Quiz 5 - Lewis Structures, Bonding, and Chemical Reactions
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
______________ are used to keep track of valence electrons in atoms
Lewis symbols
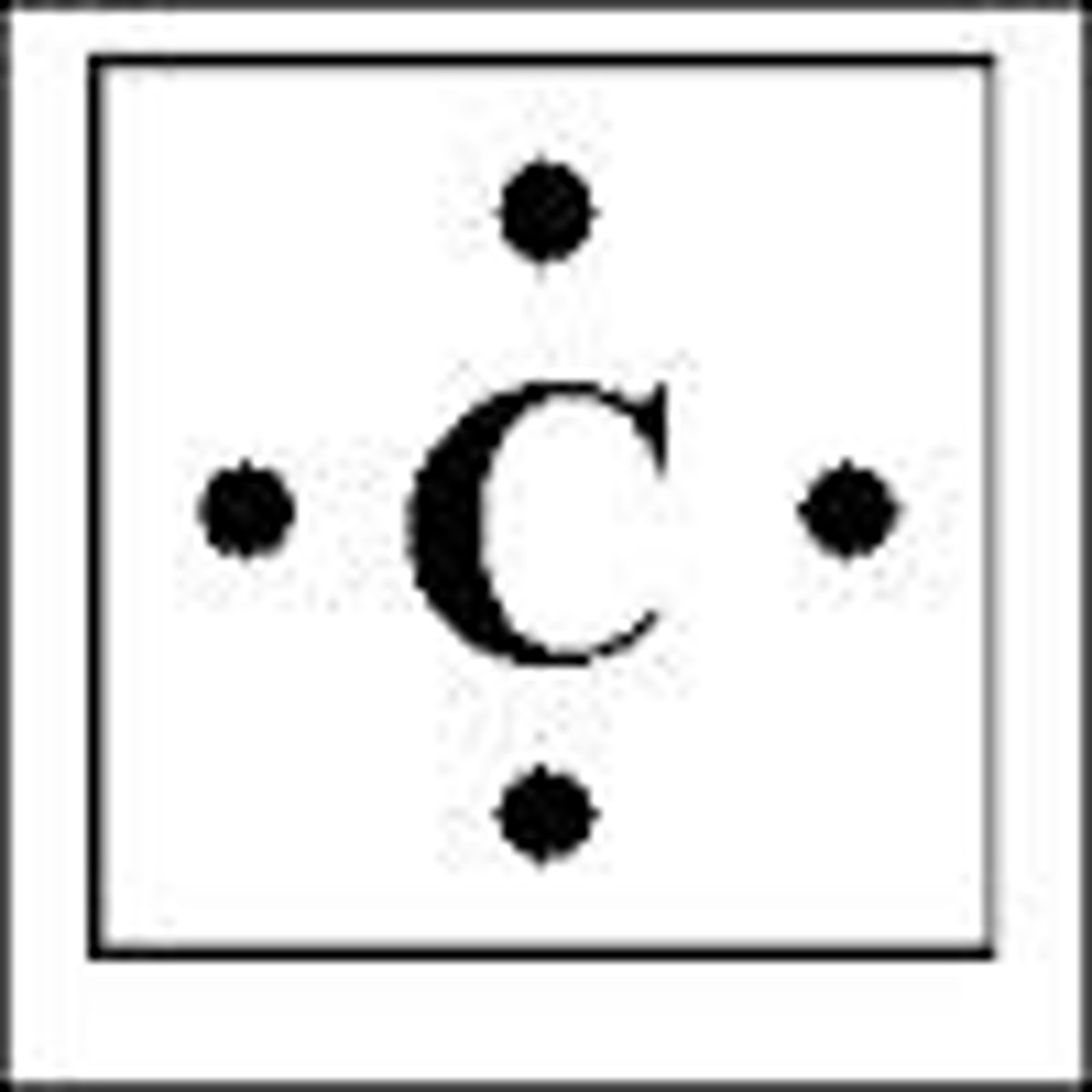
What is the lewis symbol for C?
