Pleura & Lungs
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
_______ is the superior of the manubrium: lies opposite the ______ border of the body of T_
Suprasternal notch, lower, 2
_________ ______ is between the sternal attachment of the ___ costal cartilages.
Subcostal angle, 7th
______ _____ is the lowest part (formed by ___ rib) is at the level of the ______ vertebrae
Costal margin, 10th, 3rd lumbar
_________ is the muscle behind the xiphisternal joint.
Diaphragm
__________ summit of the _______ dome of the diaphragm is at the _______ border of _th rib at the midclavicular line .
Midrespiratory, right, upper, 5
_____ dome reaches as far as the lower border of rib __ on the left.
Left, 5
_____ is in the ___ intercostal space _ inches from midline (male); _______ of T4 crosses the nipple.
Nipple, 4th, 4, dermatome
______ is in the ______ ventricle; point of maximum pulsation;____ intercostal space ___ from the midline.
Apex beat, left, 5th, 3.5
Levels of the landmarks of the Scapula:
Superior Angle: ________
Spine: ________
Inferior Angle: ________
T2, T3, T7
The Right Lung forms the __________________ joint, and reaches the midline behind _______ _______ and continues until the __________ joint.
Sternclavicular, sternal angle, Xiphisternal
______ lung deviates laterally and extends for a variable distance beyond lateral margin of sternum at the ____ costal cartilage to become the _________ _______.
Left, 4th, cardiac notch
_______ border: Curved line crossing __ rib and ___ rib and reaches the __ rib.
Lower, 6th, 8th, 10th
In the Lower border:
6th rib = mid-_________
8th rib = mid-_________
10th rib = _________
Clavicle, axillary, vertebral column
________ border: extends down from spinous process of ___ cervical to the ____ thoracic vertebra ___ inches from the midline.
Posterior, 7th, 10th, 1.5
_______ fissure - from spinous process of __ to __ angulation.
Oblique, T2, T6
The _________ fissure is present only in the ______ lung, which meets the oblique fissure at the mid_______ lne in the ___ intercostal space.
Horizontal, right, axillary, 4th
______ line of pleural reflection is identical to the apex of the lung
Cervical pleural
_______ border of _ pleura - behind SC joint almost reaching the midline behind sternal angle up to xiphisternal joint.
Anterior, R
________ border of __ pleura, at the level of __ costal cartilage; deviates lateral to extend to lateral margin of the sternum to form the ________ _______
Anterior, L, 4th, cardiac notch
______ border of pleura - cross ___ rib in midclavicular line and ___ rib midaxillary line and reach ____ rib lateral border of erector spinae
Lower, 8th, 10th, 12th
________________ recess - distance between two (lung and pleural border)
Costodiaphragmic
True or False: The Lung and the pleura all have the same landmarks except for the lower border of the lung.
True
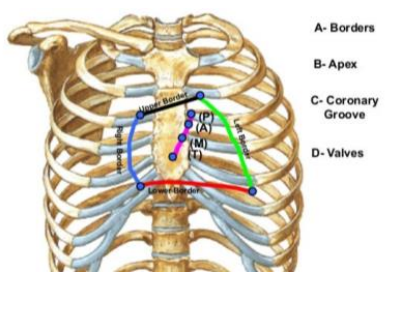
Surface Anatomy of the Heart:
_________ - formed by the left ventricle, corresponds to apex beat at ____ left intercostal space ___ inches from midline.
Apex, 5th, 3.5
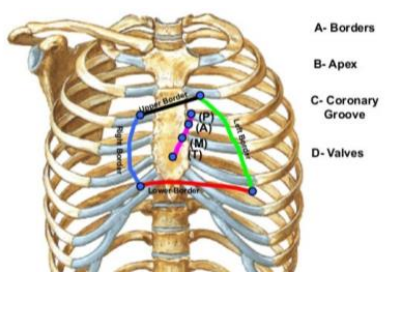
Surface Anatomy of the Heart:
______ border
______ ____ costal cartilage (Sternal angle)
_______ is also found here.
Superior, 2nd, left, roots of great blood vessels
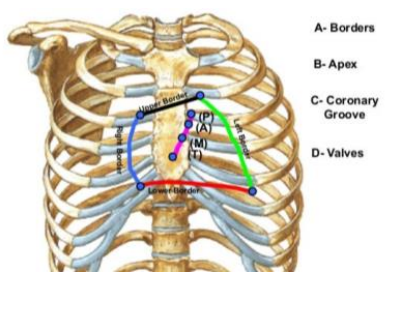
Surface Anatomy of the Heart:
