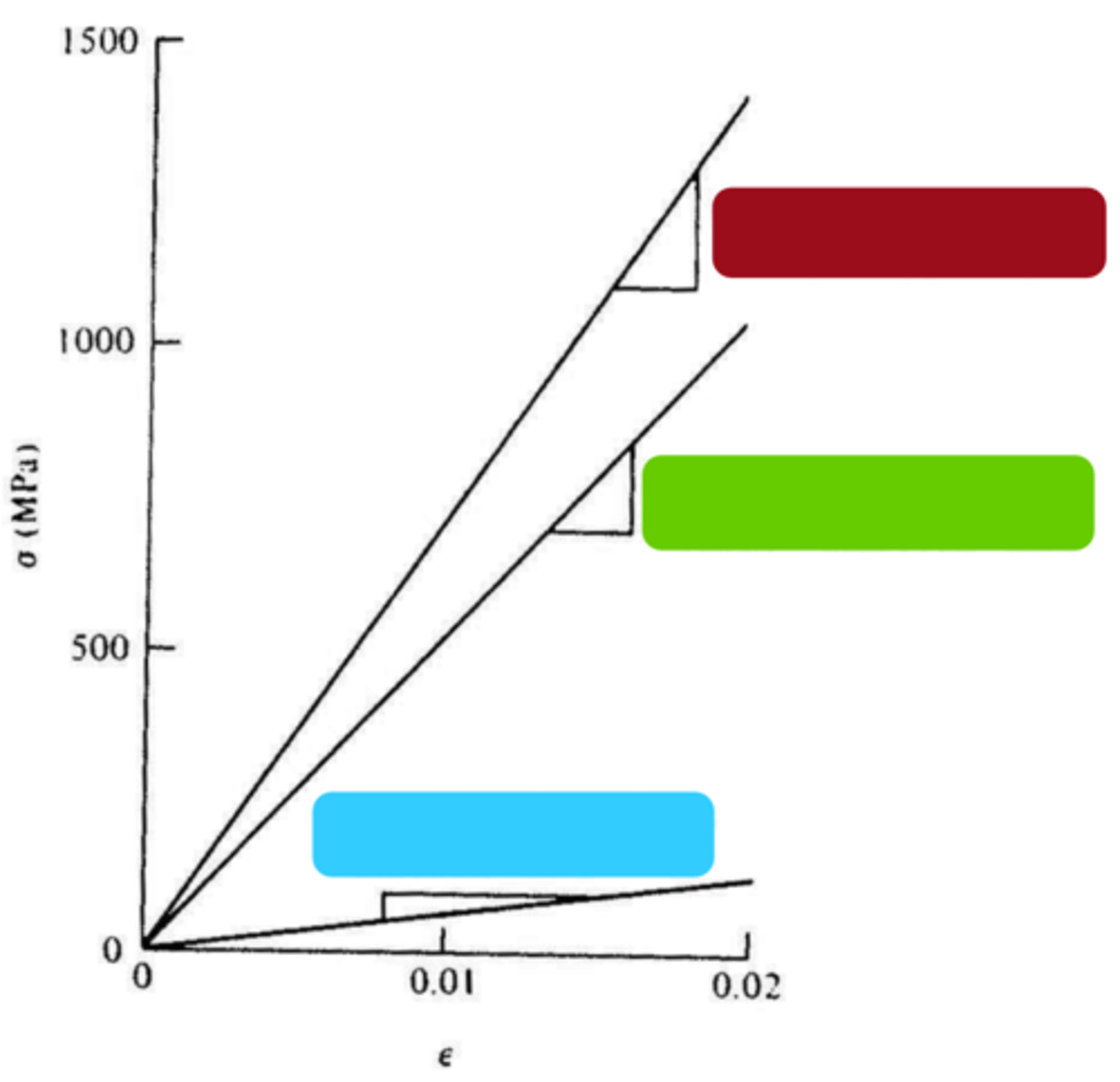
isostress
loading perpendicular to the reinforcing fibers
sum
isostress: the total elongation of the composites in the direction of stress application is the ______ of the elongations of matric and fiber components
