Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 4
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
solution
Homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
solvent vs solute
solvent - greatest quantity
solute - smaller quantity, gets dissolved
When is a solution aqueous
the solvent is water
Is pure water conductive
no
electrolyte
A substance that creates aqueous solutions that contains ions. It dissociates into Ion in the solution
nonelectrolyte
A substance that creates aqueous solutions that does not contain ions. It does not break up into ions
which types of compounds create electrolytes/nonelectrolytes
Ionic compounds - electrolytes
molecular compounds - nonelectrolyes
dissociate
the act of a compound breaking apart into ions during the act of dissolving
Why is H2O good for dissolving (thus dissociating) ionic compounds
It's partial charges
H ions are partial positive
O ion is partial negative
solvation/ solvated state
solvation is an interaction of a solute with the solvent, which leads to stabilization of the solute species in the solution. One may also refer to the solvated state, whereby an ion in a solution is surrounded or complexed by solvent molecules
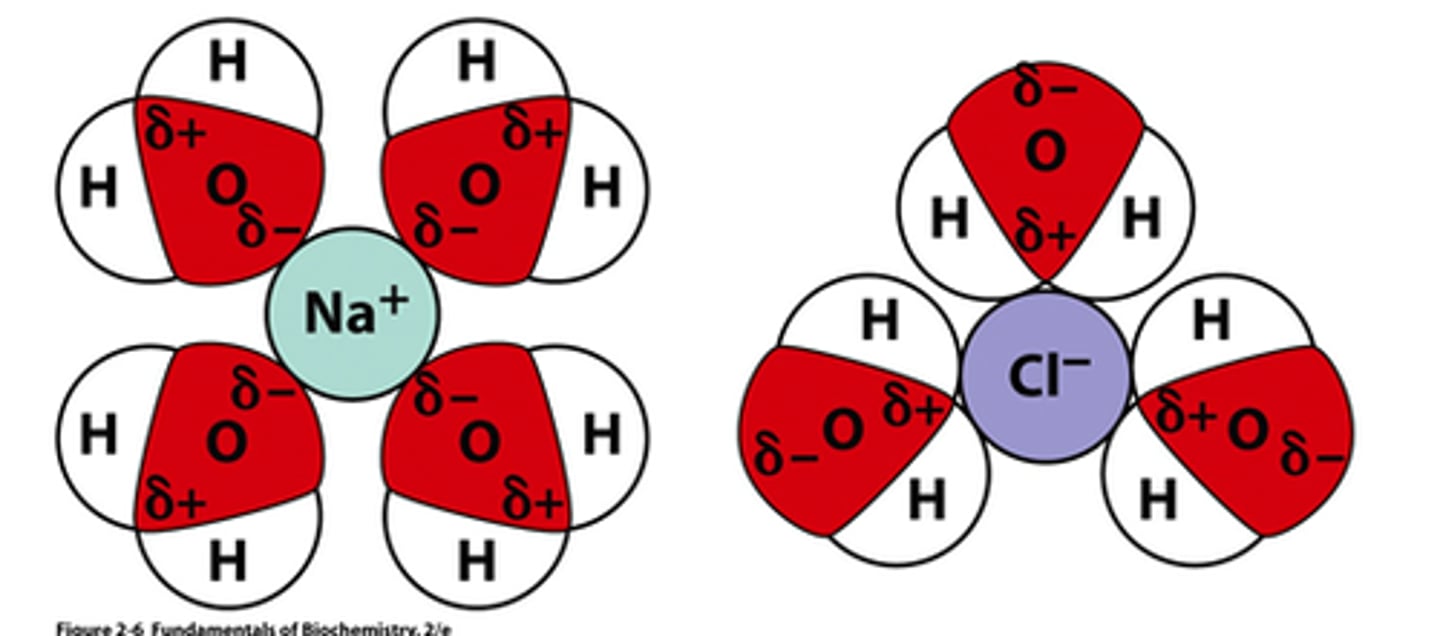
What kinds of molecular compounds dissolved into ions
acids
ionize
convert (an atom, molecule, or substance) into an ion or ions, typically by removing one or more electrons
Strong electrolytes vs weak electrolyets
strong - exist almost completely as ions in aqueous solutions. All water soluble ionic compounds, few molecular compounds
weak - exist mostly in the form of neutral molecules in aqueous solutions and only a small fraction dissociates into ions
solubility
the amount to which a substance will dissolve at a given temperature
How to write the equation for an ionizing reaction (weak electrolytes)
The two arrows mean the reaction is happening in both directions. As AH dissociates A+ and H+ recombine to become AH again.
This achieves chemical equalibrium
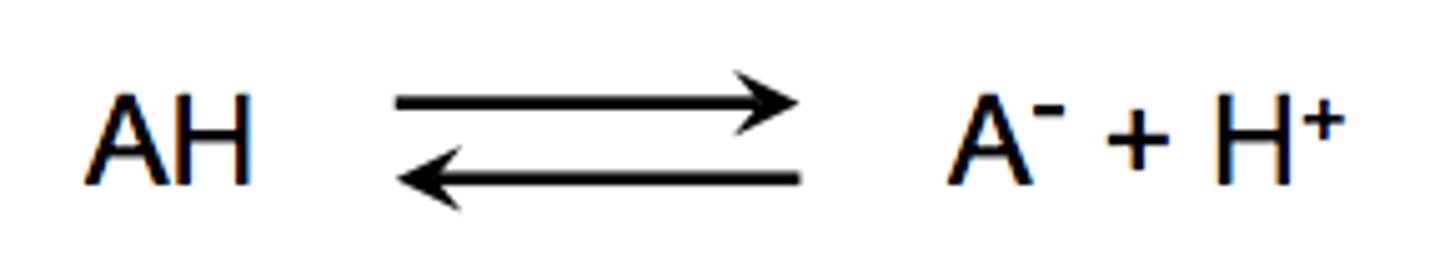
chemical equalibrium
number of each type of ion/molecule in a solution is constant
How to determine if a compound is an ionic compound
The presence of both metals and nonmetals
except if an ion contains NH4+
precipitation reaction
when a reaction in a liquid solution creates a solid
charged ions attract each other so strongly the create an insoluble solid
precipitate
the solid formed by the precipitation reaction.
are double displacement (metathesis) reactions redox reactions?
