IGCSE Biology Test Unit 4-6
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
True or False? Carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids contain carbon
True. Carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids contain carbon.
What are the chemical elements present in carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are made of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen.
True or False? Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all made of glucose
True. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all carbohydrates built from many molecules of glucose joined together.
What are the chemical elements present in proteins?
Proteins contain carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen. Some contain small amounts of other elements such as sulfur.
What is the product when proteins are broken down into smaller molecules?
When proteins are broken down into smaller molecules amino acids are produced.
What are the chemical elements present in lipids?
Lipids are made of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen.
True or False? Fats and oils are built from many glycerol molecules
False. Each molecule within fats and oils contain a single glycerol molecules joined to three fatty acids.
What is the test for starch?
The test for starch involves adding iodine solution to a food sample. A positive result is a colour change from orange-brown to blue-black.
True or False? A positive iodine test will turn the solution from red to blue-black
False. A positive test for starch using iodine will turn the solution from brown/orange to blue-black.
What is the test for glucose (a reducing sugar)?
The test for glucose involves adding Benedict's solution to a sample and heating it in a boiling water bath. A positive result is a colour change from blue to brick red.
What is the starting colour of Benedict's solution?
The starting colour of Benedict's solution is blue.
What is the test for the presence of protein?
The protein test involves adding Biuret solution to a food sample. A positive result is a colour change from blue to violet/purple.
What is the starting colour of Biuret solution?
The starting colour of Biuret solution is blue.
What is the test for lipids?
The test for lipids involves mixing a sample with ethanol and then adding the ethanol solution to cold water. A positive result is a cloudy white emulsion forming. Note that a sample containing solid pieces of food may need to be strained before a positive result can be clearly seen.
What does the DCPIP test for vitamin C involve?
The DCPIP test for vitamin C involves the addition of a food sample to blue DCPIP solution. If vitamin C is present then the DCPIP will become colourless.
Which of the food tests must be heated to observe the results?
The Benedict's test for glucose (a reducing sugar) must be heated to observe the results.
Describe the structure of DNA. (Extended Tier Only)
DNA consists of two strands coiled around each other to form a double helix. The strands are held together by a series of paired bases with bonds in between.
Identify the four nucleotide bases found in DNA. (Extended Tier Only)
The four nucleotide bases in DNA are
True or False? Nucleotide base A pairs with G in DNA. (Extended Tier Only)
False. A pairs with T in DNA base pairing.
Describe how bases pair together in DNA. (Extended Tier Only)
Bases in DNA pair together via complementary base pairing
What sequence of bases would pair with the DNA base sequence below (Extended Tier Only)
ACCGTTTGCAA. The base sequence would be paired as follows
Define the term enzyme
An enzyme is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst to speed up the rate of a chemical reaction.
What does a catalyst do?
A catalyst speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up or changed in the reaction.
True or False? Enzymes are necessary for all living organisms
True. Enzymes are necessary for all living organisms to maintain reaction speeds at a rate that can sustain life.
Define the term substrate
A substrate is the reactant of an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
State the meaning of the term active site
The active site is the region on an enzyme where a specific substrate attaches for the reaction to be catalysed.
What happens after a reaction has occurred in the active site of an enzyme?
After the reaction has occurred the products leave the enzyme's active site and the enzyme is free to take up another substrate.
True or False? Enzymes are changed or used up in the reactions they catalyse
False. Enzymes are not changed or used up in the reactions they catalyse
they can be recycled and used in further reactions.
Define the term optimum temperature
The optimum temperature is the temperature at which an enzyme works fastest.
Define the term denatured
When an enzyme is denatured its active site changes shape and can no longer bind to its specific substrate. This results in a loss of enzyme function.
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in amylase, what is the variable being changed?
The variable being changed (independent variable) is the temperature of the amylase and starch reaction mixture.
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in amylase, what is the purpose of adding iodine solution?
When investigating the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in amylase, iodine is added to detect the presence of starch. When all the starch has been digested into sugar the iodine will no longer turn blue-black.
