Microbiology Ch16 Innate Immunity
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Immunity
ability to ward off disease
susceptibility
lack of resistance to a disease
Innate immunity
defenses against any pathogen; rapid & present at birth
Types of innate immunity (6)
- physical barriers
- chemicals
- cells that can phagocytize
- inflammation
- fever
- molecules
Adaptive immunity
immunity/resistance to a specific pathogen; slow & has memory component
Physical factors of innate immunity (7)
- skin
- mucous membranes
- ciliary escaltor
- earwax
- urine
- vaginal secretions
-lacrimal apparatus
dermis of skin
inner portion made of CT
epidermis of skin
outer portion made of epithelial cells w/keratin
how does skin provide immunity
shedding & dryness inhibits microbial growth & penetration
mucus of mucous membranes
viscous glycoproteins that trap microbes & prevent tracts from drying out
lacrimal apparatus of mucous membranes
drains tears; washes eye
where are mucous membranes
epithelial layer lining gastrointestinal, respiratory, & genitourinary tracts
ciliary escalator as physical factor of innate immunity
transports microbes trapped in mucus away from lungs
epiglottis as physical factor of innate immunity
prevents microbes from entering lower respiratory tract
earwax as physical factor of innate immunity
prevents microbes from entering ear
urine as physical factor of innate immunity
cleans the urethra via flow
vaginal secretions as physical factor of innate immunity
move microbes out of the vaginal tract
Types of chemical factors of innate immunity (4)
- sebum
- lysozyme
- low pH of 1.2 - 3.0 of gastric juice
- low pH 3.0 - 5.0 of vaginal secretions
sebum as chemical factor of innate immunity
forms a protective film & lowers pH of skin to 3.0 - 5.0
lysozyme as chemical factor of innate immunity
in perspiration, tears, saliva, & urine; destroys bacterial cell walls
low pH of 1.2 - 3.0 in gastric juice as chemical factor of innate immunity
destroys most bacteria & toxins
low pH of 3.0 - 5.0 in vaginal secretions as chemical factor of innate immunity
inhibits microbial growth
Types of cells that can phagocytize in innate immunity (3)
- normal microbiota
- formed elements in blood
- lymphoid system
how do normal microbiota provide innate immunity
compete with pathogens via microbial antagonism (competitive exclusion)
microbial antagonism of normal microbiota (5)
- compete for space & nutrients
- prod. substances harmful to pathogens
- alter conditions affecting pathogen survival
- prevents overgrowth of harmful microbes
- help develop immune system
commensalism of normal microbiota of innate immunity
1 organism benefits while the other (host) is unharmed
Opportunistic pathogens among normal microbiota (6)
- e. coli
- s. aureus
- s. epidermidis
- enterococcus
- faecalis
- pseudomonas aeruginosa
probiotics of normal microbiota of innate immunity