isostress
green
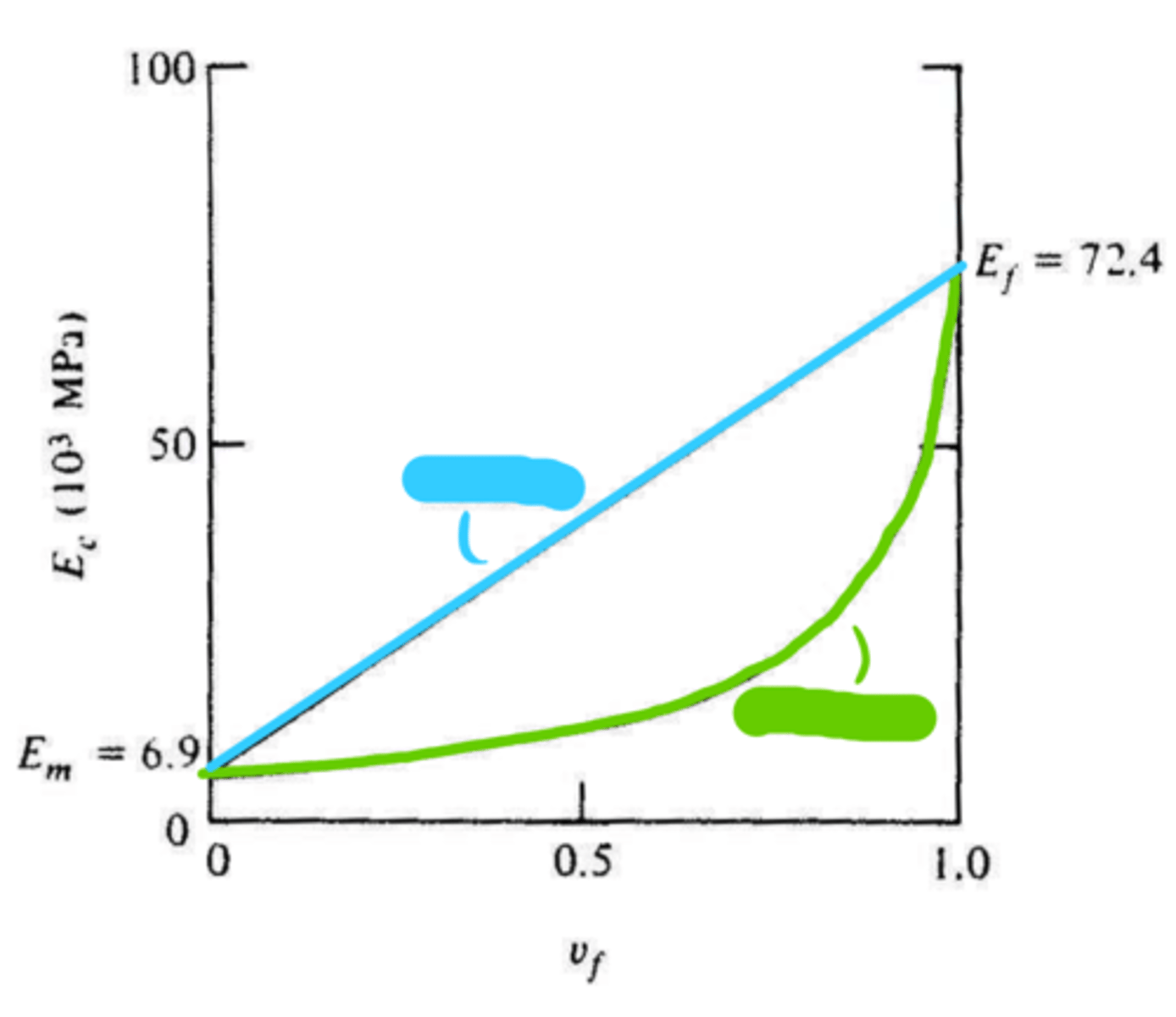
isostrain
blue
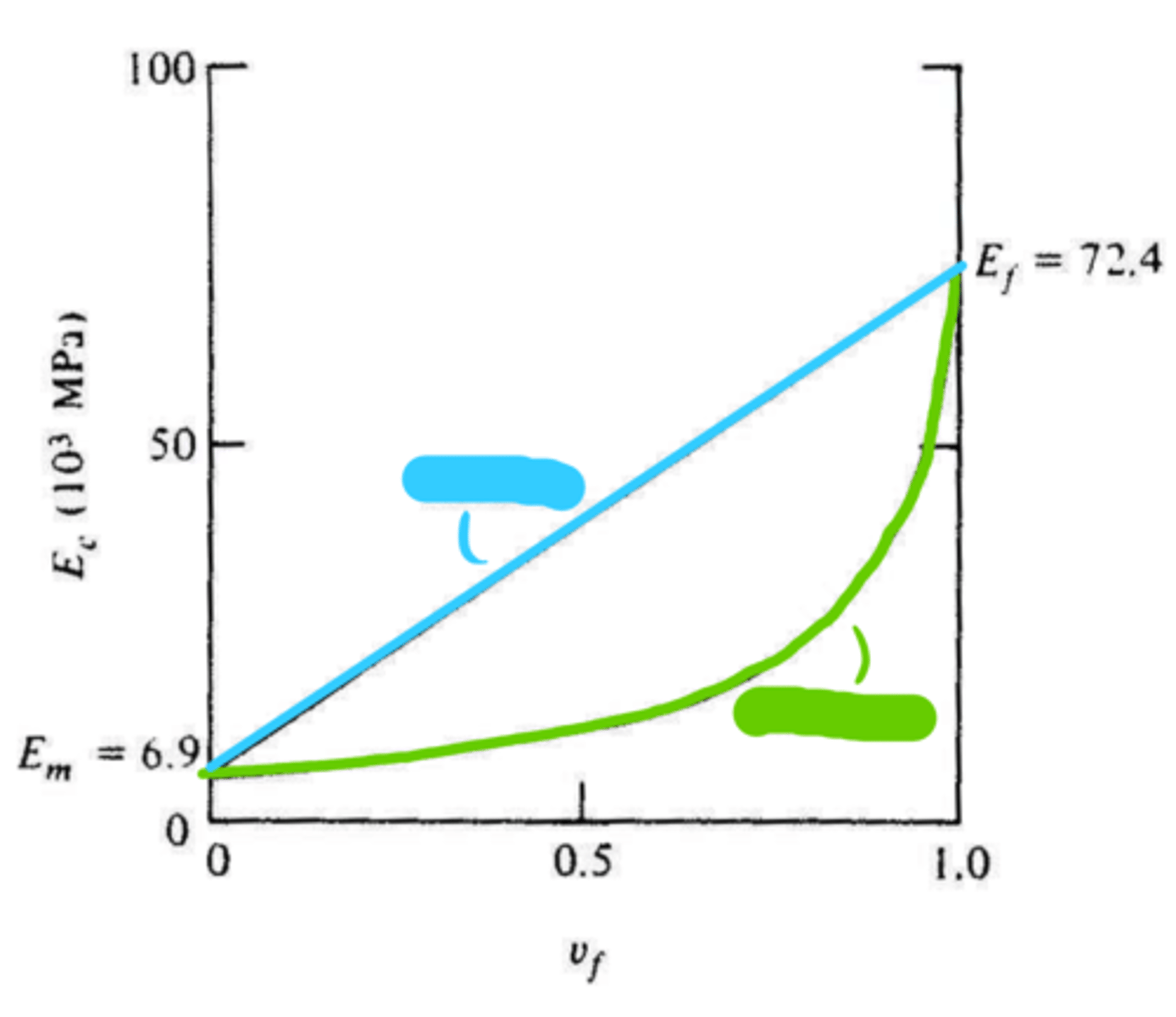
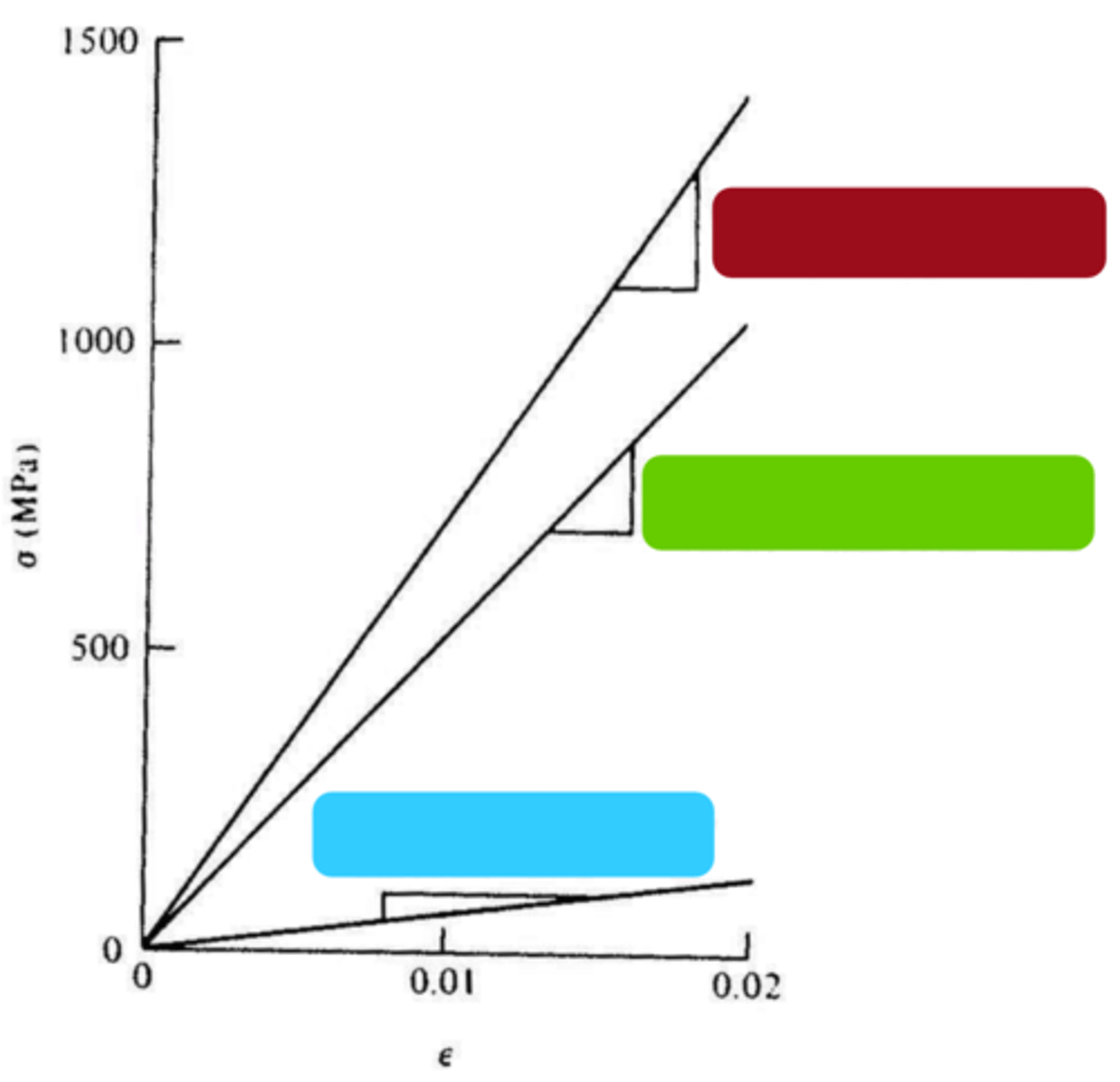
bounds
isostress and isostrain serve as upper and lower __________ for particulate composites
