Monomers & Polymers
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Spec Reference: 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.1.3, 3.1.4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Explain how plants & animals containing the same amino acids to make proteins suggests evidence for the theory of evolution
Amino acids being present within plants & animals suggests that they have all descended from the same ancestor, meaning plants & animals have evolved overtime, which is why they are mainly different but share some similarities overall
Monomer
A small, single molecular unit which can join together to form polymers
Polymer
A long, complex molecule composed of monomers
Give 3 examples of Monomers
Monosaccharides, amino acids & nucleotides
Give 3 examples of Polymers
Carbohydrates, proteins & nucleic acid
Condensation Reaction
The formation of a chemical bond between monomers involving the release of a water molecule
Hydrolysis Reaction
Breaking down a polymer into multiple monomers by breaking the chemical bond between them using a water molecule
What elements do all carbohydrates contain?
Carbon, Oxygen & Hydrogen
Monosaccharide
A monomer of carbohydrates
Give 3 examples of Monosaccharides
Glucose, Fructose & Galactose
Isomer
Molecules with the same molecular formular, but with the atoms connected in a different way
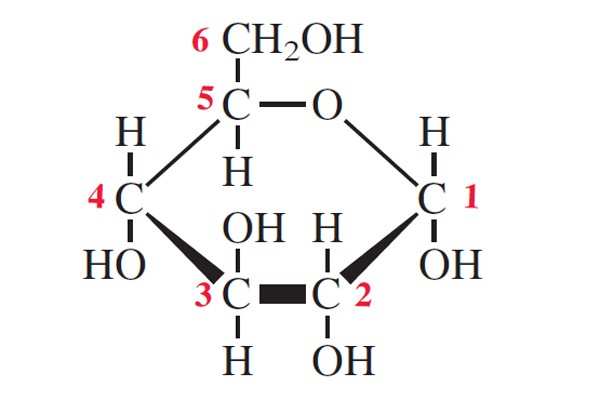
Draw alpha-glucose
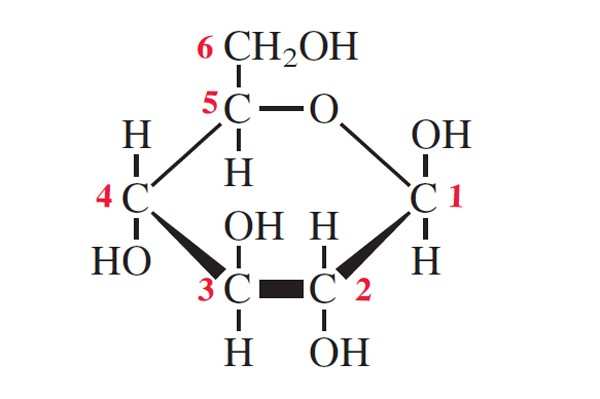
Draw beta-glucose
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides joined together by a glycosidic bond via a condensation reaction
Give 3 examples of Disaccharides
Sucrose, Lactose & Maltose
How is maltose formed?
By a condensation reaction between two alpha-glucose molecules
How is sucrose formed?
By a condensation reaction between a glucose molecule & a fructose molecule
How is lactose formed?
By a condensation reaction between a glucose molecule & a galactose molecule
What are the two types of sugars?
Reducing sugars & non-reducing sugars
Examples of Reducing Sugars
Monosaccharides, maltose & lactose
How to test for reducing sugars
Add blue benedict’s reagent to a sample & heat it in a water bath until it has been brought to a boil:
If positive - the sample will form a precipitate which will go green —> yellow —> orange —> brick red. The higher the conc. of reducing sugars, the further the colour change goes
If negative - the sample stays blue & no reducing sugars are present
How to compare the amount of reducing sugars in different solutions
Complete the benedict’s test on both solutions. Filter the solutions & weigh the amount of precipitate.
Or
Complete the benedict’s test on both solutions. Filter the solutions & use a colorimeter to measure absorbance of both amounts of precipitate.
