G202 Exam 2 Case Material
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
What is special about Unilever’s Logo
represents Unilever’s values
List some of Unilever’s values
Reduce greenhouse gases
Pollution free
better tomorrow
nature and environment
sustainability
positive transformation
science and research
recycling
transparent communication
towards betterment
_____ of Unilever’s values are sustainability focused
Over half
What is the Stakeholder Hierarchy of Unilever
Consumers-Society-Employees-Shareholders
How did the USLP hierarchy hope to improve business performance
Signaled to key stakeholders that societal issues are integrated in Unilever’s core business strategy
Describe the consumer trend toward health and protected environment
Growing trend to improve health and protected environment
What does employee motivation and empowerment around solving society’s biggest challenges lead to
innovation
Government regulations and NGO activist campaigns are focusing more on what
mitigating global social threats
Who is Trust and Transparency important for
socially responsible investoers (SRIs) that are growing in importance in capital allocations
The Sustainable Living Plan (USLP
Allows Unilever to differentiate its products in markets that are usually seen as more homogeneous
What is the result of the differentiation in the USLP
creates loyal customers from those that value sustainability
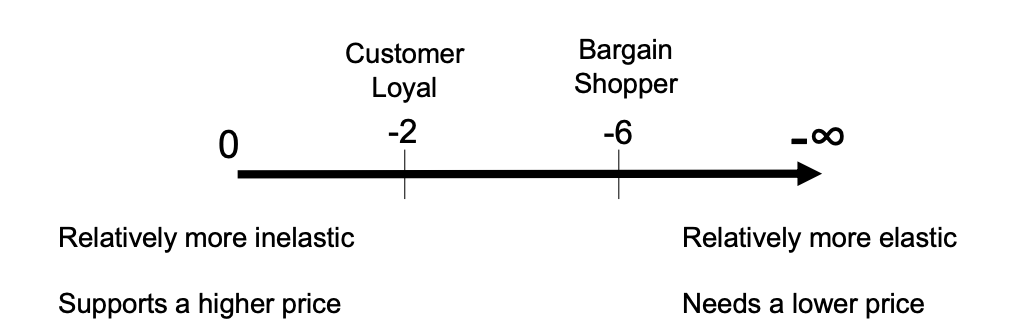
Loyal customers have more ______ demand, giving Unilever market power in pricing
inelastic
Understand this
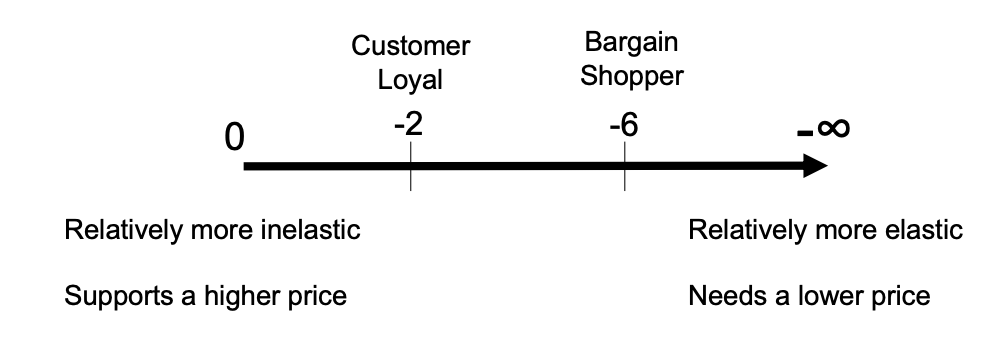
Consumer Loyalty: _____ Prices and _______Sales
Higher; more
Market shares have outpaced market growth
What improves with Employee Loyalty
Recruiting, Retention, Productivity
What increases with Investor Loyalty
Resources for R&D and Expansion
Listen on the Dow Jones Sustainability Index and GlobeScan Sustainable Leaders
Profit Maximization
Differentiation and Customer Loyalty
Pf and Qf
Found where MR=MC