True or False? In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in amylase, the iodine solution will stop turning blue-black fastest at the optimum temperature
True. In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in amylase, the iodine solution will stop turning blue-black fastest at the optimum temperature
this is because the enzyme is working at its fastest rate breaking down the starch to sugar.
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in enzymes, what happens to the rate at low temperatures?
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction, the rate of reaction will be slow at low temperatures. This is due to low kinetic energy.
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in enzymes, what happens to the rate at high temperatures?
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in amylase, the rate of reaction will decrease to zero at high temperatures. This is because the amylase enzyme has become denatured and cannot break down the starch.
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction, which variables should be kept constant?
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction the variables that should be kept constant include
the concentration and volume of enzyme solution
the pH.
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in enzymes, why must the starch and amylase solutions be placed in a water bath at optimum temperature before being used?
In a practical that investigates the effect of temperature on rate of reaction in enzymes, the reactants and enzymes must be placed in a water bath at optimum temperature before being used so that they are brought up to the correct temperature before the investigation.
In a practical investigating the effect of pH on rate of reaction in amylase, why does the iodine solution stop turning blue-black at certain pH levels?
In a practical investigating the effect of pH on rate of reaction in amylase, the iodine solution stops turning blue-black at certain pH levels because the starch is fully broken down by the amylase. This means that there is no longer starch in the solution to turn the iodine blue-black.
In a practical investigating the effect of pH on rate of reaction in amylase, what impact does the optimum pH have on the rate of amylase activity?
In a practical investigating the effect of pH on rate of reaction in amylase, at the optimum pH the iodine solution will stop turning blue-black and remain orange-brown within the shortest time period. This is because the amylase is working at its fastest rate to break down the starch.
In a practical investigating the effect of pH on rate of reaction in amylase, what impact does a very low pH, such as pH2, have on the rate of amylase activity?
In a practical investigating the effect of pH on rate of reaction in amylase, at very low pH values the iodine solution will continue turning blue-black throughout the investigation. This is because the enzymes are denatured so the rate of amylase activity has slowed down/stopped.
What is a buffer solution?
A buffer solution is a solution that resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of an acid or base.
What is the role of a buffer solution when investigating the effect of pH on enzyme activity?
Buffer solutions are used to maintain a specific pH environment for the amylase enzyme. This keeps the pH the same throughout the investigation for each of the pH conditions.
True or False? The starch and amylase solutions need to be at room temperature to investigate the effect of pH on the activity of amylase
False. The starch and amylase solutions should ideally be placed in a water bath at the optimum temperature before being used in the investigation, however it does not need to be the exact optimum as long as the temperature is kept constant throughout.
Define the term specificity in the context of enzymes. (Extended Tier Only)
Enzyme specificity means that enzymes only bind to/catalyse the reaction of one specific substrate. This is because the active site of the enzyme is a complementary shape to the substrate.
What is an enzyme-substrate complex? (Extended Tier Only)
An enzyme-substrate complex is formed when a substrate attaches to the active site of an enzyme.
True or False? Enzymes can bind to several types of substrate. (Extended Tier Only)
False. Enzymes are specific to one particular substrate(s) as the active site of the enzyme is a complementary shape to the substrate.
True or False? The substrate is the same shape as the active site. (Extended Tier Only)
False. The shapes are opposite to each other to allow them to fit together. This is a called complementary shape.
Why is enzyme activity low at low temperatures? (Extended Tier Only)
Enzyme activity is low at low temperatures due to a lack of kinetic energy. This means that few successful collisions occur between enzyme and substrate molecules and so few enzyme-substrate complexes form.
Why does increasing temperature towards the optimum temperature increase reaction rate? (Extended Tier Only)
Increasing the temperature towards the optimum increases enzyme activity as the molecules have more kinetic energy, leading to more successful collisions with substrate molecules and a faster rate of reaction.
Why does increasing temperature too far beyond the optimum temperature result in a reaction rate that decreases to zero? (Extended Tier Only)
Increasing temperature too far beyond the optimum reduces reaction rate to zero because heat breaks the bonds that hold the enzyme together, causing it to lose its shape and become denatured.