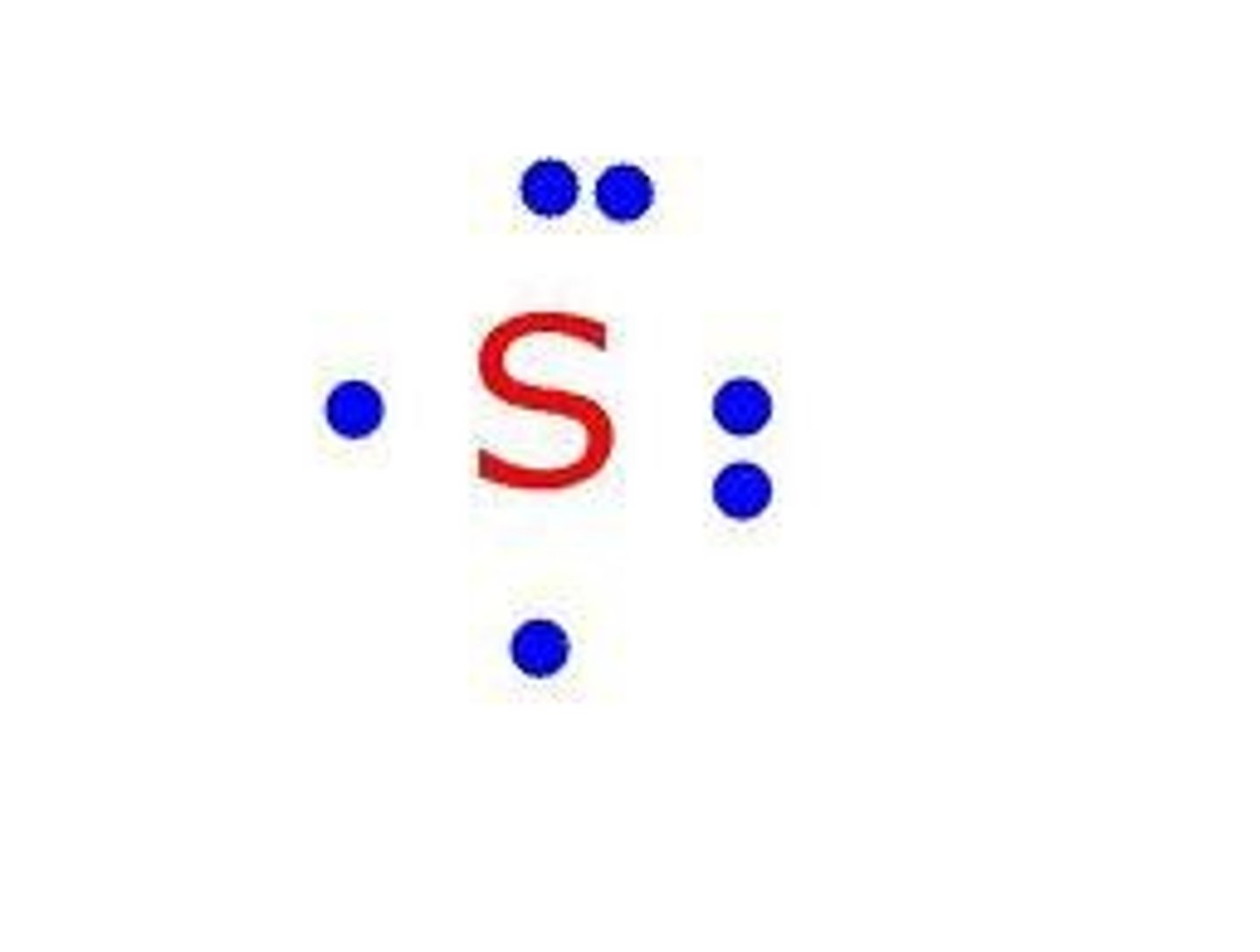
What is the lewis symbol for S?
What is the lewis symbol for Br?