How to test for non-reducing sugars
Add blue benedict’s reagent to a sample & heat it in a water bath until it has been brought to a boil:
If positive - the sample will form a precipitate which will go green —> yellow —> orange —> brick red. The higher the conc. of reducing sugars, the further the colour change goes. This shows that reducing sugars are present
If negative - the sample stays blue & no reducing sugars are present
Then, heat a new sample of dilute hydrochloric acid then neutralize it with sodium hydrocarbonate. Reheat sample with benedict’s reagent
If positive - the sample will form a precipitate which will go green —> yellow —> orange —> brick red. The higher the conc. of reducing sugars, the further the colour change goes. This shows that non-reducing sugars are present
If negative - the sample stays blue & no non-reducing sugars are present
Polysaccharide
A polymer formed when more than two monosaccharides join together in a condensation reaction
Give 3 examples of Polysaccharides
Starch, Glycogen & Cellulose
Starch
The store of excess glucose in plants
What two polysaccharides make up Starch?
Amylose & Amylopectin
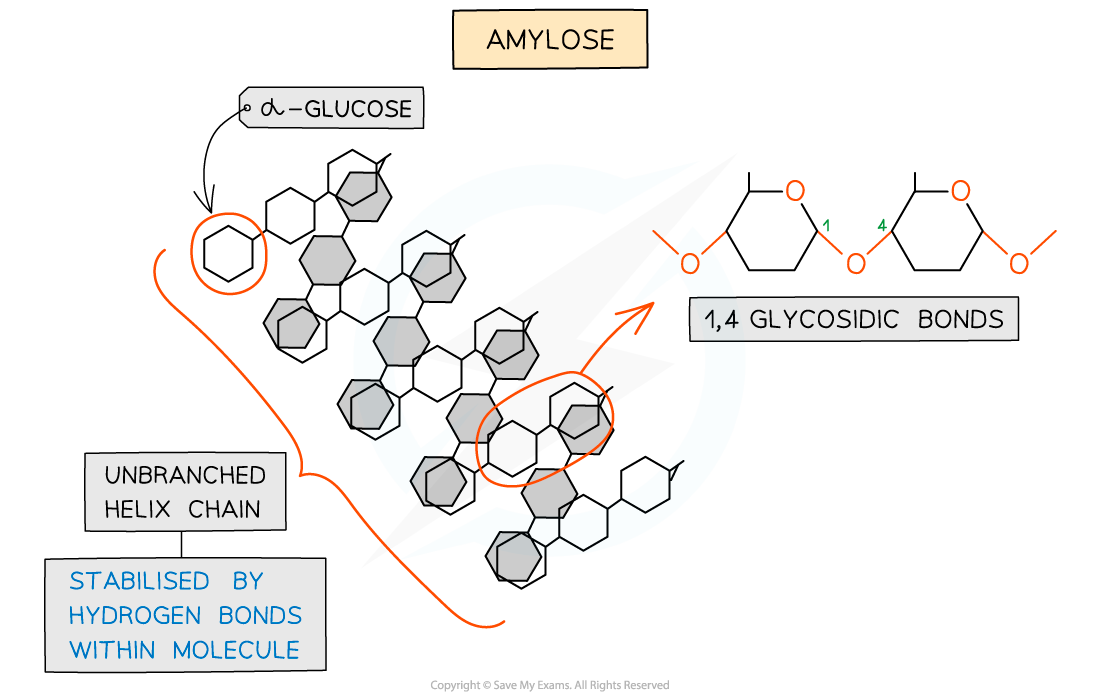
Amylose
Long, unbranched helix chain of alpha-glucose monomers
Bonded via 1-4 glycosidic bonds
The angle of these bonds give it a coiled shape, making it compact & therefore very good for storage
20% of Starch
Amylopectin
Long, branched chain of alpha-glucose
Mostly bonded by 1-4 glycosidic bonds, but when it branches, its forms a 1-6 glycosidic bond instead