What happens to an enzyme or substrate if its kinetic energy increases? (Extended Tier Only)
If an enzyme or substrate gains kinetic energy it moves around faster.
Why does the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction decrease as the pH level moves further from the enzyme's optimum pH? (Extended Tier Only)
The rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction decreases as the pH level moves further from the enzyme's optimum because extremes of pH break the bonds that hold the amino acid chain together, denaturing the active site and reducing the rate of reaction.
True or False? All enzymes denature in acid. (Extended Tier Only)
False. Different enzymes function well at different pH levels, e.g. enzymes from the stomach have a low optimum pH (around pH 2) because the stomach is an acidic environment.
Define the term photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants produce carbohydrates from raw materials using energy from light.
What is the word equation for photosynthesis?
The word equation for photosynthesis is
True or False? Photosynthesis can only occur in the presence of light and chlorophyll
True. Both light and chlorophyll are required for photosynthesis to occur.
What are the raw materials for photosynthesis?
The raw materials for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water.
What is the waste product of photosynthesis?
The waste product of photosynthesis is oxygen.
What is the product of photosynthesis that is useful for the plant?
The product of photosynthesis that is used by the plant is glucose.
What is chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll is a green pigment that is found in chloroplasts.
What is the role of chlorophyll?
The role of chlorophyll is to transfer energy from light into energy in chemicals, for the production of carbohydrates.
How do plants use the carbohydrates made in photosynthesis?
The carbohydrates made during photosynthesis can be used to produce
cellulose for building cell walls
glucose, which can be used in respiration to provide energy
sucrose for transport in the phloem
nectar to attract insects for pollination.
What is the function of cellulose in plant cells?
Cellulose provides structural support to plant cell walls and allows them to maintain a regular shape.
True or False? The carbohydrate sucrose is used for transport in the phloem
True. The carbohydrate sucrose is used for transport in the phloem. Glucose is converted into sucrose before being transported around the plant inside phloem.
Which process requires glucose for the release of energy?
Glucose is used in respiration to release energy for cells.
Name two essential mineral ions required by plants
Two essential mineral ions required by plants are
magnesium ions.
True or False? Plants need nitrates so they can build proteins
True. Nitrates are needed for the production of amino acids, which are joined together to build proteins.
Why do plants need magnesium ions?
Plants need magnesium ions for the production of chlorophyll, which is essential for light absorption in photosynthesis.
What is the purpose of the destarching step in photosynthesis investigations?
The purpose of destarching plants by placing in the dark for 24 hours is to ensure that any pre-existing starch in the leaves is used up so it does not affect the results.
True or False? Boiling a leaf in ethanol removes the chlorophyll before testing for starch
True. Removing chlorophyll by boiling in ethanol is an important step in testing leaves for starch. Removing the green colour allows the results of the starch test to be seen more clearly.
What chemical is used to test for the presence of starch in a leaf?
Iodine solution is used to test for starch
it turns blue-black in the presence of starch.
True or False? A leaf that has been destarched and then covered in foil for 24 hours will turn blue-black when iodine is added
False. A leaf that has been destarched and then covered with foil will not turn blue-black when iodine is added but will remain yellow-brown. This is because it will not have had light for photosynthesis, so will not have produced any new starch.
Give one variable that should be kept the same when testing the requirement for carbon dioxide in photosynthesis
A variable that should be kept the same (control variable) when testing the requirement for carbon dioxide in photosynthesis could be
the presence of chlorophyll
the temperature of the room.
Why should Bunsen burner flames be turned off before boiling leaves in ethanol when testing leaves for the presence of starch?
Flames should not be present when boiling leaves in ethanol because ethanol is highly flammable. A water bath should be used for this step.
Why do we use variegated leaves when investigating the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Variegated leaves are used when investigating the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis because they have green and white regions, where the green regions do contain chlorophyll but the white regions do not. Demonstrating that, after exposure to light, the green regions do contain starch while the white regions do not, shows that chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis.
