Carboxylic Acids and Esters
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
carboxylic acid
-carboxyl fuc grp
-contains carbonyl and hydroxyl grp
-naming; carbon w/ carboxyl grp is carbon 1
-carboxyl always at the end
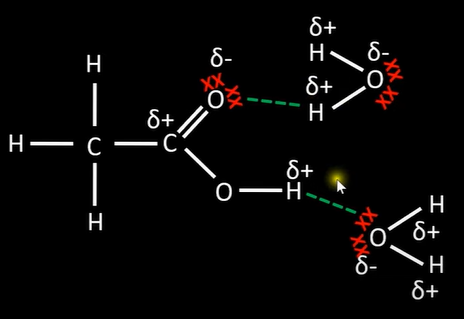
solubility
-can dissolve in polar solvent like water
-can hydrogen bonds with water molecules
-hydrocarbon part is non polar so bigger it is the less soluble carboxylic acid becomes
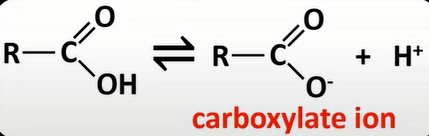
carboxylic acid chemical properties
-react w/ carbonates
-weak acid; dissociate partially to H+ ion and carboxylate ion
-equilibrium lies to left due to poor dissociation
carboxylic acid reaction with carbonate, bases, alkalis, metal oxides, metal
-carbonate: form salt, CO2, water
-bases, alkalis, metal oxides: salt and water
-metal: salt and H gas
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 →
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 →
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
CH3COOH + NaOH →
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
2CH3COOH + MgO →
2CH3COOH + MgO → (CH3COO)2Mg + H2O
2CH3COOH + Mg →
2CH3COOH + Mg → (CH3COO)2Mg + H2
acyl clhoride
-func grp: -COCl
-suffix -oyl chloride
-made by reacting carboxylic acid with thionyl chloride (SOCl2)