live microbial cultures administers to exert a beneficial effect
prebiotics of normal microbiota of innate immunity
chemicals (nutrients) that selectively promote the growth of beneficial bacteria
types of formed elements in blood of cells that phagocytize of innate immunity (2)
- granulocytes
- agranulocytes
granulocytes of formed elements in blood
leukocytes with granules in their cytoplasm that are visible with a light microscope
types of granulocytes of formed elements in blood (3)
- neutrophils
- basophils
- eosinophils
neutrophils of granulocytes of formed elements in blood
phagocytic; work in early stages of infection
basophils of granulocytes of formed elements in blood
release histamine; work in allergic responses
eosinophils of granulocytes of formed elements in blood
phagocytic; toxic against parasites & helminths
Agranulocytes of formed elements in blood
leukocytes with granules in their cytoplasm that are not visible with a light microscope
types of agranulocytes of formed elements in blood (3)
- monocytes
- dendritic cells
- lymphocytes
monocytes of agranulocytes of formed elements in blood
mature into macrophages in tissues where they are phagocytic
dendritic cells of agranulocytes of formed elements in blood
found in the skin, mucous membranes, & thymus; phagocytic
lymphocytes of agranulocytes of formed elements in blood
t cells, b cells, & NK cells; involved in adaptive immunity
Lymphoid system of cells that phagocytize of innate immunity
carries microbes to lymph nodes where B & T lymphocytes, macrophages (lymphocytes/phagocytic cells) encounter & destroy the pathogen
Mechanisms of phagocytosis (4)
- chemotaxis
- adherence
- ingestion
- digestion
chemotaxis (2)
- chemical signals attract phagocytes to microbes
- include microbial products, components of WBCs, damaged cells, complement
adherence (3)
- attachment of a phagocyte to the surface of the microbe
- PAMPs on microbes attach to TLRs on phagocyte surfaces
- opsonization
opsonization of adherence
microbe is coated w/ serum proteins, making adherence easier
ingestion (3)
- pseudopods (projections on phagocyte) extend out & engulf the microbe
- engulfed. microbe is enclose in a phagosome
- phagosome becomes acidic (pH 4) - activates hydrolytic enzymes
digestion (3)
lysosome fuses with phagosome to form phagolysosome which breaks down and destroys pathogens, leftover material forms a residual body that is removed by exocytosis
inflammation as innate immunity
- destroys injurious agent or limits its effects on the body
- repairs & replaces tissue dmged by injurious agent
fever as an innate immunity
- cytokines cause hypothalamus to release prostaglandis that reset hypothalamus to higher temp (maintained until cytokines are eliminated)
what happens when body temp falls during a fever
vasodilation & sweating
factors that make a fever a defense (4)
- phagocytes & t cells work better at higher temp