Branching allows enzymes to break down the glycosidic bonds easily, resulting in quicker release of glucose
80% of Starch
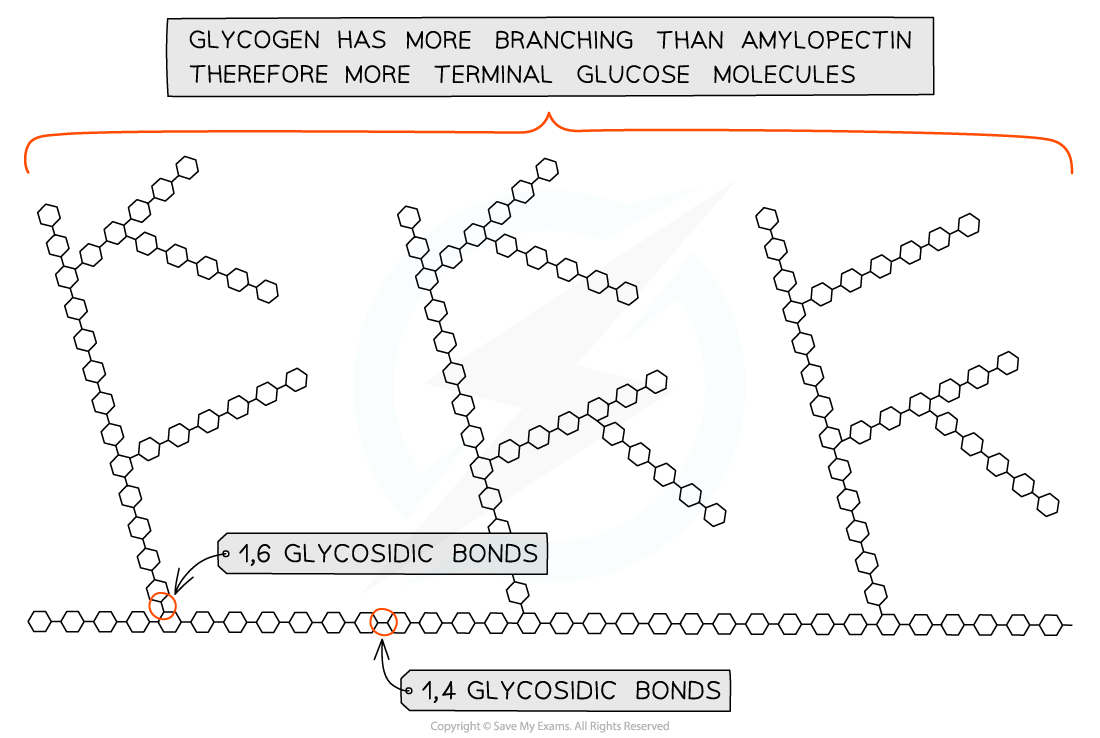
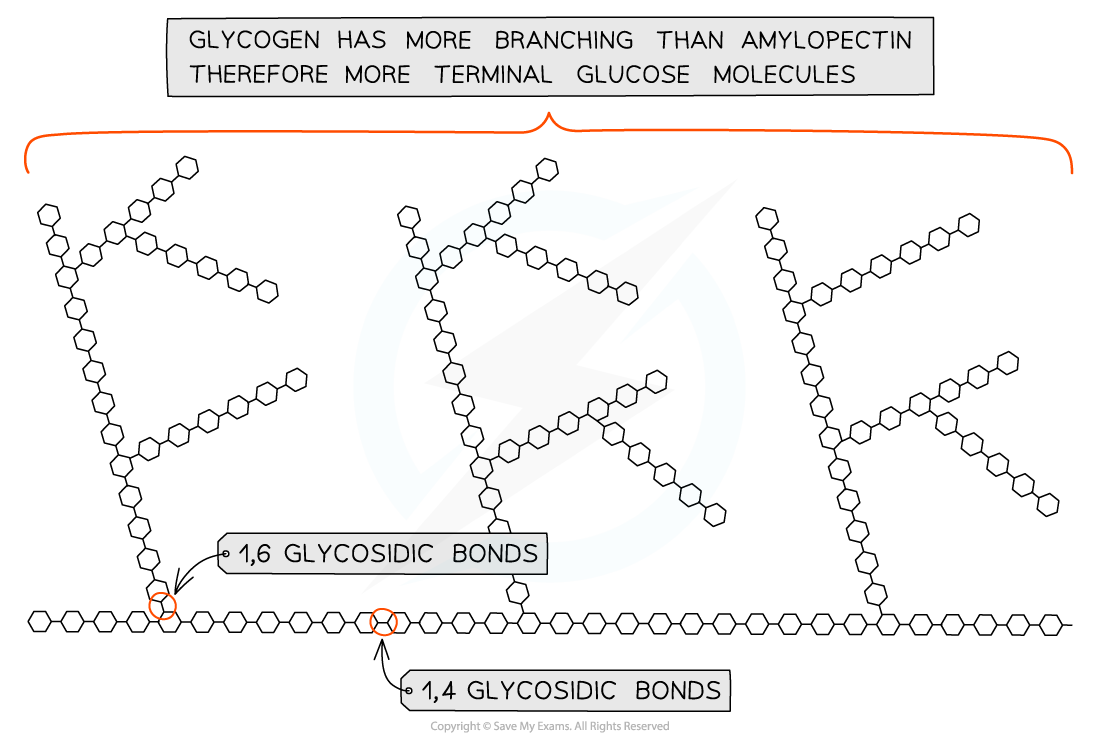
Glycogen
The storage of excess glucose in animals
Properties of Glycogen
Long, branched chain of alpha-glucose
Contains much more side branching than amylopectin, which helps it to release glucose quicker
Compact so good for storage of glucose
Cellulose
Provides structural support for the cell wall in plant cells
Properties of Cellulose
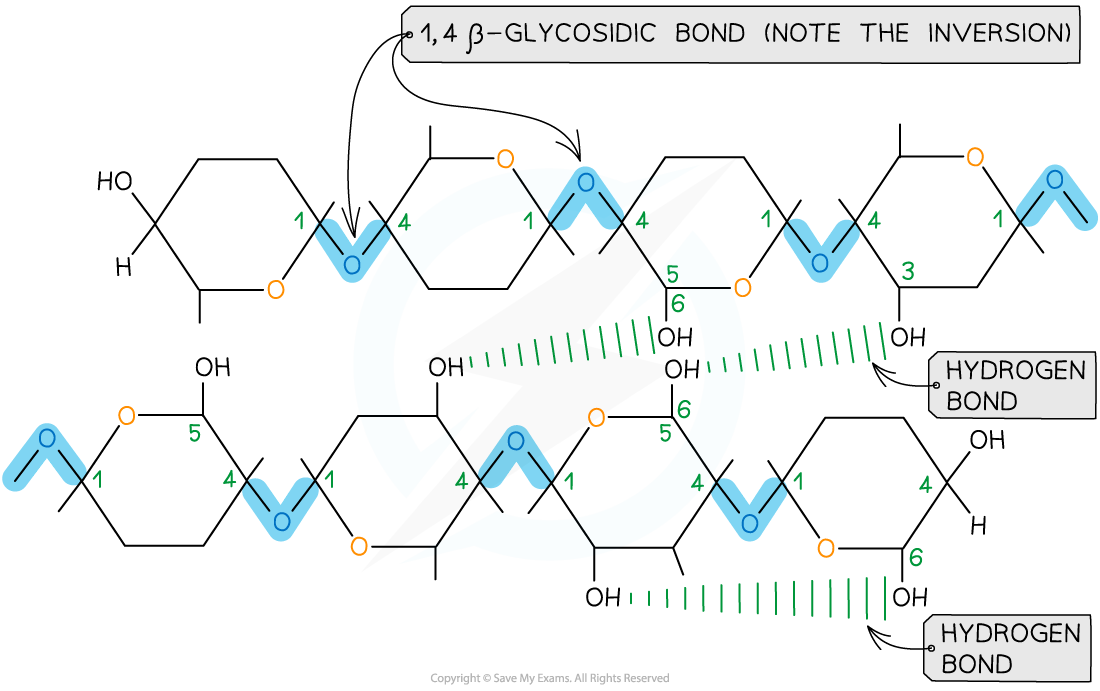
Long, straight, unbranched chains of beta-glucose
Singular straight chains of cellulose are bonded together by 1-4 glycosidic bonds
When beta-glucose bonds, they invert
Multiples straight chains of cellulose are bonded together by weak hydrogen bonds