Social Efficiency
Competition and Homogenous Goods
Pe and Qe
Found where D=MC
Inefficiency in the Market
When firms with market power under produce relative to the socially efficient output (Qf<Qe)
Firms will not go to Qe as units are not profitable past Qf
Social Impact Results
Sustainability Target
Improved Internal Resource Efficiency
USLP Problem Curbing External GHG and Water
Unilever’s Options on moving forward
Double down on USLP
Hunker Down on Profits
Pivot to Partners
Pros of Unilever Doubling Down on USLP
Early profit increase
Employees motivated and driver of innovation
Culture and brand loyalty to social accountability
Cons of Unilever Doubling Down on USLP
Not in control of GHGs and water within value chain
Diminishing returns and rising costs
What to to with brands (AXE) that don’t fit USLP
Pros of Hunkering Down on Profits
Picked all low-hanging fruit
Slow growth, rising costs
Focus on the 11 sustainable brands that are in Unilever’s top 30
Cons of Unilever Hunkering Down on Profits
Reputational loss if Unilever publicly gives up
May reduce employee morale and productivity
Miss on stakeholder trend towards sustainability
Pros of Unilever Pivot to Partners
Can’t meet all USLP goals without help
Partners can cut costs and offer expertise
Partners expand reach
Cons of Unilever Pivot to Partners
Lose control of agenda
Employee objectives may become unclear
Having others do your work may signal lack of commitment
What did Unilever do from 2010-2020
Hybrid approach. Unilver doubled down with the help of more partnerships
Recount some Unilever achievements
Reached 1.3 billion people through health and hygiene programs
Reducing the total waste footprint per consumer by 32% and achieving 0 waste to landfill across all our factories
Reducing GHG by 65%
100% renewable grid electricity
Reduce sugar across sweet tea and foods portfolio
Enabling 2.34 million women to access initiatives
51% of management is women
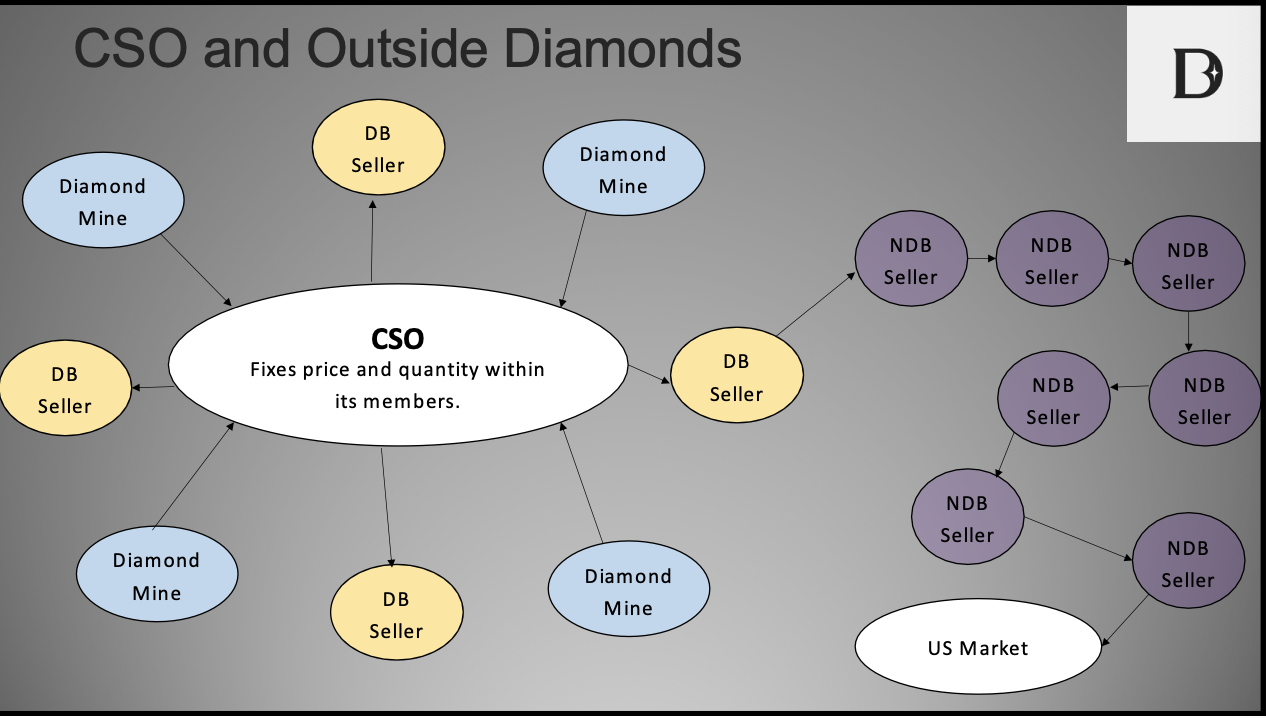
What is DeBeers?