What is the independent variable when testing the requirement for chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
The independent variable when testing for the importance of chlorophyll in photosynthesis is whether the area of leaf tested is green or white (i.e. whether or not the leaf contains chlorophyll).
When investigating the need for carbon dioxide in photosynthesis, what is the purpose of placing plants in a bell jar which contains a beaker of sodium hydroxide?
When investigating the need for carbon dioxide in photosynthesis, the purpose of placing plants in a bell jar which contains a beaker of sodium hydroxide is to absorb carbon dioxide from the surrounding atmosphere.
When investigating the need for light in photosynthesis, what will be the colour of parts of leaves that were covered in aluminium foil after testing with iodine solution?
The parts of leaves that were covered with aluminium foil during an investigation into the need for light in photosynthesis will remain orange-brown when tested with iodine. This is because these areas did not receive any sunlight and could not photosynthesise to produce starch.
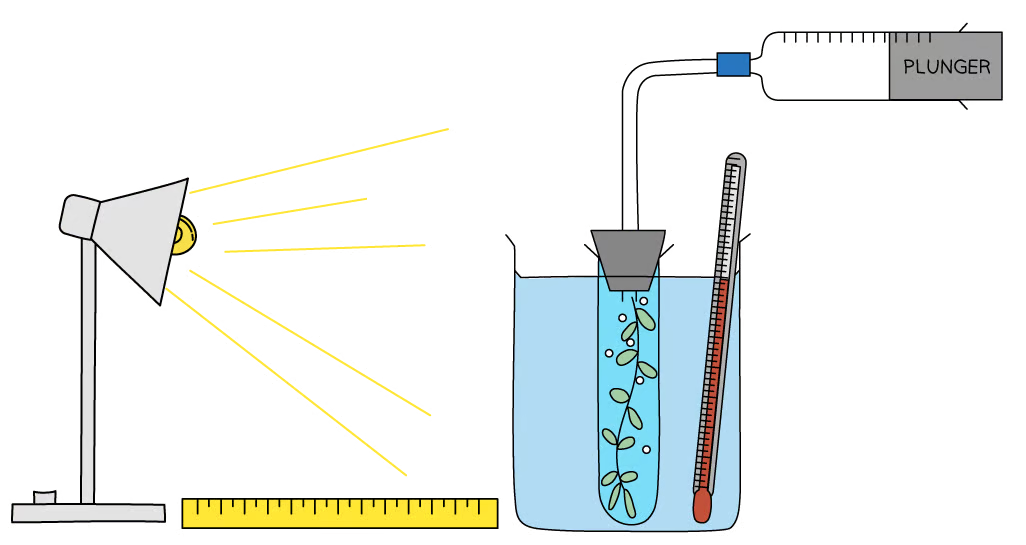
What investigation can be carried out using the practical equipment below?
The equipment shown in the image can be used to investigate the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis.