Not a redox reaction
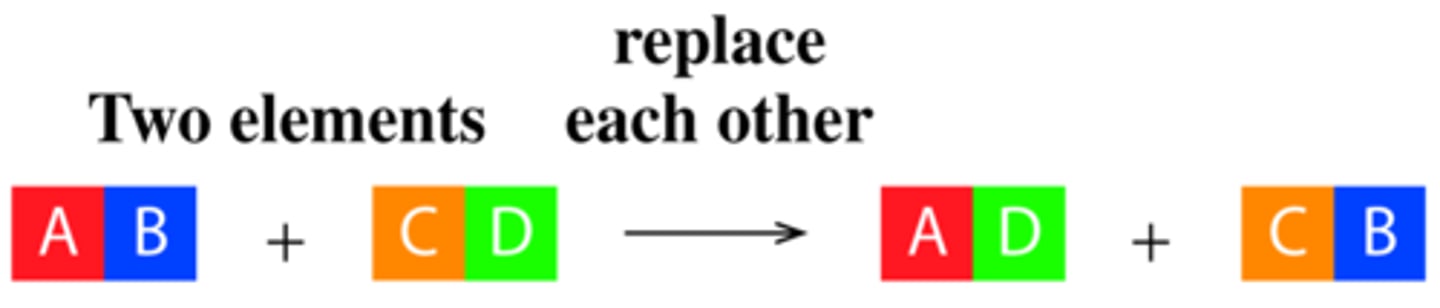
double displacement reaction
1. use the chemical formulas of the reactants to figure out which ions are present
2. write the chemical formulas of the products by combining the cation from one reaction with the anion of the other. Us the charges to determine the subscripts
3. check the solubilities. If one is insoluble it is a precipitation reaction
4. Balance the Equation
molecular equation
Does not show ionic character
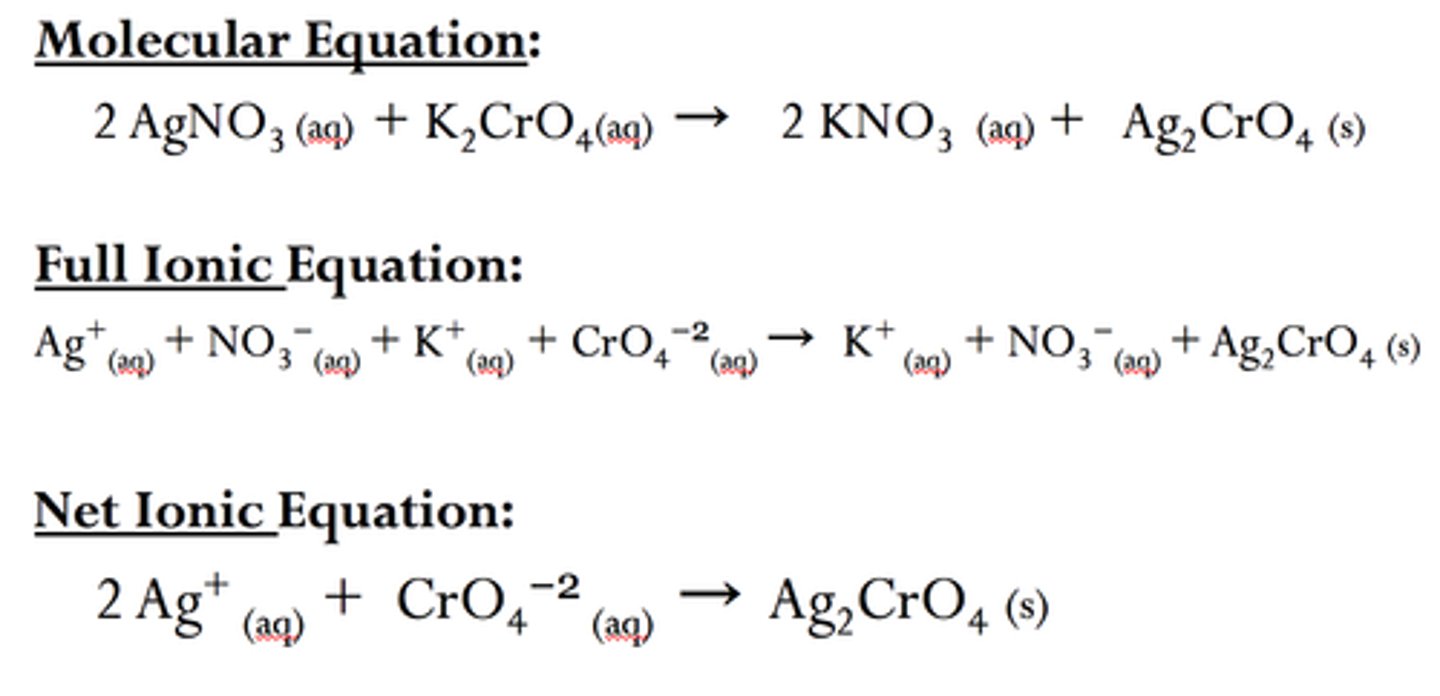
complete ionic equation
for double displacement reaction
shows ionic character
all soluble strong ions have their charges shown
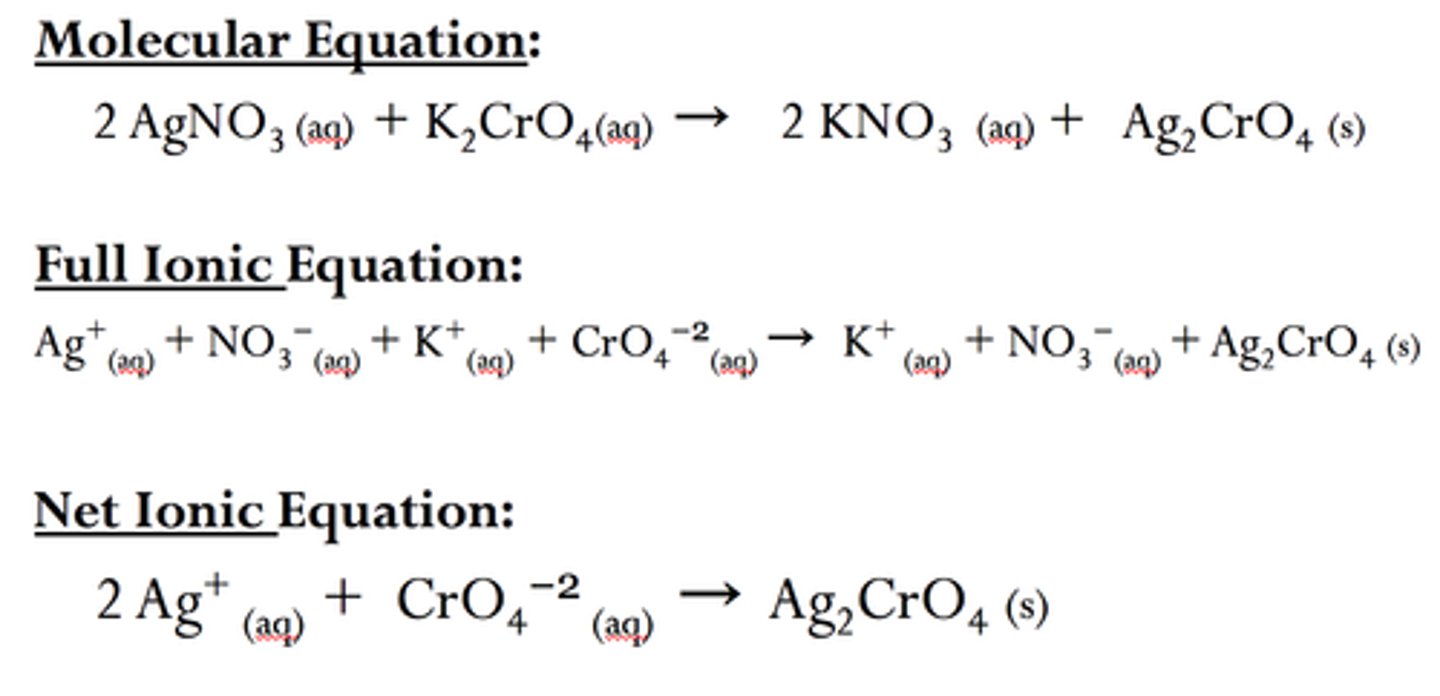
spectator ions
An ion that exists in the same form on both the reactant and product sides of a chemical reaction. Thus it has no direct role in the reaction
define net ionic equation
the equation consisting only of elements directly involved in the reaction
to form:
cross out anythin that doesn't change from left to right side
What remains is your equation
If every ion in an ionic equation is a spectator...
No reaction happens
What compounds are strong electrolyts
all ionic compounds, strong acids
What compounds are weak electrolytes
weak acids, weak bases
What compounds are nonelectrolytes
anything that is not an ionic compound, weak acids, or weak bases
Strong acids
HClO₄
HClO₃
H2SO₄
HNO₃
HCl
HBr
HI
-ic acids are strong
-ous acids are weak
Strong bases
LiOH
NaOH
KOH
RbOH
CsOH
Ca(OH)2
Sr(OH)2