A cartel - collection of diamond mines and diamond sellers
Collusive Game (Debeers)
The members of debeers collectively agree to restrict the number of diamonds released to the world market to raise the value of their diamond assets
collusion risk (debeers)
The cartel is not always stable as there can be a strong incentive for a member to cheat for a one-shot gain
Which countries deviated from the agreed upon quotas and try to take advantage of the short-term revenues
Russia, Zaire, and Israel
Which countries completely defected from the cartel
Russia and Angola
What is the role of the Central Selling Organization (CSO)
punish cheating - glue that holds the cartel together - enforces the collusive agreement
CSO makes a _______ offer where the price and quantity offered to each DeBeers Seller is ____
“take-it, or leave--it”; fixed
Stockpiling
Debeers takes diamonds out of the market, locks them in a vault and pretends like they’re not there
What market forces can DeBeers control with stockpiling
supply (stockpiles its own diamonds coming from its own mines)
demand (DeBeers acts as a “Buyer of Last Resort,” buys outside diamonds adn then stockpiles those
Anitrust laws
make monopolizing a market, cartels, excessive market power, and other collusive arrangements illegal
Why can’t antitrust laws reach DeBeers
DoJ can’t prove that DeBeers does sufficient business with US interests
What does the US Diamond market look like?
Stockpiling Bursting
Ever-growing stockpile → Bain Consulting to help
Bain recommendation:
change advertising to focus on DeBeers brand, instead of just diamonds
DeBeers’ diamonds expected to fetch 15% higher prices than rivals
However, targeted advertisements, with the DeBeers logo, could bring about more antitrust liabilities
Who and what was addressed in the DeBeers speech to the Harvard Business School
Nicky Oppenheimer addressed the antitrust policy
What did Nicky Oppenheimer state in his speech to Harvard
DeBeers should be an exception to the rule because of the economic good that they do on the African Continent
Ex: Botswana’s infrastructure investment put forth by DeBeers can be traced to double digit growth in the country’s GDP for two decades
What did DeBeers have to do based on the recommendation from Bain
Find a way to enter the US market directly to leverage its 15% premium with customers
Was Nicky Oppenheimer’s Speech compelling?
Yes. African Growth and Opportunity Act signed by the US result
African Growth and Opportunity Act
DeBeers agreed in principal to a class action antitrust lawsuit in the US (2005)
Courts approved settlements as fair (2008)
Settlement was appealed(2010) but then the supreme court upheld the settlement (2012)
Since 2008 settlement - what has DeBeers gained?
the right to open stores in the US, cutting out a lot of the intricate trades that happened outside of the US
(Houston, Naples, NY)
What was DeBeer’s brand strategy to fight competition
The brand allowed DeBeers to strategically sell off its stockpile by taking sales away from its competitors without flooding the market with diamonds
DeBeers focused on grabbing more market share within existing sales, so that it would not devalue the diamond market with excessive supply
What does the textile industry do to minimize compliance costs
locates production facilities in areas that have low regulations against toxins
what are the effects of textile producers locating themselves in areas with low regulations?
not held accountable for full costs of their production
by leaving out the full costs of their chemical hazards, the polluting industry is over-producing → net cost on society
Western governments are threatening _______ against heavy polluters
more stringent regulations
Greenpeace Detox
social activists are starting to pressure leading brands to adopt higher environmental standards
Lev'i’s Culture
Sustainability is sewn into the fabric of everything we do
How has Levi’s demonstrated their mission of “Profits through Principles”?