True or False:
The Lewis structure of all atoms except H tend to lose, gain or share electrons so each atom has 8 valence electrons (an octet)
True
Draw the Lewis structure of Cl

In order to obey the octet rule, what type of ion would N be most likely to from? Be sure to include both the sign and the magnitude of the charge for each ion
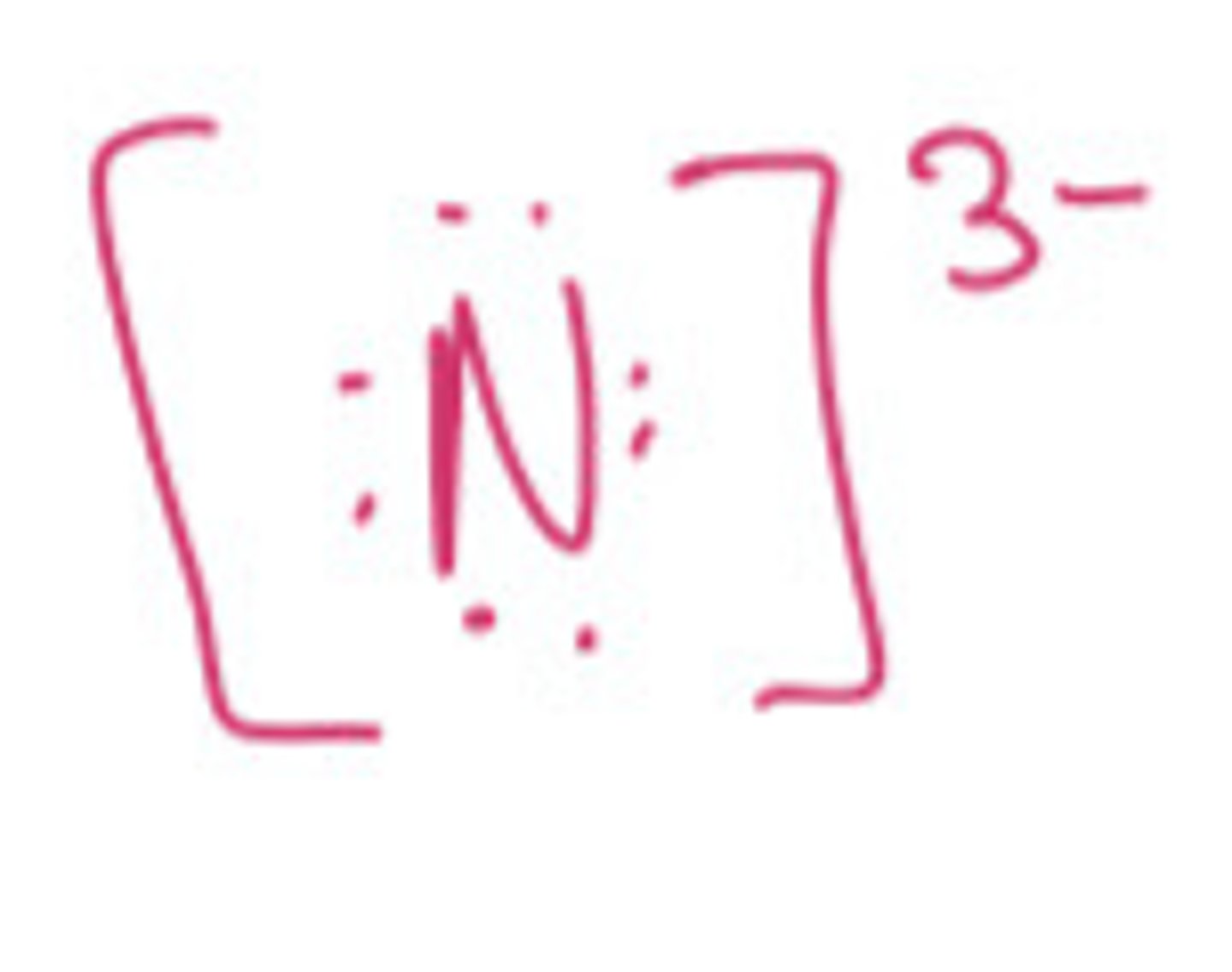
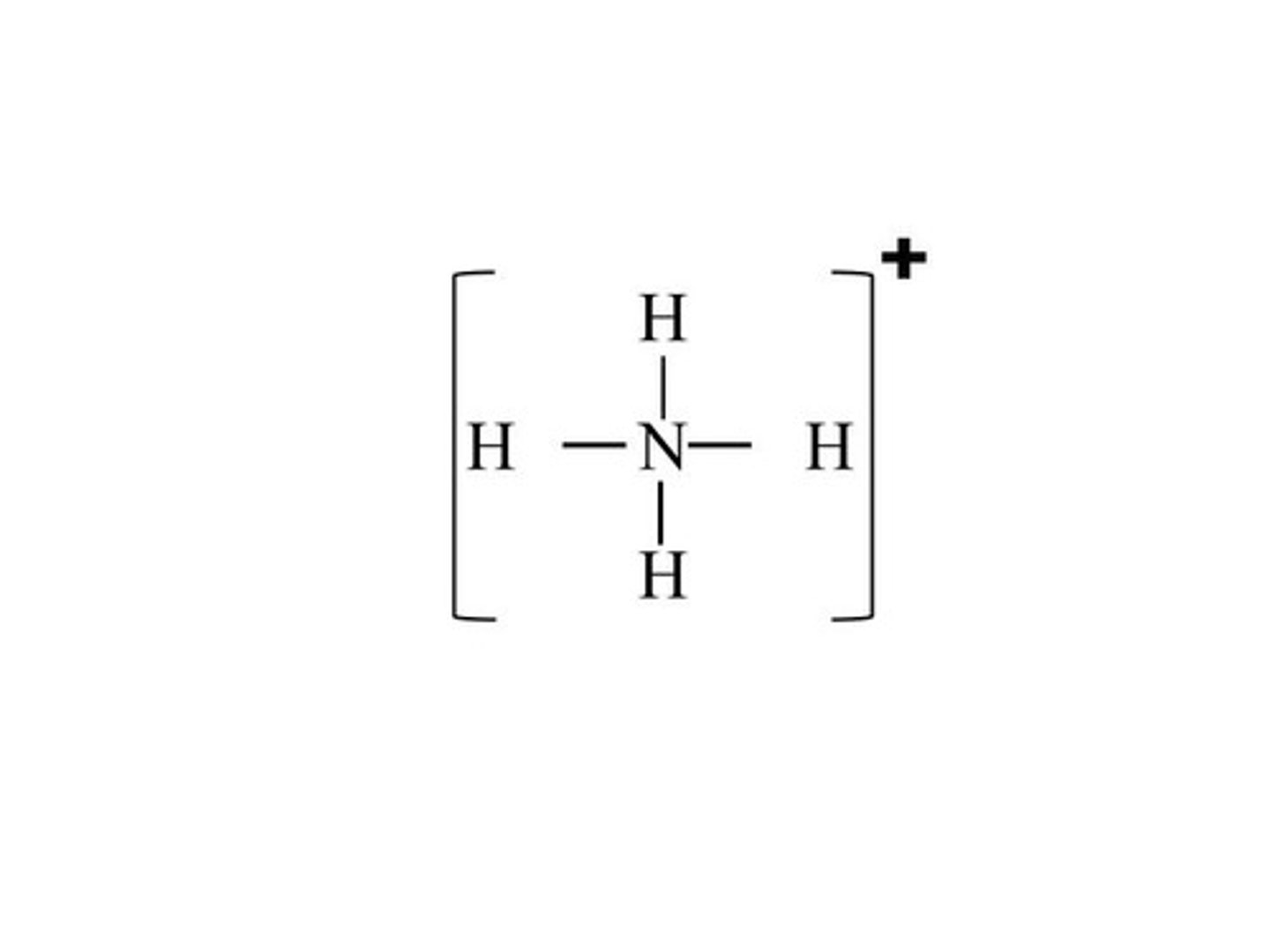
Draw the lewis model for NH4+ (ammonium)
Draw the lewis model for NF3
Draw the lewis model for CH2O
Draw the lewis model for F2
Draw the lewis model for N2
Draw the lewis model for CCl4
A ______________ consists of two electrons shared in a covalent bond
Bonding pair
______________ are electrons not involved in bonding
Lone pairs
The bond gets stronger as the bond length ___________ and bond energy _________________
- decreases
- increases
Bond order:
A single bond has the ____________ bond length and ______________ bond energy while a triple bond has the ________________ bond length and _______________ bond energy
Single bond
- longest bond length
- lowest bond energy
Triple bond
- shortest bond length
- highest bond energy
Bond order:
A _____________ bond shares 2 elections
Single (bond order of 1)
Bond order:
A _____________ bond shares four electrons
Double (bond order of 2)
Bond order:
A ____________ bond shares six electrons
Triple (bond order of 3)
True or False:
A lot of energy is needed to break the bond of ammonium (NH3) because it has a triple bond
False, NH3 does not have a triple bond
_______________ is the energy required to break a bond
Bond energy
A __________________ consists of multiple valid structures for a molecule
resonance structure
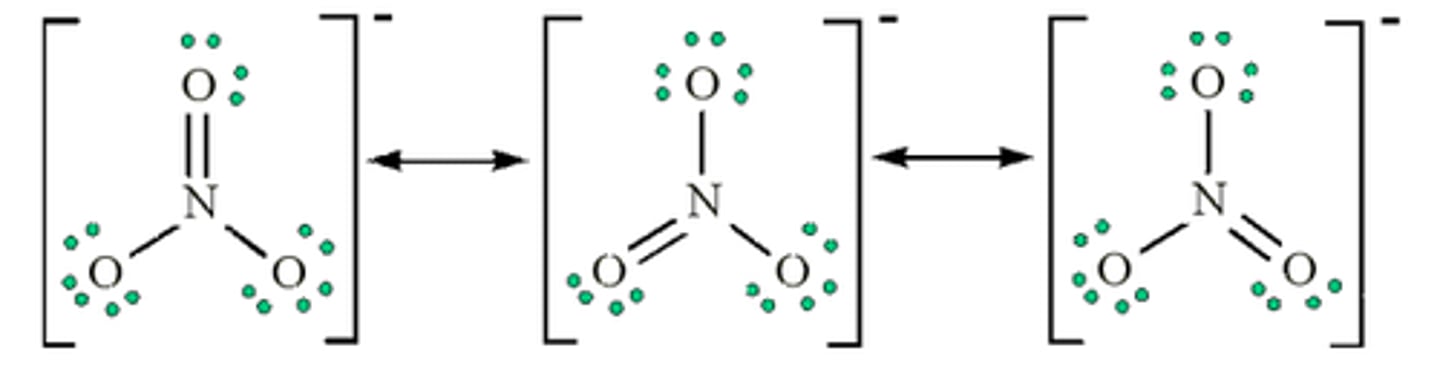
If a bond is between two of the same elements (C-C), electrons in a bond are shared ____________