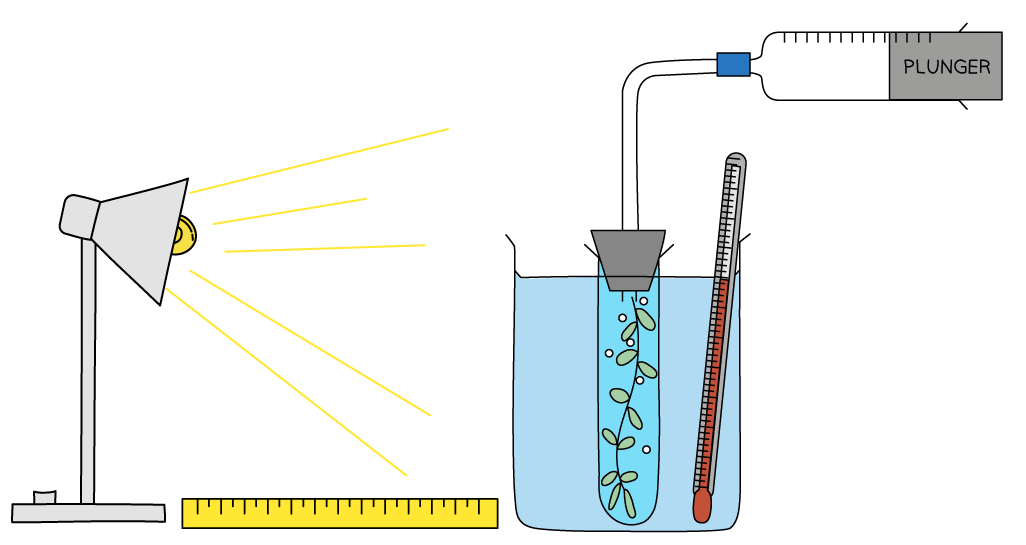
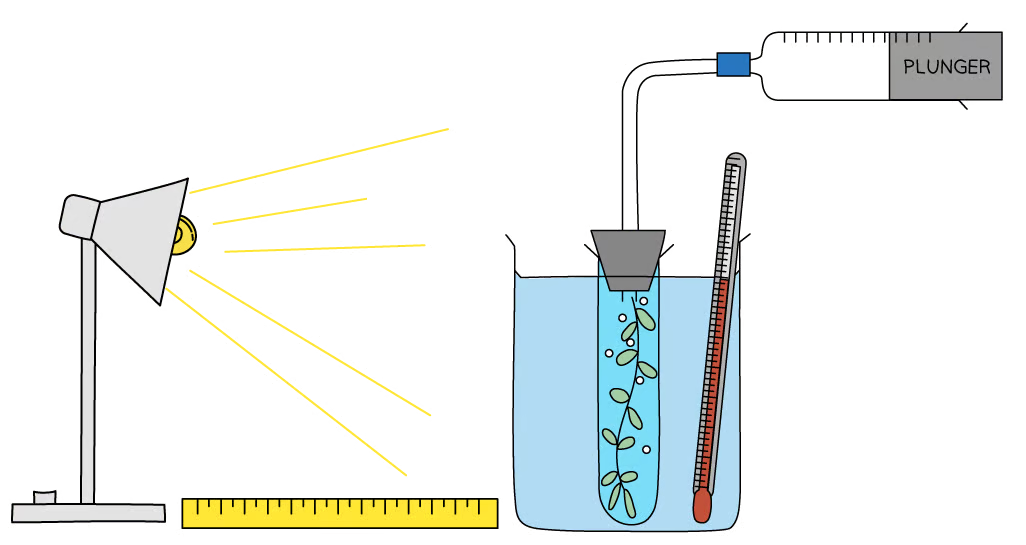
What would the independent variable be in the investigation shown?
The independent variable is light intensity, which is controlled by altering the distance between the lamp and the beaker.
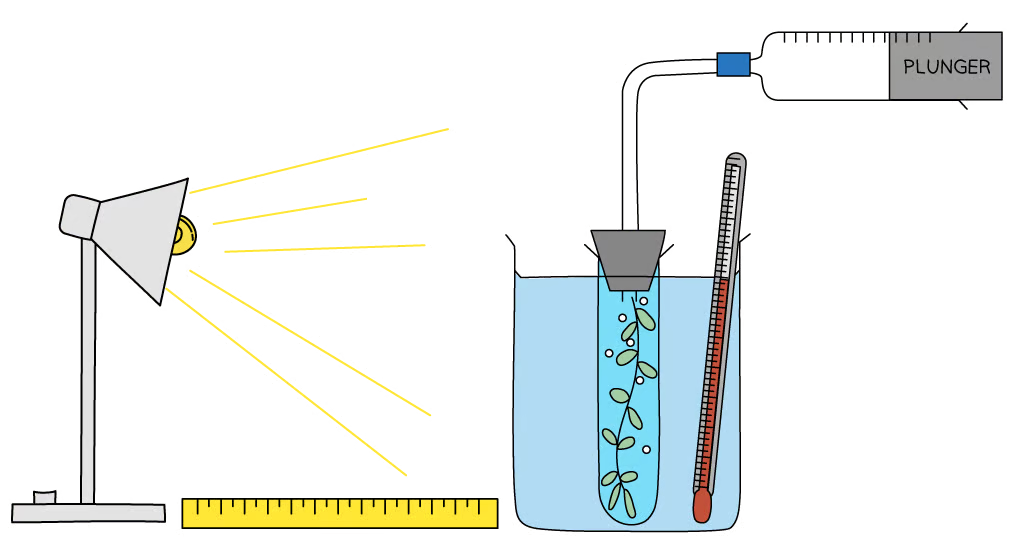
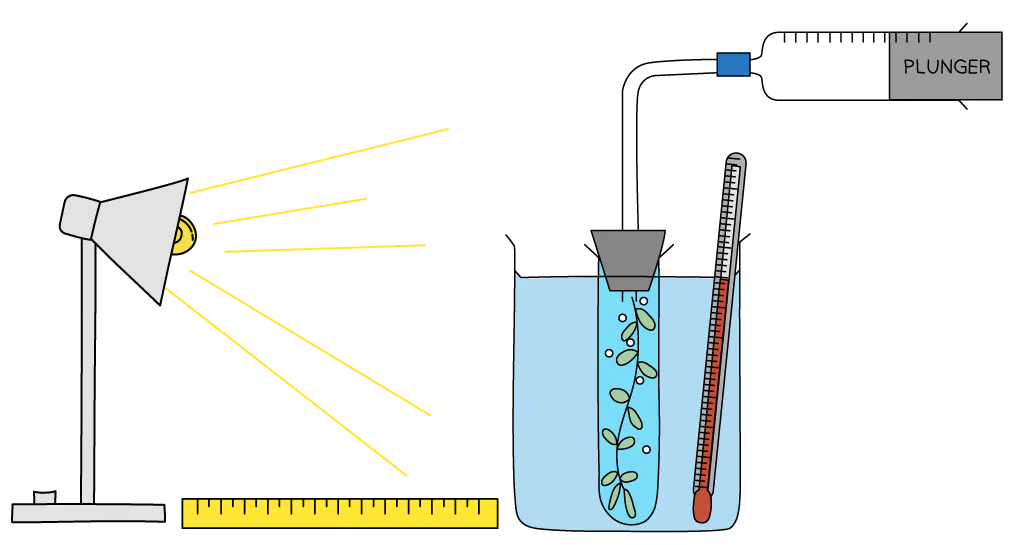
What would the dependent variable be in the investigation shown?