1950s: integrated factories in the south well before Civil Rights movement
1980s one of 1st companies to recognize HIV/AIDS and support educational efforts
1990s: one of the first companies to adopt a comprehensive code of conduct and social responsibility standards in its out-sourced factories
What does Greenpeace expect from Levi’s
Levi’s to back up its reputation for social impact
Social risk of activist campaigns (Levi’s)
directly from activist campaigns like DeTox
political risk of activist campaigns (Levi’s)
government regulatory threat for improved worker and consumer safety
consumer risk of activist campaigns (Levi’s)
organic food, chemical free health and beauty products/cleaning supplies → consumer trend of being more conscious of what goes in and on our bodies
What could be an effective strategy to mitigate the common risk of the textile industry
chemical management
Hazard Based approach (proactive product development)
Screened Chemistry: keep prohibited chemicals out of original product designs so that other risk management is unneeded
Supply chain risk based approach (reactive factory level)
Manufacturing Restricted
Substance List (MRSL): certain chemicals restricted in manufacturing process
Pollution risk based approach (reactive product level)
Restricted substance list (RSL): certain chemicals below threshold in jeans
Global effluent requirements (GER): certain chemicals below threshold in wastewater
What does the success of Screen Chemistry depend on
industry-wide adoption
what are the proft drivers of widespread adoption of screened chemistry
growing activist pressure to increase corporate accountability
governments more concerned with regulations
consumers are trending away from chemicals
Effect on chemical companies when creating a new chemical
High R&D costs
High new chemical screening costs
Spread minor processing fees over high volume of chemical sales → second mover pays significantly less than the first mover (free-loader, so industry doesnt innovate fast enough to mitigate the industy’s risks )
How is levi’s trying to avoid the free-rider problem
convince everyone to invest together
Under cooperative advantage, everyone will pay more than free-riding (individual costs are greater than a processing fee)
no one would have to incur the high r&d costs from first-mover disadvantage
Barriers to widespread adoption of screened chemistry
Resource/time commitement to follow new standard
program relies on proprietary info (rivals hesitant to share)
program competes with other existing ceritifcation programs (bluesign and greenscreen)
shortage and bottleneck of screening services (ToxServices)
Payoff from Free-riding
free-ride on positive industry reputation and enjoy lower marginal production cost
payoff from cooperation
shield industry from activist groups
joint lobbying against govt regulation
accelerate development of more sustainable clothing preferred by consumers
the ZDHC could be the coordination mechanism that lowers the cost of cooperation
ZDHC
Zero Discharge of Hazardous Chemicals - collection of multinational brands that are voluntarily committed to removing chemicals
economices of scale in innovation share best practices, improve and facilitate coordination and lower costs
what is needed from ZDHC
voluntary agreement from consensus of members, Levi’s pitches as ZDHC program, not Levi’s branded program
Is cooperative advantage illegal?
no - industry colluding on reducing a societal bad, and govts support efforts that lower the cost of improving social welfare
Levi’s Update
Levi’s, nike, h&m and c&a adopted a single standard for chemical management closely resembling the screened chemistry program
Gap put forth a similar screened chemistry program
ZDHC announced that they would take over the future development of screened chemistry
What is CC&S
the process of capturing, securing, and storing carbon dioxide
What is the goal of CC&S
Carbon Captreduce the amount of carbon that reaches our atmosphere, in order to reduce climate warming
What are the three types of CC&S
Biological- soils and trees act as natural carbon sinks
Geological- old mines and wells can store carbon (enhanced oil recovery [EOR] occurs from re-pressurizing a mature oil well with carbon dioxide injections in order to recover more oil)
Technological- synthetic carbon sinks can be engineered
Exxon released these nationally televised CC&S commercials
Carbon Capture Technology
Carbon Capture Plants
Who were the intended audiences of the CC&S commercials?