equally
Unequal sharing of electrons between atoms occurs in _____________ bonds
Polar covalent
Equal sharing of electrons between identical atoms occurs in _______________ bonds
Nonpolar covalent
____________________ and the ________________ indicates an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms
- Partial charges (positive and negative)
- arrow with a plus sign at the end
The __________________ of an atom is its attraction for electrons in a bond
Electronegativity (EN)
High electronegativity attracts more electrons. EN increases from ________________ and _________________
- B->T
- L ->R
True or False:
The greater the difference in EN between two atoms makes for a more polar bond
True
______ is the most EN element in the periodic table. The closer an element/atom is to _______, the more EN that element/atom is
F (Fluorine)
The _______________ measures the electronegativity differences between atoms (used to indicate the EN)
Pauling scale
Using the Pauling scale, determine which is more polar?
C - O vs. N - S
C - O is more polar (closer to F)
Pauling Scale:
<------------------------------------->
0 0.4 2.0
___________________ _________________ ______________
- Nonpolar covalent between 0 and 0.4
- Polar covalent between 0.4 and 2.0
- Ionic past 2.0
True or False:
In HCU (hydrogen cyanide) C is the most EN atom because it is the central atom
False, C is least EN because it is the central atom
- The furthest away from F, making it the least EN
The Central atom is the least EN atom
except for ___________
H -> can never be a central atom (forms 1 single bond)
Which is more polar?
O - Si vs. Cl - Ca
Cl - Ca (closer to F and it between 0.4 and 2.0, making it polar covalent)