The dependent variable in this investigation is the rate of photosynthesis, which is measured by recording the volume of oxygen produced within a set time period.
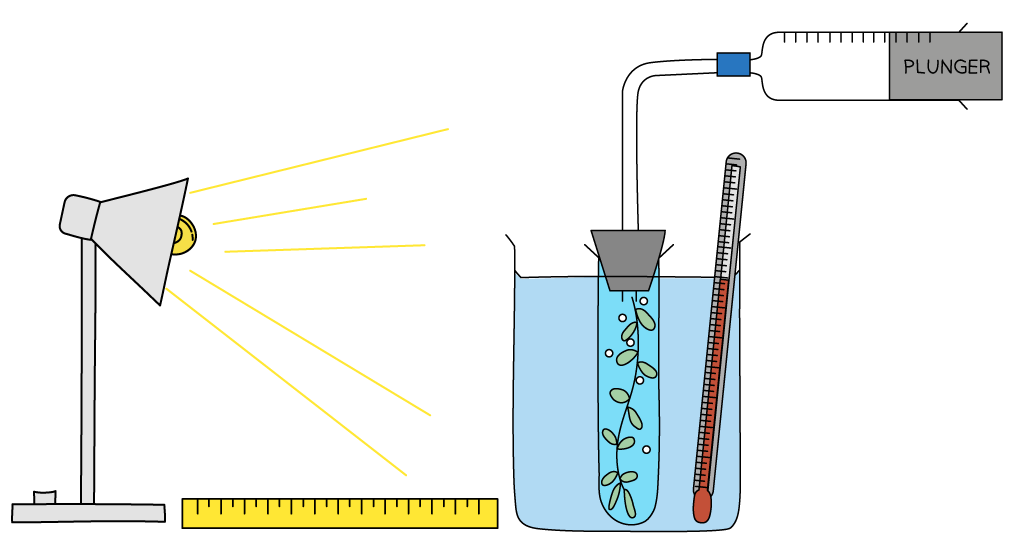
Give two control variables for the investigation shown
Control variables for this investigation would include

using the same species, length and age of plant in each repeat
dissolving sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) in the water to maintain carbon dioxide levels.