- higher temp intensifies effect/production of other antimicrobial substances (interferons, transferrins)
- higher temp slows pathogen growth
- increase metabolic rate repair process
what the complement system in innate immunity
serum proteins prod. by the liver that enhances the immune system in destroying microbes
how are proteins in the complement system organized and named
- uppercase C & numbered in order of discovery (C1, C2, C3)
- activated fragments indicated with lowercase a & b (C3a, C3b)
Pathways for the complement system (3)
- classical
- alternative
- lectin
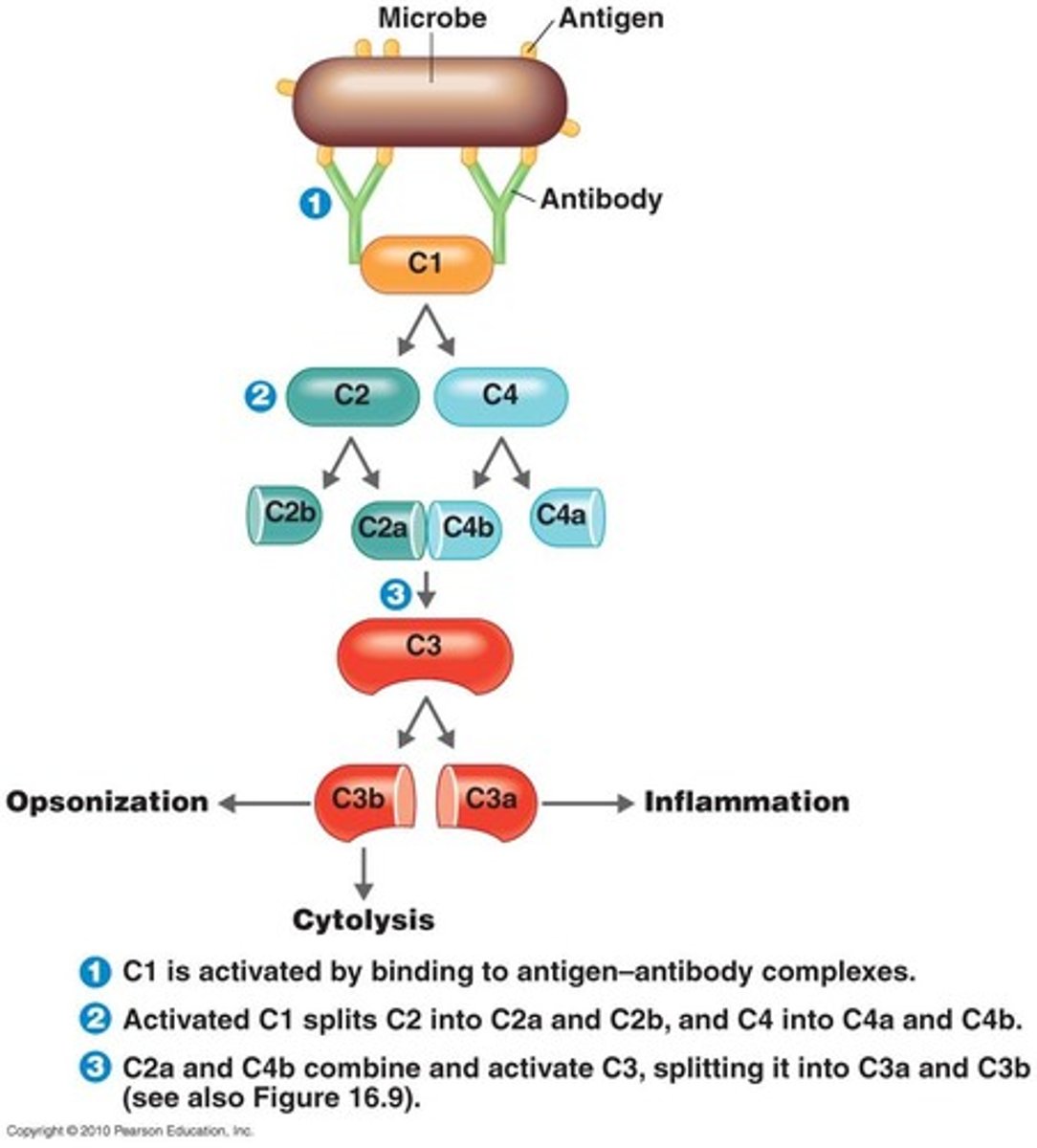
complement system; the classical pathway (5)
- antibodies bind to antigens (activating C1)
- C1 splits (activating C2 & C4)
- C2a & C4B combine & activate C3
- C3a functions in inflammation
- C3b functions in cytolysis & opsonization
complement system; alternative pathway (2)
- C3 present in blood combines with factors B, D, & P on microbe surface
- C3 splits into C3a & C3b, functioning the same in the classical pathway
complement system; lectin pathway (3)
- macrophages ingest pathogens, releasing cytokines that stim. lectin prod. in liver
- mannose-binding lectin (MBL) binds to mannose, activating C2 & C4
- C2a & C4b activate C3, which functions the same as the classical & alternative pathways
Outcomes of complement activation (3)
- cytolysis
- opsonization
- inflammation
cytolysis of complement activation
activated complement proteins create a membrane attach complex (MAC)
opsonization of complement activation
promotes attachment of phagocyte to microbe by “tagging it”
inflammation of of complement activation
activated complement proteins bind to mast cells, releasing histamine
interferons of innate immunity
cytokines prod. by cells; have antiviral activity
types of interferons (3)
- IFN-a
- IFN-b
- IFN-Y
IFN-a & IFN-b
triggers neighboring cells to prod. antiviral proteins (AVPs) that stop viral replication
IFN-y
cause neutrophils & macrophages to kill bacteria
Iron-binding proteins as an innate immunity
host proteins bind iron tightly with these proteins bc pathogen compete with host for iron (needed for growth & reproduction)
Types of iron-binding protein (4)
- transferrin
- lactoferrin
- ferritin
- hemoglobin
transferrin
in blood & tissue fluids
lactoferrin
in milk, saliva, mucus
ferritin
in liver, spleen, red bone marrow
hemoglobin
in RBCs
Bacteria response to compete with iron-binding proteins
siderophores
antimicrobial peptides as an innate immunity
short peptides prod. in response to protein & sugar molecules on microbes
antimicrobial peptides functions (4)
- broad spectrum of activity (600+)
- inhibit cell wall synthesis
- form pores in plasma membrane causing lysis
- destroy DNA & RNA
Examples of antimicrobial peptides (3)
- dermicidin (skin)
- cathelicidins (neutrophils, macrophages)
- thrombocidin (platelets)