A ___________________ is a chemical change in which an element or a compound reacts with oxygen (O2), often producing energy in the form of heat and light
Combustion reaction
________________ in a balanced chemical equation are the numbers indicating moles of a substance in reaction
Coefficients
What are the states of matter used in chemical equations and how are they represented
solid - (s)
liquid - (l)
gas - (g)
aqueous - (aq)
Write the equation:
6 gaseous CO2 molecules react with 6 liquid water molecules to give an aqueous C6H12O6 molecule and 6 gaseous O2 molecules
6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)
Combustions of methane: (balance the equation)
CH4(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g)
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
Rewrite and balance the equation:
Magnesium solid reacts with aqueous HCl to give aqueous magnesium chloride and gaseous H2
Mg(s) + HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Balance the chemical equation:
FeCl3(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + HCl(aq)
2FeCl3(aq) + 3H2SO4(aq) → Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + 6HCl(aq)
Balance the chemical equation:
CoCl2(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → CO(NO3)2(aq) + AgCl(s)
CoCl2(aq) + 2AgNO3(aq) → CO(NO3)2(aq) + 2AgCl(s)
Balance the chemical equation:
C2H6(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g)
2 x (C2H6(g) + 7/2O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g))
2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
Balance the chemical equation:
Fe(s) + O2(g) → Fe2O3(s)
4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s)
Balance the chemical equation:
(NH4)2CO3(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NH3(aq) + H2O(l) + Na2CO3(aq)
(NH4)2CO3(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → 2NH3(aq) + 2H2O(l) + Na2CO3(aq)