Ba(OH)2
Group A1
Group 2A
acids
Ionize in aqueous solutions to form H+(aq), hydrogen ions
Hydrogen ions are essentially protons
hydrogen ions
just a proton (Hydrogen is just 1 proton and 1 electron)
Monoprotic vs diprotic
monoprotic - acid that yields 1 H+ ion
diprotic - acid that yields 2 H+ ions
base
substances that accept and react with H+ and produce OH- hydroxide ions when they dissolve
A base does not have to have OH in it because it can often accept the O from the soultion
Substance that consumes H+
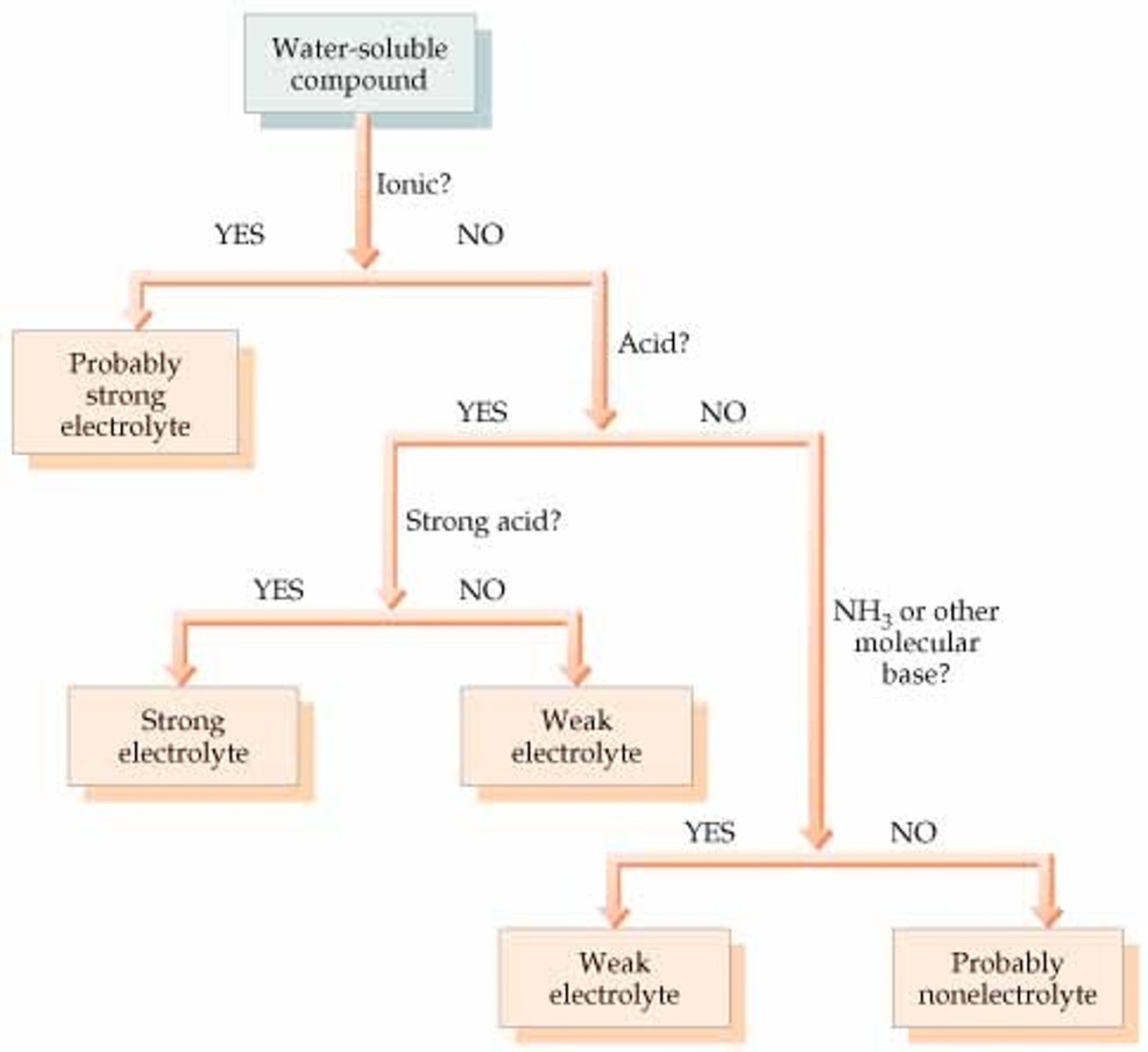
How to find out if a substance is a strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or a nonelectrolyte
neutralization action
when an acid and a base is mixed.
The products do not have any of the characteristics of the reactants
What do neutralization reactions between metal hydroxides and acids produce?
salts and water
salt
any ionic compound whose cation comes from a base and it's anion comes from an acid
Oxidation reduction reactions
electrons are transferred from one reactant to another
corrosion (redox reaction)
The conversion of a metal to a metal compound by a reaction betweeen the metal and some substance in it's enviornment
i.e. the metals ions loose an election, becoming cat ions, and combines with anions in the envirnment to form an ionic compound
oxidized
when an atom, ion, or molecule has become more positive (looses electrons)
oxidation
the losing of electrons
reduced
when an atom,ion, or molecule has gained electrons
reduction
the gaining of electrons (becoming more negative`)
Oxidation is always followed by
reduction
oxidation number
a number assigned to an element in chemical combination that represents the number of electrons lost (or gained, if the number is negative) by an atom of that element in the compound.
Oxidation reduction reactions
what is the oxidation number for monatomic ions
its the same as their charge
what is the oxidation number for neutral molecules and polyatomic ions
a hypothetical charge determined by artificially dividing up the elections in the molecule/ion.
What are the rules for determining oxidation numer
1. In elemental for the oxidation number is 0 (one element in the formula, no over all charge)
2. for a monatomic ion the oxidation number is equal to the charge of the ion (Al3+ redox number is +3)
3. nonmetals usually have negative oxidation numbers but not always
a. Oxygen is -2 except in peroxides
b. Hydrogen is usually +1 when bonded to nonmetals and
-1 when bonded to metals
c. fluorine is always -1 . The other halogens are usually -1 in
most binary compounds But when bonded with oxygen
(oxyanions) they are positive.
Certain elements have same oxidation number in all/most of their compounds
a. 1A metals are always +1 in compound
b. 2A metals are always +2 in compound
cl Fluorine is always -1 in compound
4. The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is zero. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion equals said ion's charge.