-CH3COOH + SOCl2 → CH3COCl + SO2 + HCl
what do acyl chlorides react with
-water
-ammonia
-alcohol
-primary amine
-Cl is always substituted
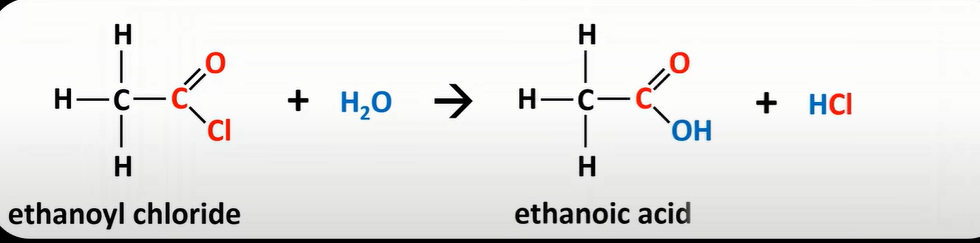
acyl chloride reaction w/ water
-produces carboxylic acid
-Cl sub for OH
-nucleophilic addition
-elimination reaction
-vigorous reaction; white misty fumes of HCl gas produced
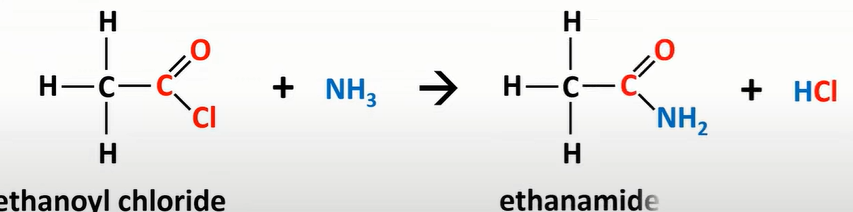
acyl chloride reaction w/ ammonia
-produces amide
-Cl sub for NH2
-nucleophilic addition
-elimination reaction
-vigorous reaction; white misty fumes of HCl gas produced
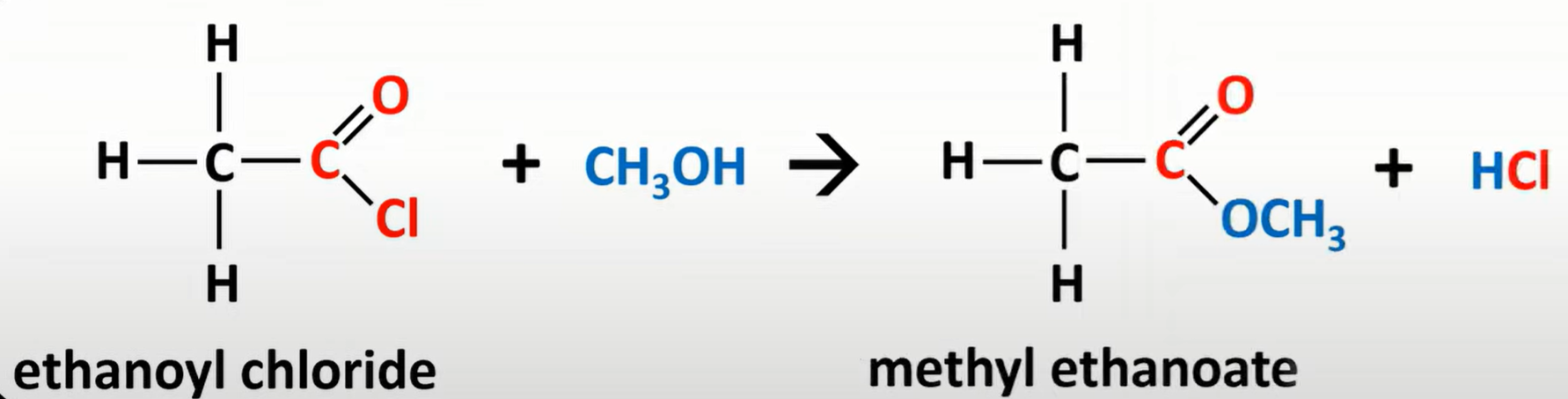
acyl chloride reaction w/ alcohol
-produces ester
-Cl sub for OCH3
-nucleophilic addition
-elimination reaction
-vigorous reaction; white misty fumes of HCl gas produced
acyl chloride reaction w/ primary amine
-produces N-substituted amide
-Cl sub for NHCH3
-nucleophilic addition
-elimination reaction
-vigorous reaction; white misty fumes of HCl gas produced

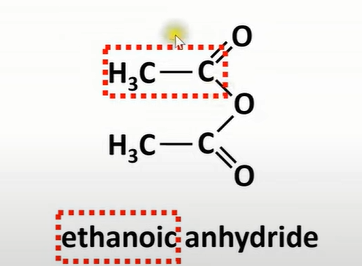
acid anhydride
-molecule made from 2 carboxylic acids that are same
how to name acid anhydride
-suffix; replace acid with anhydride
-prefix; C chain length of 1 of the acid
ways to make ester
-acyl chloride reaction w/ alcohol
-acid anhydride reaction w/ alcohol
-acyl chloride reaction w/ phenol
-carboxylic acid reaction w/ alcohol