n=1
blue
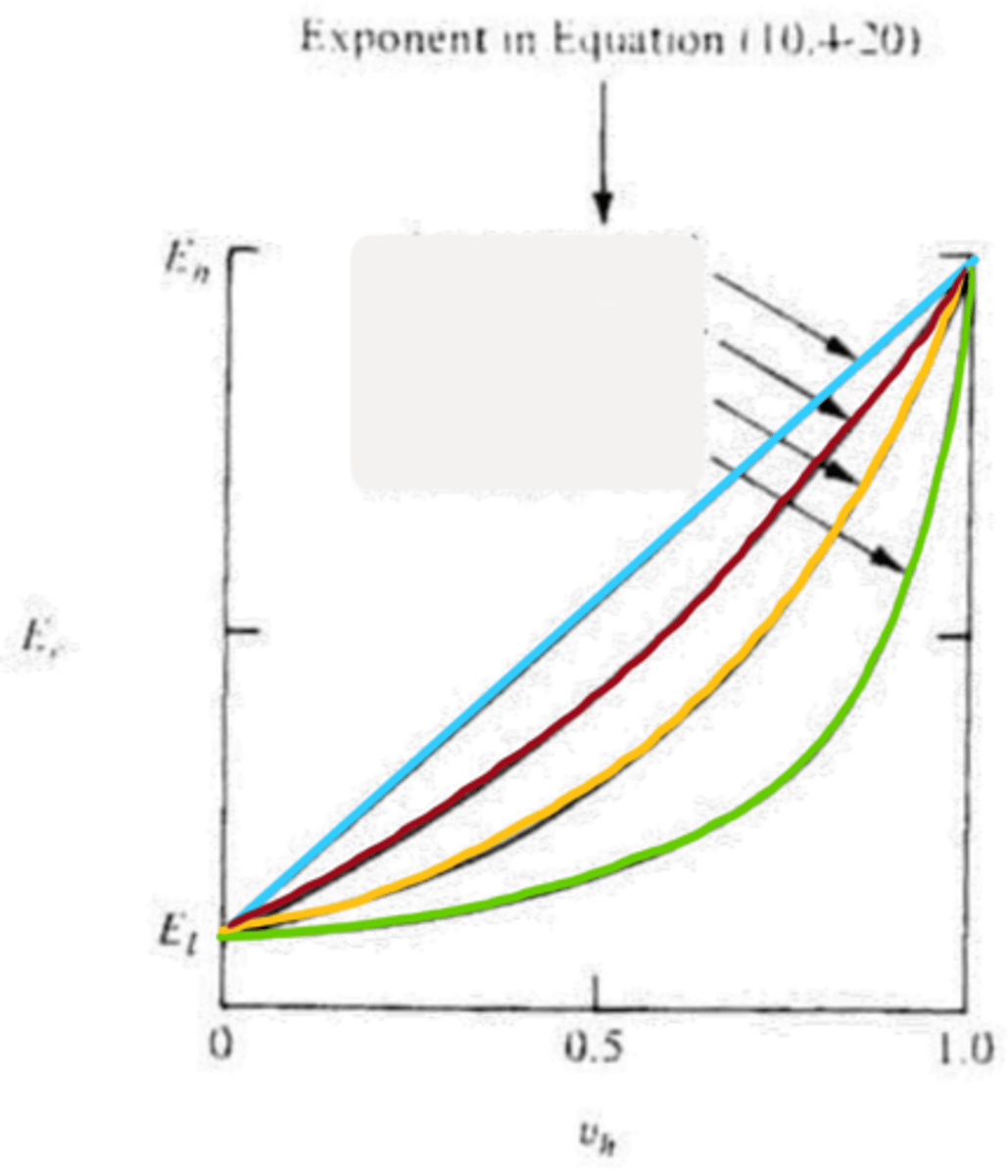
n=-1
green
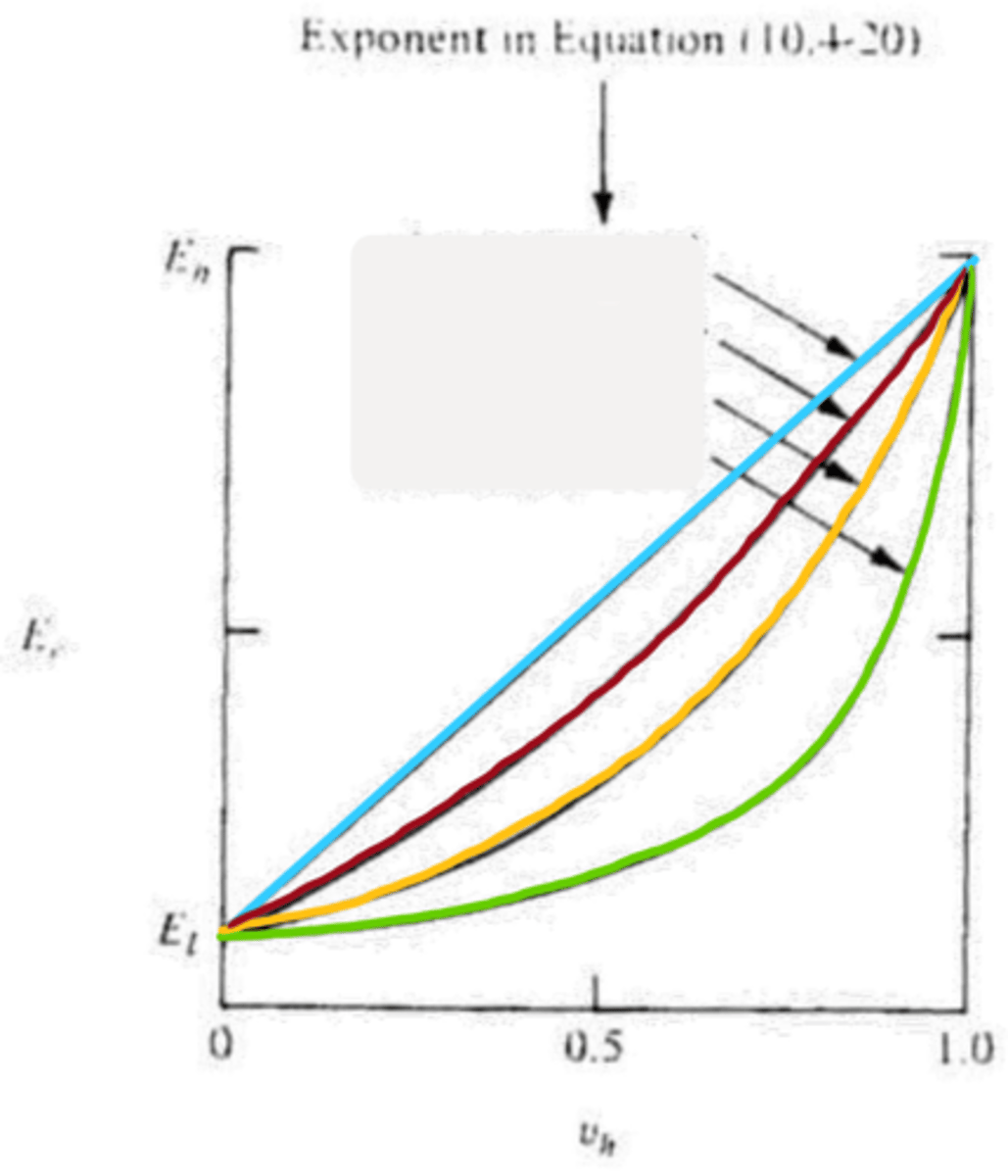
n=1/2
red
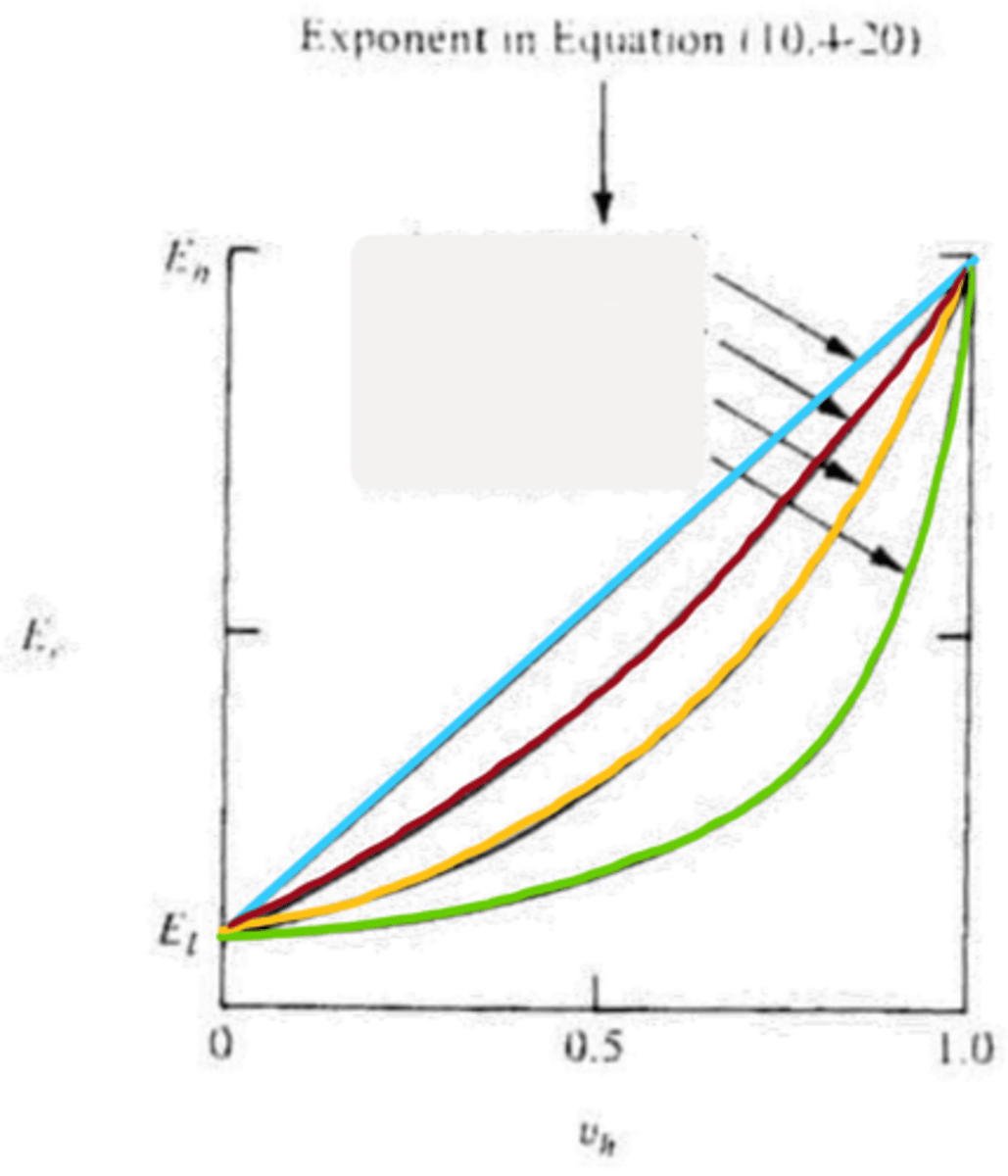
n=0
yellow
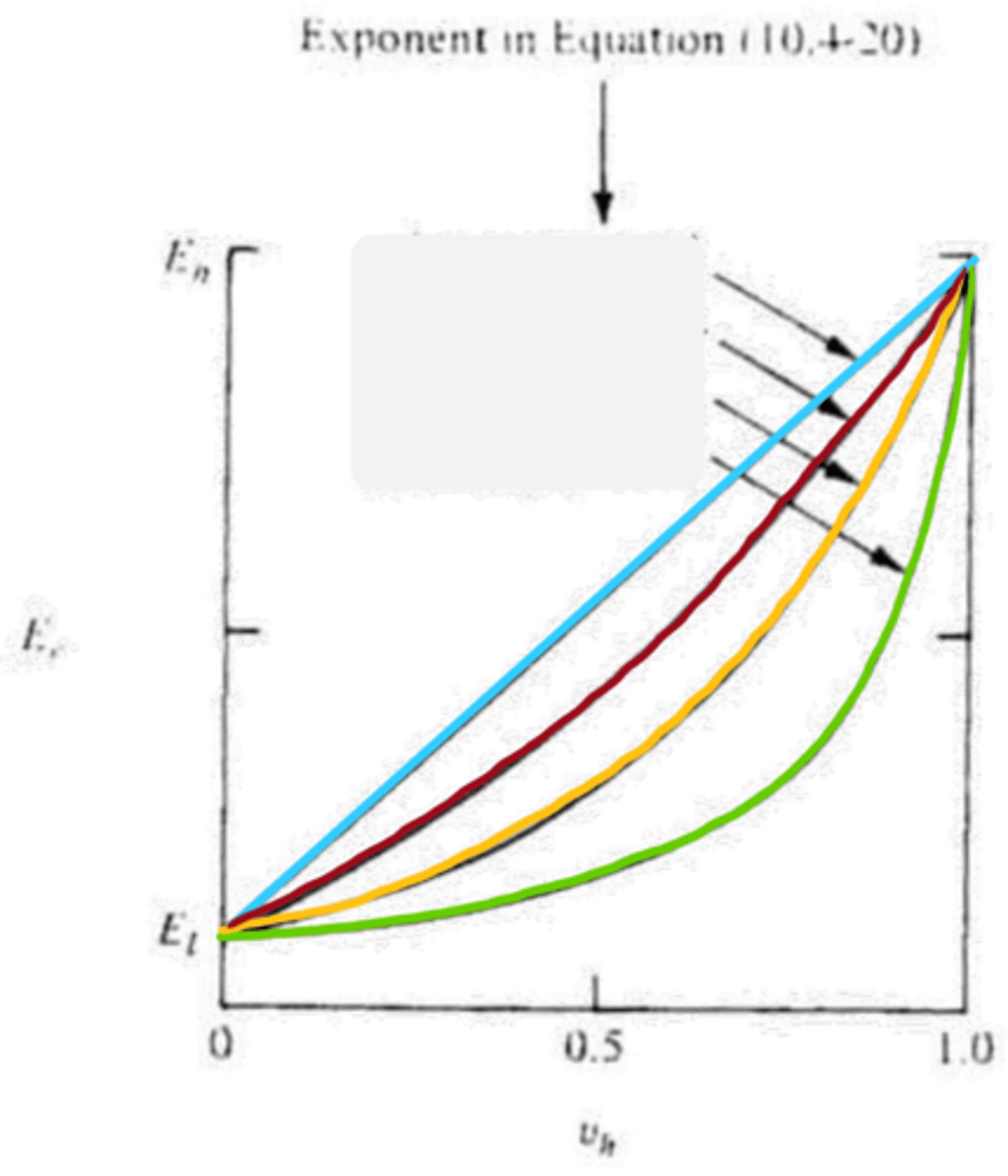
higher, lower