Employees, Socially responsible investors, and policy makers looking to pass green policies
What can companies that invest in CC&S apply for?
Apply to gain carbon credits
Explain carbon credits and VERs
Carbon credits usually come in the form of voluntary emission reductions (VERs)
VERs involve reducing, avoiding, destroying, or sequestering the equivalent of a ton of greenhouse gas (GHG) in one place to “offset” an emission taking place somewhere else
In addition to offset markets, the ICO2N members would benefit from what
If a robust international carbon trading market were to develop because the network’s CC&S emission reductions would have increased value
Indirect Social Risk of the energy market without ICO2N
Activists are targeting banks to cut off tar sands funding (ex: Please help us Mrs. Nixon, Mr. Nixon, drink a glass of water)
Politcal Risk of the energy market without ICO2N
EU, US and some Asian governments are threatening to pass policies that raise the costs of dirty energy sources
Economic Risk of the energy market without ICO2N
Renewable energy technology is maturing faster than CC&S technology and gaining cost parity with fossil fuel energy
How does Suncor and other ICO2N members mitigate their risks
Suncor enjoys reputational leadership as a founding member
Social risk: one united network that better shields each member from NGO threats (hard to cut off financing to the whole industry)
Political risk: one lobbying voice to slow down regulation on dirty energy and lobby for increased government funding in CC&S
Economic Risk: Technology must be shared within the network members
CC&S Investment Decision
$25 million is around .3% of the total $7.5 billion cost and less than 2.5% of Suncor’s annual profit
If govt covers $3.75 billion - leaves $3.75 billion for the ICO2N members to cover
1/12 of that would be $312.5 million - should Suncor invest $312.5 million before the others?
What are the opportunity costs of investing in CC&S
Oil and Gas Exploration: core competency and Alberta oilsands are rapidly being developed
Renewable Energy Technology: Wind and solar are seen as key inputs in a sustainable energy basket and are rapidly maturing
Cheaper Carbon Credits: Biological carbon sinks are a cheaper investment for reputational gains
Suncor Invests First Risks
ICO2N already mitigated social, political, and economic risks and enhanced founding member reputations
High opportunity costs as other investments are given up
First-mover disadvantage from the high learning curve costs and network free-rider (technology shared in network)
As renewable energy technologies mature…
there will be more pressure to clean up the world’s dirtiest energy supply - CC&S can help with this
Activists and voters demand more renewable energy,
governments will consider constraining dirty energy sources
2012-2016 the US (Obama and California) and the EU began to debate legislations against dirty energy
CC&S technology can help preempt or shape government regulation
Who has first mover disadvantage in the Suncor Case Update?
CC&S technology has a first-mover disadvantage
Did the ICO2N invest heavily in CC&S technology
No…
It was unreasonable for the industry to cover teh $7.5 billion and are lobbying the Canadian government to invest first
Successfully lobbied against US/EU green energy policy
Is sheltered from direct NGO activist leverage as it is hard to boycott against the energy network - Notice that energy producers are better insulated from social risk and enjoy more political influence than clothing brands, and thus were able to take less actions than the ZDHC members did
Without major investments in CC&S technology and lobbying against green legislation, the ICO2N network lost some reputation
Suncor and others formed a new energy network: Canada’s Oil Sands Innovation Alliance (COSIA)
COSIA has continued to shelter the industry from social activist threats while pressuring governments to invest in CC&S technology
If the EU’s carbon trading system continues to influence other countries to develop similar systems…
the business case for capturing carbon would improve and more aggressive investments in CC&S technology may follow