In an investigation into the effect of temperature on photosynthesis, why should light intensity be controlled?
Light intensity should be controlled when investigating the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis as light intensity will affect on the dependent variable.
In an investigation into the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis, what is the predicted outcome?
The predicted outcome in an investigation into the effect of carbon dioxide on the rate of photosynthesis is that the rate of photosynthesis will increase with increasing carbon dioxide concentration. This increase will continue until another factor becomes limiting.
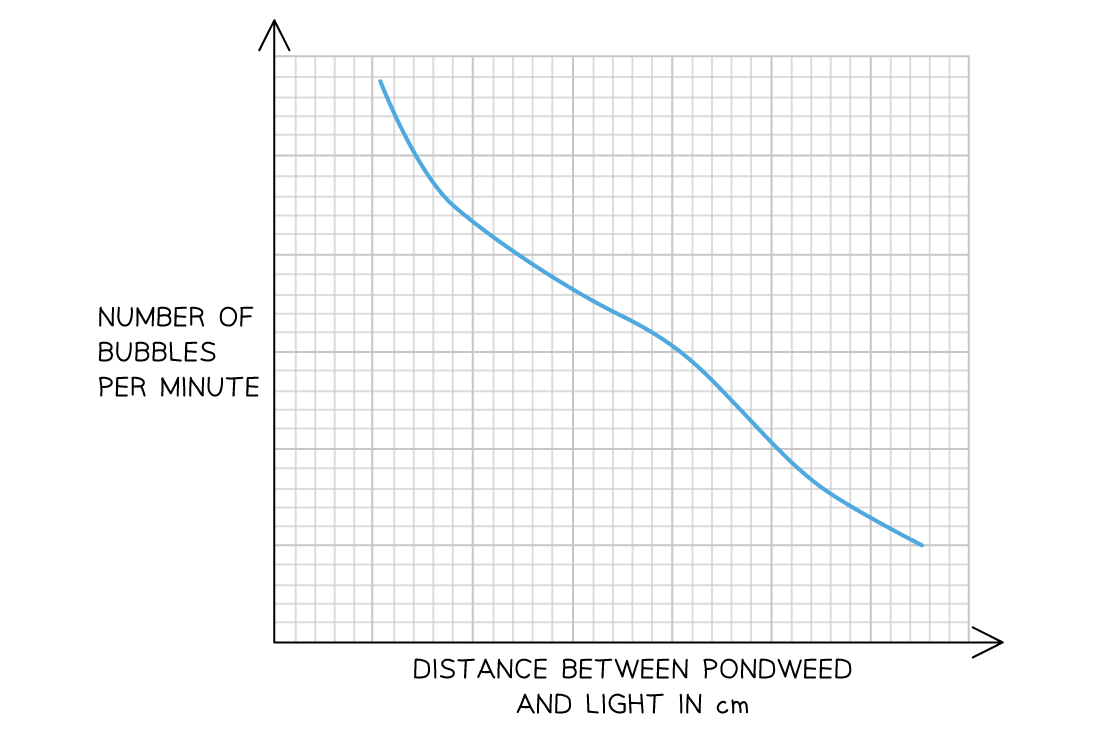
Why does bubble production decrease as distance between the light source and the aquatic plant increases in the graph shown?
The number of bubbles produced decreases as the light moves further away from the pondweed because light intensity decreases with distance
this means that rate of photosynthesis decreases and so less oxygen is produced.