5. Max oxidation number of group A is its group number (roman numeral)
6. For nonmetals the minimum oxidation number is group number minus 8.
elemental form
A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. An element is composed of atoms that have the same atomic number, that is, each atom has the same number of protons in its nucleus as all other atoms of that element.
how to distinguish between charge and oxidation number
charge = 2+
oxidation number = +2
the pattern of a reaction between a metal and an acid or metal salt
A + BX ---> AX + B
displacement reaction
a chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound. Both metals and non-metals take part in displacement reactions.
activity series
a list of metals arranged by ease of oxidation

active metals
metals that are most easily oxidized
the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals (maybe more)
noble metals
transition elements from groups 8B to 1B (maybe more)
they have low reactivity
activity series
predict the outcome single displacement reactions
Which metals can be oxidized by which metals
Each metal on the activity series can be oxidized by metals lower than it on the table
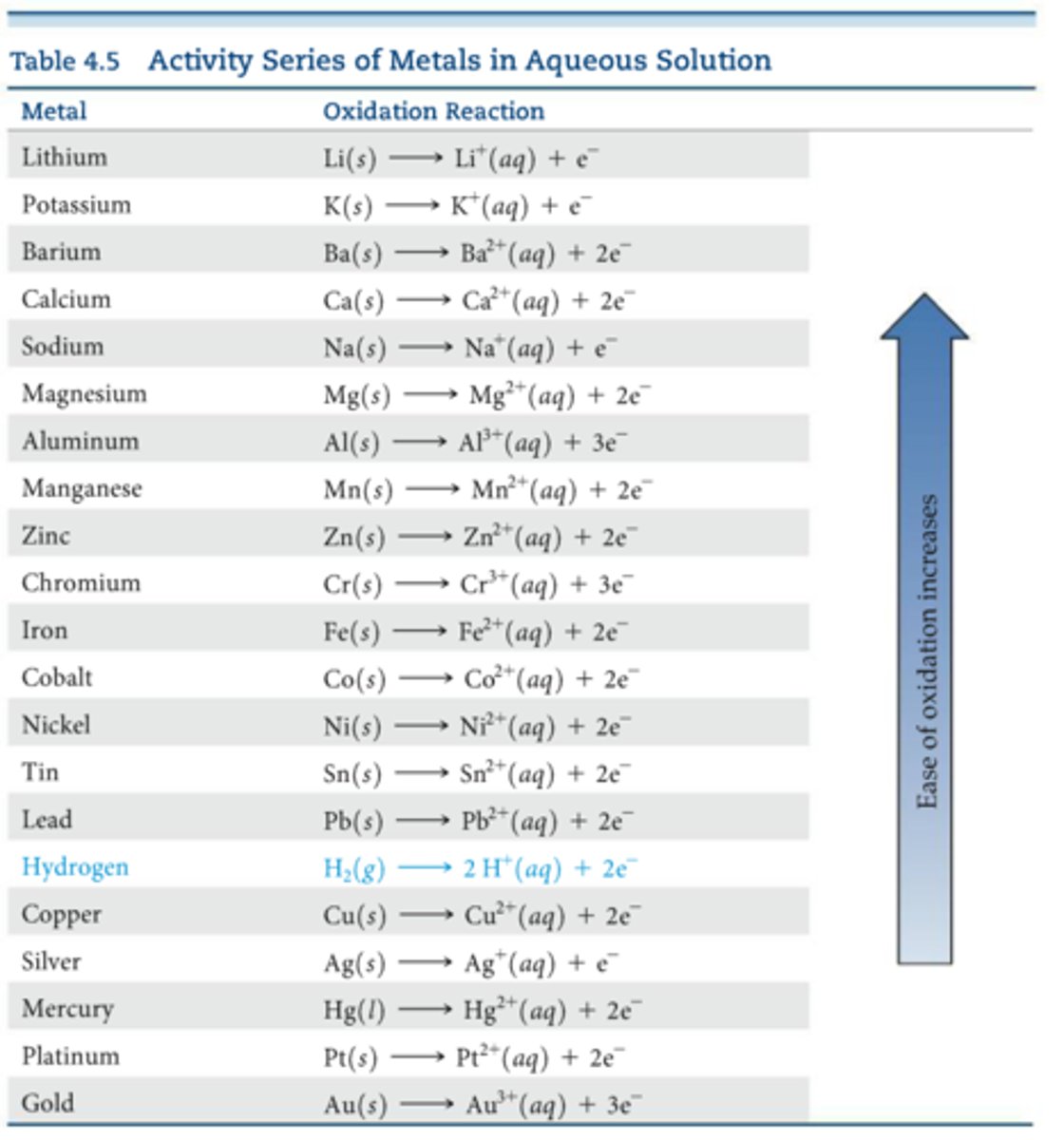
Anything under hydrogen on the activity series cannot...
react with acids to form H2
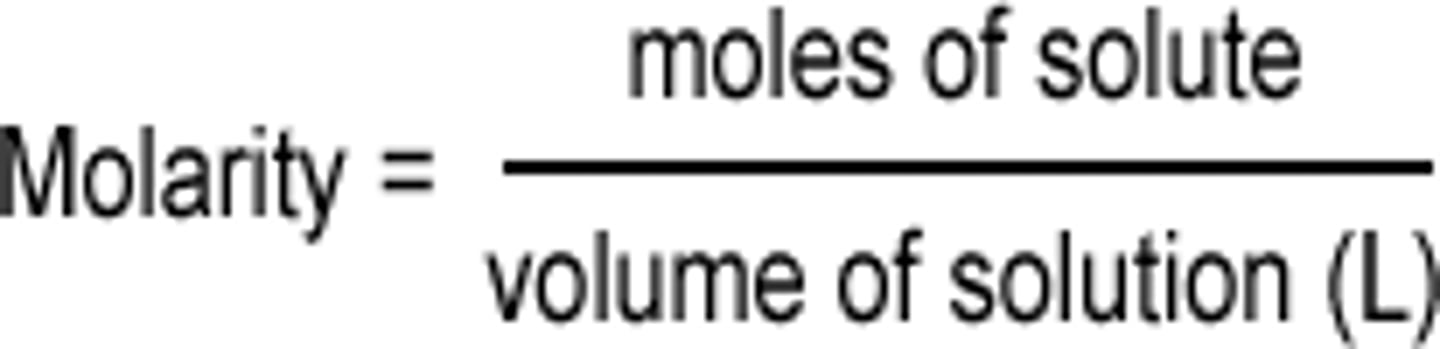
molarity equation
The concentration of a solution by how many moles of a solute is in it. (M)
MOLES OVER L
dilution
process of adding a concentrated version of a solution to another solution (usually water) gain a lower concentration of the concentrated solution.