______ border
___ right costal cartilage form the edge of sternum to the ___ right costal cartilage
________ is also found here.
Right, 3rd, 6th, Right atrium
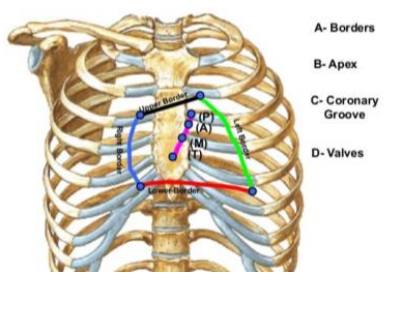
Surface Anatomy of the Heart:
_____ border
_______ costal from sternum to ____ ____
_____ is also found here.
Left, 2nd, apex beat, left ventricle
Surface Anatomy of the Heart:
_______ border formed by the right ventricle and apical part of the left ventricle; from ___ right costal cartilage from sternum to apex beat
Inferior, 6th
______ not common; occurs in motor accidents, heart may be severely contused by the impact.
Sternum fracture
_______ is the most common injury and is the bruising of the rib due to trauma.
Rib contusion
_________ commonly occurs at the ______ of the rib: ___ to ___ ribs are the common sites.
Rib fracture, angle, 5th, 10th
Common complication is ____________ due to penetration to lungs.
Pneumothorax
_______ is an injury to the ribs where a section of the rib cage has been detatched due to multiple fractures…
Flail chest
These are indications of?…
Hemothorax
Pneumothorax
Open pneumothorax
Prophylaxis
Thoracosectomy
Position of chest drain (tube) is determined by the “_____ _______”
Boundaries:
Anterior border of __________ ______
Lateral border of _______ _______
______ of axilla
_________ line level of ______
safe triangle, latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major, apex, horizontal, axilla
2nd intercostal space at the midclavicular line for the ______ approach
Anterior
2nd intercostal space at the midaxillary line for the ______ approach
Lateral
Classification of Diaphragmatic hernia?…
Congenital
In a diaphragmatic hernia, abdominal contents may move ________.
Upward
Involuntary spasmodic contraction of diaphragm..
Hiccups
Singultus (Hiccups) - Can be a symptom of _____ (inflammation of pleura).
Pleurisy
The pulmonary _____ allows movement of pulmonary ________ and large _____ during respiration.
ligament, vessels, bronchi
The pleural cavity contains ________ fluid, which lessens friction between pleural layers.
parietal
______ is found in the Inner surface of ribs, costal cartilage and sides of vertebral bodies and back of sternum…
Costal pleura
The costal pleura is supplied by the ________ nerves.
intercostal
The superior boundary of the pleural cavity above rib _ to the ________.
1, root of neck
The inferior boundary of the pleural cavity extends just above the ________.
costal margin
The space between the parietal and visceral pleura is called the ________.
pleural cavity
_____ covers thoracic surface of diaphragm; supplied by _____ and _ intercostal nerves.
Diaphragmatic pleura, phrenic nerve, 6
_____ is a Dome shape layer of _____ pleura lining the cervical extension and covers the ____.
Cervical, parietal, apex
Pleura sensitivities…
Visceral; _____
Parietal;______ & ______
stretch, pain, stretch
______ is a lower area of pleural cavity into which lung expands vertically during inspiration
Costodiaphragmatic recess
________ is to give space to the heart when it beats and for the lungs when it expands
Costomediastinal recess
Nerve that innervates both the mediastinal pleura and the diaphragm…
Phrenic nerve
Normal amount of pleural fluid is __-__ mL, and disorder when too much is produced is called _____ ______.
5, 10, pleural effusion
Collection of pus in the pleural cavity is called _______.
Empyema
The trachea starts at the lower border of the ________, and bifurcates at the ____ ____.
cricoid, sternal angle
True or False: The trachealis muscle is a voluntary muscle
False
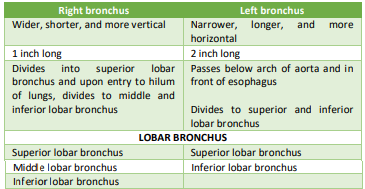
Differences between right & left bronchi… (Type 1)
1

______ is the end junction of trachea and principal bronchi that separates the opening of bronchi (start of bifurcation)
Carina
______ possess outpouching from their walls; blood exchange between blood and air takes place in the walls
Terminal bronchioles
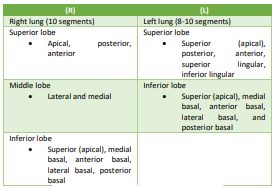
Bronchopulmonary segments (Type 1)
1
___: structure projecting upward into the neck above clavicle
___: sits on the diaphragm
______ surface: corresponds to concave chest wall
______ surface: molds into the pericardium and other mediastinal structure
_____: depression in which the root of lung is attached
Apex, Base, Costal, Mediastinal, Hilum
Non-respiratory circuit: (No gas exchange)
Bronchial ______ supplies the bronchi, connective tissue of lung and visceral pleura
Bronchial ______ rains to azygos and hemiazygos veins
arteries, veins
The ________ ______ is where gas exchange occurs.
Respiratory circuit
Intersegmental veins carry ________ blood from alveolar capillaries.
de-oxygenated
Intersegmental veins carry ________ blood from alveolar capillaries.
oxygenated