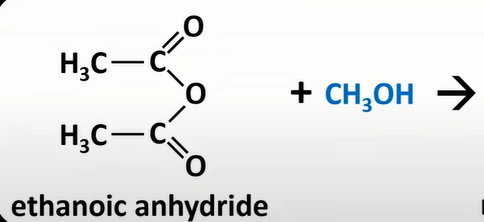
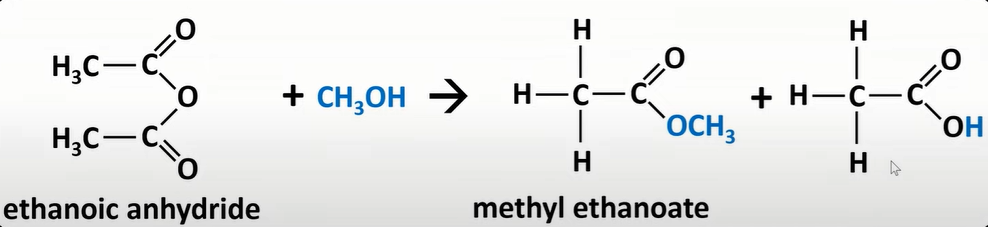
acid anhydride reaction w/ alcohol
-similar to acyl chloride but less vigorous reaction
-produce ester
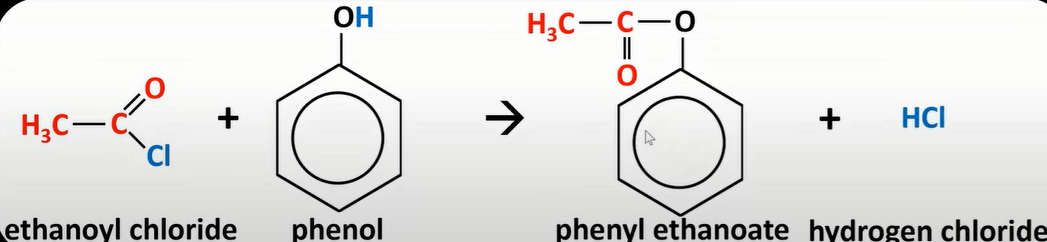
acyl chloride reaction w/ phenol
-form ester
-Cl replaced by phenol w/ O
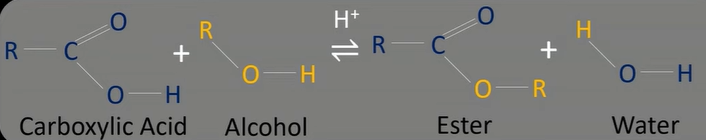
carboxylic acid reaction w/ alcohol
-w/ sulfuric acid catalyst
-produces ester and water
-OH from carboxylic acid and H from alcohol form water
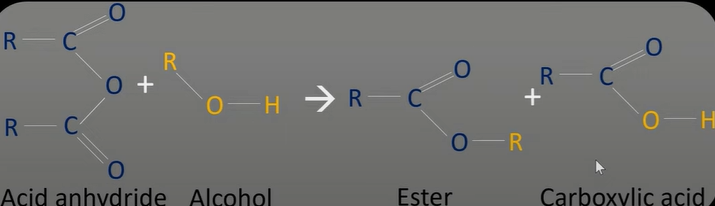
acid anhydride reaction w/ alcohol
-forms ester and carboxylic acid
ester naming
-first bit named from alcohol
-ethanol → ethyl
-second bit named from carboxylic acid (part w/ O)
-propanoic acid → propanoate
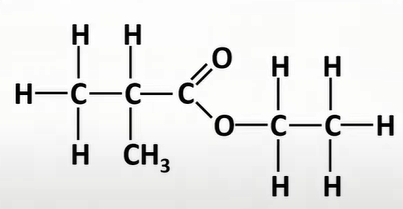
name this
-ethyl,2,methyl,propanoate
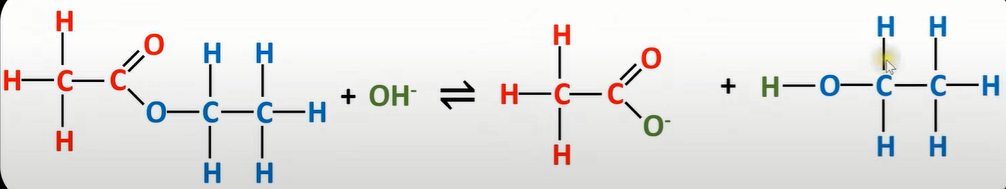
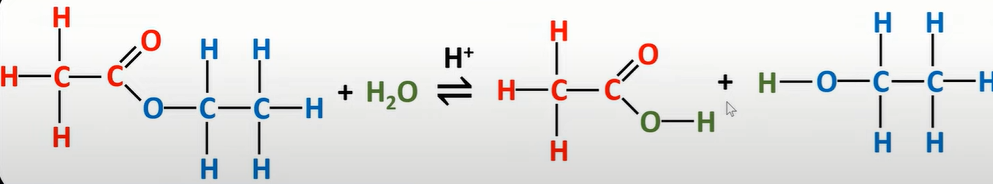
ester hydrolysis
-can be sped up using acid/base hydrolysis
acid hydrolysis ester
-dilute acid (HCl/ H2SO4) used
-to split into carboxylic acid and alcohol
-conducted under reflux as products are volatile and may be lost
-addition of water shifts equilibrium to right so more product made
base hydrolysis ester
-dilute base (NaOH) used
-split into carboxylate ion and alcohol
-conducted under reflux