This is common for commonly used chemicals.
Moles of solute before dilution =
moles of solute after diultion
Equation for dilution (can only be used for a pure solvent)
M x V (of concentration) = M
What is special about the ferric ion in regards to Exchange (Metaphesis) reactions
Fe3 stays Fe3 when moving from products to reactants
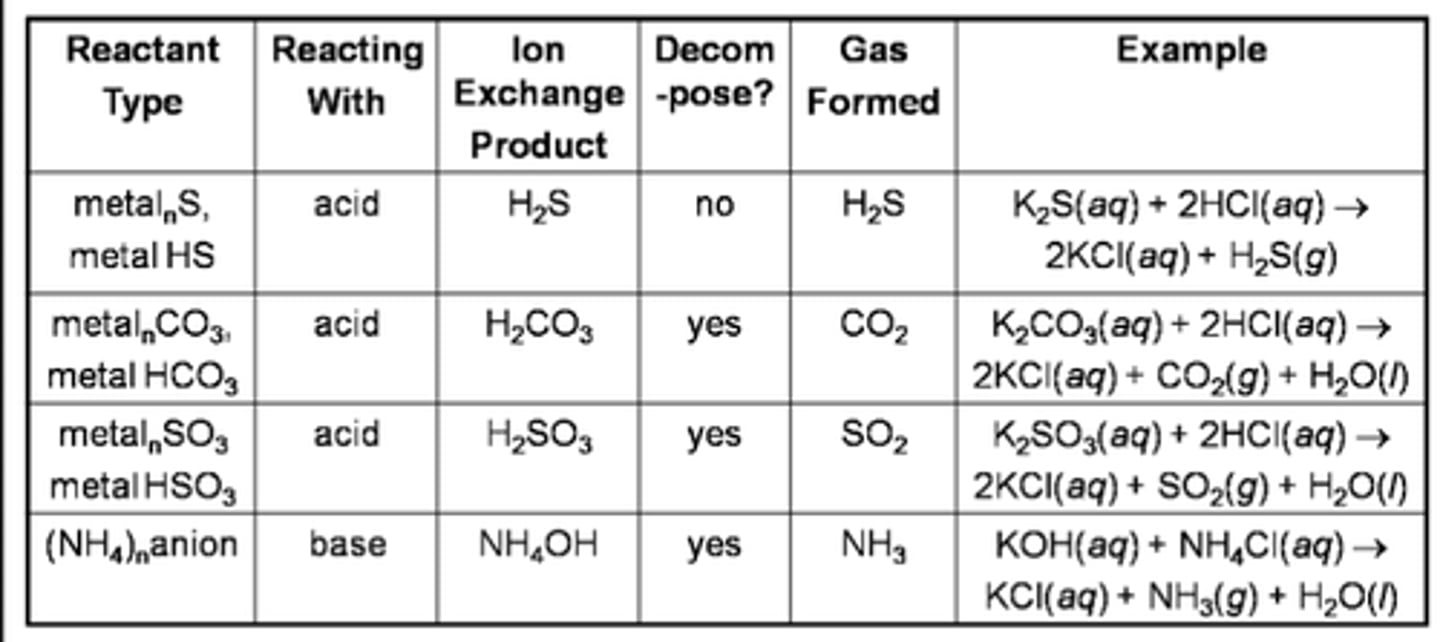
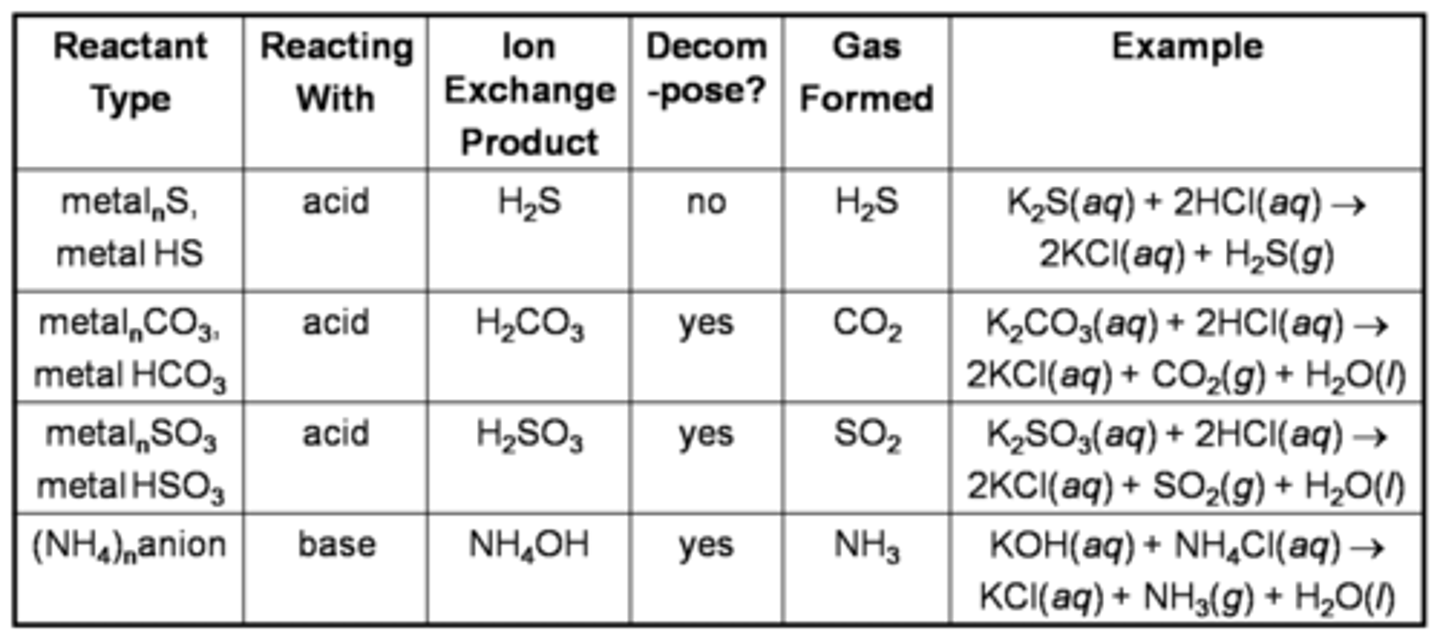
Gas-forming reactions
some double displacement reactions don't give expected products
When carbonate/bicarbonate....
Oxidizing agent vs reducing agent
oxidizing agent - substance that is reduced
reducing agent- substance that is oxidized