n=0: __________ modulus aggregate in a _________ modulus matrix
lower, higher
n=1/2: __________ modulus aggregate in a _________ modulus matrix
bonded
the equations developed for different types of composite materials assumed that the matrix is intimately ___________ w/ the reinforcing fibers
transmit
the interface between the matrix and discontinuous phase must be strong enough to ____________ the stress or strain due to a mechanical load from one phase to the other
communicate
interfacial strength: w/o this strength, the dispersed phase can fail to "________________" w/ the matrix
slipping out
interfacial strength: if matrix and fibers don't "communicate" this could lead to the reinforcing fibers ____________ ______ of the matrix
smooth
poorly bonded: __________ surface of the fibers indicated failure of the matrix to tightly bond to the fiber
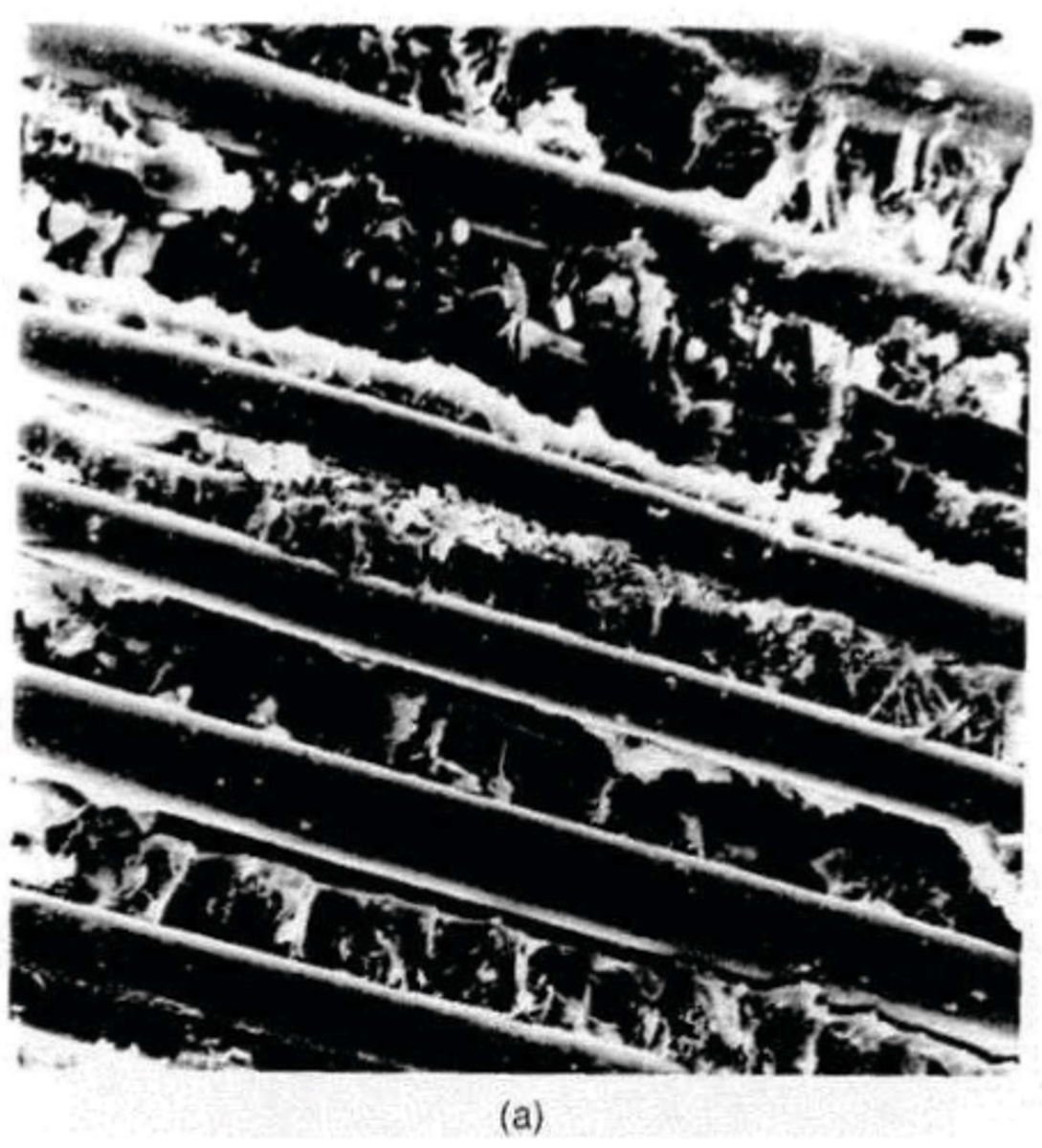

rough
well bonded: ___________ surface of the fibers and matrix indicated an integrated tight bond between matrix and fiber
2
composites are made up of _____ phases
continuous, discontinuous/dispersed
2 phases of composites?
structural, direction
composites material responses can be predicted based on: ____________ and material make up and __________ of applied load