single replacement (single displacement) reaction
A + BC ---> AB + C
are redox reactions
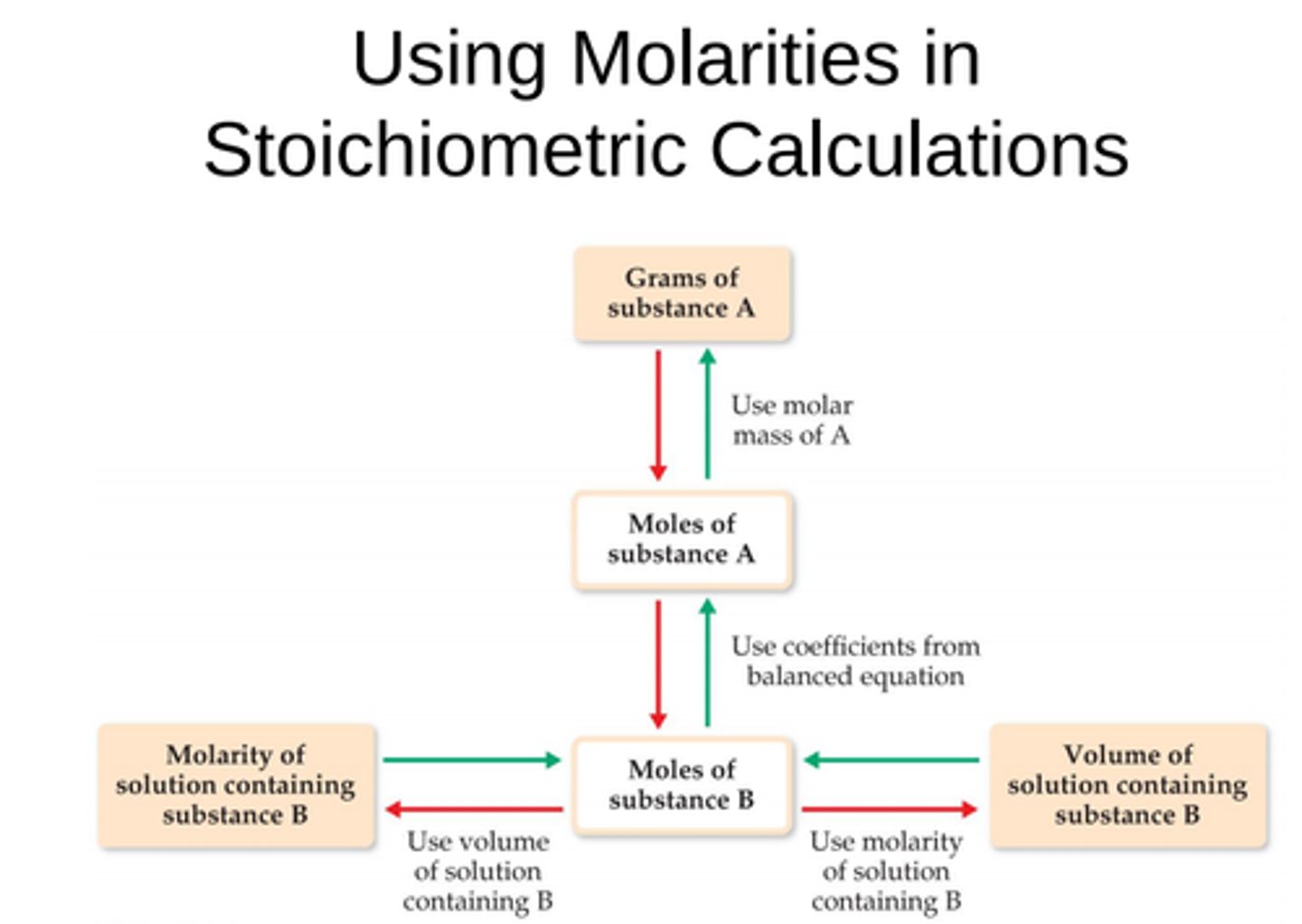
Using molarity in stoichiometry flow chart
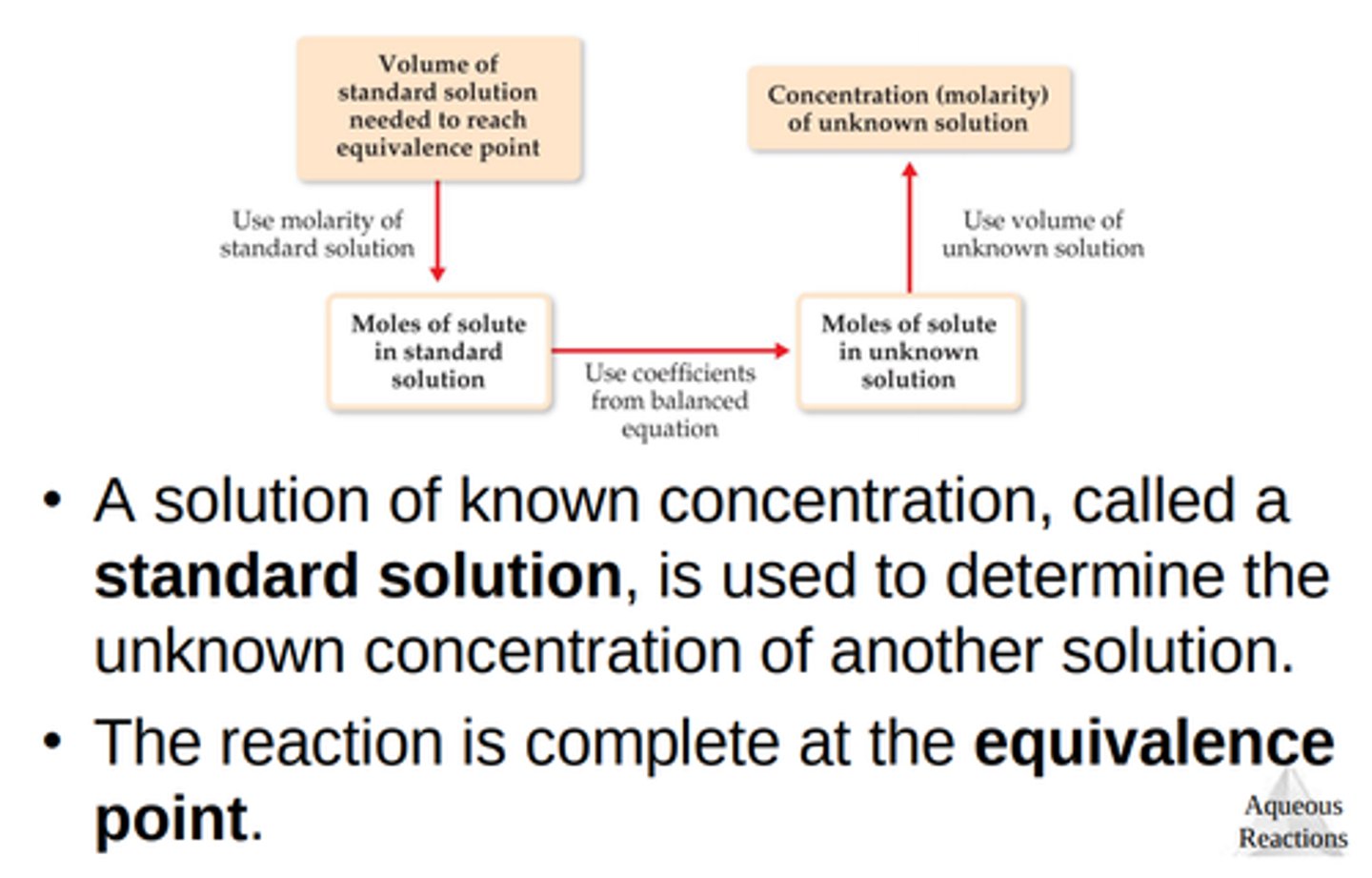
Titration flow chart
Single displacement reaction of halogens

Reactants and products of combustion reactions

what is H(OH)
H2O
Mass percent of solute (way of determining concentration other than molarity)
mass of solute/mass of solution x 100
Exceptions
Oxidation number rules

Solubility Rule 1
all nitrates are NO are soluble
Solubility Rule 2
All acetates are soluble
Solubility Rule 3
All compounds of group 1A cations (alkali metals) are soluble
Solubility Rule 4
Halides are soluble except for Ag, Hg, PB
Hydrochloric Acid
HCl Strong acid
Hydrobromic Acid
HBr strong acid
Hydroiodic Acid
HI strong acid
Chloric acid
HClO₃ strong acid
Perchloric acid
HClO₄ strong acid
Nitric Acid
HNO₃ strong acid
Sulfuric acid
H₂SO₄ (first proton) strong acid
Group 1A metal hydroxides
LiOH, NaOH, KOH, RbOH, CsOH Stong base
Heavy Group 2A metal hydroxides
Ca(OH)₂ Sr(OH)₂ Ba(OH)₂Strong base
Weak acid
HF
Acetic Acid
weak acid
Formic acid
weak acid
Weak base
NH₃
LEO the lion says GER
Lose electrons oxidation; Gain Electrons Reduction
Acid to base containing CO₃⁻ + HCO₃⁻
need H₂O (l) + CO₂ (g)